Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
A study on measuring customers' expectation and perception in private and public sector banks
Abstract :
This study attempts to measure service quality of public and private banking sector by measuring expectation and perception of customers. Descriptive Research Design was adopted to determine customers' perception and expectation about the bank. A survey has been used to collect primary data and 239 questionnaires were used in final analysis. SPSS and Microsoft Excel have been used to analyze and interpret the data. Bank service providers should continually monitor the level of fulfilment of personal needs and satisfaction with the organization, if they wish customers to remain loyal.
Keywords :
Customer services quality, Customer satisfaction, Bank service provider, Organization, Customer.Introduction :
The banking industry like many other financial service institutes is facing rapid regulatory, structural and technological changes in market, stiffer competition, new set of challenges, more demanding, more educated and better informed customers. The importance of both service quality and customer satisfaction to service organizations in general and banking in particular has received extensive attention in recent years. Hence, the objective of this study was to examine the level of service quality and customer satisfaction in two major segments of banks i.e. private and public banks.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Tarsem Lal (2018) studied the financial inclusion through
cooperative banks. To meet the objectives, 540
respondents of cooperative banks operating in three
northern states of India, i.e., J&K, Himachal Pradesh (HP)
were studied. The study emphasized that financial
services such as savings, loans, insurance, credit, etc.,
through financial inclusion has generated a positive
impact on the lives of the poor people.
Bedman Narteh (2018) tried to set integration between
SERVQUAL and BSQ models. The researcher modified
the resulting scale by including price to examine service
quality and customer satisfaction in retail bank services in
Ghana. The researcher used questionnaire and surveyed
560 retail bank customers. The authors concluded that
tangibles, reliability, assurance, empathy and price are
positively and significantly predicted customer
satisfaction.
Mohamed AbdulnaserJanahi, Muneer Mohamed Saeed
Al Mubarak, (2017) studied the impact of different factors
of customer service quality on customer satisfaction. The paper presented a model having six constructs namely
Compliance, Assurance, Reliability, Tangibility, Empathy
and Responsiveness and exhibited relationships between
these six factors and customer satisfaction in the Islamic
banking sector. The authors concluded that there is a
strong and positive relationship between the six
constructs of customer service quality and customer
satisfaction.
Chrys i Alexiadou, NikolaosStylos , Andreas
Andronikidis, Victoria Bellou, Chris A. Vassiliadis, (2017)
evaluated perception-based quality in service encounters.
The researchers studied potential mismatches in how
customers and front-line employees perceive quality in
service settings. The survey involved 165 bank branches
and 1,522 respondents (463 front-line employees and
1,059 customers). Results revealed relation between
tangibles, responsiveness and assurance when compared
customers and front-line employees perceptions but also
found mismatches between customers and front-line
employees perceptions of reliability and empathy.
Abhilash Ponnam, Rik Paul, (2017) drafted the situation
for service value expected in various phases of
relationship over time in Indian retail banking context.
The authors explored customer service value dimensions
related to Indian retail banking. The customer intimacy,
product leadership, service equity, perceived sacrifice,
service quality, and operational excellence are the service
value dimensions in context of Indian retail banking. The
authors concluded from inferential statistics that except
for operational excellence and service quality, all the other
value dimensions exhibited variation in importance over
time. Results reveal that customers in the early stages of
relationship value tangible value dimensions and the ones in advanced stages of relationship value intangible
dimensions.
Pichate Benjarongrat, Mark Neal, (2017) done research in
Thai bank and studied the service profit chain (SPC) with
a intention to identify which service features customers
understand to be most important in their customer
satisfaction and engagement. Convenience, courtesy,
competence and internal branding are the key service
features for customers in their satisfaction and
engagement. Convenience, courtesy, competence and
internal branding showed positive relationships with
customer satisfaction/customer engagement.
Hajer Zarrouk, Khoutem Ben Jedidia, Mouna Moualhi,
(2016) compared the factors affecting profitability in
Islamic bank and conventional banking in the Middle East
and North Africa (MENA) region. A panel data model was
used to know the banks' specific determinants and the
macroeconomic factors influencing the profitability. The
authors studied 51 Islamic banks operating in the MENA
region from 1994 to 2012. The authors concluded several
elements of similarities between determinants of the
profitability for Islamic and conventional banks except
inflation rate.
Jennifer Mullan, Laura Bradley, Sharon Loane, (2017)
studied perception of stakeholders for mobile banking
and identified drivers and barriers of bank adoption of
mobile banking.
