Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Contemporary Issues Faced By Customers Of Tirunelveli City In Online Retailing
Abstract :
In today's world of increasing awareness regarding sustainable development, green banking becomes a supreme issue. The
main economic agent influencing industrial activity and economic growth is the financial institutions i.e., banking sector.
This study is designed to analyze the customer's awareness of green banking initiatives in the Indian market. Some of the
relevant factors which are undertaken are Environmental Protection, E- Banking, Paperless banking, Use of renewable
resources, Sustainable banking, Corporate Social Responsibility, etc. to evaluate the level of customer's awareness on green
banking initiatives. After collection of data through a survey, this study has been analyzed using a pilot study, frequency table,
cross-tabulation, chi-square test, factor analysis, and rank analysis technique to find out the significance of individual factors
as stated above.
The finding reveals that 24.5% of the respondents agree that Green Banking promotes environmental protection. 9% of the
respondents feel that Green Banking is similar to E-Banking, 22.8% of the respondents' feet it is paperless banking. 6.8% of
them feel that it is related to the use of renewable resources. The data also reveals that the majority of the customers prefer to
adopt paperless banking in the Kolkata area. The overall findings of this study provide implications for bank managers and
bankers of different banks of Kolkata.
Keywords :
Customer's awareness, environmental protection, e-banking, paperless banking, renewable resources, sustainable banking, corporate social responsibility.Introduction
Finance is the lifeblood of business. Every business
firms directly or indirectly depend on the financial
institution for their fund. The banking sector is the
major lending agent that affects entire industrial
activity as well as the economic development of our
whole nation. Nowadays, banks have taken initiative in
envi ronmental protec t ion by inves t ing in
environmentally and socially responsible projects that
save costs and minimize risk. These initiatives help
banks to serve both commercial objectives and also their
social responsibility.
India is one of the fastest-growing countries in terms of
the emission of greenhouse gases. Among the major
cities in India, i.e., Delhi, Mumbai, and Chennai are
there in the top ten most polluted cities in the world. So
in order to highlight the role of banks in corporate social
responsibility RBI circulated a notice on 20th December
2007 for all scheduled commercial banks with the title
“CSR - sustainable development and non-financial
reporting”.
Apart from reducing risks, green banking also opens
new ways for marketing different products and
services. By this process, banks will be able to satisfy
both the commercial objective of the bank and also its
social responsibilities. Indian commercial banks are
implementing green banking technology for the
purpose of rending timely and valuable services to the
banking beneficiaries. It also rends valuable innovative
services to the banking beneficiaries. The innovative
services rending are core banking, re-engineering and
revise engineering scheme which increases the
efficiency of the bank.
The main reason for green banking is that it reduces
electricity consumption and electricity prices of the
firm. Increase in the demand for eco- friendly products.
It protects the environment from the side effects of
pollution.
Literature review
Indian Banks Association (IBA, 2014) defines green
banking as “like a normal bank, which considers all the
social and environmental/ecological factors with an
aim to protect the environment and conserve natural
resources”. Through this, the bank will act like a normal
bank controlled by the same authority, but its
operational activities are somewhat different
attributing an additional agenda of sustaining
environment. Therefore, it is associated to the notion of
sustainable banking and sustainable banking
management.
Environmental impact might affect the element of
assets and also the rate of return from banks in the longrun.
Thus, the banks should go green and play a proactive
role by taking environmental and ecological
aspects as part of their lending principles; which would
force industries to go for mandated investment for
environmental management, use of appropriate
technologies and management systems (Sekaran, 2010).
Green banking dodges as much paperwork as possible
and relies on electronic transactions for processing so
that we get green credit cards and green mortgages.
Less paperwork means less cutting of trees (Singh &
Singh, 2012). Green banking is also called ethical
banking or a sustainable banking which are controlled
by the same authorities but with an additional agenda
of taking care the earth's environment (Jha&Bhome,
2013; Karunakaran, 2014; Nath et al., 2014; Singh &
Singh, 2012).
