Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Strategies to Improve Qualities of Students with Available Resources for Better Employability: A Study of Selected B-Schools in Jharkhand
Abstract :
With the number of unemployable people rising quality of students has become a prime concern for higher education institutions. Various government initiatives are being taken to ensure there is rise in employability and higher number of people contribute towards economic growth. Thus with this concern my PhD research focuses upon challenges and strategies in improving quality of management graduate so that they become employable. This paper contains introduction which introduces the topic. Significance of research provides reason for selection of this topic for research. Scope is limited to business schools of Jharkhand. 5 objectives for this research have been identified and mentioned. For preparation of proposal various researches conducted earlier in this area were reviewed and have been mentioned in the paper. Based on the literature review research gaps were identified. For each objective research methodology adopted has been defined. Data collection has been proposed. Findings would define performance indicators which will improve qualities of students. Challenges faced during the research propose have been identified and mentioned.
Keywords :
education, challenges, Jharkhand, students.INTRODUCTION
Education plays a vital role in everyone’s life as education can help in improving the living conditions of an individual. A person who is educated has better career opportunities and thus the level of education ensures the level of success in life. A nation which has higher number of educated individuals will have better economic conditions and it will perform better.
Higher education institutions require financial resources, human resources, and physical resources. Higher education institutions face a challenge of generating enough financial resources so that they are able to provide the required infrastructure to students. Faculties, librarians, technicians, and other staff are the human resources required to ensure that proper knowledge is imparted to the students. Physical resources in a higher education are libraries, computer labs, and classrooms through which knowledge is imparted.
The prime focus of this research will in the postgraduate stage where strategies to improve the quality of students in the B-schools in India will be devised which will help in providing better employability. Quality as defined by Juran is ‘fitness for use’ and in the case of business schools the criteria for fitness for use will be defined by the corporate who hire the MBA graduates and offer them a job. Strategy as defined by Vladimir Kvint is ‘a system of finding, formulating, and developing a set of beliefs which will ensure long-term success if followed faithfully’. It is essential that the strategies which are defined for improving the quality of students have a focus upon long-term vision.
Rationale/Significant of the Research
With the global economic slowdown the aspirants for management studies have become conscious. The high fee and low return in investment has become a prime concern for such aspirants because of which there has been decline in the number of aspirants in various MBA entrance exams. The premier colleges are not affected drastically with this decline; however the tier 2 B-schools in India are affected by this decline. Thus the topic selected for the research is ‘Strategies to Improve Qualities of Students with Available Resources for Better Employability: A Study of Selected B-Schools in Jharkhand’
Scope
Scope of this research is limited to business schools in India. In the current economic scenario only 10 percent of MBA graduates are getting hired and campus placements have gone down. Most of the MBA graduates are struggling to find a job after completion of the course because of which there has been drop in the number of students enrolling for the course. This leads to vacant seats in the MBA colleges because of which sustainability of the colleges becomes a big challenge. Thus to be sustainable in the market it will be essential that these colleges focus upon providing quality education. This research will focus upon finding strategies which will help in improving the quality of students and ensure colleges are sustainable in the long run. Also it is required to examine the challenges faced by management institutions in providing quality education and find solutions to overcome these challenges. For defining the quality parameter of the students; the industry expectation with regards to employability of management graduates will be considered.
Objective of research
The objective of this research is to develop strategies which will help in improving the quality of students enrolled in the business schools of India. The idea is to improve the quality of students by improving the teaching practices and making the current mode of delivering education in business schools as student centric. This objective will help in preparing the students as per the industry expectations and thus make the students employable in various industries. In this research attempts will be made to cater to the following objectives:
- To find out ways in which student-centered approach can be adopted.
- To examine the clarity of students with regards to the current business scenario.
- To adopt customized pedagogy where the students are able to derive the relation between theoretical concepts and practical business scenario.
- To define indicators for quality of students and these indicators will be used as measurement parameters in MBA institutions.
- To adopt holistic approach where the challenges faced by MBA institutions will be considered and strategies developed will help in overcoming these challenges so that quality of students is improved effectively.
Literature Review
Deepti Gupta and Navneet Gupta in their paper Higher Education in India: Structure, Statistics and Challenges mention that there is demand supply gap. There is shortage of number of universities offering higher education. Two-third Indian colleges and universities are below standard and Indian higher education institutions are poorly connected with research centers. Also the paper highlights issues with shortage of faculty. This paper tries to mention government initiatives taken to overcome these issues
Dr. Vikrant Mishra is his paper Globalization and Indian Higher Education has given insights that the Indian higher education system lacks in terms of international quality standards. The private sector institutions focus more on commercial aspect rather than knowledge creation. There is no effective system to monitor and control violation in the norms. There are vested political interests because of which right steps are not taken towards improving quality.