The researchers have used two-round modified Delphi
study. The opinion of 72 members from six stakeholder
industries was sought. The authors concluded that global
mobile phone penetration, competitive advantage,
customer convenience, strategic importance, customer
demand, low perceived risk/security concerns and
stakeholder partnerships are the key drivers of bank
selection.
Justin Paul, Arun Mittal, Garima Srivastav, (2016)
compared the private and public-sector to check the
impact of various service quality variables on the overall
satisfaction of customers. Forward stepwise regression
was used by the researchers. The authors surveyed 500
respondents in India; equal proportion of respondents
surveyed both for private and public banks. The authors
concluded that knowledge of products, response to need,
solving questions, fast service, quick connection to the
right person, and efforts to reduce queuing time are
positively associated with overall satisfaction in private
sector context
RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
- To study and measure expectation and perception in private and public Banks.
- To identify and differentiate the best banking sector
RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
- There is no significant difference between Expectation and Perception of customers towards bank services.
- There is no significant difference between customer expectations and customer perceptions of public banks regarding service quality.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Descriptive Research Design was adopted to determine customers' perception and expectation about the bank. The study has the population base as the public and private banks located in Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar cities of Gujarat State. A convenience Sampling was used to elicit information regarding customer perception and expectation about the service quality and customer satisfaction of the major banks. The questionnaire has been personally administered on sample size of 239 chosen on a convenient basis from the cities of Gujarat State. Modified SERVQUAL instrument with five point likert type scales was used. For the analysis of data statistical methods are applied with the aid of SPSS version 16.0.
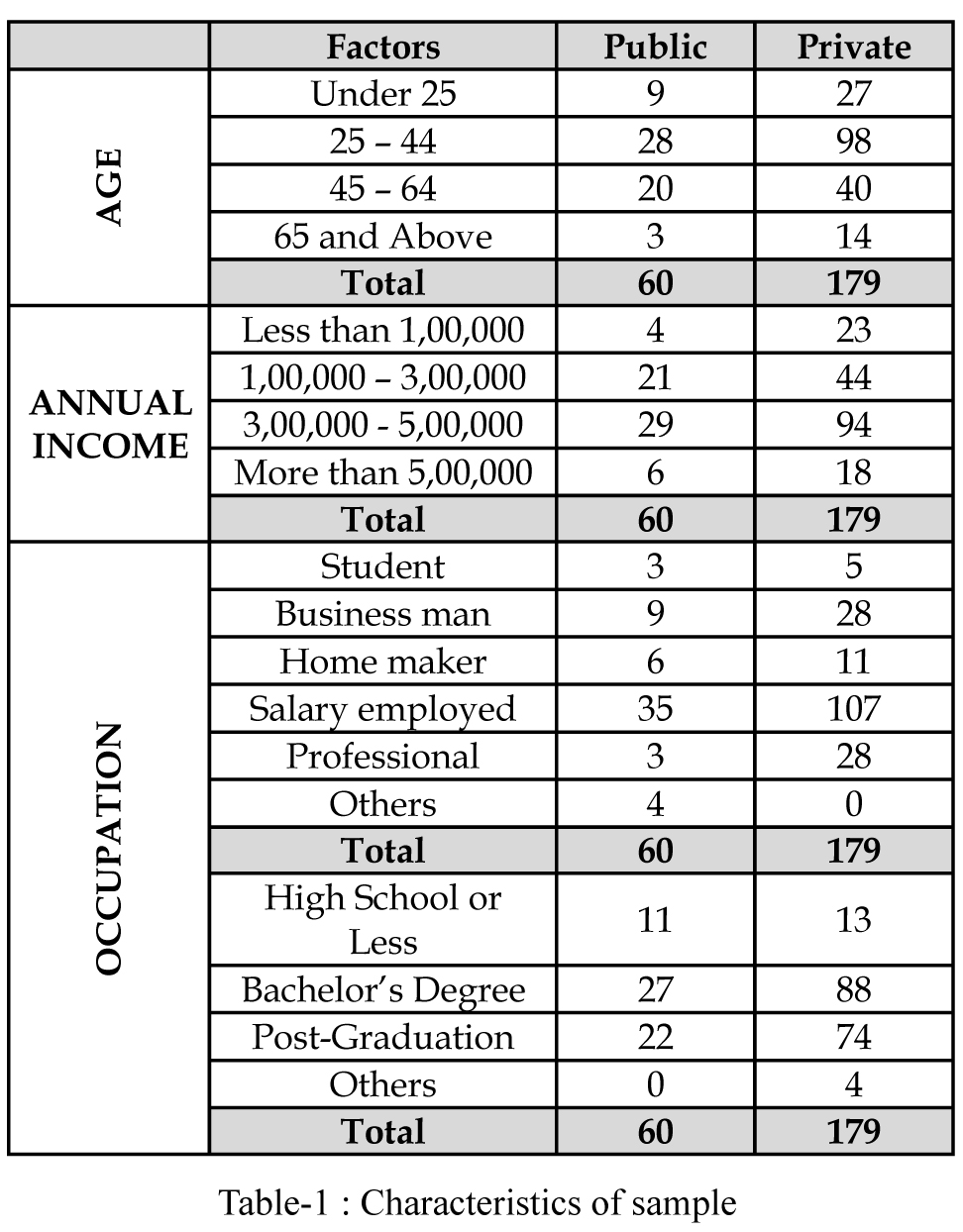
CHARACTERISTICS OF SAMPLE
DATAANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION
Factor Analysis
KMO (Kaiser – Meyer - Olkin test of sampling adequacy) :
Significance value: - 0.8936.
