Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Corporate Governance Disclosure Score and its perspectives with respect to the Indian Banking Sector
Abstract :
corporate governance involves the manner in which business and affairs of individual institutions are governed by their board of directors and senior management. Sound corporate governance can be practiced regardless of structural form used by a banking organization. The objective of the research paper is to identify the key determinants of corporate governance disclosure score of selected Indian banks. Corporate governance discloser score is calculated on the basis of 14 financial and 39 non-financial disclosure items of bank for each year. Banks listed in the BANKEX [BSE] as on 31st March 2016 are selected for the study on the basis of their free float market capitalization. Hence five PSU banks and seven private sector banks are used in the study. Thirteen hypotheses have been formed. Corporate Governance Disclosure Score has been used as dependent variable and eleven variables are taken as independent variables such as income, local ownership, board size, board independence, return on asset, net non-performing asset, capital adequacy ratio, return on equity, audit committee size, earnings per share and number of board meetings of bank. In this research work, duration of five financial years, from 2011-12 to 2015-16 have been taken into consideration. So the data collected is based on the 60 annual reports of banks of this duration. Shapiro-Wilk Normality Test, Mann Whitney Test, Kruskal-Wallis Test and Spearman's Rank Correlation have been used in this proposed study.
Keywords :
Corporate Governance, Independent Director, Audit Committee, Board Meeting, Local ownership, Income, Net Non-Performing Assets, Capital Adequacy Ratio.Introduction:-
A healthy banking system is an absolute prerequisite for a well-functioning stock market and corporate sector. The banking sector provides the necessary capital and liquidity for corporate transactions and growth. Good governance system within the banking sector is especially important in developing countries where banks provide most of the finance. Moreover financial market liberalization has exposed banks to more fluctuations and to new credit risks. Poorly governed banking systems and massive capital flight can seriously damage national economies. The banking framework is based on three pillars such as minimum capital requirement, supervisory review and market discipline.
2. SURVEY OF EXISTING LITERATURE
Kumar, Arora and Lahille (2011) suggested that a credit risk management index tool should be developed in order to have a single measure to assess the corporate governance practices followed in a given bank and the overall credit risk management framework. Pandya (2011) analyzed the effect of corporate governance structures, particularly board structure and CEO duality on the performance of Indian banks. He also examined the relationship between CEO duality and the proportion of independent directors on firm performance as measured by return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE). Mehta (2012) discussed that a major challenge to the Indian banks would be to restructure their poor quality assets which could lead to a high proportion of non-performing assets. The norms would favour the large banks because of their risk management expertise and the diversified portfolios. The banks also were required to develop new sophisticated computerized tools to reduce cost of data analysis and to get rid of most of the historical data. Agarwal (2013) established that on financial performance of firms. The study revealed that good governance had fostered better financial performance. Ratings of company along with employees' related and environmental dimensions also had significantly influenced corporate financial performance.
3. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
The objectives of the study are as follows -
- To identify the key determinants of corporate governance disclosure score of selected Indian banks.
4. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The proposed study will combine explanatory and empirical research.
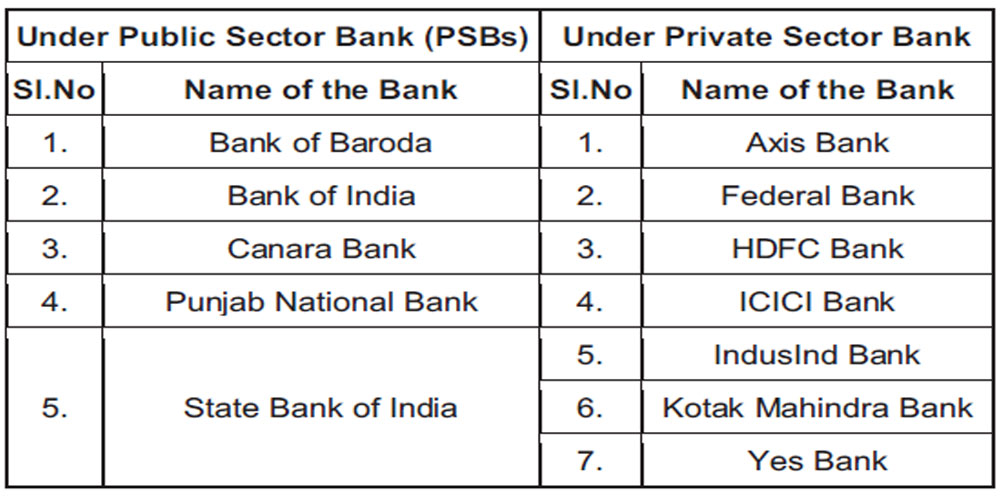
- Samples of the study: Though, corporate governance bind to all type of banks but for precise focus the banking companies listed in the BANKEX [BSE] as on 31st March 2016 are selected on the basis of their free float market capitalization. All the listed banks in BANKEX are divided in two groups - public sector banks and private sector banks to study and analyse their corporate governance practices.
