Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Normative and Positive Aspects of Happiness in Teaching Profession : A Study of Higher Educational Institutions of India
Abstract :
Happiness is a psychological concept and it is subjective in nature. Amidst all sorts of facilities and accomplishments, one won't be happy unless and until s/he feels to be happy. Similarly, with the same set of achievements, while one makes himself/herself happy, another may find him/her far away from happiness. Profession of an individual is one of the many factors that determine his/her happiness. Teaching has been treated as a sacred profession since time immemorial and hence those who like to serve the society with peace and earn respectful life, they have been preferring teaching profession. In fact, teachers prior to recent past, were deriving pleasure and happiness out of their contribution in building the nation by way of sharing knowledge. And the taught were the cause of happiness for the teachers as they were giving utmost respect to the teachers. But the dynamics of teaching profession, particularly in higher education sector of India, have been overhauled in recent years. Most of the teachers are taking up the teaching profession just for the sake of earning livelihood and getting pleasure out of negativities like number of holidays and leaves, class suspensions, no interest of the taught in the classrooms, promotions or hikes even without adding any value and so on. Keeping this in backdrop, it has been thought to unfold the positive (what it is?) and normative (what it ought to be?) aspects of happiness in teaching profession, particularly in higher education sector of India.
Keywords :
Happiness, Teaching Profession, Positive aspect, Normative Aspect, HEIs, Odisha, JharkhandIntroduction :
Teaching profession is known for its sanctity and society
building character. Hence people with good moral and
dedication to contribute were preferring teaching
profession in earlier time and they were deriving immense
happiness in teaching profession. In recent years, this
trend has been disturbed. Although not all, people with
calculative mind are entering into this profession as they
feel the work load will be much lesser as compared to any
other profession. Similarly, most of the students in recent
years take admission in higher education for the sake of the
degree or diploma without looking into value addition in
them. The connotation of 'happiness' for the teachers has
not been the same. Earlier, teachers were becoming happy
as they succeed in clarifying students' doubts on or off the
class timings. But in recent time, most of the teachers feel
happy when they restrict their teaching to manage the class
timings, students don't disturb during off-class timings,
they avail more number of off-days, leaves and class
suspensions. In fact, such teachers derive happiness from
negativity in teaching profession - becoming very
particular with respect to their rights but forget their
responsibilities. At the same time, there are also teachers
with values who are still considering teaching as noble
profession and derive happiness with all sincerity. With
this backdrop, this Paper is prepared to present both
normative and positive side of teaching profession. For
the purpose, selected higher educational institutions of
Odisha and Jharkhand have been picked up. The study is a
blend of qualitative and quantitative research. While
positive aspects of happiness in teaching profession have
been ascertained by way of in-depth interview and
observation methods, the normative aspects have been
benchmarked through existing literature review followed
by focused group discussions. It's found that there is wide
gap between positive and normative aspects of happiness
in teaching profession, in recent years.
The plan of the Paper is as follows. Section-2 of the Paper
explains the Model of Happiness and identified Gap.
Objective and Methodology of the Paper is presented in
Section-3. Normative aspects of happiness in teaching
profession are contained in Section-4. Section-5 presents
the positive aspects of happiness in teaching profession.
Conclusion of the Study is presented in Scetion-6.
Model of Happiness
Very commonly used Model of Happiness is the PREMA Model (Seligman, 2011). PERMA is the descriptor for the five essential building parameters of well-being and happiness. Those are; Positive emotion (Feeling Good), Engagement (Finding Flow), Relations (Authentic Connections), Meaning (Purposeful Existence and Achievement (A Sense of Accomplishment).
Positive Emotion
This building block of the model is a most important
linkage to happiness. It is the power to be upbeat and have
the positive perspective on the past, present, and future.
This positive perspective of life can help anybody in
relationships, work, and inspire him/her to be more 58
creative and take more chances. In everyone's life, there
are highs and lows, in stead of focusing on the lows that
increase the chances of developing depression one should
focus on the high and positive aspects of life. There are also
multiple health benefits inherent in positive emotions.
For a teacher, becoming creative and having alternative
solutions to any situation are a must. For this, s/he must
have that positive emotion which will be reflected in the
students' satisfaction and performance. Optimism with a
teacher helps his/her students develop 'never give-up
attitude'. With this attitude, the students in the front line
can excel like anything and students in the back-benches
will have a ray of hope to overcome their bottlenecks.
Consequently, the teacher will be happy as his/her
positivity will take a shape of in the form of the students'
performance.
Engagement
Finding activities for full engagement is vital for one's
happiness as it make him/her to learn, grow and nurture
his/her happiness. Everyone is different and we all need
something in our lives that completely absorbs us into the
present moment.
