Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Comparative analysis on Usage of Social Media among print and electronic media Journalists working in the Hyderabad, Telangana State
Abstract :
Emergence of social media has changed the communication among all the spheres of individual's life. The study examines the use of social media platforms, namely Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, what'sapp, wechat among the print and electronic media journalists working in Hyderabad city. It also finds out the 1% rule of thumb in comparison with the participation of print and electronic media journalists. A survey approach is used to understand why and how people actively seek out specific media to satisfy specific needs. Why do Journalists use media and what do they use them for? Users and Gratification Theory (UGT) discusses how users deliberately choose media that will satisfy given needs and allow one to enhance knowledge, relaxation, social interactions/companionship, diversion, or escape. The social media audience members are not passive consumers of media. Rather, the audience has power over their media consumption and assumes an active role in interpreting and integrating media into their own lives. Unlike other theoretical perspectives, UGT holds that audiences are responsible for choosing media to meet their desires and needs to achieve gratification. This theory would then imply that the media compete against other information sources for viewers' gratification. The study has utilized primary data from journalists of print and electronic through random sampling method.
Keywords :
Social media, 1% rule of thumb, Users and gratification, social interaction, print media and electronic media.INTRODUCTION
New developments in the technological world have made
the internet an innovative way for individuals and families
to communicate. Social media networks have created a
phenomenon on the internet that has gained popularity
over the last decade People use social media sites such as
Facebook, Twitter, and Myspace to create and sustain
relationships with others (Boyd & Ellison, 2007). These
social media sites let those who use them to create personal
profiles, while connecting with other users of the sites.
Users can upload photographs, post what they are doing
at any given time, and send personal or public messages to
whomever they choose. In this “information age,” social
media sites seem to be growing in popularity rapidly,
especially among young adults (Pempek, Yermolayeva, &
Calvert, 2008). For many connected users in India, access
to the Internet is primarily for accessing social media
networks. According to a report by the Internet and
Mobile Association of India (IAMAI), 66% of the 180
million Internet users in urban India regularly access
social media platforms. The most popular activities on
social media include maintaining one's own virtual profile
on the likes of Facebook and Twitter, posting and sharing
an update as well as replying to something a friend has
posted. While college students (33%) form the largest
demographic of active social media users in India,
working women and non-working women register just
7% and 11% respective share in that user base(Live mint,
2016). Many of these young adults use social media
networks to communicate with family, friends, and even
strangers. Social media sites have created new and nonpersonal
ways for people to interact with others and
young adults have taken advantage of this technological
trend.
The role of social media as a tool of communication and
has created new ways of mobilizing public opinion and
encouraging participation in political and civic activities
ranging from joining social groups, posting short
messages on Twitter, expressing support for social
movements (Anitha kaluvoya, 2015)
Here're the major India milestones in web, mobile, and
social media usage.
- India now has 462 million active internet users (out of a global total of 3.63 billion)
- Internet usage is growing in India at a rate of 90 percent, while the global average is just 19 percent
- India's web users have 153 million active social media accounts (from a global tally of 2.43 billion)
- India has 1.01 billion mobile connections
- India has 153 million social media users, of which 130 million are on mobile.
- India's active social media users are up by 23 percent since March 2015, compared to 26 percent global rise.
- Mobile subscriptions in India grew only by 7 percent Arto, a social network site was divided into four overarching categories that cover different features on the site (Malene Charlotte Larsen):
- The personal and branding related features (such as the profile, the picture gallery, the blog, the notice board etc.).
- The social and contact enabling features (such as the guest book, the debate forum, the clubs etc.).
- Entertainment (such as games, videos, jokes etc.).
- Support and practical information (such as rules, safety guidelines and support section) (Larsen, 2005; Larsen, 2007a).
Components of Social Media
Frakes (2010) mention that social media can be said to have three components:
- Concept (art, information, or meme);
- Media (physical, electronic, or verbal);
- Social interface (intimate, direct, community engagement, social viral, electronic broadcast or syndication, or other physical media such as print).
Telangana State The 29 state of the Indian subcontinent and has major metropolitan city i.e. Hyderabad. The state capital is the center for all international, national, and state media houses.