Exhibit 1: List of Banks listed in the BANKEX
[BSE] as on 31st March 2016
Data Analysis
- A corporate governance disclosure score (CGDS) was computed by using the formula:

Period of the Study
In this research work, the duration of five financial years from 2011 - 12 to 2015 - 16 have been taken into consideration. So all the data collected is based on the annual reports of this duration only.
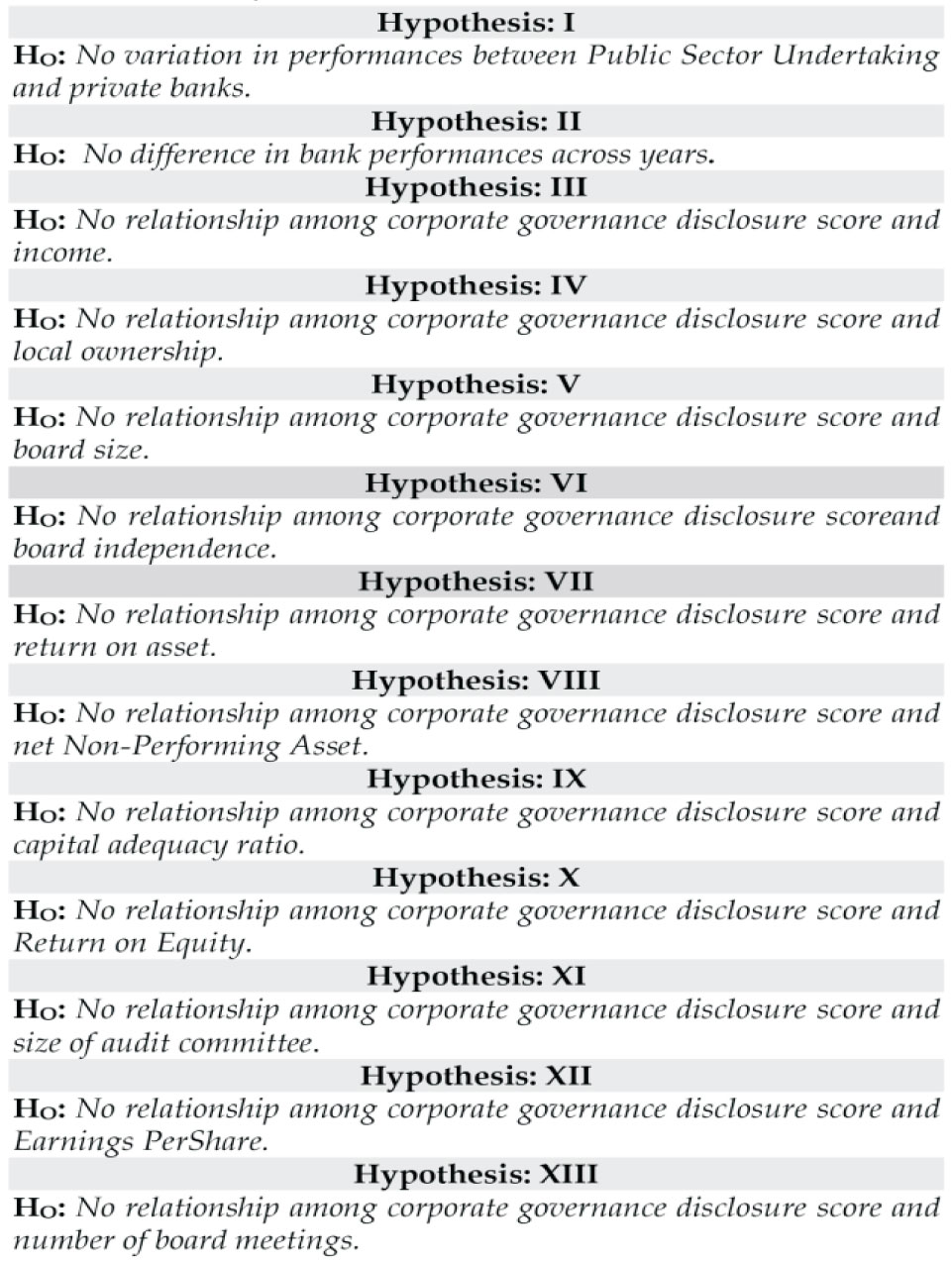
Research Hypothesis
Directors' report, Auditors' report, Financial statement, Schedules, Subsidiary, Consolidated financial information, Notes on
accounts, Significant accounting policies, Related party disclosures, Segment reporting, Risk management, Basel disclosures,
Dividend and Other performance indicators etc.
