Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Neuro - Economic 'Agent' In Business Transformation
Abstract :
Conventionally, object of neuro - management theory and neuro - management cognitive psychology, business stake holder economic choice in transformation of an economy has recently become a research focus in systems neuroscience. Since ancient times scholars at many levels of reduction have studied choice in transformation of an economy-making. Over the last three decades, social and natural scientists have tried to appreciate how we make choice in transformation of an economy, using different strategies. Since the 90s, groups of inter - related scholars have begun to combine social and natural scientific approaches to study choice in transformation of an economy in an emerging discipline called 'Neurobusiness management'. Assumption is that by combining theoretical and empirical tools from neurobusiness stake holder science, cognitive psychology and neuro - management into a single approach, resulting synthesis will offer insights valuable to all three-parent disciplines. Studies seem to support that conclusion. Theories have begun to restructure neurobusiness stake holder appreciating of choice in transformation of an economy-making, and findings suggest constraints on theoretical models developed in neuro - management and psychological domains.
Keywords :
Brain Maneuvers, Cogent Efficacy, Cognitive Capacity and Business stake holder Pronouncement Skills.Introduction
'It takes three to tango': Brain, cognition and cogent and practical business stake
holder enhancement
........ Perez-Centeno, Victor
At a lower level of reduction, psychologists studying
mechanisms of pronouncement and choice in
transformation of an economy seek to appreciate
mental constructs that guide choice in transformation of
an economy making at process-based level of analysis.
Mental dynamics form algorithmic components of
psychological models of choice in transformation of an
economy. These models seek not just to predict
comportment but capture accurately mental events that
precede choice in transformation of an economy. As
such, they are complicated that neuro - management
models. Although this convolution often makes them
more realistic it does so at a cost, because these models
are hard to test completely. At a yet lower level of
reduction, neurobusiness stake holder researchers have been trying to appreciate cognitive pathways and
computations that give rise to choice in transformation
of an economy - making comportment. These scientists
have sought to appreciate, at a physical level, how it is
that the brain achieves choice in transformation of an
economy by studying computational architecture of
the brain. Of course, challenge is one of scale.
Appreciating how choice in transformation of an
economy is made simply by tracing cognitive
pathways has constrained studying simple choice in
transformation of an economy.
Pronouncement is a calculated progression that marks
commitment to an uncompromising intention. There
are two 'forces', upon balancing of which entirety
functions. They are 'positive' and 'negative' powers of
nature, or 'subjective' and 'objective' sides of
experience. There are two sides: one, which 'receives'
and another which is 'received'. Pronouncement
neuroscience offers a novel approach to study of
individual and interactive pronouncement making by combining methods of emotional experiments,
functional neuroimaging and formal models. Despite
extensive research, researchers still do not know exactly
how brain works and what it hides in its darkest
corners. What is our brain capable of? In addition, as
humanity's reliance on technology and computers
grows stronger, can progress make brains weaker?
How do cogent and practical business stake holders
make (better) business pronouncements? How can
effective cogent and practical business stake holders
change pronouncement attitudes? What determinants
act and interact to produce comportment? What are
they good at in the environments? How do they work
and how brain does implement them? How does this
implementation constrain comportment? Cancogent
and practical business stake holders separate
contributions of each for business pronouncement
making? Can players replace principled notion of 'au
fait consent'? What are the 'traps' that prevent from
making best business pronouncements? How to set
priorities, generate alternatives and evaluate
alternatives in order to choose the best? What
information is desired to help make the finest
pronouncement-making process? What are the
effective styles in business pronouncement making
framework? Finally, concern of mind - brain
relationship needs to be investigated.
In light of discussing theories and applications in
business pronouncement, it is important to decide on
techniques being used. Can we modulate comportment
affecting brain? How to resolve reservations with need
for business pronouncement? What are the constituent
dynamics underlying cogent and practical business
stake holder efficacy task performance? Are different
cogent and practical business stake holder efficacy's
uniquely linked to different brain regions? How do
changes in brain efficacy contribute to changes in
cogent and practical business stake holder efficacy?
Risk and return; are they related? What are cogent and
practical business stake holder efficacy issues? Can risk
be managed? Is it possible to identify risk-prone and
risk-averse persons? How cogent and practical business
stake holders do choose risky prospects? Do cogent and
practical business stake holders use pronouncement
aids when working with risk estimations? What
symptoms of cogent and practical business stake holder
efficacy issues find it hard to figure out how to get
started on a task? Should neuro - management be
concerned with such notions at all? Which courses of
action are under consideration in business
pronouncement set? How do rules and analogies
feature? If the two business pronouncement problems
are clearly described, how can we predict which will be more difficult. How do they affect probability as well as
just pronouncements? Do groups make business
pronouncements that are fundamentally different from
individuals? Do groups make better business
pronouncements? Which should we choose? What are
the alternatives to consequentialist models of business
pronouncement dynamics? Should these concerns be
of interest to explore? Proposition builds strongly on
prescriptive review on business pronouncement
making. Descriptive view focuses on how business
pronouncements are essentially made. Attempt
(perhaps) contributes towards providing a conceptual
review framework for appreciating intersection of
neuroscience, neuro - management and cognitive
psychology. This is to offer through review of brain
activity at time of cogent and practical business stake
holder pronouncement making, describe standard
brain - based models capable of envisaging observed
cogent and practical business stake holder
comportment. These include exploring anatomy of
neuro - discourses to functions of 'neuro - biologism'.
Ordinary life is full of choice in transformation of an
economy and choice in transformation of an economy.
An important concern for many researchers is how
people make (neuro - management) choice in
transformation of an economy. Specifically,
researchers are interested in the assumptions, beliefs,
habits, and tactics that people use to make everyday
choice in transformation of an economy. Research
suggests that brain considers various sources of
information before making a choice in transformation
of an economy. Traditional approach is to compare
pronouncement or a choice in transformation of an
economy to a standard or 'benchmark.' The comparison
enables evaluation of whether a particular
pronouncement is 'good' or 'bad' relative to the
standard. Normative models which offer standards are
important because clear sets of rules or axioms, such as
those derived from comportment economics (expected
utility theory) can be used to test predictions about
human comportment. When comportment deviates
from the predictions of normative models attempts can
be made to ascertain why and, often, techniques for
overcoming such biases. This approach with its focus
on deviations from normative models contrasts the
ideal of a homo comportment economics with the
apparent reality of a cognitive miser (or even loser) and
has been enormously influential and useful. However,
how does it do this? In addition, why does the process
sometimes go awry, causing impulsive, indecisive, and
confused choice in transformation of an economy; that
lead to perilous and potentially dangerous
comportments? Human comportment is not the product of a single process, but rather reflects
interaction of different specialized subsystems. These
systems usually interact seamlessly to determine
comportment, but at times, they compete. Result is that
brain sometimes argues with itself, as these distinct
systems come to different conclusions about what we
should do. Human comportment is not under constant
and detailed control of careful and accurate hedonic
calculations. It is product of an unstable and irrational
and practical complex of reflex actions, impulses,
instincts and habits. The bottom concern is; How to model
the pronouncement-making process?
Cogent and practical business stake holder efficacy is
cognitive capacity necessary to manage
pronouncement, sentiment and procedures. It refers to
high-level cognitive skill to manage and direct cognitive
ability and comportments. This study was designed to
help appreciate what effective cogent and practical
business stake holders really do. Study examines
person age difference in conjecture of psyche and
cogent and practical business stake holder functions to
explain variation in severity of efficacy symptoms that
account for inconsistency in comportments symptoms.
This model consists of continuum ranging from
quantity-oriented cogent and practical business stake
holder (observed to display significant activities and
performance) to quality- oriented traditional cogent
and practical business stake holder (observed to exhibit
interface with outsiders, controlling and planning
activities and perceived to have quality performance).