Significance of Study
This field of study is important because sociability is an underlying theme in using forms of social media. Since this social media phenomenon is continuing to grow at a fast pace, it is important to understand the usage pattern among journalists whose objective is to update the information seekers. Social media has become a convenient tool for the media personnel to get information for news coverage and also updating the news to the viewers or readers. Presently the print medium newspapers have not only gone online, but having exclusive mobile applications which will flash news alerts. It's the same case in television channels, the channels are also having mobile applications which are also providing news not only in video format but also in text. At this juncture it's a challenge for the journalist to be techno savvy and keep on updating the news by linking up information sources through social media.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Megan Sponcil and Priscilla Gitimu in the study on Use of
social media by college students: Relationship to
communication and self-concept has examined social
media use among college students and how it affects
communication with others, and college students' selfconcept.
The findings provide implications for future
research on why these social networking sites have gained
popularity.
Thomas E. Ruggiero (2000) in the article Uses and
st Gratifications Theory in the 21 Century has asserted that
the emergence of computer-mediated communication has
revived the significance of uses and gratifications. He also
explained the necessary of inclusion of concepts like
interactivity, demassification, hypertextuality, and
asynchroneity in Contemporary and future models and
researchers should also explore interpersonal and
qualitative aspects of mediated communication in a more
holistic methodology.
Anitha kaluvoya (2015) in the paper Social Media Use by
Political Parties in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh has
contended the use of social media by political parties in the
newly formed states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana's
general elections, 2014. The study found that the reach and
influence of social media at national level is more when
compared with regional level. The study concluded Social
networking sites have been given lesser importance in
both the states.
Malene Charlotte Larsen in the study Online Social
networking: from local experience to Global Discourses
has explored use of social network sites and different
experiences of Danish teenagers in the use of social
networking technologies. The author has demonstrated
how young people relate not only to a local context, but
also a broader societal level when addressing the issues of
online behaviour.
Lauren Campbell and et al (2016) in the study Social media
use by physicians: a qualitative study of the new frontier
of medicine has examined that Participants identified
multiple perceived benefits and barriers to social media
use by physicians; further, four major themes were
identified. First, participants often saw themselves as
rugged individualists who set their own rules for social
media health communications. Second, participants
expressed uncertainty about boundaries or strategies for
social media use. Third, participants described using
social media much like traditional media, as a one-way
communication platform, rather than as an interactive
forum. Finally, participants expressed disparate views
regarding the time involved in participating in social
media; some felt that time spent on social media was
unproblematic to fit into their day while others felt that it
was an impediment to patient care.
Ioannis Leftheriotis and Michail N. Giannakos (2014) in
the study Using social media for work: Losing your time
or improving your work has contended that in the case of
social media for work, employees make extended use of
them no matter their age, also that both utilitarian and
hedonic values influence employees to use more social
media for their work, at least in the insurance sector. The
study confirms that there is an important relation between
the use of social media and the work performance.
Charles O. Omekwu and et al (2014) in the study The Use
of Social Networking Sites among the Undergraduate
Students of University of Nigeria, Nsukka has examined
that mostly all the student were using the social
networking sites in interaction with friends, connecting to
their class mates for online study and for discussing
serious national issues and watching movies etc. the study
recommended that university Authorities should
organize seminars to enlighten students on the not-so
good aspects of social networking sites etc.
Sue Burzynski Bullard (2015) in the study of Editors Use
Social Media Mostly to Post Story Links has examined that
editors use social media, they primarily use it to post links
to stories on Facebook and Twitter. Far fewer use social
media to interact with audiences by posing questions and
responding to comments.
S.M. Al-Jubayer (2013) in the study The Use of Social
Networking Sites among Teenagers: A Study of Facebook
Use in Dhaka City has identified two distinctive categories
of teen engagement with digital media: friendship-driven
and interest -dr iven. Whi le f r iendship-dr iven
participation centered on “hanging out” with existing
friends, interest-driven participation involved accessing
online information and communities that may not be
present in the local peer group.
Zizi Papacharissi () in the paper Uses and gratifications
presents that the strength of the perspective lies in its
ability to describe, explain and expect media uses and
consequences. The flexibility of the theoretical model
proposes progresses from the motives and individual
dispositions to patterns use and possible cognitive,
attitudinal and behavioral effects.