The KMO is a statistic indicates the proportion of variance in
research variables that might be caused by underlying factors.
High values (close to 1.0) generally indicate that a factor analysis
may be useful. So here the value is 0.8936 and it is closer to 1. So
it can be said that factor analysis is useful for data.
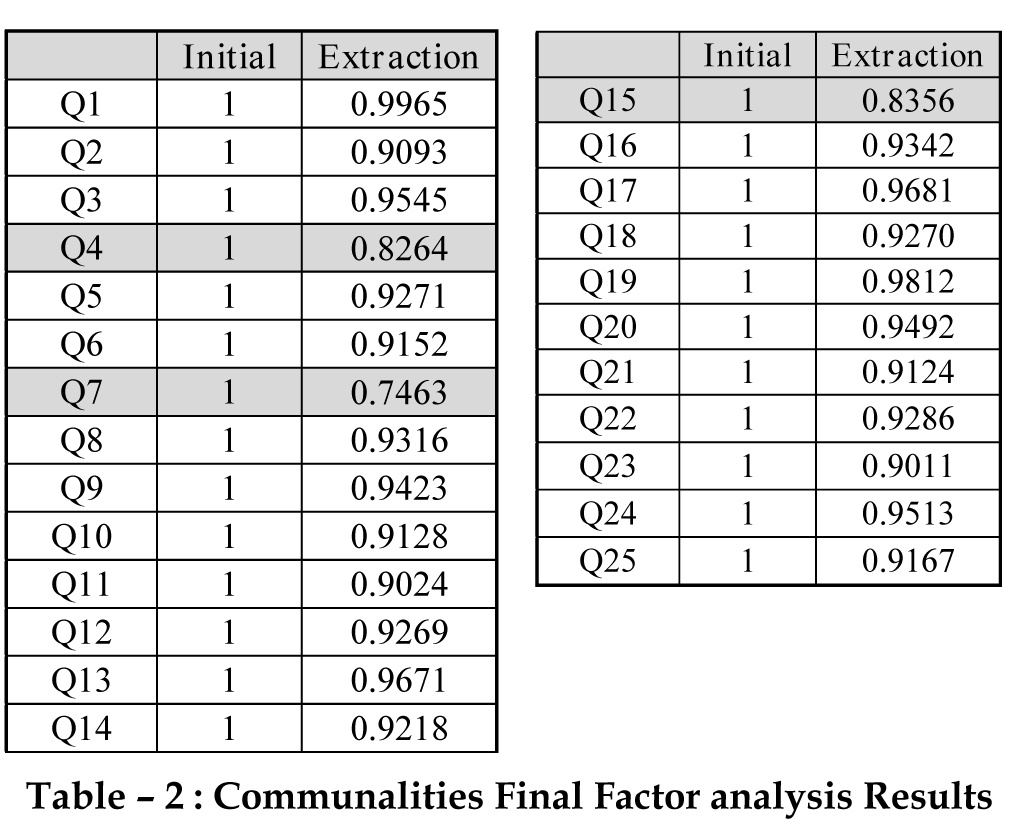
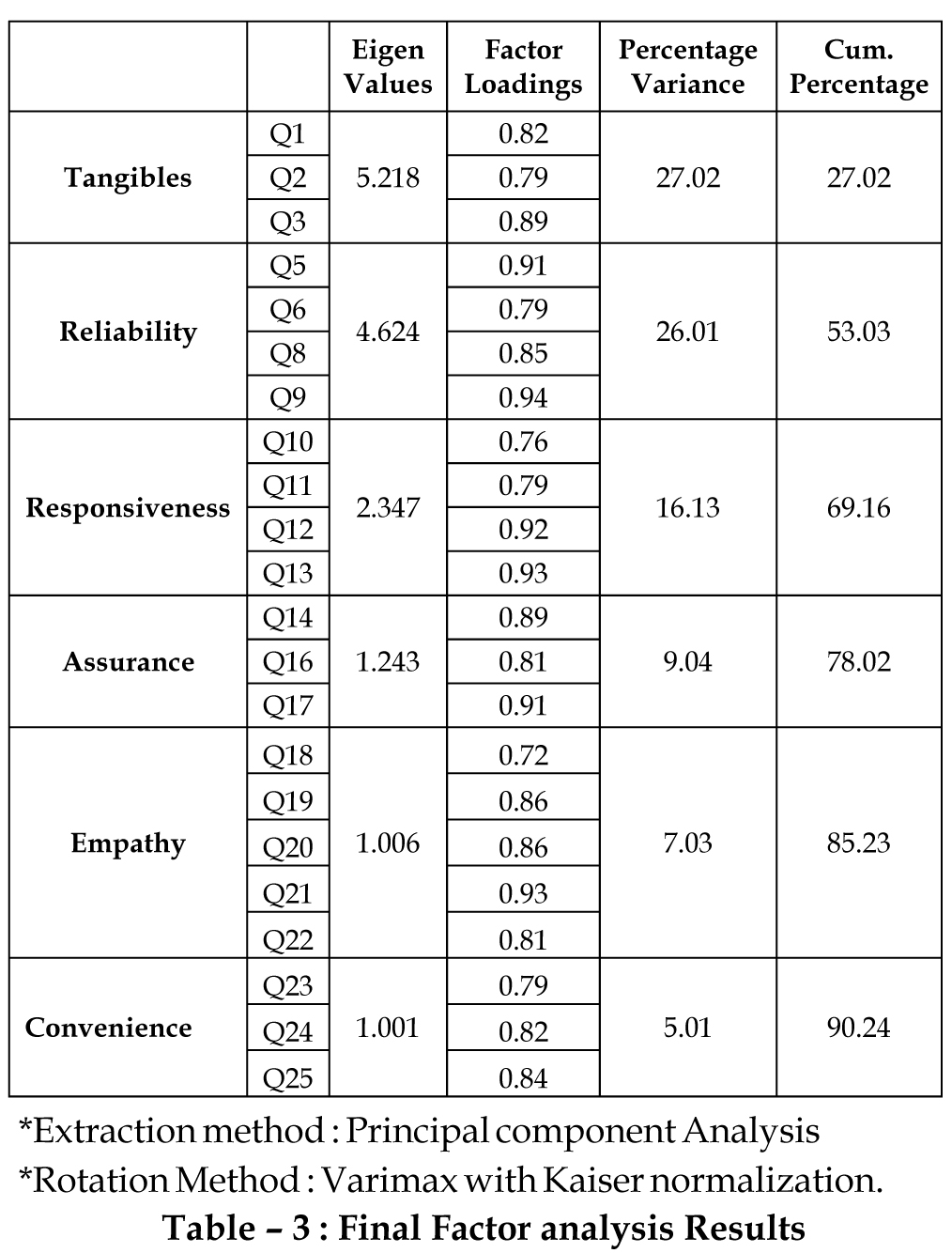 The rotated factor matrix shows that three components
have less than 0.5 Eigen values and 22 components explain
90.24Percent variance of total variance. The components
which have lesser value (less than 0.90) it should be deleted
in factor analysis. From the above two tables it can be said
that 3 components Q4 (Materials Associated with the
service will be visually appealing at bank) from Tangibility
dimension, Q7 (Banks will perform the service right the
first time) from Reliability dimension, Q15 (Customers of
banks will feel safe in transaction) from Assurance
dimension is not important and it is removed for further
survey.
The rotated factor matrix shows that three components
have less than 0.5 Eigen values and 22 components explain
90.24Percent variance of total variance. The components
which have lesser value (less than 0.90) it should be deleted
in factor analysis. From the above two tables it can be said
that 3 components Q4 (Materials Associated with the
service will be visually appealing at bank) from Tangibility
dimension, Q7 (Banks will perform the service right the
first time) from Reliability dimension, Q15 (Customers of
banks will feel safe in transaction) from Assurance
dimension is not important and it is removed for further
survey.