This descriptive model helps identify needed cogent
and practical business stake holder activities and skills
for quantity and quality performance in today's
organisations. These findings are discussed in terms of a
proposed distinction between aspects of model of mind
and related executive control skills.
Every person is acogent and practical business stake
holder. Cogent and practical business stake holder ship
is a occupied assertiveness, an approach of thinking, a
concrete everyday practice and increasingly an identity
marker for ways of being and living within liquid
modernity. Cogent and practical business stake
holdership is nowadays a broadly endorsed and
accepted signifier for forms of organising that targets
human, organisational, and economic renewal and
growth. Organisational neuro - cogent and practical
business stake holdership is an emerging field in neuro -
management and organisational cognitive psychology
that studies the role of brain in workplace
comportment. The aim is to investigate how
neurocogent and practical business stake holdership
and its methodological toolkit advance theory and
research in organisational comportment. Cogent and practical business stake holdership is unique and
stimulating humanoid endeavour. Speculation of
brain's propensity to distinguishing cerebral states;
attitude, intents, requirements, pretends
comprehension, etc. to oneself and others furthermore
to appreciate that others have beliefs, desires,
intentions and perspectives that are dissimilar from
one's own. Conjecture of brain is a surmise insofar as
the brain is not directly evident. The supposition that
others have brain is termed a conjecture as each human
can barely perceive subsistence of his/her own brain
through mediation. No one has unswerving
admittance to brain of another. It is characteristically
implicit that others have brains by parallel with one's
own .This assumption is based on shared nature of
interface, efficacies and perceptive of others sentiment
and dealings.
Choice in transformation of an economy research has
been influenced by homo comportment economics
metaphor with emphasis on normative models and
deviations from predictions of those models. In
contrast, principal metaphor of cognitive psychology
conceptualizes humans as 'information processors'.
Pollination between the two areas is important. A wide
range of models and metaphors has been proposed to
explain and describe 'choice in transformation of an
economy making in ingenious ways. This encourages
cross-fertilization between cognitive cognitive
psychology and choice in transformation of an
economy research by providing an overview of current
perspectives that continues to highlight benefits of
synergistic approach: cognitive modelling of multiattribute
choice in transformation of an economy
making. Expansion of neurobusiness stake holder
neuro - management parallels development of
cognitive science. Neurobusiness stake holder neuro -
management has bridged contrasting fields of neuro -
management and cognitive psychology. Neuro -
management, cognitive psychologyand neurobusiness
stake holder science converge into a single, unified
discipline with ultimate aim of providing single,
general theory of human comportment. This is the field
in which consilience operates. Researchers and
psychologists offer conceptual tools for appreciating
and modelling comportment. Neuro business stake
holder researchers offer tools for the study of
mechanism. The goal is to appreciate dynamics that
connect sensation and action by revealing
neurobusiness stake holder mechanisms by which
choice in transformation of an economy are made.
Humans share an organisational sphere and it is
possible for people on one side of the world to cause
huge harm to others' pronouncement dynamics on other side. Fissure amongst judiciousness - based
scrutiny that adopts utility-maximizing proxies and real
anthropological comportment has been acknowledged
in economics, cognitive psychology and other social
sciences. In recent years, there has been developing
attention in shepherding comportmental exploration
across sub - areas to address this gap. In one direction,
some control perceptions on pronouncement making.
In the other, computational tools help gain appreciating
comportment to learn about comportment models from
user - generated data. Business stake holders have
unique approach to pronouncement making, deal with
high uncertainty, ambiguity, time pressure and
emotional stress. Making cogent tactical
pronouncements is a neuro - management action.
Traditional neuro - management relies on revealed
choice in transformation of an economy to appreciate
desires of individuals and predict an action adds
observation of underlying circuits leading to
pronouncements. Neuro imaging has transitioned from
mapping confined effects to evolving extrapolative
models of perceptual events that assimilate data
scattered across brain structures. Neuron - management
is a fledgling discipline investigating role of brain for
pronouncement making in neuro - management
perspective by using neuro - tactical signatures
(hereafter, NTS) to build models that explain and
predict circuit of comportment. It aims to investigate
how brain behaves in circuit of higher cognitive
functions. Research reveals cognitive basis of
pronouncement based on NTS links to neuro -
management activity. By modeling NTS, it is possible to
provide for predilections that form representation of
choice in transformation of an economy. This opens
direction for experimental investigation in NTSneuro -
management. NTSneuro - management models rely on
pronouncement makers' utility functions satisfying well
- defined axioms. Though these account for observed
comportment, anomalies are identified in state of
uncertainty circuits. Issue is how to optimize
pronouncement making?
Having conjecture of brain allow one to element
pronouncement, requirements and intention to others,
forecast or elucidate actions and hypothesize intentions.
As initially distinct, it enables to value that
psychological state can be root of, explicate and
calculate comportment of others. Being able to feature
mental states and perceptive them as cause of
comportment implies that the brain as an author of
representation. If a cogent and practical business stake
holder does not have conjecture of brain, it may be a
symptom of cognitive or developmental mutilation.
Existing deliberations have ancestry in cogent and practical debate (Descartes' Second Meditation) that set
basis for making allowance for discipline of brain
dynamics. Familiar divergent approach in
philosophical journalism, to conjecture of brain is
conjecture-conjecture and simulation - conjecture.
Conjecture-theorist envisions absolute conjecture to
cogent and practical about others' brains. Conjecture is
developed mechanically and instinctively, though
instantiated interactions. It is intimately associated
perception that quality mind, actions, effectiveness,
properties, realization and link to corporeal body
(brain). Mind-body rapport dilemma isgenerally seen
as key concern in philosophy of mind.
Cogent and practical business stake holder efficacy
(cognitive influence and cogent and practical business
stake holder - attention organism) is umbrella term for
neuro - management (regulation, power) of cognitive
dynamics. Cogent and practical business stake holder
scheme is a theorized cognitive structure that directs
cognitive dynamics. Prefrontal areas of frontal lobe are
necessary but not solely sufficient for hauling out this
efficacy. Conventionally, cogent and practical business
stake holder efficacy has been synchronised by
prefrontal regions of frontal lobes. Nevertheless it is a
matter of unending contest. Frontal and non-frontal
regions are essential for integral efficacy. Probably,
frontal lobes need to play a part in fundamentally the
whole efficacy. Cogent and practical business stake
holder system is ideated to be profoundly drawn in
handling situations exterior domain of mechanical
dynamics that explain imitation of set comportments;
those that engross scheduling or 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement- making, those involve
inaccuracy rectification, where response are not wellrehearsed,
in principle tricky situations and that
necessitate overcoming of tough response.
Cogent and practical business stake holder efficacy
(cognitive influence and cogent and practical business
stake holder-attention organism) is umbrella term for
neuro - management (regulation, power) of cognitive
dynamics. Cogent and practical business stake holder
scheme is a theorized cognitive structure that directs
cognitive dynamics. Prefrontal areas of frontal lobe are
necessary but not solely sufficient for hauling out this
efficacy. Conventionally, cogent and practical business
stake holder efficacy has been synchronised by
prefrontal regions of frontal lobes. Nevertheless it is a
matter of unending contest. Frontal and non-frontal
regions are essential for integral efficacy. Probably,
frontal lobes need to play a part in fundamentally the
whole efficacy. Cogent and practical business stake
holder system is ideated to be profoundly drawn in
handling situations exterior domain of mechanical
dynamics that explain imitation of set comportments;
those that engross scheduling or 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement- making, those involve
inaccuracy rectification, where response are not wellrehearsed,
in principle tricky situations and that
necessitate overcoming of tough response.