Shannon Greenwood and et al (2016) in the Social media
Update by Pew Research Center has presented the
research update of social media usage over the past
decade. Also the usage and demographics of media
platforms.
ACE Professional Development Grant (2013) conducted
53 surveys to study how reporters use social media about
the use of Twitter, Facebook, Pinterest and blogs, allowing
us to gain some insight in how general and agricultural
reporters use social media. And the study found that
younger journalists were more apt to be using social media
for news gathering and disseminating, while the older
reporters were more likely to use it only when forced to by
their employer. there was an exception to this rule. One
editor who might be defined as “older” is considered an
innovative leader in the use of social media, for both
information gathering and story dissemination.
Marcus White (2014) in the study Twitter And Television:
A Uses & Gratifications Study Of Twitter Usage And
Television Viewing results identified the motivations of
relaxation and escape, companionship and social
interaction, and entertainment and enjoyment as similar
for television and Twitter. The motivations for insight and
information and collecting knowledge or learning were
not similar for television and Twitter.
Jacques Richard Ludovic Froget and et al (2013) in the
study on Uses and Gratification Perspective on Social
Media Usage and Online Marketing explores the use of
Facebook in Mauritius under the lens of the famous Uses
and Gratifications theory. The study also looks into the
socio-demographic characteristics of Facebook users in
Mauritius and how the differences might effect on its
usage. It is discovered that there is a difference in
Facebook use between groups of different monthly
income level.
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The study is exploratory in nature and used survey method with a structured questionnaire to collect the data.
Research Questions
The following questions are explored in the study :
- To study the social media usage patterns of journalists working in print and electronic mediums in Hyderabad.
- To understand the social media usage in comparison with Print and Electronic media Journalists
Sample
The sample for this study is categorized into individuals working in Print and Electronic medium in Hyderabad, Telangana State, India. The sample was selected on Random basis. The analysis in this paper utilizes surveybased data collected from over 60 media personnel in total (Print medium-30 and Electronic-30). Considering the literacy of the respondents, the self-administered survey questionnaire was in the English language. The respondents are working in major newspaper dailies and electronic channels in Hyderabad. Most of them are from secretariat beat.
Measures
To measure the variables, a standard questionnaire was used in the literature. Respondents were requested to rate the items on a five-point Likert scale which ranged from Never (1) to Very Often (5), and also very uncomfortable (1) to very comfortable (4). The questionnaire consisted of both open ended and close ended questions to understand the usage pattern of the journalists.
THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
Users & Gratifications theory was earlier used in the
traditional media settings such as newspaper and
television. Later with the advancements in technology
researchers applied the same theory on new media. A key
characterizing feature of new media is interactivity, which
enables the users to provide content in response to a
source or communication partner.
According to theorists, human need gratification can be
categorized into five groups.
- Cognitive needs - information sharing, acquiring knowledge from the surrounding, exploring and
- curiosity to know. The study reveals that electronic media journalists share more information than print media journalists. the feature of exploring things is more in electronic journalists.
- Affective needs - Pleasure, emotional experiences. In the usage analysis the electronic media journalists are more expressive and share emotional experience through various posts, updating information on the social media. They are most of the time connected to social network sharing their emotions with the friends/ family/ co-workers. Journalists working in both the mediums experience the pleasure of watching information on the social network, chatting, sharing information but electronic media journalists experience more compared to print.
- Personal identity - develops social status, improve selfconfidence, need for self-respect. The print and electronic media journalists provide their identity on social network by providing information such as mail id, mobile number, posting photos and views. The electronic media journalists apart from information share their pictures, videos and also location. And electronic media journalists are very comfortable in sharing such information. They also actively participate in commenting the posts, videos.
- Integration and social Interaction - build family and friends, connect with the outside world. Social media is the major platform to improve social interaction. It also connects the individual with the outside world with bulks of information. The media personnel are majorly attracted towards social media due to its feature of ins tant acces s to informat ion, communicating with friends, providing platform to participate in discussion boards and present one's views.
