Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Risk Management : A brief study on the strategies adopted in selected industries with specific focus on Indian IT services' organisations
Abstract :
Risks are inherent to every industry, although the nature of risks might differ between each industry segment. Risks can impact a
particular industry in the form of losses on financial, health, manpower, infrastructural, environment, quality, reputation, etc. More
and more business houses are expanding their foot-print globally which also means increased risk factors to deal with. Therefore, Risk
Management (RM) has become a key focus area within the organisations. Independent RM function is established in most of the
organisations to identify, monitor and control various risks to their business.
RM strategies adopted by an organisation are customized to handle & mitigate potential risks faced by them. Organisations are
gradually moving towards Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) which would holistically address the risks at a broader level rather
than dealing risks at individual element level. This article analyses the risk elements and risk management processes for a selected set
of industries along with a specific focus on Indian IT services organizations.
Keywords :
Risk Management, industry, potential risks, Enterprise Risk ManagementIntroduction :
Risk by definition is potential of gaining or losing
something of value. Something of value can be Financial,
Health, Property, Personal, Quality, etc. Risk is also an
uncertain condition or event that has an impact on at least
one objective of any project that is undertaken. Risks are
common across all industries and to name a few, IT,
Banking & Financial Services, Infrastructure, Logistics,
and Healthcare.
Managing risks aka Risk Management (RM) is therefore
an important objective or focus area within any
organization. Risk Management is the identification,
evaluation, and prioritization of risks. Making informed
decisions by consciously assessing what can go wrong, as
well as the likelihood and severity of the impact is at the
heart of RM. Independent RM function is established
within most of the organizations.
During the course of this article, the key elements of Risk
Management (RM) across a few industries are elaborated
and the strategies adopted for an effective RM is
explained. This article will then focus on RM strategies
adopted specifically in Indian Information Technology
(IT) services organizations and looks to draw comparisons
with the broad RM strategies implemented across
industries.
Defining Risk and Risk Management
Risk can be broadly classified under 3 categories namely,
Preventable Risks, Strategy Risks and External Risks.
Preventable risks are internal risks, arising from within the
organization that are controllable and ought to be
eliminated or avoided. Strategy risks are the ones that
companies voluntarily accepts in order to generate
superior returns from its strategy. External risks are
certain risks that arise from events outside the company
and are beyond its influence or control.
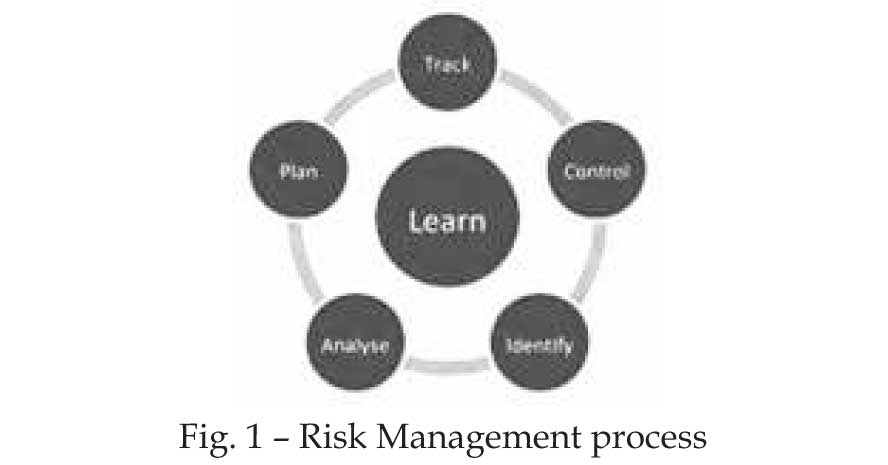
This process of risk management as depicted in the below
diagram defines six logical steps through which the team
manages current risks, plans and executes risk
management strategies. It is to be noted that below are
logical steps and they do not need to be followed in strict
chronological order for any given risk.
Risk Management adopted in selected industries
Risk Management strategies adopted in certain selected industries is detailed below.
Risk Management in Financial Services sector
Risk Management in a financial firm, be it Bank or
Financial Institution, is primarily concerned with financial
risks like bankruptcies, internal irregularities, frauds, etc.
This is in sharp contrast to RM for an industrial firm, which
generally focuses on physical risk. Since financial risk
occurs in the context of the interactions between
individuals with conflicting agendas, corporate risk
managers spend a good deal of time thinking about
organization behavior. The challenge of a modern
corporation is to ensure wealth maximization of their
stakeholders that is consistent with their risk preference.
On the other hand, risks have to be managed effectively
with a balance of providing adequate financial returns.