Reviews of Works
Technovation (technovation + 'Managevation') is a
crucial factor for survival and competitive strength of
organizations. For manufacturing units, technovations
of the product system and of the dynamics generating
these products are essential. Majority of literature
focuses either on product technovation or on process
technovation. Referring to the convolution and
inherent dynamics of industrial technovation process
pronouncement-making in technovation neuro -
management is a challenging job. In addition to
numerous interactions with the environment,
convolution of technovation dynamics in
manufacturing units results from interactions between
product and process technovation. This paper provides
modeling dynamics of technovation dynamics
reflecting the interdependencies of the product-process technovation system. The model gives an insight into
the dynamic consequences of actions in technovation
neuro - management and allows testing different
technovation strategies. Conclusions concerning the
implementation of product and process technovations
in manufacturing units are drawn (Satpathy; 2008).
Business 'Managevation' models represent a multidimensional
phenomenon which spans across various
units, functions and dynamics of organisations (Da
Silva and Trkman, 2013; Baden-Fuller, 2010).
Concurrent research on 'Managevation' reflects this
multi-dimensional nature and investigates
'Managevation' business models from different
viewpoints in separate streams which so far fail to
converge into a common apprec iat ing of
'Managevation'(George, and Bock, 2011). While
scholars operational and practical 'Managevation' -
business models as system-level unit of analysis to
appreciate how firms create and deliver value to gain
'Managevation' competitive advantage (Teece, 2010),
studies in 'Managevation'neuro - management field
focus more on role of business models for bringing new
products, 'Managevation' and technologies to markets
(Spieth, Schneckenbergand Ricart, 2014; Zott, Amit and
Massa, 2011). At the same time, cogent and practical
business stake holders struggle to efficiently develop
and implement new business models in corporate
practice (Chesbrough, 2012). In short, topic of business
'Managevation'models is both important for research
and practice, and it offers range of avenues for further
'Managevation research which conceptualises and
integrates its key components of 'Managevation' into a
common framework.
Goal of Neurobusiness stake holder neuro -
management is to combine approaches into a discipline
that employs constraints and to inspire analysis.
Combination has been largely restricted to combining
neurobusiness stake holder science, cognitive
psychology and neuro - management to organise
biological insights into a unified conceptual framework.
Expected Utility or Neurobusiness stake holder Game
Theory define computational goal of cognitive
architecture for choice in transformation of an
economy-making. Neurobusiness stake holder insights
into algorithms by which choice in transformation of an
economy is accomplished can be expected to serve as
constraints. While nearly all neurobusiness stake holder
researchers recognise impact neuro - management
theory has had on biological studies of choice in
transformation of an economy, mainstream researchers
doubt that the second stage will (or even should) occur.
Social scientists doubt, in a general way, that reductive
program of the natural sciences can be extended to social sciences. During the past two decades, empirical
studies of business stake holderchoice in
transformation of an economy in which uncertainty,
inconsistency and incomplete information are present
have produced rich findings. Since late 90s, inter -
related scholars have combined social and natural
scientific approaches to study of choice in
transformation of an economy making into
'Neurobusiness stake holderneuro - management'. In
1998 less than 20 papers a year were published that
included 'brain' and 'choice in transformation of an
economy-making' as keywords. In 2008, nearly 200
articles bearing those keywords have been published.
Central assumption is that by combining both
theoretical and empirical tools into a single approach,
resulting synthesis offers valuable insights. Theories
have begun to restructure neurobusiness stake
holderappreciating of choice in transformation of an
economy - making and neurobusiness stake holder
biological findings are beginning to suggest
constraints on theoretical models of choice in
transformation of an economy making developed in
neuro - management and psychological domains.
Probably the first paper to combine neurobusiness
stake holder scientific data and rigorous mathematical
theory was Shizgal and Kent Conover (1996) review in
'On Cognitive Computation of Utility'. The paper
sought to describe neurobusiness stake holder
biological substrate for choice in transformation of an
economy making using normative theory. In 1999 this
was followed by Platt and Glimcher's publication of
'Cognitive correlates of choice in transformation of an
economy variables in parietal cortex' which argued
that: 'Neurobusiness stake holder researchers have
begun to focus increasingly on study of sensory-motor
processing, but many describe these dynamics remain
rooted in classic reflex' and went on to 'describe a
formal neuro - management-mathematical approach
for physiological study of sensory-motor process, or
choice in transformation of an economy-making'. This
paper was rapidly followed by papers uniting neuro -
management and psychological theories of choice in
transformation of an economy making with
measurements in human brains. Kahneman employed
psychological Prospect Theory of Choice in
transformation of an economy Making via brain
scanning experiment. The experiment revealed that
brain activation in ventral striatum matched predicted
subjective valuations. The second reflected
collaboration between McCabe and Smith. This
represented use of game theory in human
experimental data. Critical insight that these papers
offered was evidence that choice in transformation of an economy - making systems of brain can be viewed as
fundamentally two-part system. Areas in frontal cortex
and basal ganglia form first of these two parts. These
areas learn and compute values of available actions and
it is as a set of valuation structures that these areas
principally contribute to choice in transformation of an
economy-making. Outputs passed to fronto-parietal
circuits that actually 'decide' between options based on
these antecedent valuations and pass these choice in
transformation of an economy to motor system for
execution. Subsequent studies have largely supported
segregation of cognitive architecture into valuation and
choice in transformation of an economy making
systems. Levels of interconnection between these two
are being explored (Wikipedia; 2019).
Forty years ago Neisser (1967) introduced the idea that
intelligent organism operate in a perception-action
cycle: the senses take in information from the
environment, the mind / brain performs computations
on that information and the outputs of those
computations are used to channel subsequent goaldirected
actions. A key facet of this 'information
processing' metaphor is that biological organisms are
capacity limited; there is a limit on how much
information can be processed and thus the organism
needs to be selective in what it attends to in the
environment i.e., information taken in via the senses. In
general, study of choice in transformation of an
economy has been partitioned into three main
approaches. For most researchers, goal of studying
human choice in transformation of an economy
comportment is prediction. These scientists seek to
develop formal mathematical models, typically based
on rigorous axiomatic foundation, which can predict
choice in transformation of an economy humans do, or
should, make. These models typically take as inputs
state of external world and generate as outputs actual
choice in transformation of an economy made by human
choosers. For a mainstream researcher, a model is useful
if it makes accurate predictions; whether or not the
algorithm it employs mimics the actual process of choice
in transformation of an economy - making is irrelevant
to accomplishing this end. For this reason, neuro -
management studies of choice in transformation of an
economy - making can be viewed as aimed towards
achieving both; compact and abstract models of choice
in transformation of an economy possible. The yield is
high-level, and often normative, theories that state
testable neurobusiness stake holder hypotheses.
Human performance has been subject of active research
from several perspectives. Neurobusiness stake
holderneuro - management explains human choice in
transformation of an economy-making, ability to process multiple alternatives and choose an optimal
course of action. It studies how neuro - management
comportment shape appreciating of brain and guide
models of neuro - management via. Neurobusiness
stake holder science, neurobusiness stake holderneuro
- management, cognitive and organisational cognitive
psychology. As research in choice in transformation of
an economy - making comportment becomes
computational, it integrates approaches from
theoretical biology, computer scholarship and
arithmetic. Neurobusiness stake holderneuro -
management adds by using methods in comportment
and cognitive mechanisms. By using tools from various
fields, Neurobusiness stake holderneuro -
management offers an integrative way of
appreciatingchoice in transformation of an economy
making. If further proof were needed, neurobusiness
stake holderneuro - management offers evidence to
explain choice in transformation of an economymaking,
ability to process multiple alternatives and
choose optimal course of action. It studies how neuro -
managementcomportment shape appreciating of brain
and guide models of neurobusiness stake holder.