Goolam Mohamed Bhai in his paper Quality Assurance Mechanisms in Higher Education mentions that it is difficult to define quality of higher education. He suggests that conducting internal and external academic audit for institutional could improve the quality of education. There should be a mechanism of accreditation for programs and for institutions. There has been increase in the number of students while available resources are diminishing.
Suresha. R and B. C. Mylarappa in their paper mention that there is more focus on elementary education while higher education is being neglected in India. India has largest number of higher education institutions in the world but gross enrolment ratio is low. There is shortage of resources for higher education which affects the quality of education.
Dr. Suhas Avhad in his paper mentions that there is shortage of funds for significant reforms in higher education system. Higher education system is connected with political and social systems. There should be a realistic perception regarding what is possible in improving quality of higher education institutions.
Padmini Srinivasan, Vasanthi Srinivasan and R.V. Anand in their paper mention that there are no bodies to ensure integration of ethics and CSR in curriculum of business schools. Students in India enrolled in MBA education do not have prior work experience. Lecture method is the most preferred mode for delivery of courses. There are challenges in bringing new and relevant cases centered around India. This paper tries to suggest that exciting ways should be used for teaching courses. There should be strong faculty interaction through conferences and workshops
Vidya Yerneni and Dr. Supriya Jha in their paper mention that orientation of higher education should be vibrant, competitive, meaningful, and purposeful. There should be suitable assessment and accreditation mechanism to ensure quality standards in higher education. There should be methods for teacher preparation and sustaining quality of teachers. Amount of research work conducted in quality of higher education is not much.
Dr. P. Arunachalam in the paper mentions that there are new challenges and opportunities in higher education because of rapid changes. The major challenge is to make higher education accessible to all. There are pressures to enhance access and equity and also maintain high quality of excellence. India one of the fastest developing countries and to maintain growth rate there is need to increase number of institutes. Teaching methodology followed should be such that students get an opportunity to think, innovate, challenge existing ideas and generate new ideas. Transparent and full-proof method of evaluation should be adopted. Students should be encouraged to select subject combinations. Institutions should setup social accountability cells. RTI should be implemented in higher education institutions.
Murad Ali and Rajesh Kumar Shastri in their paper mention that there are lots of innovative experiments being conducted to improve the performance of higher education sector. For applying TQM in higher education system more funds are required. With budget constraints from government in higher education the institutions should provide quality education at lower costs.
Chiranjib Sen in the paper mentions the reasons for shortage of faculty in higher education institutions. As per the paper academic careers are unattractive in comparison with other professions. Work environment and service conditions have become difficult and salaries are low because many institutions face funds shortage. There are policy constraints because of which institutions have an upper limit over increasing the number of faculty members. Minimum faculty-student ratio is not achieved which affects the quality of education. There is trade-off between the net operating income and quality of education. This paper suggests that strategies should be developed to attract and retain talented faculty members. Certain expenditure should be fixed towards increasing quality of education.
Fabrice Henard and Soleine Leprince-Ringuet in their paper stress upon student centered approach where all students get opportunity to learn. Pedagogical methods should address the student needs. Whole institution and learning environment should be considered in quality teaching. Indicators should be identified which are able to measure the effectiveness of quality teaching.
Problem Statement/Research Gap
The existing literature survey indicates that not much research has been conducted in this area. However there are articles which have tried to mention about the challenges involved in providing quality education to students enrolled in the higher education. Thus this study will try to address these challenges and develop strategies in view of the issues faced by higher education institutions in providing quality education.
Research Methodology
- To find out ways in which student-centered approach can be adopted For this objective, students who are preparing to join the MBA institutions will be surveyed. The students enrolled in post graduate management program will be surveyed. Across Jharkhand 15 management institutions will be approached and at random 20 students per institute will be selected. During the questionnaire survey the reasons for joining MBA institutions will be examined and the risk-return parameter will be determined.
- To examine the clarity of students with regards to the current business scenario. For this objective, students who have already joined the MBA institutions will be surveyed using a questionnaire. Students who are enrolled in the first year will be considered for this objective. In Jharkhand 15 MBA institutions will be approached and at random 20 students from first year per institute will be selected.
- To adopt customized pedagogy where the students are able to derive the relation between theoretical concepts and practical business scenario. For this objective, students who have completed their first year and summer internship will be surveyed using a questionnaire. Students who are enrolled in the second year will be considered for this objective. In Jharkhand 15 MBA institutions will be approached and at random 20 students from second year per institute will be selected.
- To define indicators for quality of students and these indicators will be used as measurement parameters in MBA institutions. For this objective, corporate will be approached who recruit the MBA graduates and through questionnaire survey their expectations regarding new recruits will be gathered. 50 corporations from various industries will be approached for this objective.