Key risk elements of the industry are as given below :
a) Market risk – defined as the potential of changes in
the market prices of an institution's holding which
may have an adverse impact on its financial
condition.
b) Credit risk – defined as a potential economic loss
from the failure of an obligor to perform according to
the terms and conditions of a contract or agreement
c) Operational risk – many other risks that are generally
grouped under this category like Legal risk,
Reputational risk, Accounting risk, Enterprise risk,
etc.
Management of Risks in financial firms consists of following measures :
a) Risk measurement or analysis : Measuring overall
risk of firm's position can be done in two principle
ways; a statistically based approach called Value at
Risk (VaR) or an approach based on economic insight
called stress testing or scenario analysis
b) Risk Control : Two fundamental and complementary
approaches are (i) place detailed limits on amount
and type of risk (ii) provide incentives to lower
management to optimize the trade-off between
return and risk
Risk Management in Insurance sector
Companies in the process of providing insurance and
other financial services, assume various kinds of actuarial
and financial risks. At the same time, they are major
providers of funds to the capital market. They use their
own balance sheet to facilitate the transactions and to
absorb risks associated with them. Therefore, risk
management and necessary procedures for risk control is a
crucial task for insurers.
Key risk elements of the industry are as given below :
a) Actuarial / Insurance risk – arising from assumptions
that actuaries implement into a model to price a
specific insurance policy may turnout wrong or
somewhat inaccurate
b) Systemic risk –disruption to the flow of financial
services that is (i) caused by an impairment of all or
parts of the financial system; and (ii) has the potential
to have serious negative consequences for the real
economy [Financial Stability Board]
c) Credit Risk – defined as the risk of loss due to the
inability or limited willingness of a borrower
(obligor), issuer or counterparty to meet its financial
obligations. For insurers, the source of credit risk may
include (i) Investment portfolio risk (ii) Counterparty
risk (iii) Reinsurance counterparty risk (iv)
Country/Transfer risk
Management of Risks in the sector consists of following
measures :
Journey of corporate risk management in insurance
industry has witnessed significant improvements in last
few decades, moving away from element-wise risk
management towards Enterprise Risk Management
(ERM). ERM is a step towards more defined and
formalized RM. ERM typically comprises of 8 interrelated
components as defined below:
a) Internal environment
b) Objective setting
c) Event identification
d) Risk assessment
e) Risk response
f ) Control activities
g) Information & Communication
h) Monitoring
a) Supply risk – like supplier opportunism, inbound
product quality, transit time variability, supplier
insolvency, etc.
b) Demand risk –like demand variability, forecast
errors, competitor moves, etc.
c) Operational risk – Inventory ownership, asset and
tools ownership, Product quality and safety issues,
Currency issues, etc.
Management of Risks in the sector consists of following
measures :
Risk management is a continual process that involves
long-term dedication of supply chain members. Below are
the typical strategies adopted for handling and mitigation
of several risks :
a) Risk Identification – Using multiple sources and
classifying risks into supply, operations, demand and
security risks
b) Risk assessment and evaluation – Decision analysis,
case studies and perception based
c) Selection of appropriate risk strategy – avoidance,
postponement, speculation, hedging, etc.
d) Implementation of supply chain risk management strategy – complexity management, organizational
learning, information technology and performance
metrics
e) Mitigation of supply chain risks – Preparing for
unforeseen risk events
Risk Management in Indian IT Services' sector
Software projects generate variable performance
outcomes and are high risk activities. Industry surveys
suggest that only about 35-40% [12] [13] of software
projects succeed within the agreed Cost, Time, Quality
and Scope. Billions of dollars are lost annually through
project failures or projects that do not deliver promised
benefits. The need to manage risks increases with the
system complexity, both technical and non-technical.
Risk elements as argued by Boehm and Ross (1989) [10] fall
into two categories as defined below:
a) Generic risks – which are common to all projects like
Manpower attrition, Scope creep, Network issues,
Location outages, etc.
b) Project-specific risks – which are specific to a
particular project like Technology complexity,
Requirement gaps, Schedule variance, etc.
Risk Management in IT services is more than a process or
methodology. It is a real-time threat management
capability that is developed within an organization,
through learning, practice and other mechanisms, over a
period of time. Risk Management process as defined in the
pictorial (Fig. 1) of this article is a general guideline
followed in many of the IT organizations.
Risk Management typically involves two broad steps
namely:
a) Risk Assessment
- Risk identification
- Risk analysis
- Risk prioritization
- Risk management planning
- Risk management execution
- Risk monitoring and control
Since Indian IT services organizations manage projects
that are outsourced from their customers located in
various global geographies, the expectation from the
customers are very high in delivering projects with right
quality and within agreed timelines. Also, competition
within the Indian IT industry is very high and hence they
are always at the risk of losing a customer to the
competition if the project deliveries at not up-to the mark.