Deciphering brain - environment transactions requires
mechanistic appreciatings of neurobusiness stake
holderdynamics that implement value-dependent
choice in transformation of an economy-making. There
is a crucial difference between 'thinking about
thinking' and actually enhancing brain and mental
dynamics by developing latent potential of each
individual. Theoretical accounts posit that human
brain accomplishes this through series of cognitive
computations, in which expected future reward of
different choice in transformation of an economy
options are compared with one another and option
with highest expected value is selected. This whistlestop
tour through some of the 'facts' about the cognitive
system serves to orient our thinking about what needs
to be considered when we attempt to build and
implement cognitive models. Given that multiattribute
pronouncement is 'simply' another task
performed by the system, it is important that our
attempts to model how it is done are embedded both
theoretically and empirically in what we already know
about the operation of that system. Thus some key
facets to consider are: capacity limitation, distinction
between automatic and controlled processing and the
role that memory plays in their interaction, ability to
learn, translation of cause-effect learning to the
development of categorization, and regulation of
cognition. In the following sections we examine some
of the ways in which these facets are incorporated into
the models and metaphors proposed by the contributors to this issue. If human brain is often
compared with a computer, goals for biological brains
are determined by need for survival in uncertain and
competitive environments. How to handle brains
behind businesses in age of dramatic change and
growing uncertainty? What then are the coherent brain
dynamics underlying prediction, control and choice in
transformation of an economy-making?
Quantification of choice in transformation of an
economy has been a major area of research for
neurobusiness stake holder scientists. This is, in part,
due to the 'Matching Law' that stipulates that relative
response rate on concurrently available alternatives
'match' available relative reinforcement rates. This
theoretical construct describe response allocation in
complex situations. People often fail to design 'rational'
choice in transformation of an economy. Neuro -
management determinants are subject to multiple
biases that affect events, act upon them and learn from
experience. These comportments have disastrous
consequences. When faced with complex choice in
transformation of an economy, individuals engage in
simplifying strategies. Adaptive choice in
transformation of an economy making relies on
strategic simplifications of choice in transformation of
an economy problems. Yet, cognitive mechanisms that
shape these remain largely unknown. Although brain
encodes specific choice in transformation of an
economy factors, much less is known about how brain
selects among multiple strategies for managing
computational demands of complex choice in
transformation of an economy - making task. Advances
in brain connectivity have made it possible to identify
hubs; brain's connected regions. Such regions
coordinate brain functions due to their connectivity
with regions with variety of specializations. Current
structural and functional connectivity methods
generally agree that default mode network (DMN)
regions have highest comprehensive brain connectivity.
Control of comportment is fundamental to human
choice in transformation of an economy making.
Evidence suggests a front parietal brain network
implements such control across diverse contexts.
Lateral prefrontal cortex (LPFC) region predict
performance in high control task and exhibit high
connectivity. Critically, connectivity in this region show
highly selective relationship with individual
differences in fluid choice in transformation of an
economy making. LPFC facilitates ability to implement
control dynamics central to human choice in
transformation of an economy making. The ability to
rapidly reconfigure minds to perform tasks is important
for adapting to an ever-changing world. Further, it is unclear how this kind of task preparation changes.
Research suggests that prefrontal cortex is essential to
perform tasks (Wikipedia; 2019).
Neurobusiness stake holder choice in transformation
of an economy - making is as a mental process
(cognitive process) resulting in selection of a course of
action among alternative scenarios. Every choice in
transformation of an economy - making process
produces a final choice in transformation of an
economy. Process must be regarded as a continuous
process integrated with environment concerned with
logic of choice in transformation of an economy
making, rationality and invariant choice in
transformation of an economy making. This reflects
interaction of choice in transformation of an economy
making-related regions. Specific brain systems
potentiate choice in transformation of an economy
makings depending on strategies, traits and context.
Therefore, choice in transformation of an economy
making is a reasoning or emotional process which can
be rational or irrational, based on explicit assumptions
or tacit assumptions. This exhibits formulation of
'neurobusiness stake holder choice in transformation of an
economy making paradox'. Neuro - managementhas
always relied on careful modelling of choice in
transformation of an economy making. They are
described by utility functions that represent goals and
interact at (Nash) equilibrium. Discrepancies between
theoretical predictions and observed comportment
mismatch led researchers to developed theories of
choice in transformation of an economy - making that
are a better fit for neurobusiness stake holder data than
traditional models. Methodology consists in building
models to demonstrate relationship between cause and
neurobusiness stake holder anomaly.
Cogent and practical business stake holders both
respond to and help to create 'Managevation' novelty.
This 'Managevation' novelty may involve new art
efacts and ways of doing things, but also new ways of
being and working. What are the relationships
between cogent and practicalbusiness stake holder
comportments, identities and contexts? As
organizations continue to move into increasingly
global 'Managevation' arenas, 'Managevation'
competitiveness reaches new levels with continuous
needs to change and improve quality and efficiency
while controlling costs. Oftentimes, technology is seen
as a solution to realizing competitive advantage. This
'Managevation' approach is predicated on ability to
integrate weakest, least reliable and most
unpredictable component into the system; human.
Anthropoid resources neuro - management can
contribute to realizing an enterprise's 'Managevation' strategy. The ability to harmonize humans into
socio-technological 'Managevation' systems is the lynch
pin to drive global 'Managevation' competitiveness.
From another perspective, Granovetter (1992) viewed
'Managevation' activity as embedded in 'Managevation'
contexts and markets as institutions resulting from
socially situated individuals embedded in networks of
personal relations, often with a mix of non-economic
and 'Managevat ion' economi c goal s . Thi s
interconnectedness between 'Managevation' cogent
and practical business stake holder, activities and
'Managevation' context means that cogent and practical
business stake holdership can be understood as a
'Managevation' process, not simply as an isolated
individual 'Managevation' activity (Gartner, 1985;
Bygrave, 1989; Bygrave and Hofer, 1991). Following
from this, we can also say that 'Managevation' cogent
and practical business stake holder identity is shaped by
ongoing structures of 'Managevation' relations as part
of certain 'Managevation' contexts ('Managevation'
contexts) e.g. Gartner (1985); Aldrich and Zimmer
(1986); Carsrud and Johnson (1989); and Anderson
(2000).
In 2003, Glimcher reviewed history of neurobusiness
stake holder science and argued that history was
striking in its lack of normative models for higher
cognitive function. Glimcher proposed that neuro -
management could serve as source for normative
theory. Camerer, Loewenstein and Prelec published on
how neurobusiness stake holder science can inform
neuro - management (2005) which served as a manifesto
from the neuro - management side. Camerer argued
that failure of traditional neuro - management to make
accurate predictions reflected inattention to
me chani sm. Appr e c i a t ing how choi c e in
transformation of an economy is made yield
algorithmic alternatives to neoclassical theory with
enhanced predictive power. Faruk Gul and Pesendorfer
published in 2008 'The Case for Mindless Neuro -
management'. They suggested that neurobusiness stake
holder biological measurements, per se, lay entirely
outside province of neuro - management. Second, they
argued that while reductionist approaches that seek to
link mechanistic insights to larger theoretical
frameworks have been successful in natural sciences,
these same reductionist approaches are unlikely to be
able to relate natural scientific phenomena to social
scientific theory. In essence, they argued that insights
into biological mechanism are unlikely to have much
impact on neuro - management theory.
One potential area where comportment economics can
contribute is in appreciating the dynamic dynamics by which the brain coordinates its diverse systems to
perform new, complex tasks. This problem has
received remarkably little attention in neuroscience
research, although it is well-explored terrain in
comportment economics. Sanfey (2006) reviewed two
general ways in which neuroeconomic attempt make
important contributions to research on choice in
transformation of an economy-making. First,
incorporation into neuroscience and cognitive
psychology of formal, rigorous economic modeling
approach, and second, awareness within the economic
community of evidence for multiple systems involved
inchoice in transformation of an economy-making.
Current challenge is to ensure that researchers are
communicating productively; often, terms such as
'choice in transformation of an economy',
'pronouncement' and 'choice in transformation of an
economy' are used in different ways by different fields.
Due to the breakthrough of the cognitive network
technology, there has been an increasing amount of
cognitive network application research. Classification
of publications reveals that a large amount of research
has been published in the last five years. Researches by
Raju S. Bapi, V. S. Chandrasekhar Pammi, K. P.