- To adopt holistic approach where the challenges faced by MBA institutions will be considered and strategies developed will help in overcoming these challenges so that quality of students is improved effectively. For this objective, the authorities and faculty members of management institutions will be approached where through the questionnaire survey the challenges in implementing various quality indicators will be examined. Also through the questionnaire the MBA institutions will provide a score for each indicator provided by the corporate. 15 B-schools in Jharkhand will be approached for the survey.
Data proposed to be collected
The secondary data will be collected from studies conducted in this area in India and other countries across the globe. Whereas the primary data as mentioned above in the methodology will be collected from corporate, first and second year students enrolled in various B-schools, and authorities and faculty members of B-schools. Random sampling technique will be used for selecting the respondents for this research.
Relevance of Projected Findings
The relevance of this finding will be that first by surveying the students preparing for MBA entrance exams unbiased information will be obtained regarding the reasons for applying for post-graduate courses in business administration. The quality indicators obtained from corporate will be linked with the student’s requirement for PGPM, PGDM and MBA education. The gaps which exist between the performance indicators and student’s requirements will be identified and thus a better strategic plan can be developed.
Challenges / difficulties
Across India there are various colleges which are offering PGPM, PGDM and MBA courses and it will be difficult to collect data from each and every college. Also with large amount of data, analysis will become a time taking process. Thus to ensure a timely collection and analysis of data the sample of business schools have been restricted to Jharkhand. Some of the business schools might not be willing to provide the required information during survey and this could affect the data collection process. Data will be collected from humans and there could be a possibility where the real state of the respondent’s mind is not reflected. To ensure that unbiased, true, and fair data is collected all the necessary precautions will be taken.
Research So Far
Data has been collected from corporate and mean and standard deviation has been found. Below are the results of mean and standard deviation.
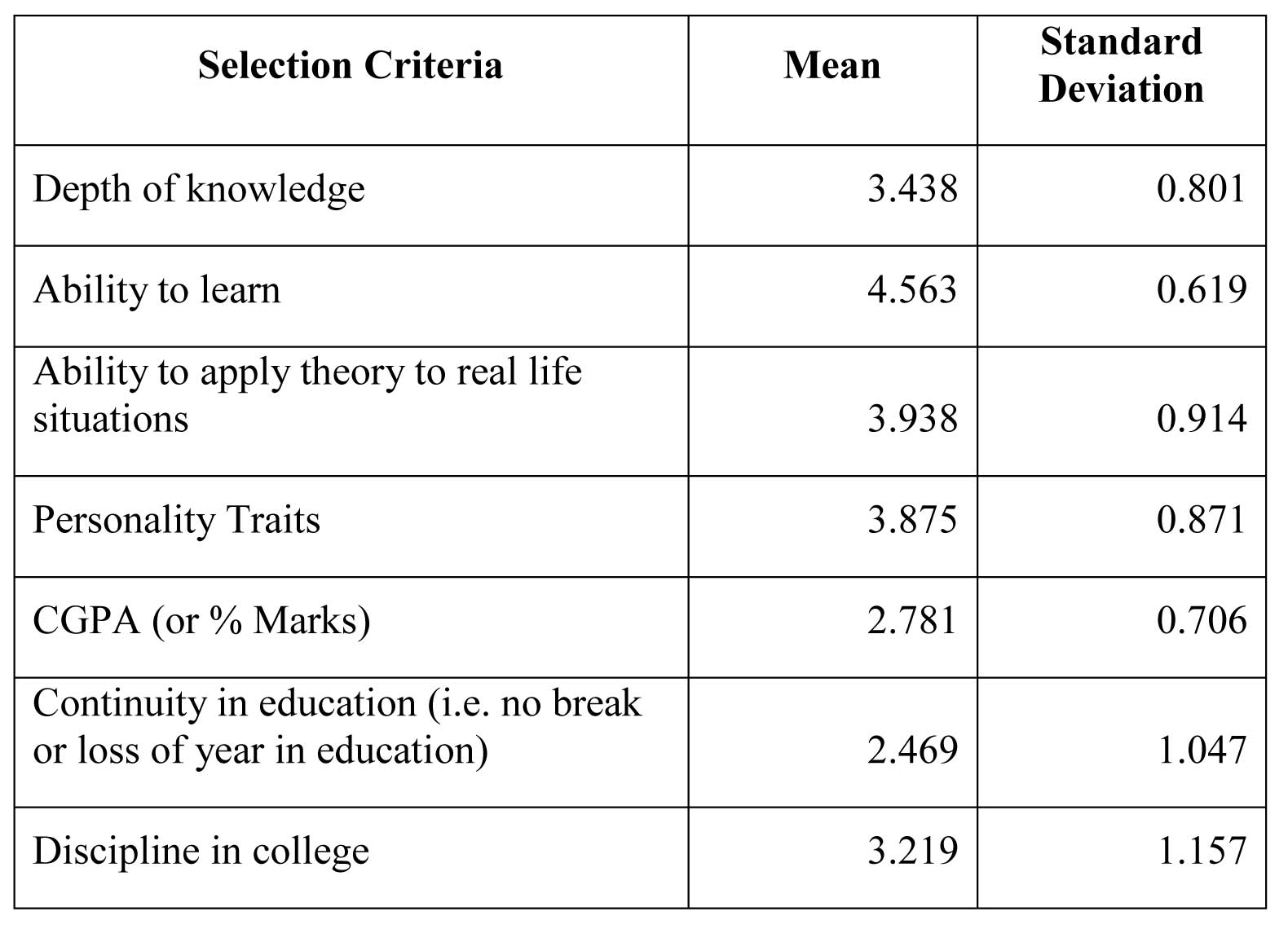
First question is related to the selection criteria and below table gives the findings.
