Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
A Study on Customers' Perception towards E-Wallets in Ahmedabad City
Abstract :
This paper attempts to study and measure the customers' perception regarding E-wallets in Ahmedabad city. A survey has been used to collect primary data and 102 questionnaires were used in final analysis. SPSS and Microsoft Excel have been used to analyze and interpret the data. Graphical Representation, t-test, ANOVAs and chi-square analysis have been used.Study results show thatpeople are aware and willing about the online payments through E-wallets and there is a tremendous increase in growth rate after demonetization. Word to Mouth publicity have higher impact on information spread compare to other methods such as advertisement on social media, Magazine, TV and Government promotion. So companies and government both should create awareness by organising cashless society workshops/seminars. This study set out to enlarge understanding of how consumers evaluate E-wallets services in Ahmedabad city. This paper makes a valuable contribution given the fact that there are only a limited number of comprehensive studies dealing with the E-wallets services in Ahmedabad city.
Keywords :
Factors, Buying Behavior, Customer, Software Product, Software Market.1. Introduction
The payment industry has undergone a drastic shift from barter system to E- wallets. Customers globally are not very comfortable with transferring money through the internet, especially the older generations. Digital wallets give them the sense of security by acting as a wall between the bank and the vendor. Since digital wallets have a limit to the cash that they can hold, any loss—in the event of a security breach—is limited. Further, for all the stakeholders a wallet leaves a money trail that helps in solving disputes. At a time when hacking and data theft is becoming a clear risk, use of wallets will increase going forward . Hence, current research is aimed to investigate the customers' perception regarding E-wallets in Ahmedabad city.
2. Theoretical framework : Types of e-wallets permitted in India
As per the Reserve Bank of India, there are three kinds of ewallets
in India: closed, semi-closed and open2.
Closed e-wallets : These are wallets issued by an entity for
facilitating the purchase of goods and services from it.
These instruments do not permit cash withdrawal or
redemption. As these instruments do not facilitate
payments and settlement for third party services, issue
and operation of such wallets are not classified as payment
systems. Hence, RBI approval is not required for issuing
them. Eg. Cab services, e-commerce and mobile
companies create e-wallets for making payments towards
purchase of products from them /for usage of their
services. They provide cash backs for payments made
through this channel. This is one way of ensuring loyalty
of their customers.
Semi-Closed e-wallets : These are wallets which can be
used for purchase of goods and services, including
financial services at a group of clearly identified merchant
locations/ establishments which have a specific contract
with the issuer to accept them. These wallets do not permit
cash withdrawal or redemption by the holder.
Wallets for amounts upto Rs.10,000/- can be created under
this category by accepting minimum details of the
customer, provided the amount outstanding at any point
of time does not exceed Rs. 10,000/- and the total value of
reloads during any given month also does not exceed Rs.
10,000/-. Amount upto Rs.50,000/- can be created in
wallets by accepting any 'officially valid document' which
is compliant with anti-money laundering rules. Such
wallets are non-reloadable in nature.
Amount upto Rs.1,00,000/- can be created by with full
Know Your Client norms (KYC) and can be reloaded.
Eg.AirTel Money, which is used for making payments for
a range of services like money transfer from Airtel Money
to another bank account or any other Airtel Money Wallet
or paying select utility bills.
Open e-wallets : These are wallets which can be used for
purchase of goods and services, including financial
services like funds transfer at any card accepting merchant
locations [point of sale (POS) terminals] and also permit
cash withdrawal at ATMs / Banking Correspondents
(BCs). However, cash withdrawal at POS is permitted
only upto a limit of Rs.1000/- per day subject to the same
conditions as applicable hitherto to debit cards (for cash
withdrawal at POS). Eg. M-Pesa is an open wallet run by
Vodafone in partnership with ICICI Bank. Axis Bank's e-
Wallet Card', can used for making payments on sites that
accept Visa cards, with a minimum limit of Rs 10, and a
maximum limit of Rs 50,000, and a validity of 48 hours.
3. Review of literature
R.Varsha .Thulasiram(2016) found that E-wallet which are
considered as an hi-tech platform for money transacting
and payments have been perceived to be comfortable and
reliable, indicating high levels of acceptance .The e-wallet
service providers need to strategize targeting not only at
students and the youth, but also other age groups.