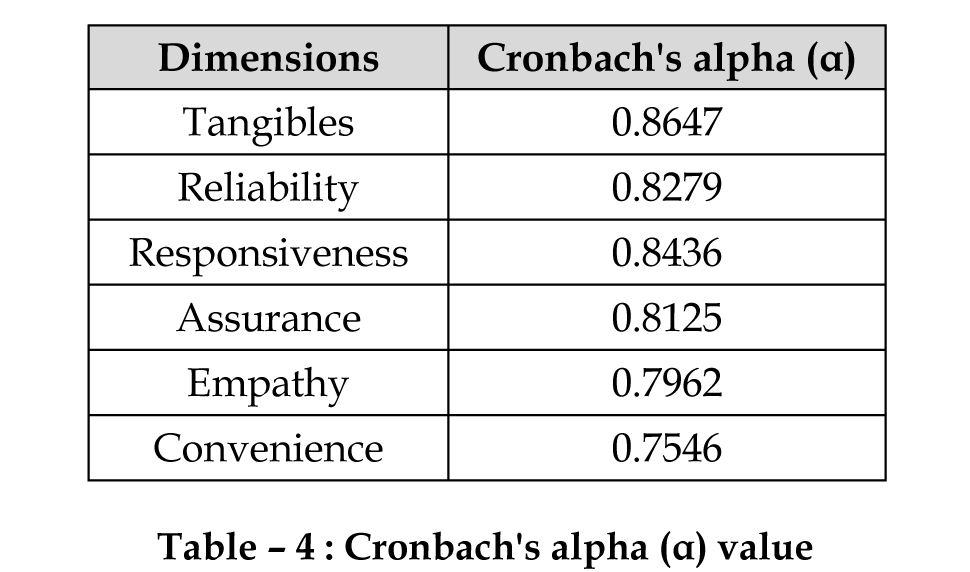
Reliability Testing
A measure of construct reliability (Cronbach's Alpha) was
computed for each dimension to assess the reliability of
the set of items forming that dimension. The coefficients
range from 0.8647 to 0.75462. As a rule 0.70 or more
represent satisfactory reliability of the items measured.
Gap Analysis
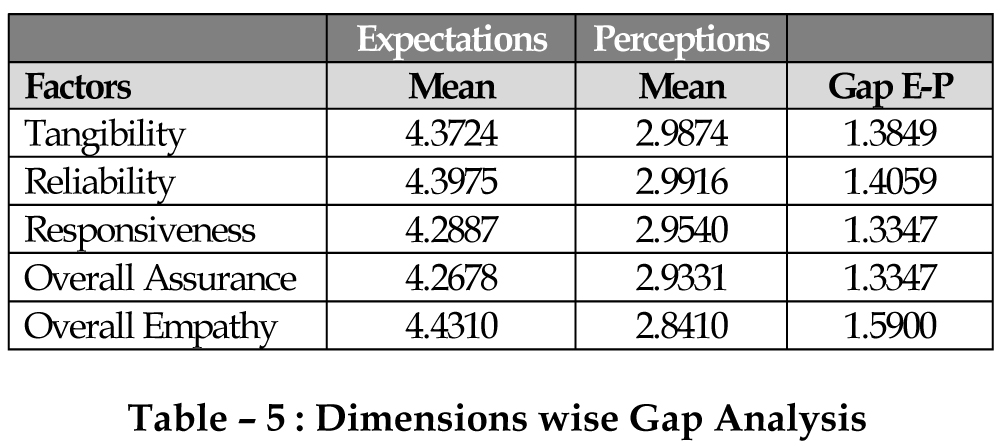
The analysis shows that there is a major difference between the servicequality expectations versus perception of the customers for all the banks.It can be seen that the Empathy dimension is having the largest gap, followed by Reliability.
Public Sector Bank :
Hypothesis:There is no significant difference between
customer expectations and customer perceptions of public
banks regarding service quality.