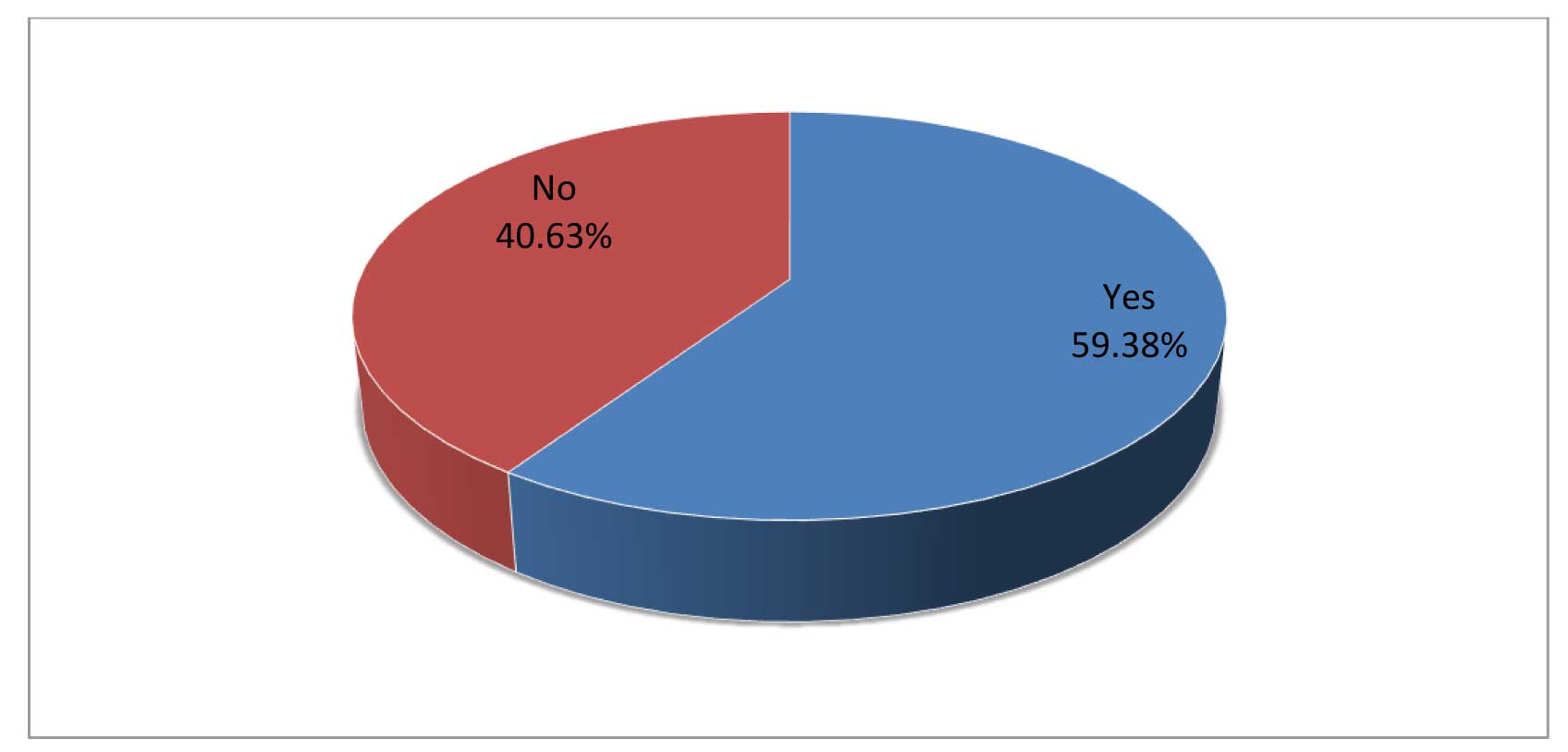
Second question tries to find whether corporate use CGPA for screening or not
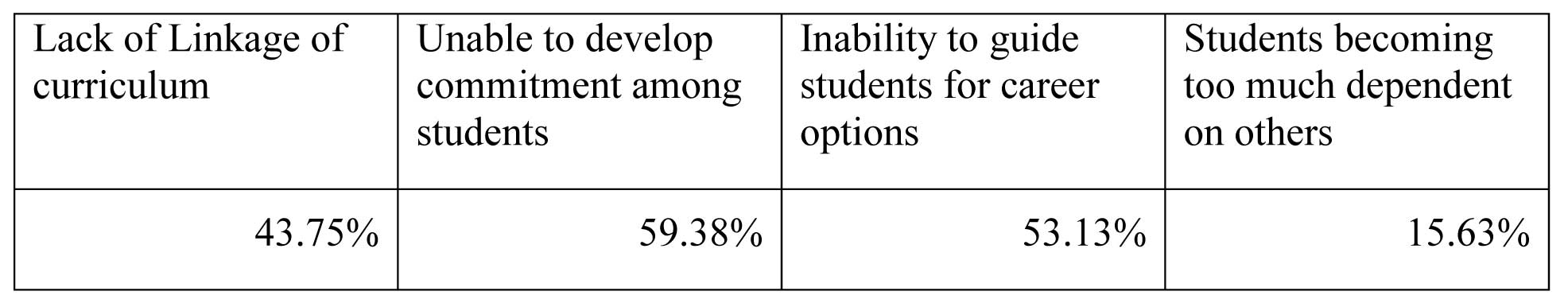
Third question is related to gap (s) mostly observed with business-schools in meeting corporate requirements
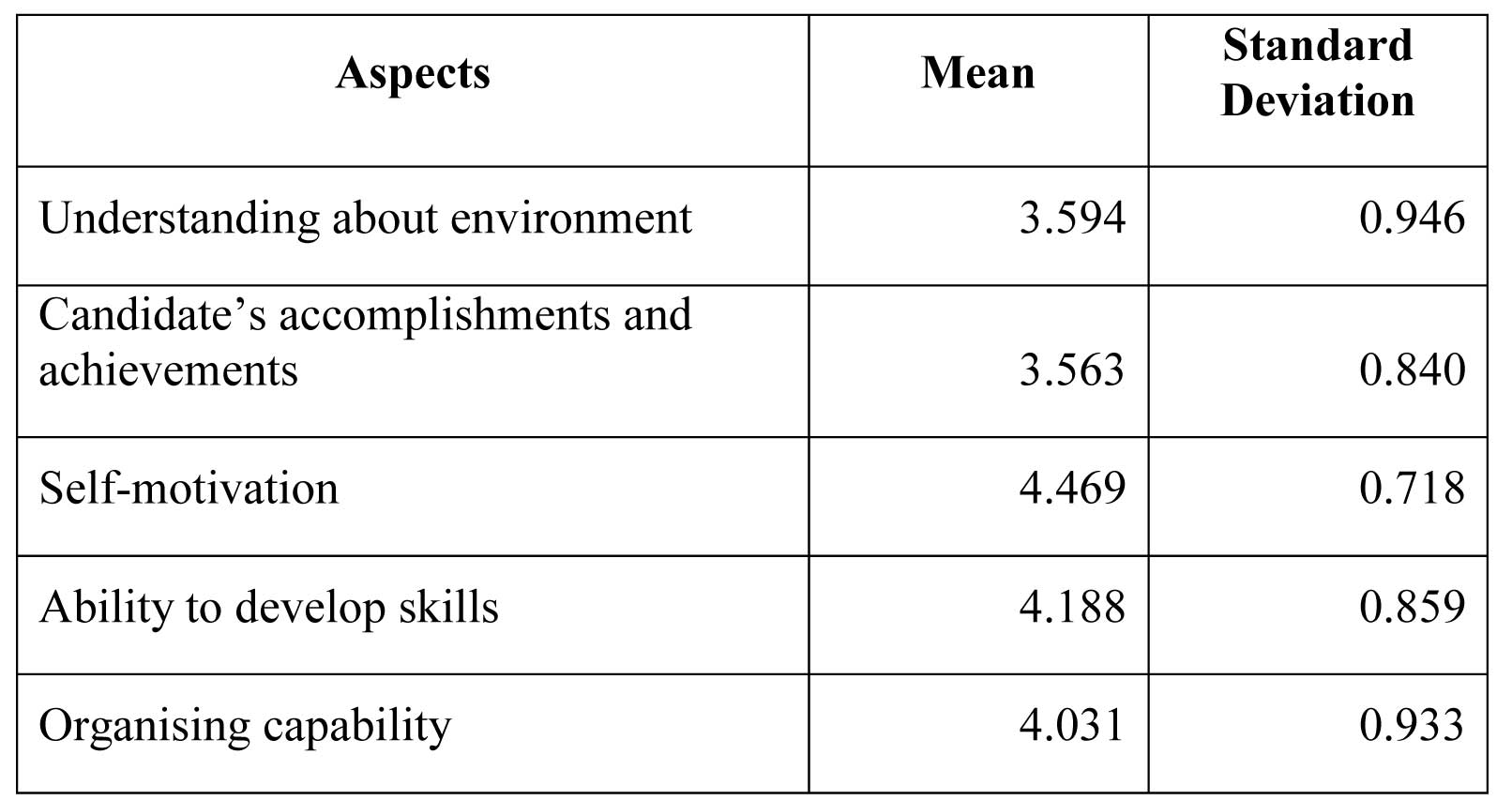
Fourth question looks at importance of various aspects of volunteer work or extra-curricular activities of students in recruitment
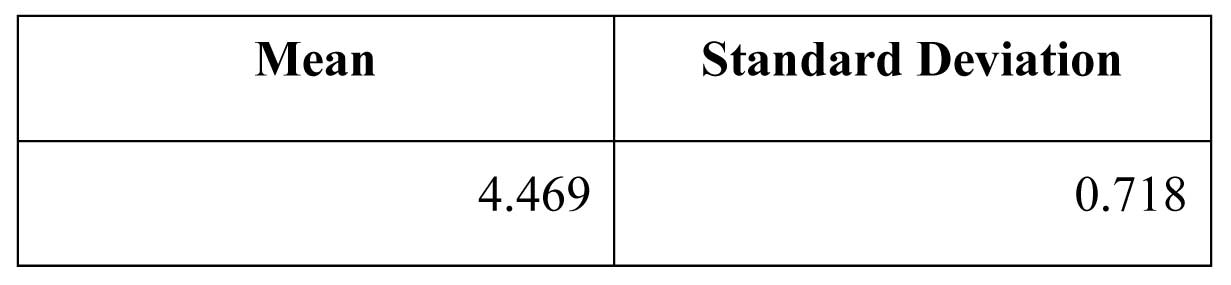
Fifth question is related to need for training of fresh recruits.
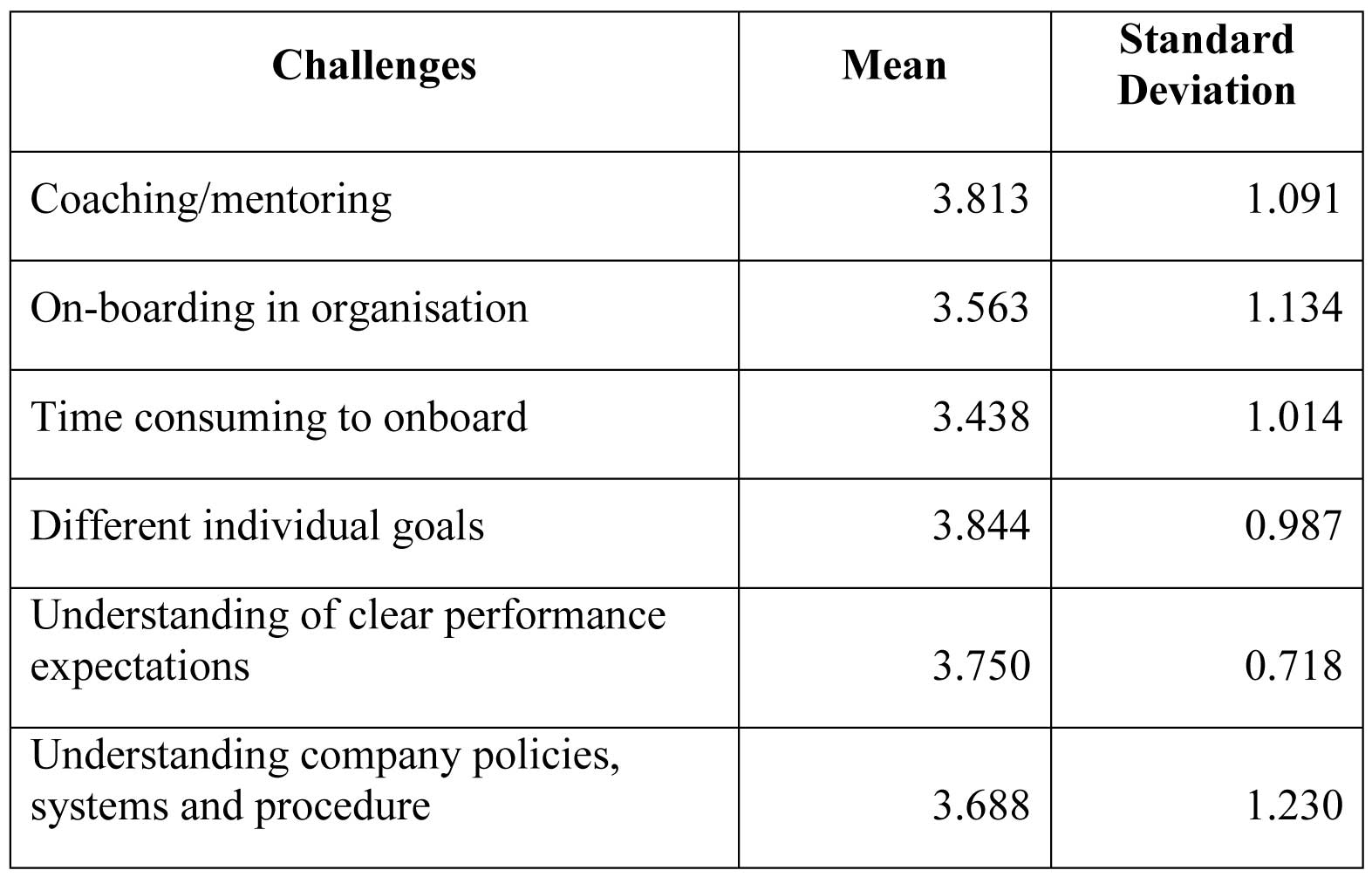