Message from the Chairman, Letter from Managing Director and Chief Executive Officer, Vision and Mission Statement,
Ownership/ Shareholding Structure/ Pattern, Shareholders' Rights, Statutory Details of the company, Size of the Board,
Composition of Board, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Duality, Information about independent Directors, Role and
Functions of the Board, Changes in the Board Structure, Audit Committee Remuneration and Nomination Committee,
Investors' Grievance Redressal Committee, Other Committees, Composition of the Committees, Functioning of the
Committees, Organizational Code of Ethics, Biography of the Board Members, Number of Directorship hold by each Member,
Number of Board Meetings, Attendance in Board Meetings, Director's Stock Ownership, Director Remuneration, Employee
Relation/ Industrial Relation, Corporate Social Responsibility, Environmental Responsibility, Financial Inclusion
Norms/Policy, Internal Control System, Auditor Appointment and Rotation, Auditor Fee, Notice and Agenda of the Annual
General Meeting, Separate Corporate Governance Statement/ Section.
EMPIRICAL STUDY
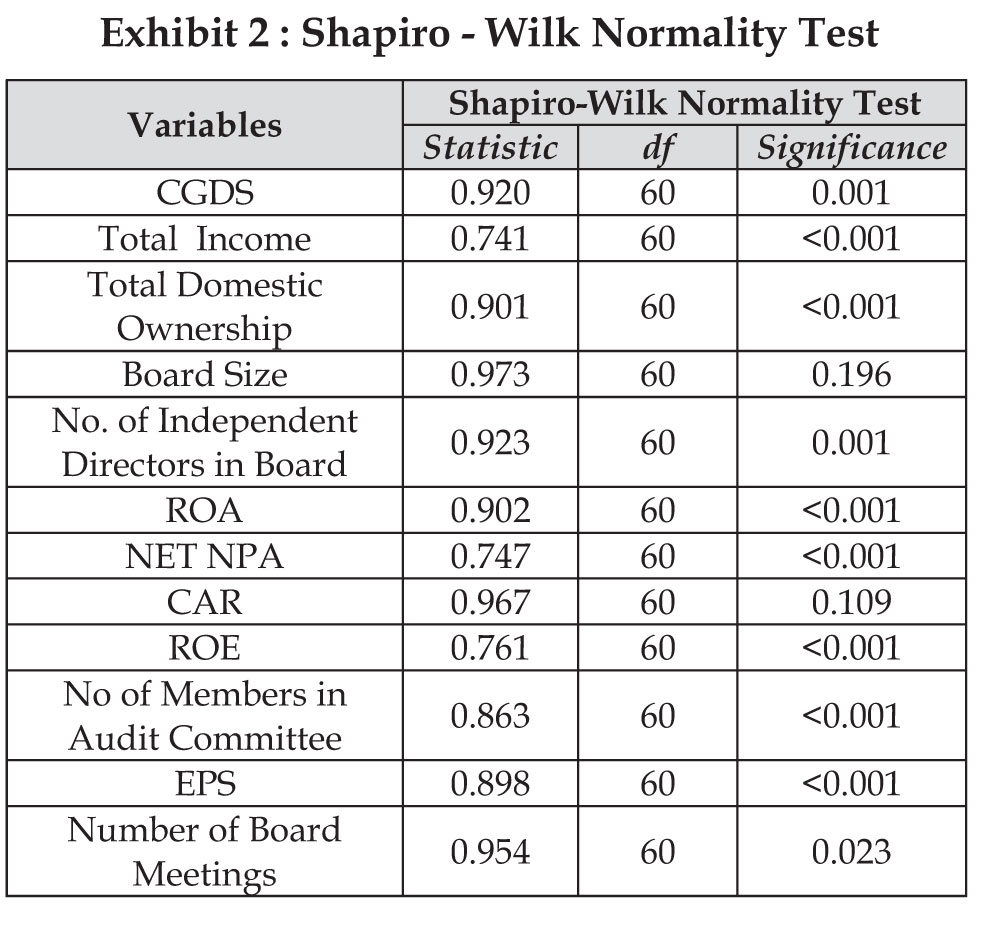
At the outset five years' data of 12 (Twelve) banks have been considered. The dataset incorporates 12 variables such as corporate governance disclosure score, income, domestic ownership, board size, Number of independent directors in the board, Return on Asset, Net Non-Performing Asset, Capital Adequacy Ratio, Return on Equity, number of members in audit committee, Earnings Per share and Number of board meetings in a year. It is to be noted that before running multiple regressions, it is necessary to check whether the data set is following normal distribution or not. H Data is following normal distribution. O: H : Data is not following normal distribution 1 For fulfilling the above, Shapiro - Wilk Normality Test is conducted below.