A true teacher, particularly in higher education, is as such
fully engaged with teaching and allied activities such as
Question Paper Setting, Evaluation, Research in the form
of writing articles, Presenting Papers in national and
international Seminars and Conferences. Besides, in
current scenario, teachers are also engaged in institution
building activities.
Relationships
Human life without any relationship is lifeless. Most important aspect of life is relationships and social connections. Thriving on love, connection, intimacy, and a brawny physical and emotional interaction, human beings build up the society. with other humans. Through positive relationships with your near and dear ones, individuals spread love and get the happiness. It is only strong relationships that gives support in difficult times. For a teacher, while having relationships among his/her near and dear ones gives personal happiness, connecting to students and helping them out in the need of the hour, results in professional happiness.
Meaning
Happiness is nothing but realization of one's existence. If
anybody is well aware of his/her presence in the world
and knows the purpose of his/her creation, s/he will
easily overcome all odds and have the happiness in the
fist. To become more satisfied and happier by enjoying the
tasks, one has to realize the greater impact of one's work
and why one chooses the pursuit.
If a teacher understands the purpose of his/her existence
as a teacher, teaching becomes excellent so also learning.
At the same time, to become happier, teachers should also
be particular about the purpose of their students.
Accomplishments
Goals and aspirations in life are must for any sane
individual. Through goals and ambition, one can achieve
things that can give him/her a sense of accomplishment,
provided s/he puts the required efforts in right direction.
In order to be happy, goals and ambition need to be
achieved. For that one should make realistic goals that can
be met. Just putting in the effort to achieving those goals,
pending the result, gives a sense of satisfaction and when
one finally achieves those goals, a sense of pride and
fulfillment is attained. Having accomplishments in life is
essential to thrust ourselves to grow and flourish.
Although existing literature speaks about PREMA Model
of Happiness and its implementation in different walks of
life, implementation of the same in teaching profession has
not been a point of attraction for the researchers. But the
Model has every requisite to be fitted to teaching
profession as well. Considering this, the present study is
thought of.
Objectives and Methodology
ObjectivesFollowing are the Objectives of this study.
- To ascertain how the teachers (of higher educational institutions of India) should be happy in professional front - Normative aspect (Ideal State of Affairs)
- To unfold how the teachers (of higher educational institutions of India) are feeling happy in professional front - Positive aspect (Real State of Affairs)
Sample Design
For the purpose, four higher educational institutions (HEIs) of Jharkhand and Odisha have been selected as per the convenient sampling method. Different stakeholders of selected HEIs such as teachers (faculty members), students and Management representatives. Number of teachers considered is 20, number of students considered is 50, number of representatives of Management considered is 15 and number of established veteran teachers of the society (not from the selected HEIs) considered is 10.
Methodology
- To ascertain how the teachers (of higher educational institutions of India) should be happy in professional front - Normative aspect (Ideal State of Affairs), existing literature have been studied and two focused group discussions (FGDs) have been conducted with 10 established veteran teachers (5 for each FGD). Three more FGDs have been conducted among Management representatives and view points of 50 students have also been collated.
- To unfold how the teachers (of higher educational
institutions of India) are feeling happy in professional
front - Positive aspect (Real State of Affairs);
- wPersonal Interview Method has been adopted to get information from 20 faculty members
- w15 Management representatives have also shared their feelings regarding the said objective
Normative Aspect of Happiness in Teaching Profession
To be happy, a teacher must be effective. An effective teacher, as ascertained through existing literature review, FGDs and view points, should have the following traits.
- An Engaging Personality and Teaching Style
- Clear Objectives for Lessons
- Effective Discipline Skills
- Good Classroom Management Skills
- Good Communication with Parents
- High Expectations
- Knowledge of Curriculum and Standards
- Knowledge of Subject Matter
- Passion for Children and Teaching
- Strong Rapport with Students
Learning Management System (LMS)
Learning Management System (LMS) or e-learning is an
arrangement that implant hi-tech innovations within the
learning environment. It is a system that uses internet
technology for delivering information to students with
interactions through computer interfaces. It is designed to
be used in different educational processes to improve the
performance of learning. It may be used in many forms, i.e.
as an add-on to conventional lectures, asynchronous
distance learning, learning management systems or online
learning. The LMS is comprehensive package of creating
content, delivering content, monitoring student
participation, assessing student performance and grading.
Mostly LMSs are web-based and facilitate access to
learning content and administration. As teachers create
courses within a Learning Management System, they have
the opportunity to post assignments, monitor student
progress and work, post content (videos, documents,
links, and more), and to flip their classrooms.