Although banking is never considered a polluting
industry, the present scale of banking operations have
considerably increased the carbon footprint of banks
due to their massive use of energy (e.g., lightning, air
conditioning, electronic/electrical equipments, IT, etc),
high paper wastage, lack of green buildings etc.
Therefore, banks are suggested to adopt technology,
process and products in which would result in
substantial reduction of their carbon footprints as well
as develop a sustainable business (Bhardwaj and
Malhotra, 2013).
A study on socially responsible banking in India
elucidated that green banking starts with the aim of
protecting the environment; whereby before granting a
loan, the banks consider whether the project is
environment friendly and has any implication for the
future. A company will be given a loan only when all
the environmental safety standards are adhered to
(Bihari, 2011).
Khondokar Morshed Millat, Rubayat Chowdhury and
Edward Apurba Singha (2012) focused on the definition
of green bank as an ethical, sustainable as well as
socially responsible bank that depends on a unit or a
group of a team that defines not only more than a
banker, but also an environmentalist like all-rounder in
a game. He also appreciated the budget at the inception
of Green Banking of banks for the year 2012 and green
finance through Environmental Risk Rating (EnvRR).
Ahmed, Zayed and Harun (2013) explained the green
banking as a multi-stockholders' endeavor and
elucidated that the green banking is the outcome of
RIO+20 summits where the different nation raised
their voice over environmental safety. And from factor
analysis, they identified the six influencers affecting
green banking that are economy, policy, demand,
pressure, environment and legal factors that have a
combined variance about 65.25% of green banking
decisions.
Research gap
Previous research has established some concepts regarding green banking issues but not enough is known regarding the customer's awareness of green banking initiatives in Indian context. However, through this study, we like to establish whether abovestated factors do have an effect on the awareness level of customers regarding green banking initiatives in Kolkata.
Objectives of the study
The objective of this research paper is to know the awareness level of the customers with respect to Green Banking initiatives undertaken by the different branches of State Bank of India in Kolkata chapter.
Research methodology
In this study, descriptive research design has been implemented. This type of research design is undertaken to describe the characteristics of the variables.
Pilot study:
Before executing the project a pilot study has been done with the help of a pre-designed questionnaire. By this process, we have tried to judge the feasibility and scope of the project.
Data Collection:
To conduct this study, primary data were collected throughpre-tested structured questionnaires which were given to the customers of different branches of State Bank of India and their responses are recorded for further analysis. Secondary data was also used and collected from various published reports of Reserve Bank of India, other public and private sector banks, reputed journals, etc.
Sampling:
175 customers of different branches of State Bank of India in Kolkata are interviewed for the collection of data. Convenience sampling technique has been used for data collection purpose. Data was collected from 17th May, 2019 to 31st July, 2019.
Statistical package:
SPSS software has been used for the analysis of the data. Frequency table, crosstabulation, chi-square test, factor analysis, and rank analysis technique has also been used for data analysis purpose.
Data analysis
Frequency Distribution:
Demographic profile of the customers has been judged on the basis of age, gender, educational qualification, occupation, annual income and period of relationship with the bank.
(a) Period of relationship with State Bank of India: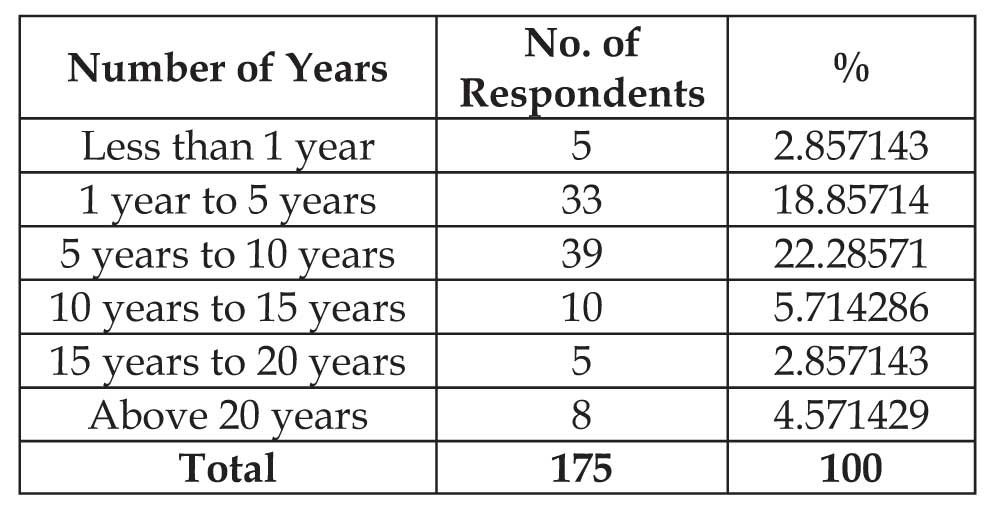
It is clear that 39% of the customers are maintaining the relationship with SBI for 5 to 10 years. Next, 33% of the customers have a relation with SBI for 1 year to 5 years.