Findings and Interpretation
All variables except board size and capital adequacy ratio are significant.
Hence null hypothesis is rejected for the remaining 10 variables at 5% level of significance. Data is not
following normal distribution. Hence, ANOVA, t-test, Pearson correlation coefficient and regression cannot
be done for this data.
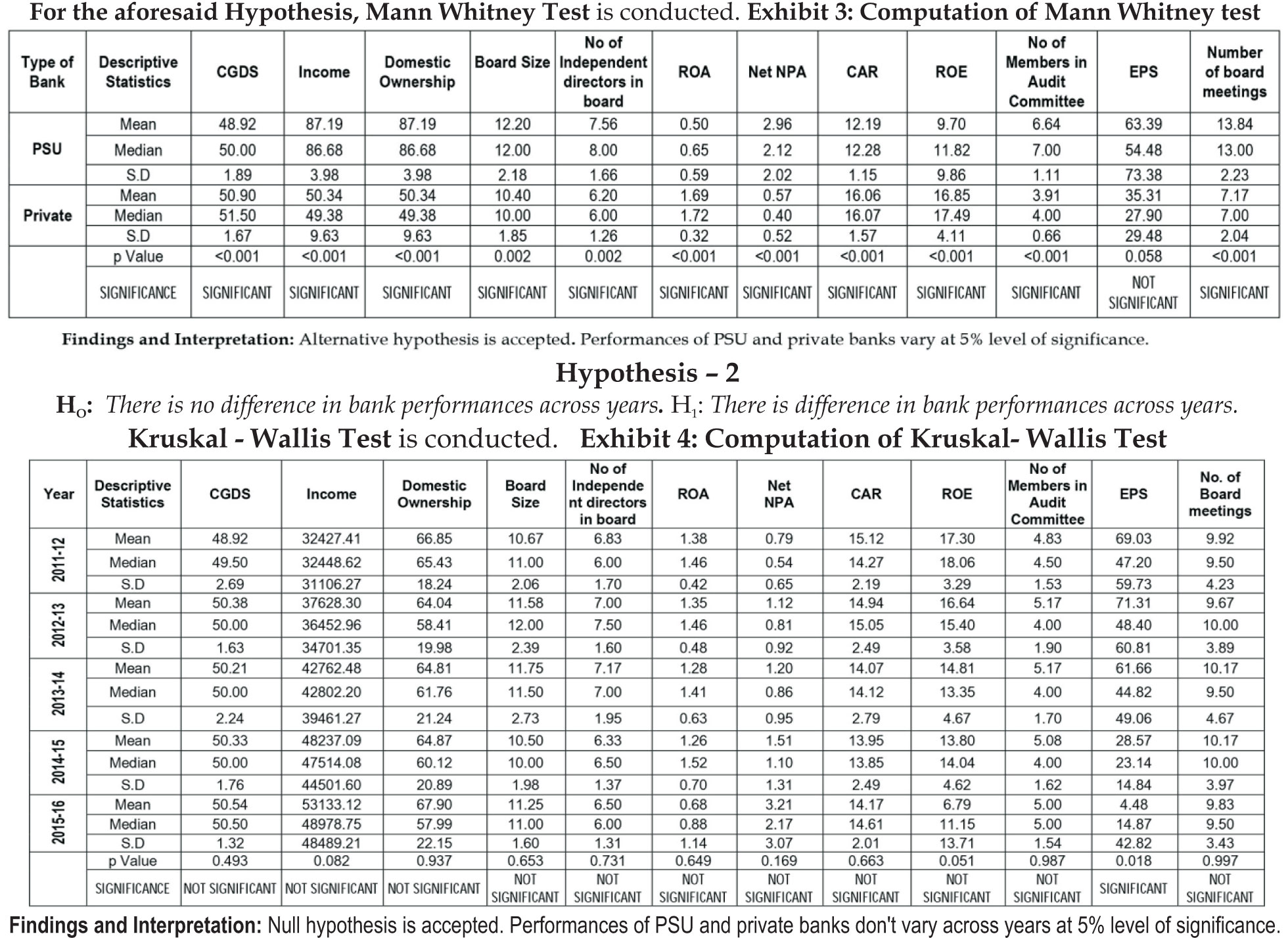
Hypothesis - 1
H0 : There is no variation in performances between PSU and private banks. H : There is variation in performances between PSU and private banks.