Miyapuram cent re around Cognit ive and
Computational Neuroscience perspective. Studies by
Satpathy (20011-2014) centre around Issues in Neuro -
Neuro - managementChoice in transformation of an
economy Making, Inquiry into Neuro- Economic
Choice in transformation of an economy Modeling,
Neuro - Choice in transformation of an economy
Computational Modeling, Neuro Based Challenges,
Neuro - management Perspective, Neuro -
Perspectives in Sustainable Progression, Cognitive
'Paths' in Techno - Business stake holder Continuum,
Explorations in Neuro - Choice in transformation of an
economy Making, Paradigm Tectonics in Neuro -
Choice in transformation of an economy Making,
Reflections On Neuropsychological - Choice in
transformation of an economy Making, Anthology on
Business stake holder Neuro - Choice in transformation
of an economy VUCA Architecture, Business stake
holder Neuro - Choice in transformation of an economy
Mechanism, Theoretical Challenges In Neuro - Choice
in transformation of an economy Making and
Paradoxical Issues in Neuroneuro - management of
Choice in transformation of an economy- Making.
Key Concerns
Neurocogent and practicalbusiness stake holdership
incorporates the interior characteristics of the cogent
and practical business stake holders to study cognitive
basis of 'Managevation'. Neurocogent and practical
business stake holdership provides deeper appreciating of how they make their own
'Managevation' oriented pronouncements, and how
others decide. Are we hard-wired to be risk-averse or
risk- seeking? How is a 'fair 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement' evaluated by the brain? Is it possible
today to predict the purchasing intentions? Can we
modulate economic comportment affecting the brain?
Effective neuro - management is a result of persistent
efforts in multiple dimensions be it the formulation of
strategies or the smooth functioning of day-to-day
activities. The convolution in neuro - management
partially arises due to how organisations juggle
between the efforts that focus on long-term objectives
and handling daily nitty-gritty. In order to ensure
effective functioning of organisations, it becomes
extremely important for organisations to invest time
and effort in developing cogent and practical business
stake holder competencies. A structured effort in this
direction would not only lead to formulating successful
organisational strategies but would also ensure proper
execution of day to day operations (ASCI; Hyderabad).
Risk neuro - management and 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement theory is a hopeful matrimony linking
two completely significant characters of mind-boggling
heredity. 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement
presumption is conjecture about 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncements. The subject is not
amalgamated one. To the converse, there are many
diverse ways to conceive about 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncements with dissimilar traditions.
To theorize about 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncements is approximately the same as to
theorize about human activities. How to resolve
reservations with need for 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement, recalling that 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement not to act in anticipation of more
information is still a 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement? Risk psychoanalysis and numerical
'Managevation' oriented pronouncement supposition
can make available various strategies. Capability
bearings are inevitable part of individual activities with
daily life being a sequence of capability bearings.
Distinctively, researchers are interested in conventions,
beliefs, conducts and strategies to make capability
bearings. Any iteration of capability as an
anthropological endeavour would need explanation of
substrates, mechanisms and variable effects of
emotional influence upon cogent and practical
functions operative in capability bearing-making
dynamics relevant and relative to ecological resources.
Cognition considers sources of data before capability
bearing. Nonetheless, how does it do this? Why does process sometimes go awry, causing impulsive,
indecisive and confused capability bearings that lead
to potentially dangerous comportments? Competence
convolution - oriented neuro - cogent and practical
business stake holder capability bearing making offers
tools for modeling comportment. With different
disciplines approaching through characteristically
different techniques and substantial advances, concern
of how we design and how we have to craft
pronouncements/capability bearings has engaged for
decades. This chapter analyses cognitive bases of
capability bearing predictability and value,
parameters in Capability of expected utility.
Competence - multiple - systems approach to
capability bearing - making, in turn, influences
Capability, a perspective strongly rooted in
organisational cognitive psychology and competence
cogent and practical business stake holdership.
Integration of these offers exciting potential for
construction of near - accurate models of capability
bearing - making.
Some key research issues in this context are; what are
the constituent dynamics underlying cogent and
practical business stake holder efficacy task
performance? Are different cogent and practical
business stake holder efficacy's uniquely linked to
different brain regions? How do changes in brain
efficacy contribute to changes in cogent and practical
business stake holder efficacy? Risk and return - are
they related? What are cogent and practical business
stake holder efficacy issues? Can risk be managed? Is it
possible to identify risk-prone and risk-averse
persons? What diagnosed? What How cogent and
practical business stake holders do chose risky
prospects? Do cogent and practical business stake
holders use any computer-based 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement aids when working with risk
estimations and/or 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement problems? What symptoms of cogent
and practical business stake holder Efficacy Issues
Finds it hard to figure out how to get started on a task.
Can focus on small details or the overall scenario, but
not both at the same time? Has trouble figuring out
how much time task requires. Does things either
quickly and messily or slowly and incompletely. Finds
it hard to incorporate feedback into work or an activity.
Sticks with a plan, even when it's clear that the plan
isn't working. Has trouble paying attention and is
easily distracted. Loses a train of thought when
interrupted. Needs to be told the directions many
times. Has trouble making 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncements? Has a tough time switching gears
from one activity to another. Doesn't always have the words to explain something in detail. Needs help
processing what something feels/sounds/looks like.
Isn't able to think about or do more than one thing at a
time.
Neuro - Perception
New brain imaging technologies have motivated neurocogent
and practicalbusiness stake holder studies of the
internal order of the mind and its links with the spectrum of
human 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements from
'Managevation' oriented pronouncement making among
fixed gambles to 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement
making mediated by market and other institutional rules. We
are only at the beginning of the enterprise, but its promise
suggests a fundamental change in how we think, observe and
model 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement in all its
contexts.
............ (Smith; 2002).
Capability bearings are inevitable part of cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder activities. Making cogent
strategic choice in transformation of an economy is a
cogent and practicalbusiness stake holder action.
Cogent and practicalbusiness stake holder plays
substantial role in gainful advance with initiative, skill
and motivation to express and execute. Any iteration of
capability, as an anthropological endeavour, would
need some explanation of substrates, mechanisms and
variable effects. Exploration on cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder neuro - oriented
pronouncement has extended from neuro - oriented
comportment to cogent and practical approach with
focus on dynamics that ensue prior to response. Any
prototype, in convolution continuum, accounts for
verdicts that aid neuro - oriented 'deciding to decide',
'choosing to choose', 'deciding to choose' and 'choosing
to decide'. These are 'bordered boundaries' wherein
cogent and practicalbusiness stake holder has to arrive
at optimal pronouncement. Cogentand
practicalbusiness stake holders make pronouncements
that involve optimising trade - offs to weigh merits and
demerits of all alternatives. There are unresolved
problems in state of convolution. Issue is how to
optimize pronouncement-making in convolution
arena? In this chapter, cogent and practical neurocogent
and practicalbusiness stake holdership techniques have
been incorporated to explain cognitive basis of cogent
strategic choice in transformation of an economy -
making and examine dynamics in cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder's brain. Chapter
emphasises on neuro - ophthalmic' perspectives to
appreciate how eye movements articulate choice in
transformation of an economy making regardless of
vicissitudes.
How cogent and practicalbusiness stake holder
'Managevation' is oriented pronouncement making
dynamics carried out in brain? Do we interpret
resear ch f indings when neurocogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder logical results conflict?