(b) Opinion about E-Banking: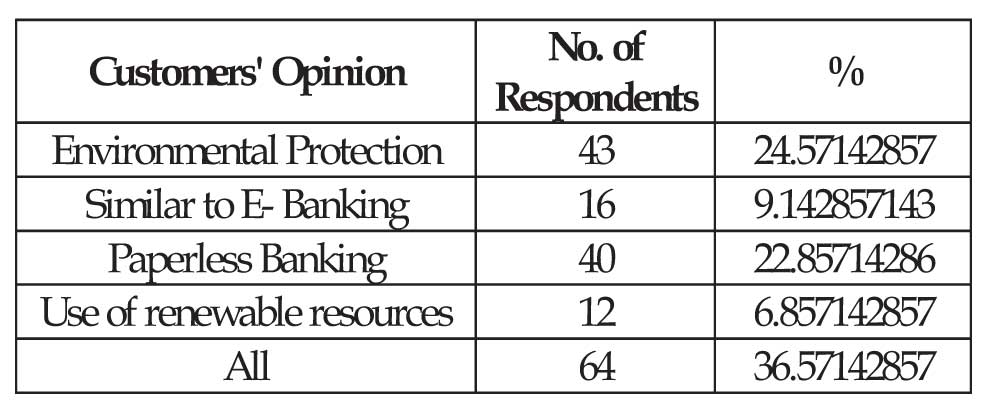
From the chart, it is clear that 24.5% of the respondents say that Green Banking promotes environmental protection, 9% feel that Green Banking is similar to EBanking, 22.8% feet that it is paperless banking, 6.8% of them feel that it is related to the use of renewable resources and remaining 36.5% feel that it covers all the above options.
Factor Analysis:
Rotated Component Matrix shows the correlation of each variable with other factors from the contribution of variables. The correlations possible values range from +1 to -1.
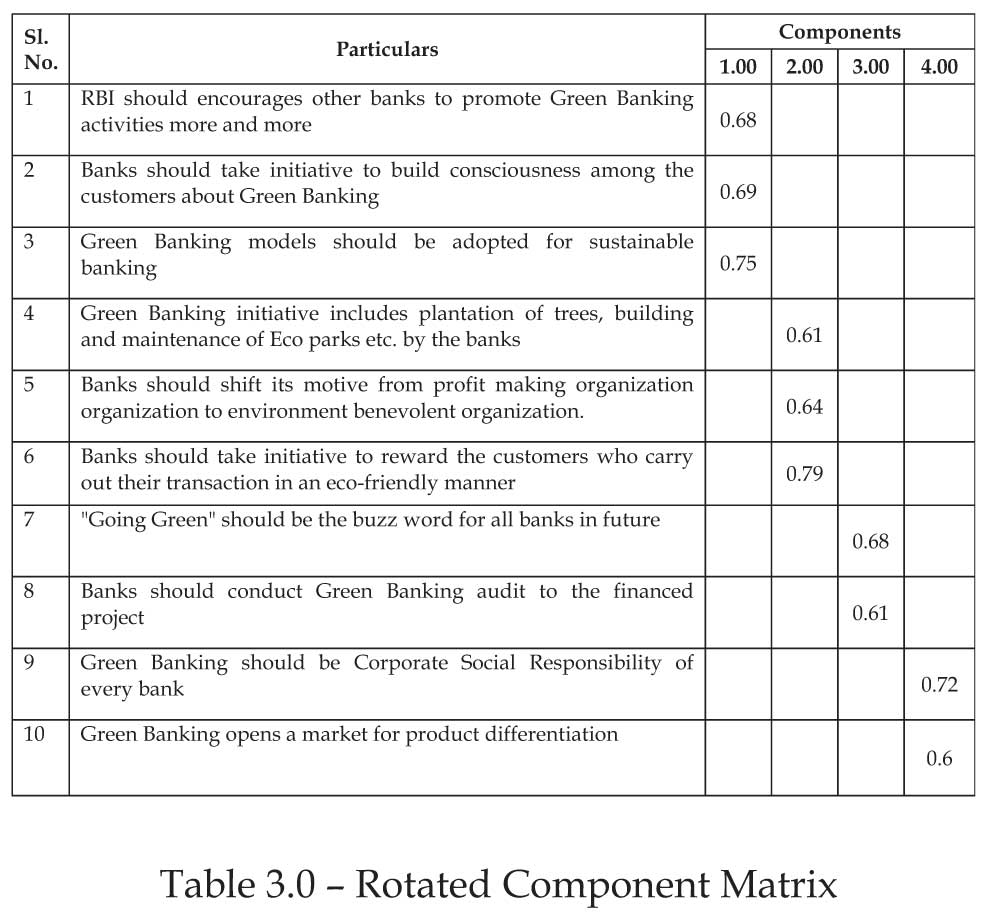
In Table 3.0 all the items that are loaded are reduced
into 4 significant factors. These factors can be explained
by arranging the variables from the questionnaire, into
4 groups based on the highest Component Matrix
loadings per statement. Factors are as follows:
Factor 1:Variables 1 to 3 of Table 3.0 suggests that Green
banking cell must be framed by every bank and it must
take measures to formulate policies for Green banking
and implement the green strategic plan.
Factor 2:Banks should promote Green Banking
activities seriously in order to implement environmentfriendly
practices and reduce the carbon footprint from
banking activities. Factor 3:Green Banking should be
included in the curriculum of most of the banks. Banks
should conduct Green Banking audit to the financed
project and award loans to its customers only when
environmental safety standards are followed. Reserve
Bank of Indiashould make it mandatory for every bank
to disclose its Green Banking activities in an annual
report.
Factor 4:Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a
process where generally banks contribute ethically to
economic development. Among various CSR banking
activities, Green Banking is a newly emerging one.
Identification of the factor as CSR strategy is carried out
from variables mentioned in Table 3.0 particulars 9 to
10.
Rank Analysis:
Rank is allotted to different variables by calculating frequency and means scores of the responses collected. Rank 1 is given to highest score and proceeded accordingly. In order to know the satisfaction level of Green Banking applicants and to understand the most preferred way of implementing Green banking rank analysis has been carried out.