Dr. Ramesh Sardar (2016) summarized that M-wallets
have emerged as the most significant contributor in
pushing cashless and electronic payments. Over time
when mobile payments will represent a significant part of
retail sales, there should be inter-operability between
different wallets. As most of respondents are concerned
about the security of mobile payments, the security system
should be strengthening.
Pawan Kalyani (2016) found that Digital wallets which are
popular and associate to the online business company are
more popular and those with the banks are doing fine,
mobile companies' e-wallet is restricted to the mobile
users. People are using a few services mostly for
recharging the DTH and paying bills, Shopping etc. The
awareness and practical Usability of the e-wallet is low,
that should be increased by adding more value added
services to it.
Vidyashree DV, Yamuna N, Nithya Shree G (2015)
concluded that People are more aware about the online
payments through mobile applications and there is a
wider increase in growth rate. Pay tm and Pay u Money is
giving 2 level security authentication to safeguard our
payment details. The digital payment system has to take
necessary steps to overcome delay in processing of
payments.
Alan Cole, Scott Macfaddin, Chandranaraynswami,
AlpnaTiwari (2009) concluded that much of work in this
area has been concerned with use of mobile phones as a
surrogate for a credit card or smart card. There is
numerous application, each ending with one or two
different user interface, each possibly requiring a separate
login, falls far short of what we believe is required to make
mobile phone a viable replacement for physical wallet. He
commented that to accomplish this goal requires a unified
architecture, able to accommodate an open set of content
types. Standards will also be an important aspect of this
work, enabling independently-developed services from
multiple providers to interoperate with one another.
4. Research methodology
4.1 Need/importance of the study
The recent fearless decision of the Indian government to
demonetize all the old currency notes of 500 and 1000rs
has been a burning factor through the country.Due to
these crises, almost 70% of the people's spending capacity
has been reduced and almost it is very hard to pay their
basic needs like medicines, grocery items and Vegetables.
Now the new Indian scenario has made Indians think
3 about the digital payment system. So, the context of this
decision it is extremely significant to study the consumers'
perception towards-wallets.
4.2 Objectives of the study
To Study the customers'
awareness and satisfaction about E-Wallet services.
To know their security concerns about related services.
4.3 Sampling Design
Descriptive research design and
non- probability based convenience sampling method has
been used to get the information about E-wallet.
4.4 Methods of Data Collection
For conducting this
research, a structured questionnaire was prepared and
sample of 102 people was taken for analysis. The
instrument poses a set of 23 questions designed to assess
customers' awareness and satisfaction of service. A fivepoint
Likert-type scale is used in this study, anchored by
“strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”. The data was
collected from the respondents with the help of
Quantitative method via a survey.
4.5 Research Tools
SPSS and Microsoft Excel have been
used to analyze and interpret the data. Multivariate
techniques like ANOVAs, chi-square, t-test have been
used to test the various hypotheses.
4.6 Hypotheses
There is no significant difference between respondent's
occupation and satisfaction level of using E-Wallet
services.
There is no significant difference among different age
groups regarding their satisfaction on E-Wallet Services.
There is no significant difference between gender of the
respondents and awareness of respondents about EWallet
services.
There is no association between the gender of respondents
and sources of awareness about government's initiative of
promoting E-Wallet services.
4.7 Limitation & Scope of the Study
The study is confined to the Ahmadabad city of Gujarat.
So, the conclusion derived from the research cannot be
made applicable as it is for the other parts of the states or
other states. Future researchers are advised to take
diversified samples to arrive at generalisation. Future
researchers can make state wise comparison with larger
sample size. The research is just a small step in
understanding the constructs of awareness and
Satisfaction. The causal relationships between the two
have not been investigated, customer satisfaction and
there effect on fewer complaints, Security aspects, word of
mouth, and switching etc. can be explored by future
researchers. Lot of scope exists for research into the safety
and security issues of E-wallets for its effective adoption.