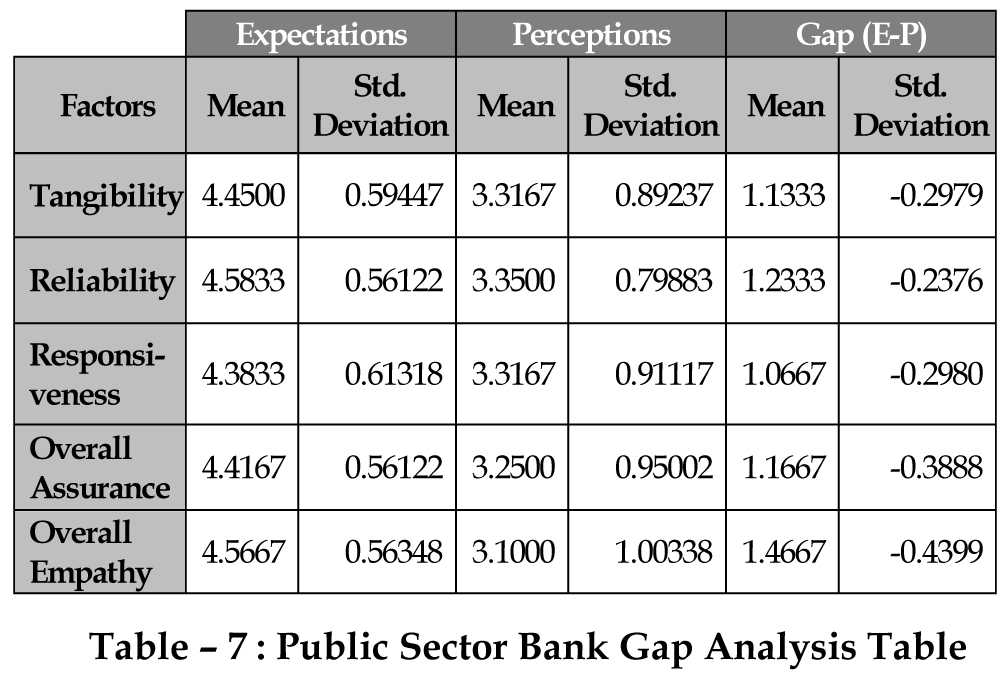
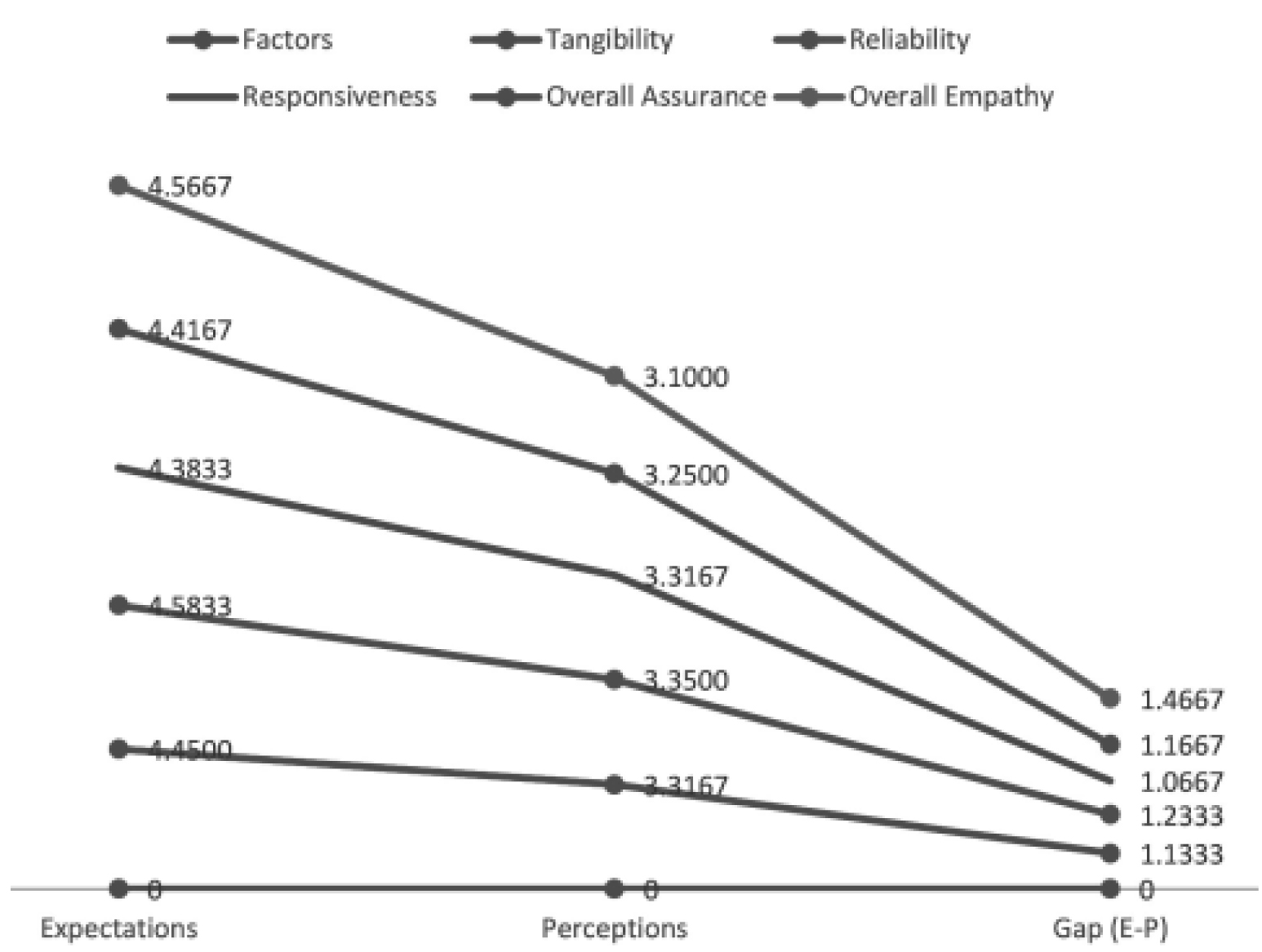 The analysis shows
that there is a major
difference between the
service quality
expectations versus
percept ion of the
customers for public
sector banks. The
above table reveals that
in the reliability
dimension public
sector performs well.
And there is a high gap
between expectation
and perception in
empathy and
convenience
dimension. Similarly
private banks are
analyzed.
The analysis shows