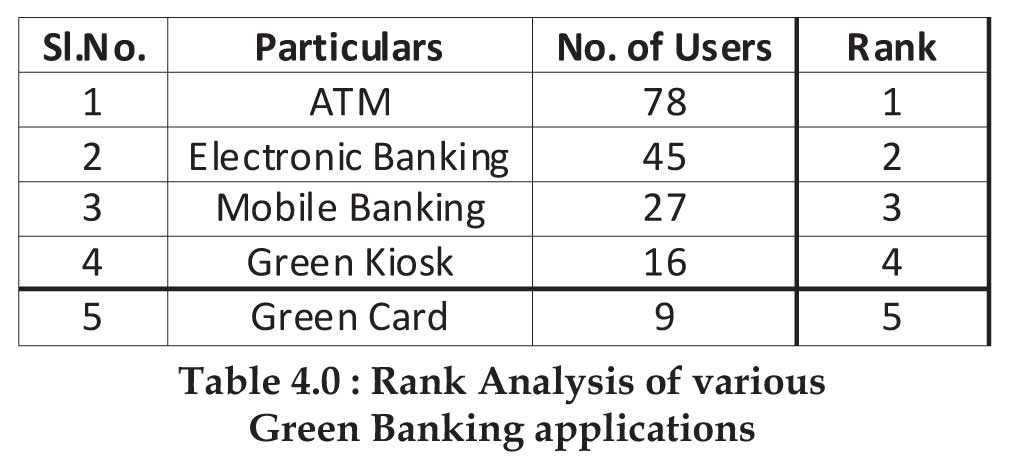
From above Table, it can be concluded that majority of customers use ATM card and E-Banking and mobile banking rank 2nd and 3rd position respectively. Green banking products possess a lower rank on the list.

From Table 5.0 it is clearly understood that the majority of the customers prefer to adopt paperless banking. Use of solar panel is one of the energy consumption methods and it gets the second rank. Introducing Green Banking financial products such as green loan gets third preference. As many numbers of office staff can use common transport at a time to save fuel consumption get second preference. Finally, the last preference is given to the green building.
Findings and implications
- There is a lack of awareness among banking users about green banking. It is the duty of the bank to create awareness among the customers about the benefits of green banking;
- Strategies should be framed and followed to popularize Electronic Banking and mobile banking among users. The training program should be organized by banks to educate and guide customers on how to carry out transactions in an eco-friendly manner;
- For further development customers feedback is valuable. Banks should give focus on this area;
- Last but not the least green banking has to be included in the curriculum or an activity in school or college level study;
Conclusion
The result of this study shows that promoting environment friendly practices and reducing carbon footprint from banking activities is an important area to uphold in recent area. It involves use of E-Banking, mobile banking, green kiosk, E-statement, online transaction, green loans, ATM etc. But introduction of various green banking products are useless without proper utilization in a proper way. Green banking has become Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) of every bank. Indian banks have already taken several initiatives to popularize green banking but when compared globally, they are lagging behind. Banks should continuously work on improving and introducing several green banking products. In order to enhance green banking activities banks should acquire support of government, NGOs, business organization and the customers.
References:
- Ahmad, F., Zayed, N. M., &Harun, M. A. (2013). Factors behind the Adoption of Green Banking by Bangladeshi Commercial Banks. ASA University Review, 7.2, 241-255.
- Bhardwaj BR, Malhotra A (2013) Green Banking Strategies: Sustainability through CorporateEntrepreneurship. Greener Journal of Business and Management Studies 3 (4), 180-193, ISSN: 2276-7827.
- Bihari SC (2011) Green Banking – Socially Responsible Banking in India. The India Banker VI (1).
- Indian Banks Association (2014) Green Banking Innovations; Indian Bank 'Association. [Cited 10/2/2015]. Available from: http://www.theindian banker.co.in/html/sto_5.htm.
- Jha N, Bhome S (2013) A Study of Green Banking Trends in India. Abhinav132 (2), 127-132. ISSN –2320- 0073.
- Karunakaran R (2014) Green Banking – An Avenue to Safe Environment. Galaxy international Inter disciplinary Research Journal 2 (2). ISSN 2347-6915.
- Millat, K. M., Chowdhury, R. &Singha, E. A. (2012). Green Banking In Bangladesh: Fostering Environmentally Sustainable Inclusive Growth Process. Dhaka, DHK: Bangladesh Bank.
- Nath V, Nayak N, GoelA (2014) Green Banking Practices – A Review. IMPACT: International Journal of Research in Business Management 2 (4), 45-62. ISSN (E): 2321-886X; ISSN (P): 2347-4572.
- Sekaran S.C. (2010) The role of Green banking in Environmental Management, Articlesbase.
- Singh H, Singh BP (2012) An Effective and Resourceful Contribution of Green Banking towards Sustainability. International Journal of Advances in Engineering Science and Technology 1(2).