Hypothesis: 3 - 13
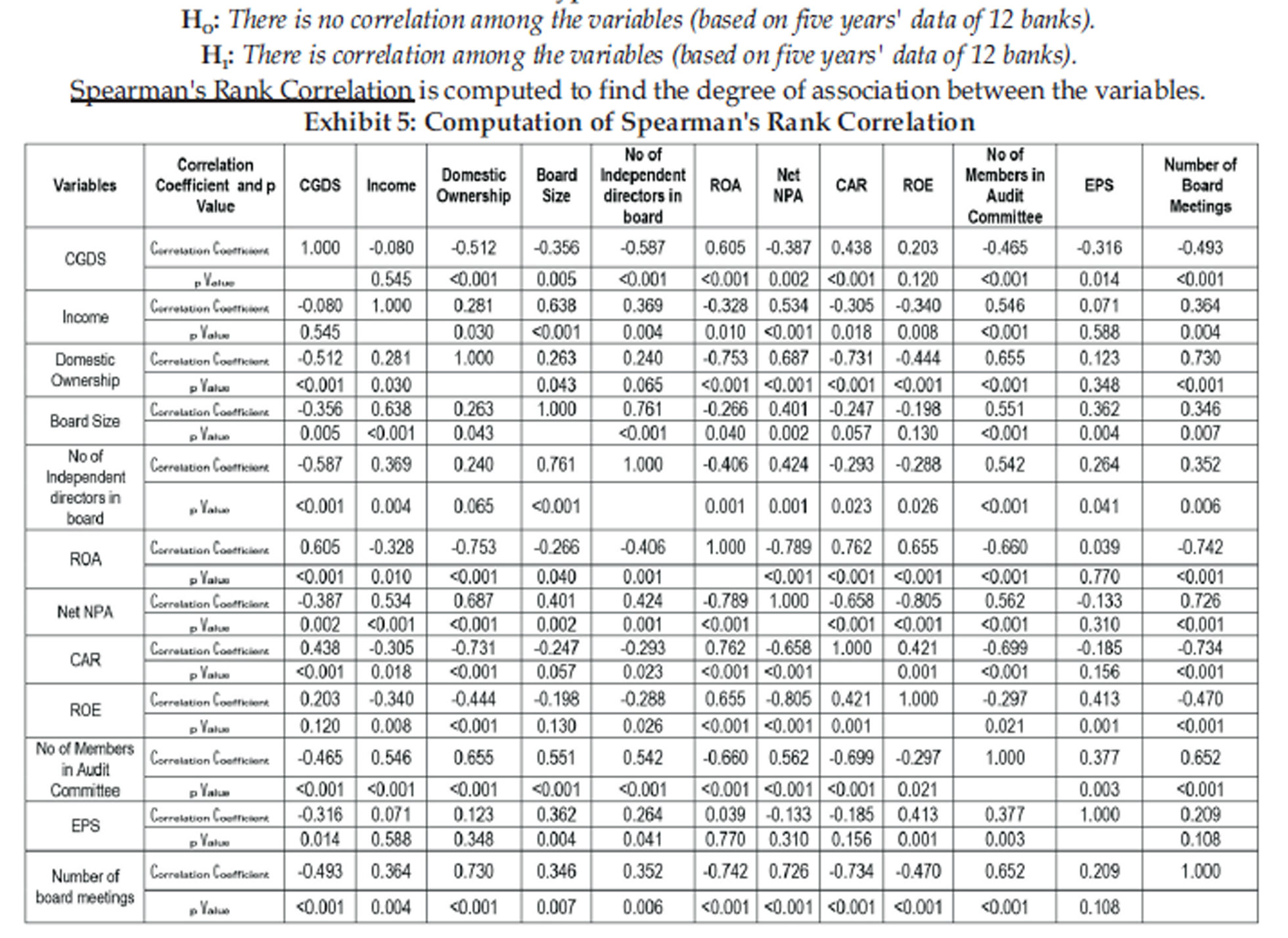
Findings and Interpretation:
Alternative hypothesis is accepted for domestic ownership, board size, board independence, return on asset, net NPA, capital adequacy ratio, audit committee size, earnings per share and number of board meetings in a year. Null hypothesis is accepted for income and return on equity. Degree of association between corporate governance disclosure and domestic ownership in bank, corporate governance disclosure and board size in bank, corporate governance disclosure and number of independent directors in the board, corporate governance disclosure and return on asset, corporate governance disclosure and net NPA, corporate governance disclosure and capital adequacy ratio, corporate governance disclosure and no of members in audit committee, corporate governance disclosure and earnings per share as well as corporate governance disclosure and no of board meetings in a year are significant at 5% level of significance. On the other hand, degree of association between corporate governance disclosure and average income as well as corporate governance disclosure and return on equity are insignificant at 5% level of significance.