Hence, IT organizations adopt a clearly defined Project
Management (PM) practice based on models defined by
reputed institutes like PMI, CMMI, etc. Risk Management
is an integral part of the PM practices. Risk Management
(RM) guidelines are well defined and documented within
the organizations. Periodic internal and external audits are
conducted to ensure the effectiveness and compliance to
the RM policies. Being proactive in risk prevention and
control is at the heart of good risk management.
Potential Risks are identified at various stages of the
Project lifecycle like a) Proposal stage b) Contractual stage
c) Project initiation stage and d) Project execution stage.
Risk monitoring and control is a continuous activity
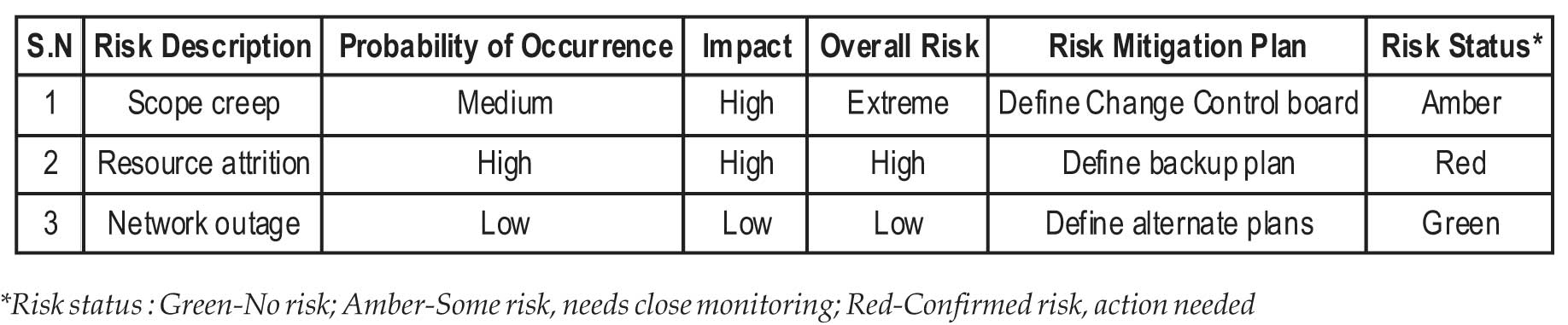
throughout the project lifecycle. Below is a sample risk
register followed within the project which helps in
monitoring and controlling the project risks at several
stages.
Conclusion
It is clear from this article that every industry faces several
risks as part of their operations, be it internal or external
risks. However, risk elements could vary by the type and
nature of the industry. Higher the complexity of the
industry operations, higher will be the risks. Therefore,
Risk Management is an important function with the
organisations. Element-wise RM is giving way to more
formalized ERM.
Indian IT service organisations face typical risks by way of
servicing their predominantly international clientele.
Industry surveys depict just 35-40% of successful software
projects. Therefore, RM gets a focused attention within the
IT organisations. Based on the analyses done in this article,
it can be concluded that the Risk Management Process (like
risk identification, analysis, control, etc.) followed within
the IT organisations broadly matches that of the other non-
IT industries.
References :
- Kaplan Robert S., Mikes Anette (June 2012). Managing Risks: A New Framework Harvard Business Review.
- Steven Allen. Financial Risk Management – A practitioner's guide to managing market and credit risks. Wiley Finance.
- Financial Risk Management. Dun & Bradstreet – Tata McGraw-Hill Professional.
- P.K.Gupta. Insurance and Risk Management. Himalaya Publishing House, Second Edition.
- Systemic Risk in Insurance – An analysis of insurance and financial stability. The Geneva Association Systemic Risk Working Group, March 2010.
- Credit Risk Management. EY Article.
- Ila Manuj, John T. Mentzer (January 2008).Global supply chain risk management strategies. IJPDLM, Journal of Business Logistic, 29(1).
- Supply Chain Risk Management: A compilation of best practices. Supply Chain Risk Leadership Council (SCRLC), August 2011.
- Bennet P. Lientz, Lee Larssen, Risk Management for IT Projects. BUTTERWORTH-HEINEMANN An imprint of Elsevier (2006).
- Barry W. Boehm, Rony Ross (July 1989). Theory-W Software Project Management: Principles and Examples. IEEE Transact ions on Sof tware Engineering.
- Ronald P. Higuera, Yacov Y. Haimes. (June 1996). Software Risk Management. Carnegie Mellon University: Software Engineering Institute.
- CHAOS Manifesto .(2013)The Standish Group.
- Driving Business Performance – Project Management Survey 2017. KPMG report.