Sixth question is related to challenges faced with fresh management graduates after they join the organization
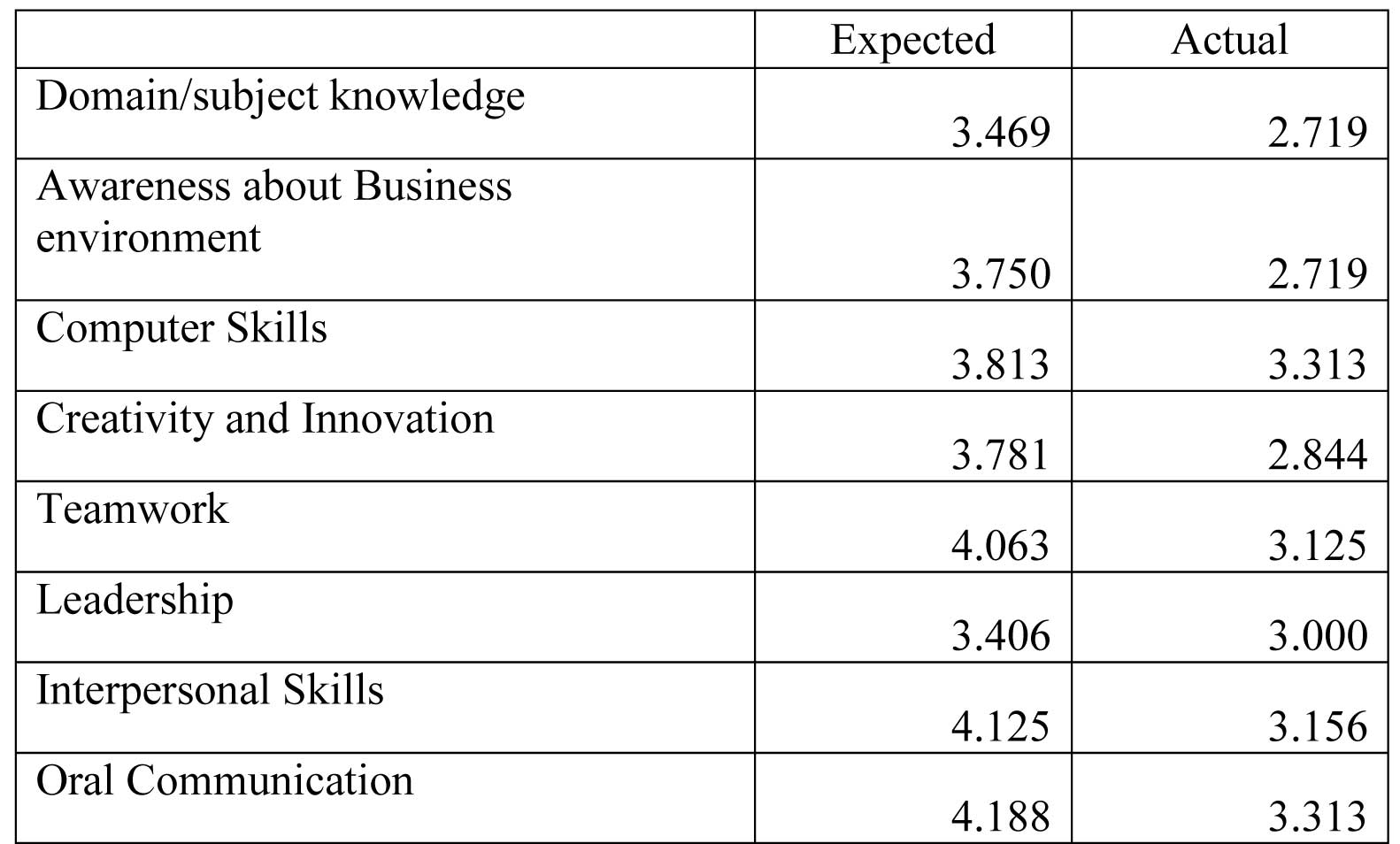
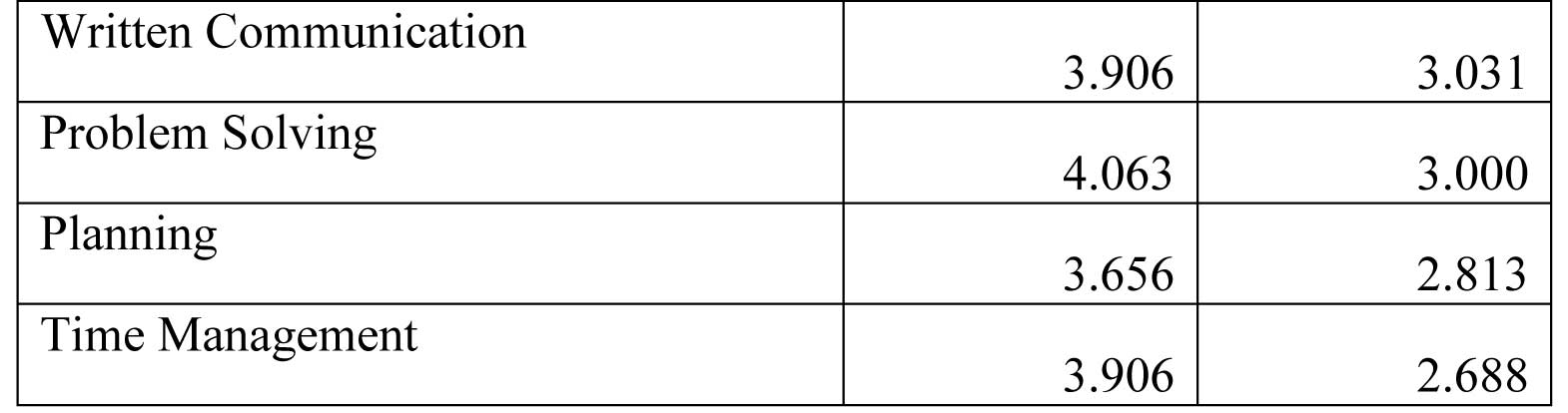
Seventh question is related to various skills which corporate expect while recruiting and the actual position after fresh graduates have joined job.
Acknowledgements
I would like to extend my thanks to my research guide Dr. Rumna Bhattacharyya and my research supervisor Dr. Vanshi Dhar whose advices have been helpful in my research. I would also like to thank Dr. S.C. Swain who has always been prompt in responding to any queries related to the research. I hope in the guidance