6. CONCLUSION
H is accepted for hypothesis 1. Performances of 1 Public Sector Undertaking and private banks vary at 5% level of significance. H is accepted for O hypothesis 2. Performances of Public Sector Undertaking and private banks don't vary across years at 5% level of significance. H is accepted for O hypothesis 3. There is no relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and income at 5% level of significance. Correlation Coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and income is insignificant. H is accepted for hypothesis 1 4. There is inverse relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and local ownership at 5% level of significance .Correlation Coefficient between corporate governance disclosure index and average domestic ownership in bank is significant (-0.512). H is accepted for hypothesis 5. There is 1 inverse relationship between corporate governance significance. Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and board size is significant (-0.356). H is accepted for 1 hypothesis 6. There is inverse relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and board independence at 5% level of significance. Correlation coefficient between Corporate governance disclosure score and number of independent directors in the board is significant (-0.587). H is 1 accepted for hypothesis 7. There is positive relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and ROA at 5% level of significance. Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and return on asset is significant (0.605). H is accepted for hypothesis 8. 1 There is inverse relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and net NPA at 5% level of significance. Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and net NPA is significant (-0.387). H is accepted for hypothesis 9. 1 There is direct relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and capital adequacy ratio at 5% level of significance. Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and average capital adequacy ratio is significant (0.438). H is accepted for hypothesis 10. 0 There is no relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and ROE at 5% level of significance. Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and return on equity is insignificant.H is accepted for hypothesis 1 11. There is inverse relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and audit committee size at 5% level of significance. Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and no of members in audit committee is significant (-0.465). H is accepted for hypothesis 12. 1 There is inverse relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and EPS at 5% level of significance. Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and earnings per share is significant (-0.316).H is accepted for 1 hypothesis 13. There is inverse relationship between corporate governance disclosure score and number of board meetings at 5% level of significance .Correlation coefficient between corporate governance disclosure score and no of board meetings in a year is significant(-0.493). Hence local ownership, board size, board independence, return on asset, net NPA, capital adequacy ratio, audit committee size, Earnings per share as well as number of board meetings in a year are key determinants of corporate governance practices of banks.
REFERENCES
- Agarwal, Priyanka (2013), 'Impact of Corporate Governance on Corporate Financial Performance', Journal of Business and Management, 13 (3), 1 - 5. lBalaraman, R. and Chatterjee, D. P. (2010), 'Risk Management - An Overview', (Indian Institute of Banking and Finance. Ed.) New Delhi: Macmillan Publishers. ,
- Banerjee, Abhijit, Shawn, Cole and Esther, Dufio (2004), 'Banking Reform in India', In S. B. Berry, India Policy Forum (Vol. I). Washington DC: Brookings Institution Press.
- Chopra, Kiran (1987), 'Managing Profits, Profitability and Productivity in Public Sector Banking', Jalandhar: ABS Publications.
- Kumar, Muneesh, Arora, Anju and Lahille, Jean- Pieree (2011), 'Construct of Credit Risk Management Index for Commercial Banks', Banks and Bank Systems, 6 (1), 16 - 25.
- Mehta, Meera (2012), 'Demystifying Basel III for Indian Banks', International Conference on Technology and Business Management.
- Pandya, Hemal (2011), 'Corporate Governance Structures and Financial Performance of Selected Indian Banks', Journal of Management and Public Policy, 2 (2), 4 - 21.
