Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
A Study On Online Recruitment (E-Recruitment) Portals Adoption (Usage): Role Of Demographics In Kolkata City
Abstract :
In early-1990s, with the advancement of and information and communication technology and increased internet usage have witnessed the transformation of the conventional recruitment methods to online recruitment (e-recruitment).Multinational and IT companies even use their websites to recruit people while others capitalized this change to become e-recruitment service providers.Most of the e-recruiters provide free services to applicants or jobseekers to post their resume´s online in their databases.As global competition persists and industries becoming more skill intensive, the recruitment of talent workers becomes essential, and attracting the right applicants at the right time is getting tougher than ever. Over the years electronic commerce has become very popular and changed the way of hiring employees. The use of conventional recruitment methods no longer suffices and timely to attract a sufficient pool of qualified applicants. Many organizations have turned to adopting sophisticated recruitment strategies or combining various recruitment methods to attract them. In this scenario this study is an attempt to explore the awareness, adoption and frequency of usage of electronic recruitment portals (e-recruitment portals) by customers in Kolkata city with an objective of understanding the role of demographics variables (age, income, gender, education etc.)
Keywords :
electronic recruitment, online recruitment awareness, e-recruitment adoption, e-recruitment portals, demographics.1. Introduction :
As global competition persists and industries becoming
more skill intensive, the recruitment of talent workers
becomes essential, and attracting the right applicants at
the right time is getting tougher than ever. The use of
conventional recruitment methods no longer suffices and
timely to attract a sufficient pool of qualified applicants.
Many organizations have turned to adopting
sophisticated recruitment strategies or combining various
recruitment methods to attract them. For example, by
combining newspaper ads with executive search, or
employment agencies, and others for recruitment; but this
only adds to the increased of recruitment costs per hire. In
the early-1990s, with the advancement of internet
technology, many have witnessed the transformation of
the conventional recruitment methods for online
recruitment. Some corporate companies even use their
websites to recruit people while others capitalized this
change to become an e-recruitment service providers.
The third-party e-recruiters provide services to companies
who are interested to use their web sites for job
advertisements and viewing potential applicants' posted
resumes at a fee lower than most conventional recruitment
methods. Most e-recruiters provide free services to
applicants or jobseekers to post their resume´s online in
their databases. With this free posting, the growth of
resume´s is inevitable. Millions of resumes are posted to
famous e-recruitment websites, becoming a true market;
uncontrolled and unconstrained by geography.
Online recruitment uses the power of the internet to match people to jobs. Fundamentally, it is about advertising vacancies on either job sites or corporate websites. At this very basic level, it is particularly effective at getting an important level of response. While it may generate hundred more applications than traditional print advertising, simply attracting more candidates is only part of the job. Few example of online recruitment portals are naukri.com, times jobs.com, monsterindia.com, indeed-one search, all jobs, jobsahead.com, careerbui lder.com, shine.com, freejobalerts.com, facultyplus.com jobsahead.com etc.
1.2 Benefits of Online Recruitment (e-recruitment) over Traditional Recruitments :
Wide geographical reach
Advertising online opens a
much wider candidate pool than advertising in print. This
gives you a much better chance of finding the right
candidate for the job.
Speed
Jobs posted online go live in literally minutes and
candidates can do responds immediately.
Lower cost
This may surprise, but technology in online
recruitment is not expensive. By saving on time, design
and print costs and targeting precisely the best sites for the
best candidates. Online recruitment is a very cost-effective
option.
Automating the process
The pre-selection process can
be tailored to individual companies' needs. This way one
can sift and sort candidates who meet exact needs.
Automating the application process also gives a level
playing field for all candidates whether they come directly
to your company's site, via a recruitment consultant or in
response to a print advertisement.
Interaction with candidates
Working online via
websites and email is the way of the future. It's not just the
youngsters who are logging on to find jobs either.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW :
According to Galanaki, (2002) online recruitment (erecruitment)
process is started by posting vacancies on the
corporate website or on an online recruitment vendor's
website, and allowing applicants to send their resumes
electronically through the e-form or email.
As per opinion of Tong and Sivanand, (2005) online
recruitment (e-recruitment) emerges as a handy and
advantageous method over traditional methods of
recruitment e-recruitment enable the firm to perform the
tasks in speed and improves the process One of the
outcomes of the growth of e-recruitment technologies has
been that applying for jobs has become simpler and more
streamlined.
Executives of Malaysia believe that e-recruitment can lead
them to a new competitive position in regional labor
markets due to the importance of knowledge workers and
resource-based competition (Poorangi et al., 2011; Ahmed,
2009).
Galanaki, (2002); Khan, (2010) as stated that lower cost
investment, shorter recruitment cycle, reach to a wider
range of applicants, better quality of applicants,the
opportunity to address specific market niches, and issue
attraction of passive job-seekers; are described as the
strong sides of the Internet recruitment.
Additionally, the advertisement and its attributes are
important factors in e-recruitment as Buda (2003) found
that the recruitment advertisement is to be effective when
it should include positive information at the start when
being advertised through non-expert sources (e.g. general
media).
The review of the above literature provides an indication
that online recruitment (e-recruitment) is acknowledged
as being an important aspect of job/candidate searching
for jobseekers and organizations. Moreover, e-recruiting
is becoming more effective recruitment tools, creating an
avenue to build relationships between job seekers and
organizations (Mooney, 2002).
3. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES :
- To study the awareness of online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal.
- To understand the adoption (usage) of online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal.
- To examine the role of demographic (Age, Gender, Educational qualification) variables on adoption (usage) of online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal.