5. Analysis
Demographic profile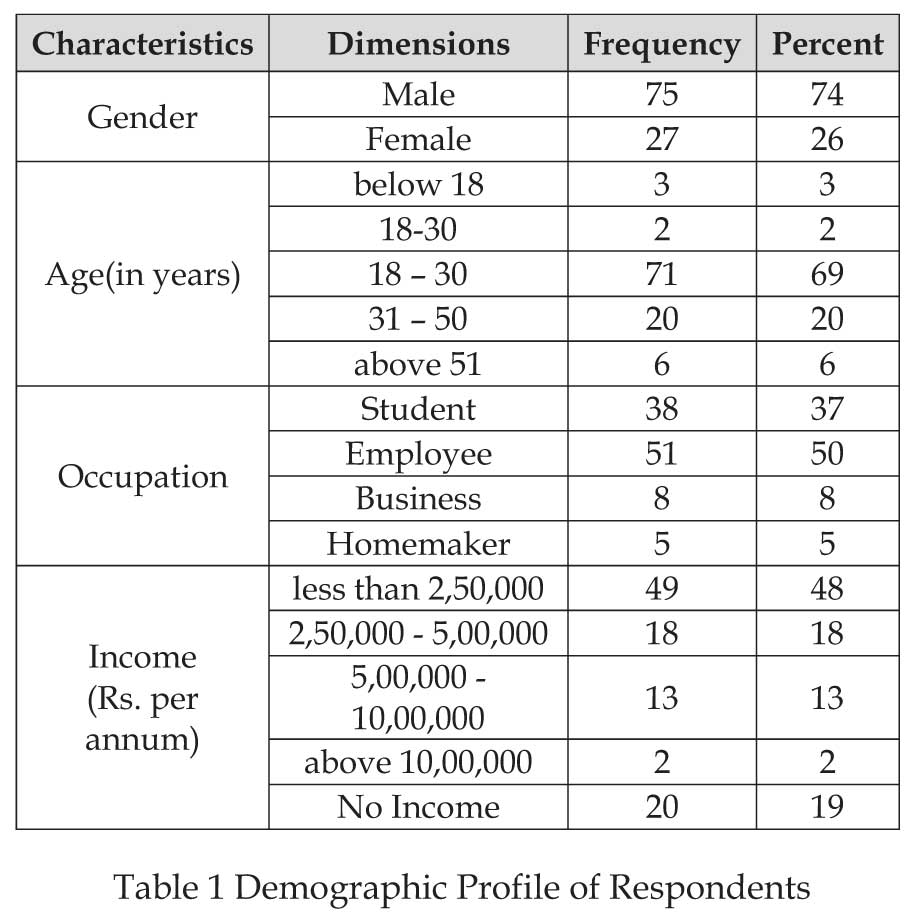
H1:There is no significant difference between respondent's occupation and satisfaction level of using EWallet services.
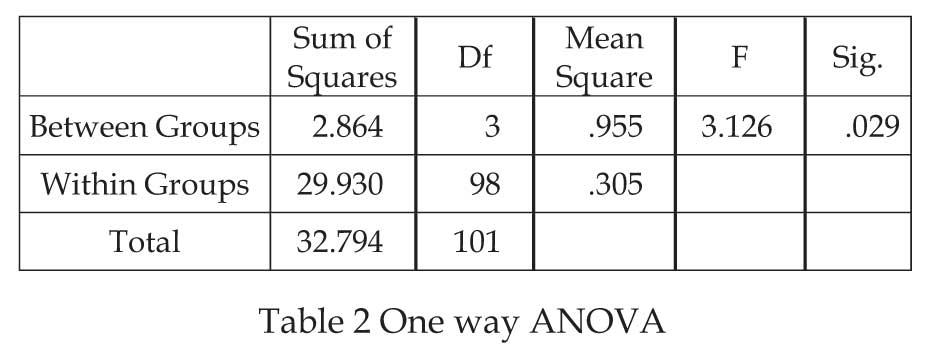
The significance value obtained is .029 which is smaller
than 0.05, so we reject null hypothesis. Thus it can be
concluded that there is significant difference among
satisfaction level of using E-Wallet Services when
classified by respondent's occupation.
H2: There is no significant difference among different age
groups regarding their satisfaction on E-Wallet Services.