Knowing how brain is working explains little about
what mind produces; what we think, what we believe
and how we craft 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncements. What are the general implications of
neurocogent and practicalbusiness stake holderneuro -
management? Neurocogent and practicalbusiness
stake holder techniques permit to look inside brain
while it experiences outcomes and crafts
'Managevation' oriented pronouncements to examine
implications. Central argument is that 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement - making is at core of cogent
and practicalbusiness stake holder functions and
future of any organisation lies on vital 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncements made. 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement usually involves three steps:
recognition of a need, dissatisfaction within oneself
(void or ne ed) , 'Manageva t ion' or i ent ed
pronouncement to change (fill void or need) and
conscious dedication to implement the 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement. However, certain critical
issues coupled with factors such as uncertainties,
multiple objectives, interactive convolution and
anxiety make 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement
making process difficult. At times when making an
'Managevation' oriented pronouncement is complex or
interests are at stake, and then need for strategic
'Managevation' oriented pronouncement - making
arises. Neuro - management is influenced by multiplesystems
approach to 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement-making, a perspective strongly rooted
in cognitive psychology and neurocogent and
prac t i calbus ines s s take holder cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holdership. The integration of
these disparate methodologies offers exciting potential
for construction of models of 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement-making (Satpathy: 2012).
Concerns that need to be answered (Satpathy: 2012)
include; how to choose in tough situations where stakes
are high and there are multiple conflicting objectives?
How should Cogent and practicalbusiness stake
holders' plan? How can we deal with risks and
uncertainties involved in an 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement? How can we create options that are
better than the ones originally available? How can we
become better 'Managevation 'oriented
pronouncement makers? What resources will be
invested in 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement -
making? What are the potential responses to a particular problem or opportunity? Who will make this
'Managevation' oriented pronouncement? Every
prospective action has strengths and weaknesses; how
should they be evaluated? How will they decide?
Which of the things that could happen would happen?
'Managevation'- Oriented Pronouncement
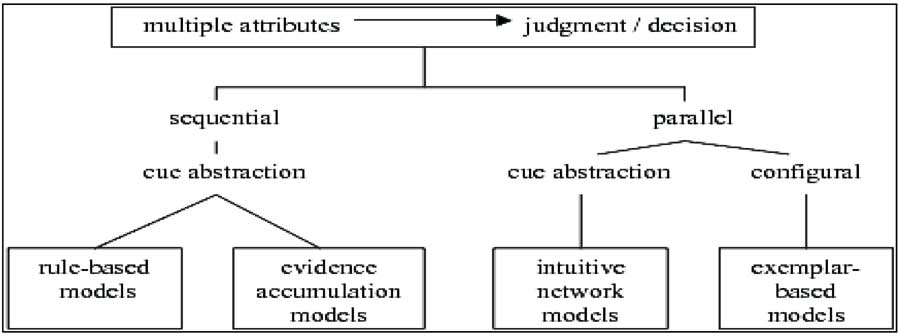
Relational Model
Choice in transformation of an economy making is one
of the simplest act of human comportment mainly
because in a days' time a person takes minimum a
hundred choice in transformation of an economy big
and small; Impactful choice in transformation of an
economy those have influence on a large number of
situations, time, people and resources need a
thoughtful mind, capacity to appreciate the dynamics
between seemingly unrelated variables and a high level
of intellect and of course positive intentions. However,
most of the day to day choice in transformation of an
economy are routine, short term and in general are not
considered choice in transformation of an economy at
all. Cogent and practicalbusiness stake holderchoice in
transformation of an economy specifically strategic
choice in transformation of an economy need systems
thinking approach, a macro perspective, a kind of
philosophical/spiritual detachment and a higher level
thinking pattern where choice in transformation of an
economy have a higher order purpose and is beyond
the personal/ professional needs of individuals. It
happens at the neuro level which means quite to a large
extent it is beyond the control of individual
manipulative comportment. Thus, high level choice in
transformation of an economy are expected from
individuals those have professional personal maturity,
integrity and the competence needed to see things
beyond their life time. What we refer to as 'big scenario'.
A high level choice in transformation of an economy
making capability thus requires the capacity to process
a fairly large amount of data, memory, learning, discarding/eliminating unwanted data and
appropriate use of useful data available while very well
knowing that a part of data is still not available with
choice in transformation of an economy makers. Thus
the need to use gut feelings, emotions, intentions,
become necessary to validate our thoughts and plan of
action leading to concrete choice in transformation of
an economy and confidence in those choice in
transformation of an economy as well. Various
parameters; tangible and intangible aspects have to be
cognitively processed in order to arrive at robust a
choice in transformation of an economy which affects
large number of stakeholders.
How do cogent and practicalbusiness stake holders
make choice in transformation of an economy? The
dominant paradigm in empirical and theory work in
cogent and practicalbusiness stake holdership is to
assume that cogent and practicalbusiness stake
holderchoice in transformation of an economy are
made by fully cogent and practical 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement-makers. These models often
assume cogent and practicalbusiness stake holders
seek to maximize the present value of current and
future earnings, solve a dynamic optimization
problem, and play a Bayesian Nash Equilibrium. An
increasing amount of research, however, has
documented that these (and other) standard
assumptions are often violated. In their place, several
formal models of alternative assumptions have been
developed and tested (SSRN abstract; 2011559).
'Managevation' oriented pronouncement-making is
regarded as the cognitive scheme resulting in selection of belief or course of action in the middle of a number of
substitutepotential. Every 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement-making process produces a final choice
in transformation of an economy that may or may not
promptaction. 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement-making is the study of identifying and
choosing alternatives based on the values and choice in
transformation of an economy of the 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement maker. 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement-making is one of the central
activities of neuro - management and is a huge part of
any process of implementation.
Organisations of today are in great need of improving
their skills when it comes to 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement making, and especially the designing
of 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements. By the
designing of 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements
is meant the preparatory stages of 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncement making (Nutt; 1984). It is
argued that the design of 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncements is a process that in many ways is
shaped by factors such as identities, values, and
influences. The task of the 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncement maker tends to be reduced to a choice in
transformation of an economy between ready-made
alternatives. To be able to appreciate how these factors
impact organisational 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncements, the focus must be set on the neuro -
management level. It is the neuro - management that
shoulders the chief responsibility for designing
collective actions, such as 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncements. Our propositions indicate that the
following measures must be taken in order to improve
the quality of organisational 'Managevation' oriented
pronouncements (Selart; 2014):
- Uniqueness of individuals occupied in 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement making, affect svalue of 'Managevation' orient ed pronouncements and should be taken into explanation in plan of 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements.
- Managevation' oriented pronouncement maker or designer of 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements is supposed tofit into place members to craft a collective mental scenario.
- Getting members to articulate and carve upgeneral values should perk up 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement making process.
- Managevation' oriented pronouncement-making can also be regarded as a problem-solving activity terminated by a solution deemed to be satisfactory. It is, therefore, a reasoning or emotional process which can be cogent and practical or irrational and practical and can be based on explicit assumptions or tacit assumptions. Cogent and practicalchoice in transformation of an economy theory encompasses the notion that people try to maximize benefits while minimizing costs.
- Human performance with regard to 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements has been the subject of active research from several perspectives:
- Psychological : exploratory individual 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements in framework of a set of needs, choice in transformation of an economy and values the individual has or seeks.
- Cognitive: 'Managevation 'oriented pronouncement-making process regarded as a continuous process integrated in communication with the environment.
- Normative : the analysis of individual 'Managevation' oriented pronouncements concerned with the logic of 'Managevation' oriented pronouncement-making and judiciousness and the invariant choice in transformation of an economy it leads to.
Convolution-Orientation: Cogentand
practicalbusiness stake holders mark convolutionoriented
capability bearing in complex situations. This
marker has alternatives and must choose best
alternative (optimised combination). When made,
events may have occurred (maker has no control). Each
(combination) of alternatives result in some
quantifiable significance. Diverse choice in
transformation of an economy orderings and
capability bearings possibly surface depending on
which cognition paths are activated. This conceivably
contradicts convolution- oriented neuro - cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder postulate that one
complete choice in transformation of an economy
ordering provides sufficient data to predict capability
bearing and comportment.
Consistency properties are internal to convolution
bearing that describes comportment. There are four
requirements for cogent and practical component of
convolution bearing. It must be capable of filling need
for personal level explanation of causes of bearing.