LMS in India is basically intended for distance education
programs wherein the students get deprived of classroom
deliveries of faculty members. But to make the teachinglearning
effective, there is the need of incorporating LMS
in Classroom teaching-learning System. The combination
of traditional learning (face-to-face lectures) and webbased
courses is known as “blended learning”. This mixes
the features of virtual and real environments to provide a
holistic information production and enhance the students'
learning experience. Incorporation of LMS by educational
institutions will enhance and support classroom teaching
and offer courses to a larger population of learners. HEIs
across globe use LMSs to deliver online courses and
augment on-campus courses. In India, the use of LMSs is
primarily confined to online courses only. However, off
late, a few advanced HEIs have used the same in their oncampus
programs in order to improve the quality of
teaching-learning process.
Benefits of LMS
- It offers a centralized source of learning
- It helps in enhancing performance through tracking and reporting tools.
- It allows users to be evaluated before they take the course, while they are in the course, and when they finish the course.
- The content and information in the course can be easily upgraded.
- It simplifies the learning process as the students can access the contents of the sessions beforehand if they access internet.
Outcomes-Based Teaching and Learning (OBTL)
OBTL is focused not on what the teacher intends to teach
but rather the emphasis is on what is the outcome from the
learner of that teaching is intended to be. Detailed, wellwritten
learning outcomes or competence descriptors
allow both teaching staff and learners to have a clear
picture of the behaviour that is expected of the latter at the
end of a course. This can help to provide direction and
stability in the course, and can also help to guard against
over-reliance on a particular staff member or distinctive
interpretation of syllabuses. It is, of course, strongly
recommended that the students should always be
included in this pre-knowledge of objectives. All too often
in the past, their only clue as to what was required of them
came from a study of previous exam papers - a situation
that is difficult to defend, since students have quite
enough problems to face without being involved in
academic 'guessing games'.
Outcome expected / Learning Outcome should be
prepared at three levels – for the Program (Ex. MBA, BBA,
B. Tech. etc.), for the Course (Ex. Quantitative Methods,
Marketing Management, etc.) and for each Session. At
teachers' level, the outcome expected from the students
may be sketched at two levels – Outcome expected at the
end of each session and Outcome expected from the
Course on completion of the Course. But Outcome
expected on completion of the Program will be prepared
by the Deans/Principals of the Faculties. While the
teachers prepare the Outcome sheet, they need to consider
the background of the students, constraints imposed by
the Academic Regulatory Bodies and the requirements of
the Market.
At the end of the Courses, students' feedback needs to be
taken and the same is to be mapped with the outcome
sheet. While designing the outcome expected from the
program, top priority needs to be given to the