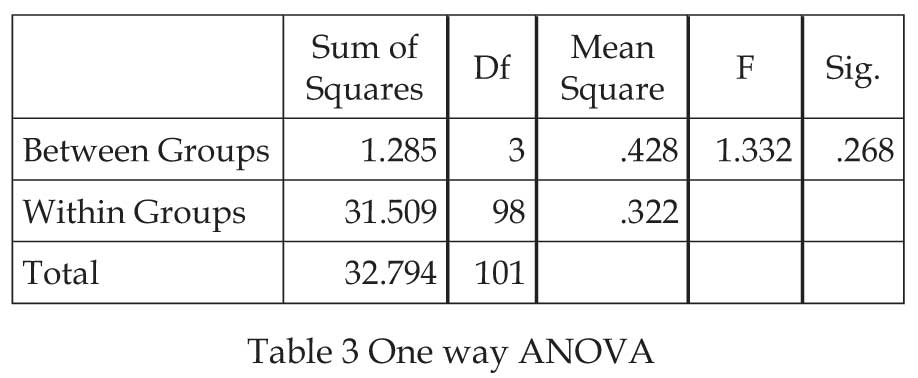
The significance value obtained is .268 which is not smaller
than 0.05, so researcher is fail to reject null hypothesis.
Thus it can be concluded that there is no significant
difference among different age groups regarding their
satisfaction on E-Wallet Services.
H3:There is no significant difference between gender of the
respondents and awareness of respondents about E-Wallet
services.
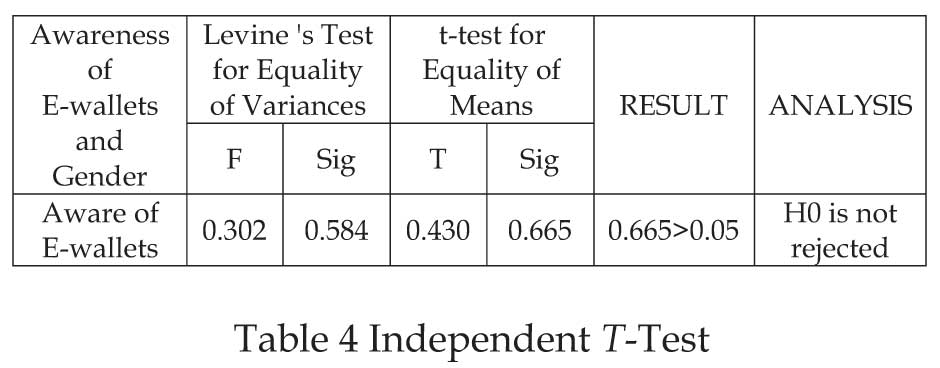
It is interpreted from the above table that there is no
significant difference in awareness of respondents
about E-Wallet by when classified by their gender.
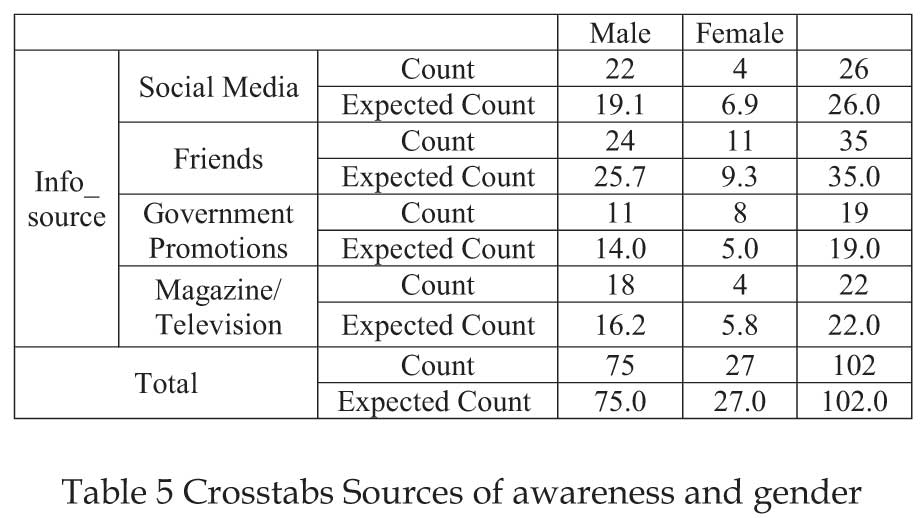
Table 5 Crosstabs Sources of awareness and gender H4 : There is no association between the gender of respondents and sources of awareness about government's initiative of promoting E-Wallet services.