4. RESEARCH HYPOTHESES :
H1: There is a significant difference between male and
female respondents in terms of the adoption (usage) of
online recruitment (e-recruitment) portals.
H2: There is a significant difference among the
respondents with different age groups in terms of the
adoption (usage) of online recruitment (e-recruitment)
portals.
H3: There is a significant difference among the
respondents with different education in terms of the
adoption (usage) of online recruitment (e-recruitment)
portals.
5. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY :
The Research methodology is a science of collecting, identifying and presenting facts in such a way that it leads to unearthing some truths or angles of reality. Research in common parlance refers to search for knowledge. In this study, quantitative research has been used.
5.1 Research Design :“A research design is the logical sequence that connects the empirical data to the study's initial research and ultimately its conclusions” (Yin, 1994). Research approach quantitative approach and research design used explorative and descriptive. Explorative research has been carried out for the purpose of understanding the erecruitment awareness and adoption (usage) in Kolkata city. The descriptive research is a type of conclusive research.
5.2 Sampling Technique and Sample Size :The sampling technique used is non- probability purposive sampling. The sample size taken for the current study is 116. The data were collected proportionately between male and female to study their adoption pattern.
5.3 Data Collection Method :
Primary data
Primary data collected through the wellstructured
questionnaire.
Secondary data
Secondary data were collected from
internet, journals, books etc.
The data are collected by questionnaire. It consists of a list of questions, which are relevant in getting the facts. The questionnaire has been constructed based on two-types: they are multiple choices and close ended questions. The scale ranges from 1 to 5, 1 - Strongly agree, 2 - Agree, 3 - Neutral, 4 - Disagree, 5 - Strongly disagree.

Table No. 17 : Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage) by age
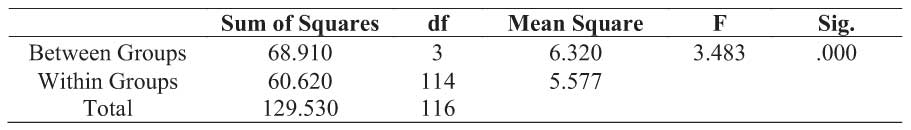
Interpretation :
above table based on the significant value it is identified that there is a significant difference with the various age groups respondents in terms of Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage). Hence, the alternate hypothesis is accepted. It can be concluded that Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage) differs with age.
Table No.18 : Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage) by education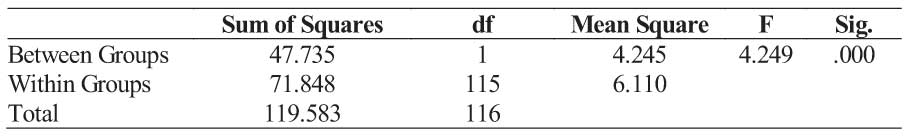
Interpretation :
above table based on the significant value it is identified that there is a significant difference in the education level of the respondents versus Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage). Hence, the alternate hypothesis is accepted. It can be concluded that Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage) differs with education.
Key Findings of the Study :
The data collected were analyzed carefully and the following findings were drawn :
- The results indicate that gender does not have a significant impact on Online recruitment (erecruitment) portal adoption (usage).
- ANOVA results show that the variance in Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage) by age is statistically significant. In other words, Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage) varies with different age groups.
- ANOVA results show that the variance in Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage)by education is statistically significant. In other words, Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal adoption (usage) varies with different educational levels.
Other Findings of the Study :
- From the study, it is administered that almost all the respondents including male and female are aware about the online recruitment (e-recruitment) portals.
- From the study, source of awareness of the online recruitment (e-recruitment) portals is mostly social media, followed by friends and new paper.
- From the study, it is inferred that the mostly male respondents using Online recruitment (e-recruitment) portal compare to the female respondents.
- The majority of the respondents adopting e-recruitment portal belongs to the 18-25 years of the age group and followed 26-30 years of the age group.
- From the study it is inferred that the respondents using online recruitment portals are mostly post-graduates and graduates.
Limitations of the Study :
- The study adopted purposive sampling method which is non-random, and there may be a chance of sampling bias.
- This study did not address extensively the perceptions of users toward e-recruitment portals.
- The present study has been confined to Kolkata metro city of West Bengal state of India.
Conclusion
In the present scenario of increasing penetration of internet usage, preference of smart phones by different cross sections of the society and developments in information technology. Online recruitment (erecruitment) portals like, naukri.com, timesjobs.com, monsterindia.com, indeed-one search all jobs, jobsahead.com, careerbui lder.com, shine.com, freejobalerts.com, facultyplus.com jobsahead.com etc. in the developing country like India awareness and adoption (usage) is bound to play a significant value exchange between job seekers as well as job givers.
References :
- Byars, L.L. and Rue, L. (2000). Human Resource Management, 6th ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, NY.
- Cappelli, P. (2001). Making the most of on-line recruiting. Harvard Business Review, 79.
- David Yoon Kin Tong (2009). Study on the E-Recruitment technology adoption in Malaysia.
- Galanaki, E. (2002). The decision to recruit online: A descriptive study. Career development international, 7(4),243-251.
- Khan, N. R., Awang, M., & Ghouri, A. M. (2013).Impact of e-recruitment and job-seekers perception on intention to pursue the jobs.
- Yoon Kin Tong, D., & Sivanand, C. N. (2005). E-recruitment service providers review : International and Malaysian. Employee relations, 27(1),103-117.
Bibliography :
- G.C. Beri & C.R. Kothari, Research Methodology.
- Peters, K. (2001).Five keys to effective e-recruiting. Ivey Business Journal.
- K Aswathappa, Human Resource Management, 5th ed., Text and Cases, McGraw-Hill.