- Escapism - the need to escape from unpleasant activities to pleasant. The integration of media i.e. use of mobile phone with smart features have enabled the user to divert himself from the ambience he/she at. The escapism in this context is the individual is more informative about worldly happenings and incidents and busy in updating the information. Literally escaping from the activities and ambience happening around the individual. The media personnel are busy in social media to know events information and also competing with one another in providing breaking news details to the concerned office as early as
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
USAGE PATTERN
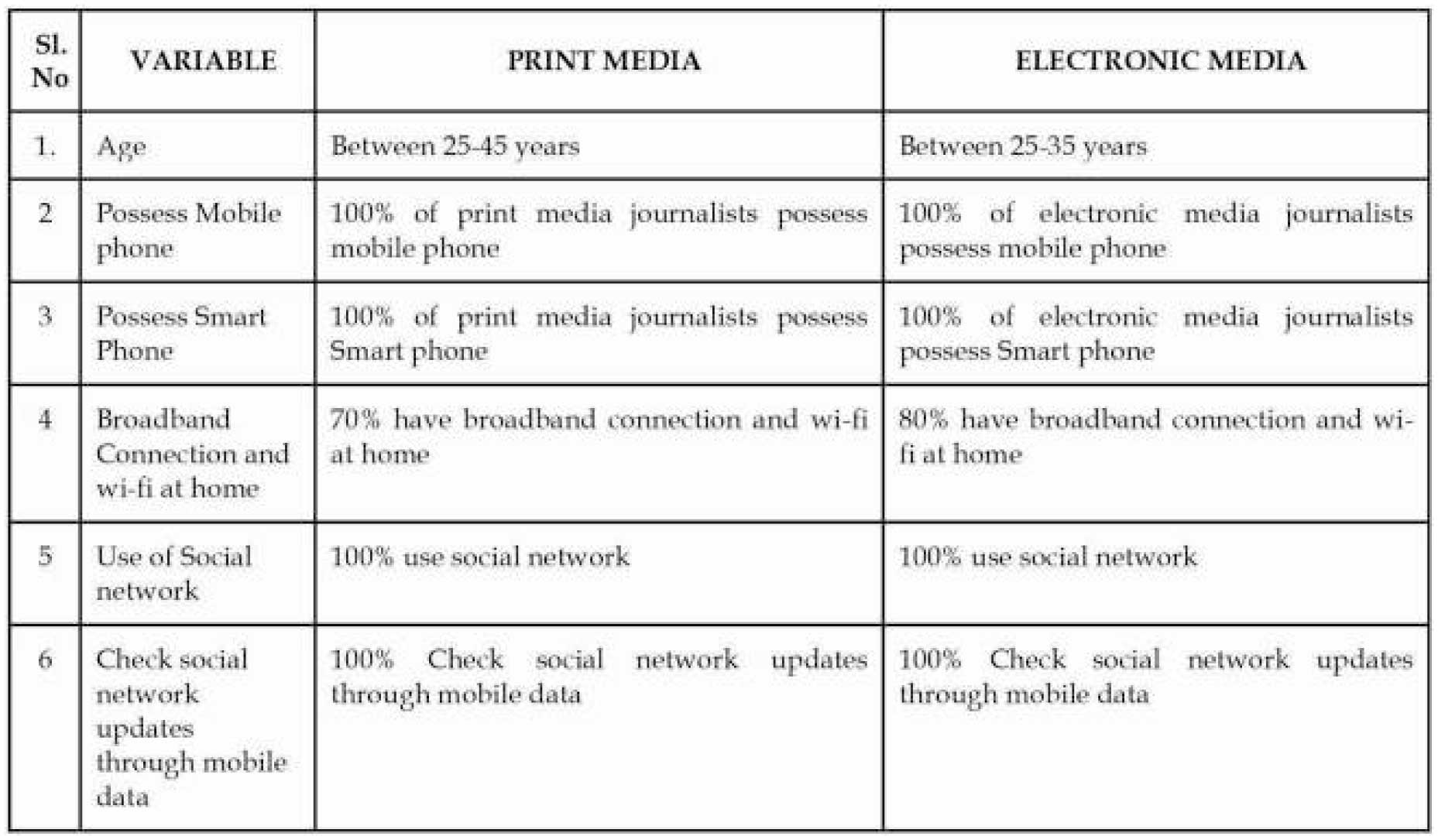
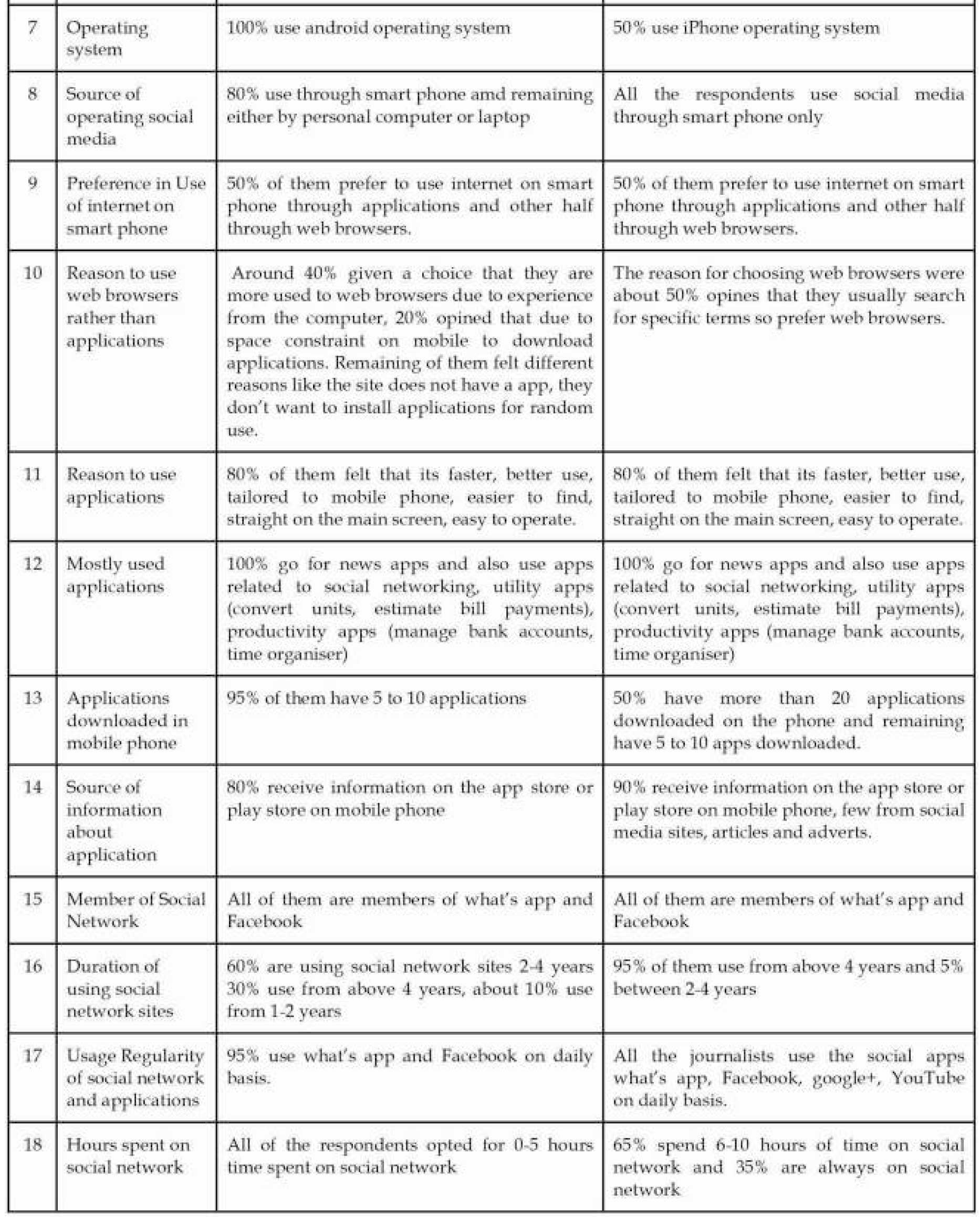
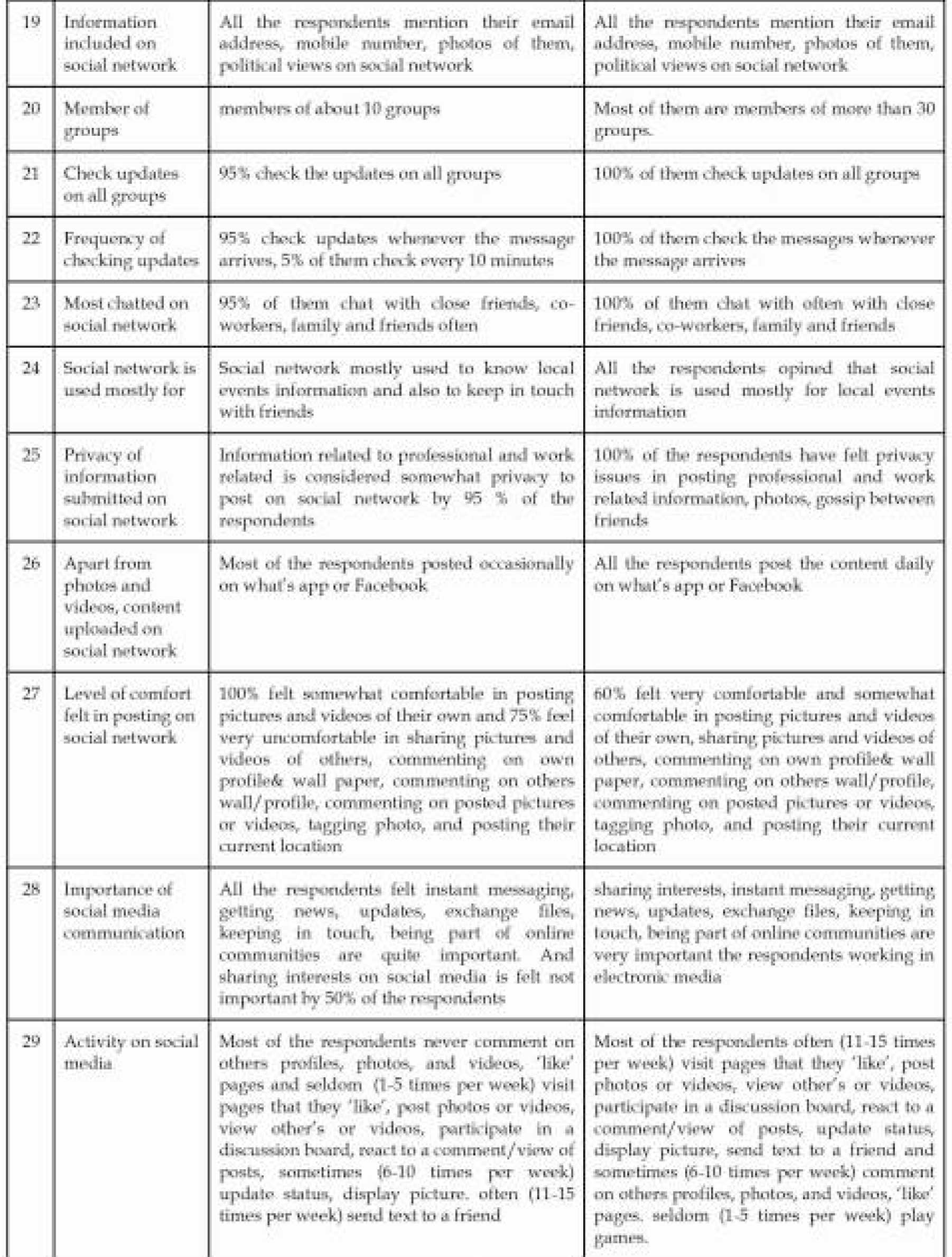
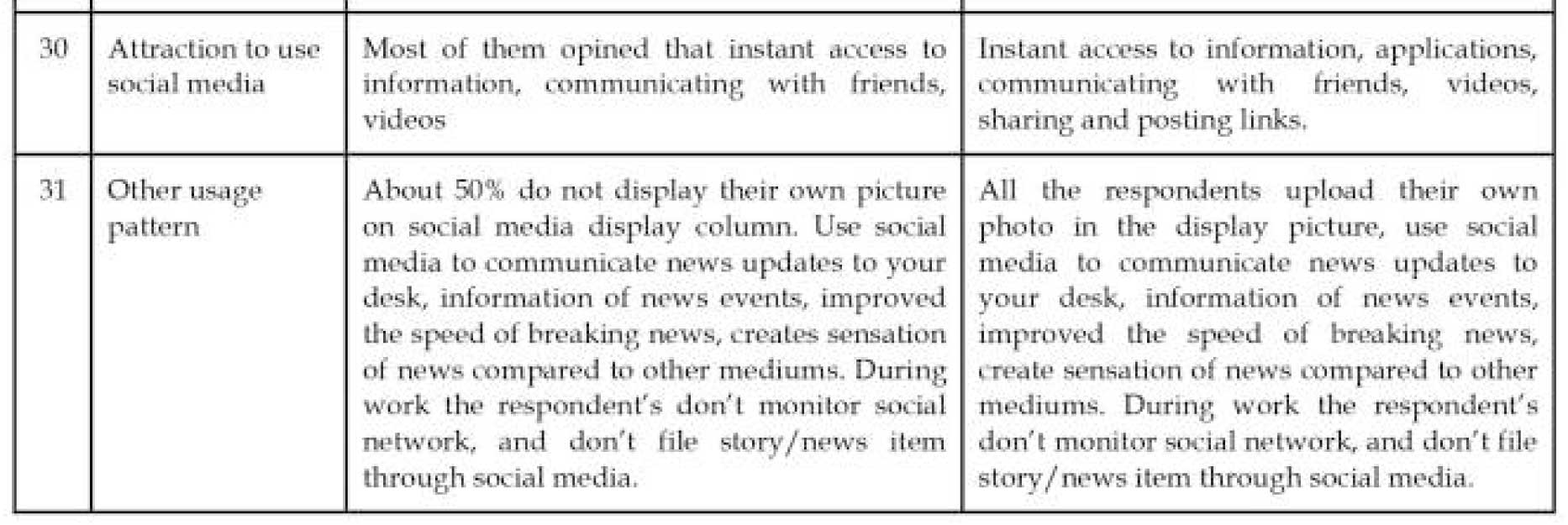
CONCLUSION