requirements of the market.
Positive Aspect of Happiness in Teaching Profession
Having discussed how a teacher should be happy, it is
pertinent to know how the teachers in recent time are
becoming happy. Among 20 teachers studied, hardly four
teachers (20%) do possess the traits required to be an
effective teacher and do adapt themselves to changing
environment very fast and as such they become happy, in
true sense. Remaining 80% of the teachers feel to be happy
amidst many odds in them as presented in Table-1.
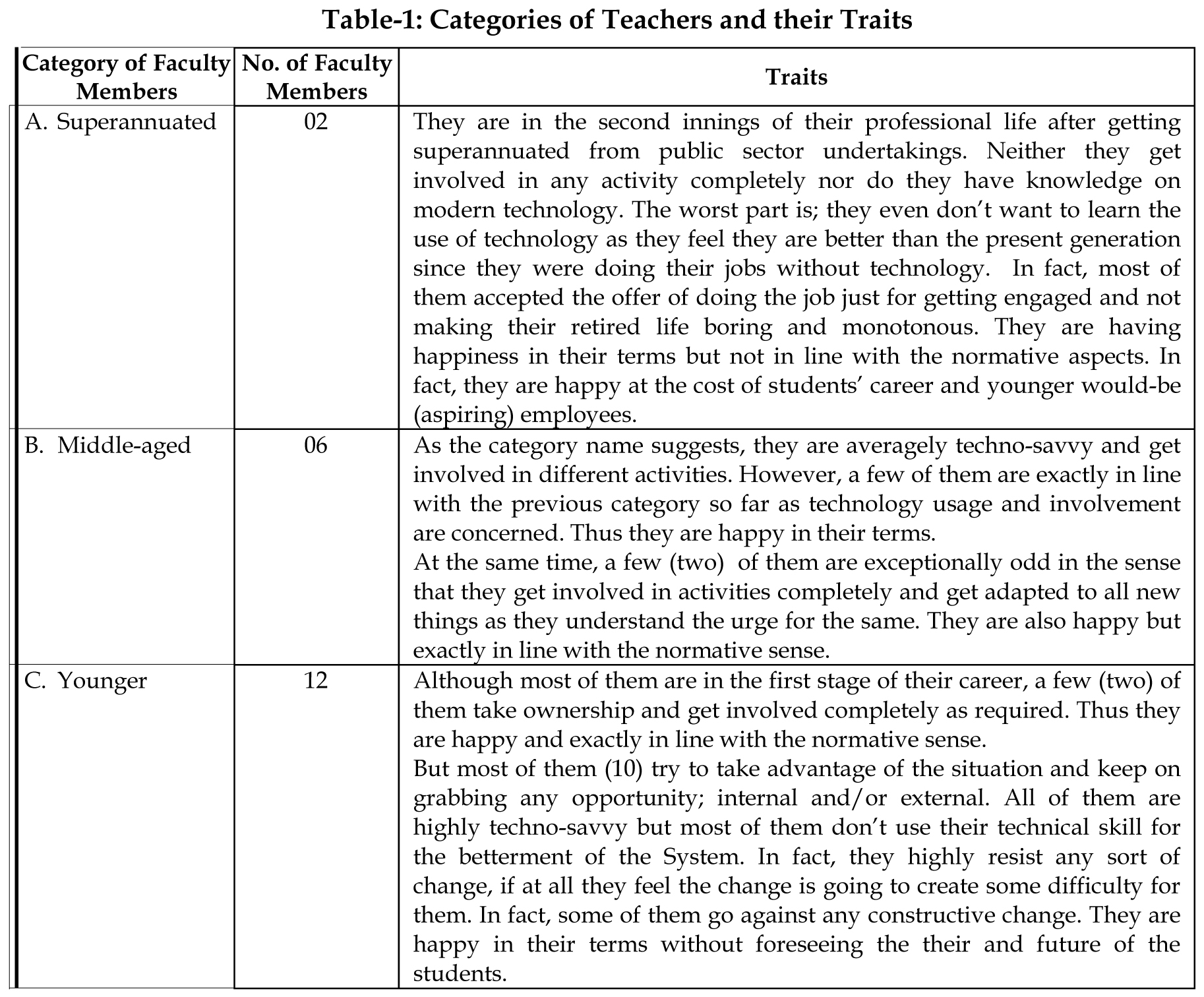 Source : Pr imary Data; Basis – Personal Interview and
Observation
Source : Pr imary Data; Basis – Personal Interview and
Observation
Conclusion
Happiness is an integral part of teaching profession. If a teacher does not enjoy the profession, neither s/he nor the students will be happy. Those who come to this profession by choice, they get happiness in true sense and as such there is no deviation between happiness in normative sense and positive sense. But the percentage of such teachers in Indian HEIs is very dismal. On the other hand, teachers who come to this occupation by chance also get the happiness for not doing their job what they are supposed to do. To have happiness in teaching profession, people should join it by choice and take the responsibility of the taught concerning their learning. PERMA Model should be practiced by each teacher in letter and spirit to have at least professional happiness. Once professional happiness is achieved, many odds in personal front will also be mitigated.
References
- Fredrickson, B. L. and Branigan, C. (2005) Positive emotions broaden the scope of attention andthought action repertoires, Cognition and emotion, 19, 2005, 313- 332.
- Gopalkrishnan, V. (2009) Determinants of job satisfaction of self-financing college teachers, Journal of Community Psychology and Research, 26(3), 2009, 300- 310.
- Ishwara, P. and Laxmana, P. (2008) Correlates of job satisfaction among teachers in selected universities in Karnataka state, Experiments in Education, 36(5), 2008, 11-19.
- Kaur, G. and Sidana, J. J. (2011) Job satisfaction of college teachers of Punjab with respect to area, gender and type of institution, Edutracks, 10(11), 2011, 27-35.
- Kumar, S. and Patnaik, P. S. (2004) A study of organizational commitment, attitude towards work and job satisfaction of postgraduate teachers, Journal of Educational Research and Extension, 41(2), 2004, 1-15.
- Mehrotra, A. (2005) Leadership styles of Principals, New Delhi: Mittal Publication. lPost, S. G. and Altruism, (2005) Happiness and Health: It's good to be good, International Journal of Behavioural Medicine, 12 (2), 2005, 66-77.
- Saha, K. (2013) Job Satisfaction of the Junior College Teachers of Assam in relation to Some Selected Variables, The CTE Journal, XI (1), 2013, 120-124.
- Sridevi, K. V. (2011) Job satisfaction of teacher educators of University of Mysore, Edusearch: Journal of Educational Research, 20(1), 2011, 59-65.
- Seligman, M. E. P. (2012) Flourish: A Visionary New Understanding of Happiness and Well-being, Atria Books, USA.
- Swain, S. C. (2016) Acceptance and Efficiency of the Learning Management System in Campus-based Programs of Private Higher Education Institutes in India, Growth, Vol. 44, No. 3, PP. 1-7.