Second, it must provide intentional explanation. Third,
it should be capable of linking convolution - oriented
cogent and practicalbusiness stake holdercapability.
And, finally, it must relate philosophically to broader
disciplinary concerns including competence
physiology and operons. Samuelson's 'revealed choice
in transformation of an economy formulation' is scientifically more respectable to explain
comportment. Sen (2002) identifies 'internal
consistency' approach and 'self-interest pursuit'
approach by finding regularities in observed
comportment that assess consistency. In order to
predict convolution bearings, cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holders are consistent by
checking whether determinants' do or do not violate
certain axioms of revealed choice in transformation of
an economy. Added approach is 'self-interest pursuit'
approach, represented by complete choice in
transformation of an economy ordering in coherent
matrix. 'Cogent and practical' comportment provides
basis for application of utility theory in coherent
analysis that represents chooser's choice in
transformation of an economy and explains how choice
in transformation of an economy determine
convolution bearings. Convolution bearing, based on
'menu-dependence', may modify attitude towards
changing choice in transformation of an economy
ordering.
How is business stake holderchoice in transformation
of an economy making dynamics carried out in brain?
Do we interpret research findings when neurobusiness
stake holder logical results conflict? Knowing how
brain is working explains little about what mind
produces; what we think, what we believe and how we
craft choice in transformation of an economy. What are
the general implications of neurobusiness stake
holderneuro - management? The concern of explicit
intervention raises the perennial favourite issue in
cognitive science; what about the homunculus? Who or
what structure decides how to decide? Can we describe
meta-rules or criteria which select or determine the
actual information processing (strategy or evidence
threshold or similarity functions) that is used in a
specific choice in transformation of an economy
situation? Unfortunately, cognitive models tend to
become less specific and process descriptions become
more anthropomorphic when higher order process like
these are concerned. Some issues that surge out of the
above are;
- What are the biological underpinnings of above interactions?
- What biological models capture capability bearing making?
- What computational mechanisms allow the dynamics of mechanisms? Focal point is to appreciate;
- Cognitive dynamics underlying how cogent and practical business stake holders craft capability bearings;
- Appreciate mechanisms of competence imaging methodologies, and
- Integrating inter - related chapter towards capability bearing cogent and practical business stake holdership.
Concerns that need to be answered include; how to choose in tough situations where stakes are high and there are multiple conflicting objectives? How should Business stake holders' plan? How can we deal with risks and uncertainties involved in a choice in transformation of an economy? How can we create options that are better than the ones originally available? How can we become better choice in transformation of an economy makers? What resources will be invested in choice in transformation of an economy - making? What are the potential responses to a particular problem or opportunity? Who will make this choice in transformation of an economy? Every prospective action has strengths and weaknesses; how should they be evaluated? How will they decide? Which of the things that could happen would happen? The choice in transformation of an economy has been made. How can we ensure it will be carried out? These are the concerns neurobusiness stake holder researchers suspect are most crucial for appreciating complex human comportments.
Problem Analysis
- Analyze performance, what should the results be against what they actually are.
- Problems are merely deviations from performance standards.
- Problem must be precisely identified and described.
- Problems are caused by a change from a distinctive feature.
- Something can always be used to distinguish between what has and hasn't been affected by a cause.
- Causes to problems can be deducted from relevant changes found in analyzing the problem.
- Most likely cause to a problem is the one that exactly explains all the facts.
'Managevation' Oriented Pronouncement
Future Roadway
Contributions
The study of choice in transformation of an economy
making and problem solving has attracted attention.
Expanded research requires (model - based empirical)
study of behavior and offer setting for basic research on
how ill-structured problems are, and can be, solved.
Business stake holderneurochoice in transformation of
an economy making, which is much less well
understood than individual choice in transformation
of an economy - making and problem solving, can be
studied with great profit using already established
methods of inquiry, especially through intensive
studies.
Anticipated Gawp: Previous research has
demonstrated that pronouncements of intent were
significantly related to attitudinal, normative, and
affective components of choice in transformation of an
economy-making. The research failed to demonstrate
distinctiveness of the components by obtaining
convergent and discriminant validity measures. This
limitation needs to be addressed. Purpose of this
research is to elucidate principles and choice in
transformation of an economy - making mechanism in
brain. In organisational sciences, study of choice in
transformation of an economy - making is an important
preliminary step to offer foundation for analysis of
equilibrium. Neuro business stake holder analysis has
been a fruitful development in this direction. Principal
aim is to model neurobusiness stake holderchoice in
transformation of an economy making by using tools from Neuro - neuro - management and cognitive
neuroscience. This proposal aims at, first, incorporate
neuro business stake holder science and cognitive
psychology of neuro - management modelling
approach, and second, awareness of evidences for
multiple systems involved in choice in transformation
of an economy-making.
Through computational approaches, attempt will be to
clarify how cognitive circuits realize 'mental
simulation' in business stake holder choice in
transformation of an economy-making. This plan
ventures to offer a model about relationship between
rationality, emotions and underlying neuro business
stake holder underpinnings involved in choice in
transformation of an economy - making. By
characterizing effect of these influences, this study
expects to gain insight into how brain computes models
for choice in transformation of an economy making.
This work would attempt to explore
phenomena through individual action, choice in
transformation of an economy-making, and reasoning
dynamics on concept of cognitive models of choice in
transformation of an economy - making. Principal aim
of proposed study is to model neurobusiness stake
holder basis of choice in transformation of an economy
making by using tools from Neuro - neuro -
management and cognitive science. Purpose is to
elucidate principles and choice in transformation of an
economy - making mechanism in brain interaction
between variables of neurobusiness stake holder -
neuro - management choice in transformation of an
economy dynamics. Focal pointis to
appreciate cognitive dynamics underlying how
Business stake holders craft choice in transformation of
an economy and choice in transformation of an
economy, appreciate mechanisms of choice in
transformation of an economy - making and integrating
inter - related research towards contributing to
neurobusiness stake holder choice in transformation of
an economy.
Neurobusiness stake holderneuro - management offers
solution through series of measurements of brain
activity at the time of choice in transformation of an
economy. It offers conceptual and philosophical
framework for appreciating and conducting research at
intersection of neurobusiness stake holder science,
neuro - management and cognitive psychology.
Neurobusiness stake holderneuro - management theory
proposes to build brain-based models capable of
predicting observed comportment. Neurobusiness
stake holderneuro - management will shed light on
causes of comportment (and neurobusiness stake
holder anomalies) and help build theories capable of explaining and predicting choice in transformation of
an economy. Measurement of brain activity offers
information about underlying mechanisms brain
during choice in transformation of an
economydynamics. Neurobusiness stake holderchoice
in transformation of an economy modeling would help
when new information is inconsistent with goals.
Combining the above disciplines gives inter - related
insight to define fundamentals of neurobusiness stake
holderchoice in transformation of an economy making
that has eluded researchers.
Conclusion
Until now, research has not systematically integrated
influence of sub - systems of brain in choice in
transformation of an economy-making. Evidence
suggests that choice in transformation of an economy -
making depends on methodical methods to analyse
relevant brain dynamics. Due to its multidisciplinary
nature, this investigation is subject to several kinds of
misconceptions. Is the Neurobusiness stake
holderneuro - management study of choice in
transformation of an economy - making dynamics
relevant for neuro - management? The debate argues
that the concern is of scientific interest and tools from
neuro - management theory are well adapted to
address it.
While there are several benefits of using neurobusiness
stake holder techniques in appreciatingchoice in
transformation of an economy making, there are
concerns that neurobusiness stake holder science
cannot answer by itself and needs help of experimental
methodology and theories to appreciate how Business
stake holders decide. The key limitation is identifying
different regions of brain in certain situations (VUCA).