that there is a major
difference between the
service quality
expectations versus
percept ion of the
customers for public
sector banks. The
above table reveals that
in the reliability
dimension public
sector performs well.
And there is a high gap
between expectation
and perception in
empathy and
convenience
dimension. Similarly
private banks are
analyzed.
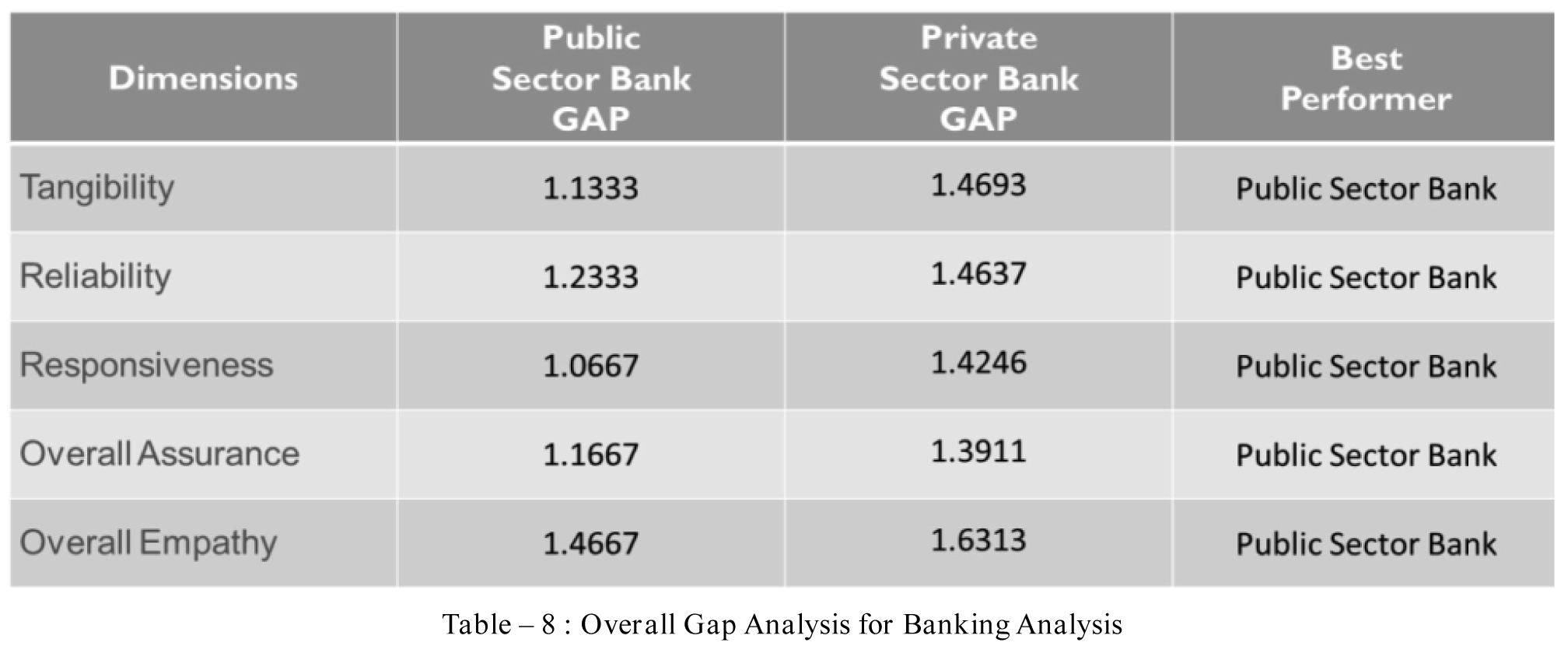
MAJOR FINDINGS
Major finding of the research were summarized as follows.