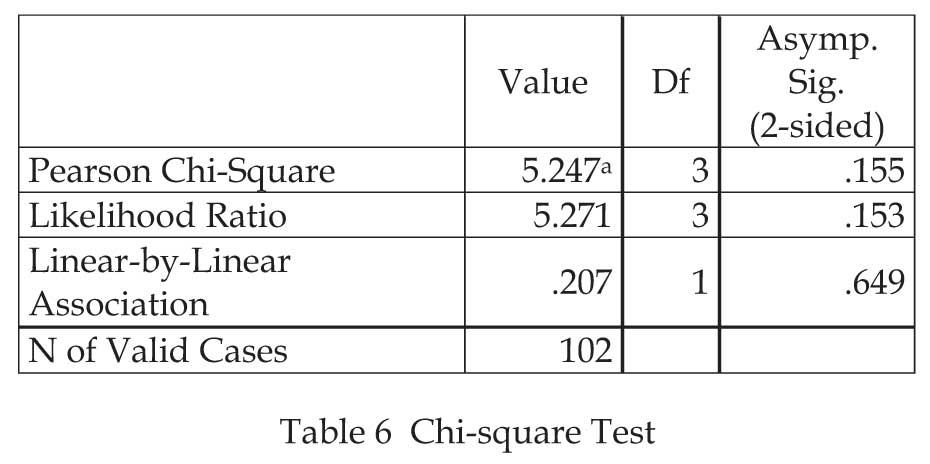
Here, significant value is greater than 0.05 so, researcher is fails to reject null hypothesis means there is no association between the gender of respondents and sources of awareness about government's initiative of promoting E-Wallet services.
Findings
Out of total 102 respondents, majority of them (74%) were male.
More than 50% respondents' age was between 18-30 years.
Approx. 50% of respondents were employee followed by
students (37%).
Nearly 50 % of respondent, such high awareness level of Ewallet
among respondents shows that E-wallet service providers
have successfully advertised the concept of E-Wallet among
general public.
Respondents got the information regarding E-Wallet from
Various sources. Word to Mouth publicity have higher impact
on information spread compare to other methods such as
advertisement on social media, Magazine, TV and Government
promotion.
More than 50% of respondents use single E-Wallet service. This
shows that respondents like to have single service provider for
uniform experience to carry out digital transaction and
payments.Majority of respondents have been using E-wallet for
one year. The concept of E-wallet is not that much old, so
adoption and use of E-wallet services is limited. Researcher can
predict that it.
Out of total respondents 72% were using Paytm. It shows the
penetration of Paytm wallet compare to other wallets. The
second most wallet used by respondents is Freecharge. It can be
can inferred that Paytm and Frecharge wallets have high
adaptation level against their competitors.
Out of Total respondents 55% respondents use E-Wallet more
than twice in a month, followed by twice in a month. This result
shows that respondents are very much inclined to use the EWallet
for various payments and transactions.
Majority of respondents(79%) were aware about government
push for E-transacations. This shows that people areatleast have
clarity on benefits of digital transactions over traditional
payment system.Approx. 87% of total respondents use E-Wallet
for mobile/DTH recharge purpose. The second most option
preferred by users is Utility and bill payment. This shows that
mobile wallets have successfully attractedthe consumers by
different cashback offers and discount.
Out of total respondents 66% respondents were satisfied with
their E-wallet service, followed by 24% users which are highly
satisfied with E-wallet services. 10% of users have neutral
opinion about their satisfaction level.
Majority of respondents(92%) agreed to prefer E-Wallet in place
of conventional payment system. This suggests that in future
adaptation level among people will be considerably high.
Data analysis suggests that respondents are concerned about all
five criteria which are mentioned above. Cashback offers are the
most considered while doing transactions/payment over Ewallet.
More than 50% of respondents agreed that they definitely
consider the all security criteria such as-leak of confidential info,
cyber crime, Malware, Phishing etc. This shows that E-wallet
companies must have to work upon security features to attract
and retain the users on their platform for longer time.
Respondents suggested creating more secure service so that they
can transact over E-wallet safely. More than 50% of users
wanted to have good offers and faster process on E-wallets.