of the university I am able to provide a meaningful insight into the problems surrounding the employability of students. I am also thankful to Vice-Chancellor, Prof. O R S Rao, respected Academic Advisor, Dr. K. K. Nag and honorable Dean and Registrar, Dr. B. M. Singh for their continuous support and encouragement.
Bibliography
- Ali, M., & Shastri, R. K (2010), “ Implementation of Total Quality Management in Higher Education”, Asian Journal of Business Management , Vol.2, No. 1, pp. 355-361.
- Arunachalam, P(2010), “ Higher Education Sector in India: Issues and Imperatives”, Journal of Global Economy ,Vol. 6, No.4 , pp.267-291.
- Avhad, S (2013), “ Emerging Issues and Challenges in Higher Education”, International Monthly Refereed Journal of Research In Management & Technology, Vol. 2, pp.53-56.
- Bhai, G. M (2006), “ Quality Assurance Mechanisms in Higher Education”, ASCI Journal of Management , Vol.36, No.1.
- Gupta, D., & Gupta, N (2012), “Higher Education in India: Structure, Statistics and Challenges”, Journal of Education and Practice, Vol.3, No.2, pp.17-25.
- Mishra, V (2013), “Globalization and Indian Higher Education”, Journal Of Educational and Instructional Studies in the World , Vol.3, No.1, pp. 8-14.
- R, S., & Mylarappa, B. C (2012), “ Development of Indian Higher Education in the 21st Century”, International Journal of Social Science & Interdisciplinary Research ,Vol. 1 No. 10, pp.70-82.
- Srinivasan, P., Srinivasan, V., & Anand, R (2012), “Status of Ethics, Corporate Governance, CSR and Environment Education in Business Schools in India: An Exploratory Study”, Working Paper, Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore.
- Yerneni, V., & Jha, S (2013), “Can Operational Tools & Techniques be Used to Achieve Excellence in Higher Education System in India – An Exploration”, International Journal of Management and Strategy, Vol. 4, No.6.