The factor analysis confirms total 22 variables which
explain 90.24 Percent of variance out of total variance and 3
variables get deleted for further survey because they are
not forming part of any grouping variables. Factor analysis
showed that tangible, assurance; empathy, reliability,
responsiveness and convenience dimensions are the
explanatory variables for predicting customer satisfaction
in Gujarat.
The reliability testing reveals that all the values of cronbach
alphas are greater than 0.75 so that it can be concluded that
collected data is reliable.
The statistical analysis shows that there exists a gap
between the customer expectations and perceptions in the
Banking sector.
CONCLUSION
The statistical analysis shows that there exists a gap between the customer expectations and perceptions in the Banking sector. The expectations of bank customers are higher than their perceptions as suggested by Parasuraman et al. (1988). This gap varies across the banking sector.It can be concluded from factor analysis that tangibility, assurance; empathy, reliability, responsiveness and convenience dimensions are the explanatory variables for predicting customer satisfaction in Gujarat.
REFERENCES :
- Al-Tamimi, N. J. (2003). “Measuring perceived service quality at UAE commercial banks”. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management Vol. 20 No. 4, pp. 458-472.
- Bakar, A.I. (2007). ''Service Quality Gap and Customers' Satisfactions of Commercial Banks in Malaysia”. International Review of Business Research Papers Vol. 3 No.4 , pp.327-336.
- Charles chi cul, B. R. (2003). “Service quality Measurement in the banking sector in south Korea”. International Journal of Bank Marketing, Vol.21 No.4 , pp.191-201.
- Dutta, K.D. (2009). “Customer expectations and perceptions across the Indian banking industry and the resultant financial implications”. Journal of Services Research, Vol. 9, No. 1 , pp.32-49.
- Eugenia Petridou, C.S. (n.d.). “Bank service quality: empirical evidence from Greek and Bulgarian retail customers”. International Journal of Quality &Reliability Management Vol. 24 No. 6 , pp. 568-585.
- Franc¸ois A. Carrillat, F.J. (2007). “The validity of the SERVQUAL and SERVPERF scales-A meta-analytic view of 17 years of research across five continents”. International Journal of Service Industry Management Vol. 18 No. 5 , PP-472-490.
- G.S. Sureshchandar, C.R. (2002). “ Determinants of customer-perceived service Quality : a confirmatory factor analysis approach”. Journal of Service Marketing, vol.16 No.1 , pp. 9-34.
- Huseyin Arasli, S.T. - S. (2005). “A comparison of service quality in the banking industry : Some evidence from Turkish- and Greek-speaking areas in Cyprus”. International Journal of Bank Marketing Vol. 23 No. 7 , pp. 508-526.
- Isa, M. A. (2008). “An examination of the relationship between service quality perception and customer satisfaction - A SEM approach towards Malaysian Islamic banking”. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management Vol 1 No 3 , pp 191-209.
- Jones, A. G. (1994). "Service Quality -Concepts and Models”. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management, Vol. 11 No. 9 , pp. 43-66.
- Kamal Naser, A. J.-K. (1999). “Islamic banking: a study of customer satisfaction and preferences in Jordan”. International Journal of Bank Marketing Vol.17 No.3 , pp. 135-150.
- Ladhar, R. (2008). “Alternative measures of service quality: a review”. Managing Service Quality Vol. 18, No. 1 , pp. 65-86.
- Marvin E Gonzalez, R. D., & Mack, R. W. (2008). “An Alternative approach in service Quality: An ebanking case study”. The Quality Management Journal, Vol.15 No.1 , pp.41-60.
- Zhou, L. (2004). “A dimension-specific analysis of performance-only measurement of service quality and satisfaction in China's retail banking” . Journal of Services Marketing Vol. 18 No. 7 , pp. 534-546.