Respondents agreed that E-wallet is attractive choice for
payment over traditional method and it support as of now to
conventional payment during the transition phase. As per the
response near 50% of response were in favor of having E-wallets
which suggests preference of E-wallet over other E-payment
modes.
6. Recommendations/suggestions
Word to Mouth publicity have higher impact on information spread compare to other methods such as advertisement on social media, Magazine, TV and Government promotion. So companies and government both should create awareness by organising cashless society workshops/seminars at school, college, workplace etc. Government can makes it mandatory for all schools/colleges/institutes to have atleast one program in one academic year. E-Wallet are used for mobile/DTH recharge purpose. The second most option preferred by users is online shopping. Authority must make fees payment and filing of IT returns compulsorily with E-wallets only to increase the growth rate of the same.
CONCLUSION
Majority of respondents (92%) agreed to prefer E-Wallet in place of conventional payment clearly illustrates that the adoption image of E- wallet among consumers in Ahmedabad has already crossed the beginning stage, to be successful in E-wallet market now depends heavily on the marketing strategies of E- wallet companies as well as the financial policy makers.
References :
- E-wallet. International Journal of Recent Research and Review, Vol. I, March 2012 ISSN 2277 – 8322.
- Alan Cole, Scott Macfaddin, Chandranaraynswami, AlpnaTiwari(2009).Toward a Mobile digital Wallet.IBM research report October 16, 2009.
- D o n a l d L . Amo r o s o , R émyMa g n i e r - Watanabe(2012).Building a Research Model for Mobile Wallet Consumer Adoption: The Case of Mobile Suica in Japan. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research ISSN 0718–1876 Electronic Version, 7, 1, April 2012 / 94- 110.
- Dr HemShwetaRathore (2016).Adoption of digital wallet by consumers.BVIMSR's Journal of Management Research ,8,1,April : 2016.
- Dr.PoonamPainuly, ShaluRathi (2016), “Mobile Wal let : An upcoming mode of bus ines s transactions”,International Journal in Management and Social Science, Vol.04 Issue-05 (May, 2016) ISSN: 2321-1784.
- Dr. Ramesh Sardar (2016).Preference towards mobile Wallets among urban population Of Jalgaon city. Journal of management (JOM) 3, 2, July–Dec (2016).
- M. Manikandan, Dr. S. Chandramohan(2015).Mobile wallet- a virtual physical wallet to the Customers. Indian journal of research, 4, 9, Sept 2015.
- Mr.Saikalyan Kumar Sarvepalli(2016).A study on the scope of the virtual wallets in indian market -issues and Challenges.international journal of multifaceted and multilingual studies, iii, viii, August 2016.
- Transacting Online.International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications,3, 1.
- N. Supriya, M. S. P. Joshna, T. VasudhaSingh(2016), “Issues and Challenges of Electronic Payment Systems”, international journal of innovative research & development January, 2016, 5, 2.
- PawanKalyani (2016).An empirical study about the awareness of Paperless e-currency transaction like ewallet Using ICT in the youth of India.Journal of management engineering and informat ion technology, 3, 3.
- PinalChauhan (2013).E-Wallet: The Trusted Partner in our Pocket.(IJRMP) ISSN: 2320-0901, 2, 4, April 2013.
- R.Varsha .Thulasiram (2016), “Acceptance Of EWallet Services: A Study Of Consumer Behavior”, International Journal of Innovative Research in Management Studies (IJIRMS)ISSN (Online): 2455- 7188, 1, 4.
- Challenges of Electronic Payment Systems”, (IJRMP) ISSN: 2320- 0901,Vol. 2, Issue 9, December 2013.
- RoopaliBatra, Nehakalra(2016),“Are digital wallets the new currency?”Apeejay journal of management and technology, January 2016 .11 ,1.
- Vidyashree DV, Yamuna N, Nithya Shree G (2015), “A Study on New Dynamics in Digital Payment System – with special reference to Paytm and Pay U Money”, International Journal of Applied Research 2015; 1(10): 1002-1005.
- http://www.moneycontrol.com/news accessed on 10th April 2017.
- http://arthapedia.in/index.php?title=Digital_/ _Electronic_Wallet_(e-wallet) accessed on 14th April 2017.
- ht tps ://www. t e chpr evue . com/e -wal l e t s - importance-indian-scenario accessed on 20th April 2017.