The study brings out an understanding that usage of social media is extensive in journalists working in electronic media compared to print medium. All the respondents working in both print and electronic medium think that social media does not give authentic information. Some respondents have disliking features in social media like containing embarrassing pictures and material, an excess of information, false information, gossips and unnecessary greetings, applications clutter, the unwanted appearance of porno content, unnecessary links and advertisement material, duplicate WhatsApp posts. The respondents like the feature of LIVE on social media and suggested to have an application which can magnify the farthest objects. The electronic medium journalists spend more hours on social media, frequently upload information, comment, react. In Internet culture, the 1% rule is rules of thumb pertaining to participation in an internet community, stating that only 1% of the users of a website actively create new content, while other 99% of the participants only lurk. Accordingly, electronic media journalists are active participants in using social media compared to journalists working in print media.
REFERENCES
- Megan Sponcil and Priscilla Gitimu in the study on Use of social media by college students : Relationship to communication and self-concept, Journal of Technology Research.
- Ruggiero E Thomas (2000). Uses and Gratifications Theory in the 21st Century. Mass Communication and society.
- Anitha kaluvoya(2015).Social Media Use by Political Parties in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh.
- Malene Charlotte Larsen.Online Social networking: from local experience to Global Discourses”.
- Lauren Campbell, Yolanda Evans, Megan Pumper and Megan A. Moreno (2016), Social media use by physicians: a qualitative study of the new frontier of medicine, BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making .
- Charles O. Omekwu, Helen N. Eke, Nneka Jennifer Odoh (2014). The Use of Social Networking Sites among the Undergraduate Students of University of Nigeria, Nsukka.
- Sue Burzynski Bullard (2015). Use Social Media Mostly to Post Story Links.Newspaper Research Journal, 36(2).
- S.M. Al-Jubayer(2013).The Use of Social Networking Sites Among Teenagers: A Study of Facebook Use in Dhaka City. Journal of International Social issues, 2.
- Shannon Greenwood (2016) .Social media Update by Pew Research Center.
- ACE Professional Development Grant (2013) study on how reporters use social media.
- Marcus White (2014).Twitter And Television: A Uses & Gratifications Study Of Twitter Usage And Television Viewing.
- Jacques Richard Ludovic Froget and et al (2013) in the study on Uses and Gratification Perspective on Social Media Usage and Online Marketing, Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research.