These techniques are not able to offer an explanation or
a reason (neurobusiness stake holder) as to why we
respond in the manner that we do. What happens in
brain or what is activated when Business stake holders
make choice in transformation of an economy or are in
process of making choice in transformation of an
economy or responding to outcomes? It does not give
insight into why we make choice in transformation of
an economy and why we respond in the manner that
we do. This is where experimental methodology
would help bolster appreciating. A synergy between
neurobusiness stake holder techniques and
experiments offer insight into appreciating Business
stake holderchoice in transformation of an economy
making.
Goal of s tudying human pronouncement
comportment is prediction. This research seeks to
develop theoretical models, based on axiomatic
foundation, which can predict business stake holder pronouncements. These models would take as inputs
state of external world and generate as outputs actual
pronouncements made by human choosers. For this
reason, research would aim towards achieving
compact and abstract models of pronouncement. To
date, neuro - management model of pronouncement
has not been informed by the way brain functions.
Analysis of observations would include not only choice
in transformation of an economy between options, per
se, but additional data, including length of time taken to
make pronouncements, number of error in
pronouncements and psychophysical model(s).
Including more than just observed pronouncements
allows data to have an additional disciplining effect on
theory. We extend this assumption of optimal
comportment to analysis of brain process producing a
pronouncement. To do this, we assume that there is an
unobservable pronouncement that an determinant
makes, consequences of which are reflected in all
observable data that can be measured in the
pronouncement process. That pronouncement is
strength of effort devoted to processing information in
reaching a pronouncement between options. As a
conclusion, we propose a model that joins predictions
of traditional psychological observations and
predictions of relative brain activation dependent on
exogenous characteristics of pronouncement
environment.
Even as it is recognised that brain (and consequent
comportment) does not operate perfectly optimally,
there are several reasons why these assumptions can
nevertheless be valuable. First, although complex
forms of comportment might not be optimal, simpler
evolutionarily conserved mechanisms might prove to
be closer to optimal, or at least to have been so in the
environment in which they evolved. Second, an
assumption of optimality can be a crucial step in
development of formal model. Formal model, in turn,
enables generation of precise, testable predictions
about Business stake holder comportment. Finally,
even when comportment (or cognitive function) turns
suboptimal, defining optimal performance can provide
a useful benchmark against which to compare actual
comportment. Identifying ways in which comportment
systematically deviates from optimality can generate
new insights into underlying mechanisms.
Neurobusiness stake holderneuro - management
model will play a crucial role in building of new reliable
theories capable of explaining and predicting
individual comportment and strategic
pronouncements. Main message is that individual is
not one coherent body. Brain is a multi-system entity
and therefore pronouncement-maker must be modelled as an organisation. Before the modern model,
organisations were modelled as individual players
characterised by an input-output production function.
Systematic study of interactions between determinants
and pronouncementdynamics within organisations
lead to novel insights. Applying similar methodology
to study business stake holder pronouncement -
making is the way to appreciate bounds of rationality.
Applying comports - mental biases to cogent and
practical business stake holders are an important and
growing area of study. It is recommended there are
several particularly promising areas for future work,
which we summarize below: Theory and lab research
on the impact of fairness on a broader range of cogent
and practicalbusiness stake holder 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncements, including welfare analysis.
Theory and lab research on choice in transformation of
an economy, particularly in coordination games.
Research on the effect of choice in transformation of an
economy on cogent and practicalbusiness stake holder
comportment using data from the field in order to
appreciate the broader applicability of the laboratorygenerated
results. Research on how alternative utility
functions, aside from choice in transformation of an
economy, might affect cogent and practicalbusiness
stake holder comportment. Examples include selfcontrol,
context effects, inattention, and reference
dependence. Research that applies the computational
and equilibrium selection advantages of alternative
solution concepts such as cognitive hierarchy to help
solve coordination games, in theory and in structural
empirical work. Field work that examines the
circumstances under which we observe bounded
judiciousness by cogentbusiness stake holders in
games, including disclosure games, entry games,
technology adoption games, and others. Theory and
lab work on the biological basis of economic
comportment, which can in turn help discipline
existing theory and inspire new models. Field work on
the role of overconfidence in cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder 'Managevation'
oriented pronouncements and firm performance.
Theory and (especially) field work on the consequences
of mixing cogent and practical and non-cogent and
practical firms. While there has been substantial
progress recently, there is much more work to be done
to appreciate when and how comport - mental biases
apply to cogent and practicalbusiness stake holder
'Managevation' oriented pronouncement-making
(SSRN Abstract; 2011559). In a sense cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holdership researchers can
look at organisational neuroscience from cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder mindset to view it as a research opportunity to exploit. Just as second entrants
can benefit from lessons learned, cogent and
practicalbusiness stake holder scholars should be
aware of what scholars have already done in leadership
and other areas to build on their body of knowledge.
The interest in connecting cogent and practicalbusiness
stake holdership with neuroscience exists, but hefty
challenges remain.
In short, the research on cognitive style in cognitive
psychology suggests that some styles might operate at
a superordinate metacognitive level, and such
metastyles will determine the flexibility with which an
individual chooses the most appropriate subordinate
style for a particular situation. More generally, the
research suggests that it is useful to organise styles
hierarchically. Such an organisation consists of
dimensions that relate to lower order cognitive
processing, to higher order complex cognitive skills,
and to metacognitive functioning. Moreover, cognitive
style can be represented in a matrix form, with its
vertical dimension representing different levels of
information processing and horizontal dimension
representing different cognitive style families.
References
- Satpathy, J. and Banerji, J. S. (2019). Neuro - Monikers in Entrepreneurial Behaviour, Poster Paper, Society for Judgment and Decision Making (SJDM) Conference, 15-18 November 2019, Montreal, Canada(International). Forthcoming
- Satpathy, J. and Banerji, J. S. (2019). Oculo - Tactical Monikers in Managerial Decision, Proceedings of Global Management Research and Education: Challenges & Opportunities (GOMRECA 2019) Conference, 09 - 10 Aug 2019, Dept. of Management, International School of Management (ISM),Patna, Bihar, India(National).
- Wadhwa, C., Satpathy, J. and Banerji, J. S. (2019). Empirical Approximations In Work - Life Balance, Proceedings of Global Management Research and Education: Challenges & Opportunities (GOMRECA 2019) Conference, 09 - 10 Aug 2019, Dept. of Management, International School of Management (ISM),Patna, Bihar, India(National).
- Satpathy, J., Malhotra, S., Hejmadi, A., Pradhan, S., Sahoo, K. and Wadhwa, C. (2019). Endoscopic View of Neuro - Preference Connectionism, European Journal of Business and Social Sciences, ISSN: 2235- 767X, Volume 07 Issue 06, June, Pp: 182 - 202, Zurich, Switzerland (International).
- Satpathy, J., Hejmadi, A. and Mishra, I. (2019). Clinical Observation On Neuro - Decision Capability, European Journal of Business and Social Sciences, ISSN: 2235-767X, Volume 07 Issue 05, May, Pp: 1091 - 1109, Zurich, Switzerland (International).
- Satpathy, J., Pati, P., Hejmadi, A., Gankar, S. and Malhotra, S. (2019). Visual Monikers in Entrepreneurial Choices, European Journal of Business and Social Sciences, ISSN: 2235-767X, Volume 07 Issue 05, May, Pp: 374 - 380, Zurich, Switzerland (International).
- Satpathy, J. and Hejmadi, A. (2019). Neurophysiological Drivers of Chaos in Entrepreneurial Decision (Poster), Neuro Psycho Economics Conference, Code: P - 05, Neuro Psycho Economics Conference, 06 - 07 June, LUISS University, Rome, Italy (International).
- Mishra, B.P. and Satpathy, J. (2019). Managerial Decision Making, Journal of Personnel Focus, ISSN: 2229 - 6506, Vol. 14, Issue (3), July, Pp: 01 - 07, Bhubaneswar, India (National).
- Satpathy, J. and Hejmadi, A. (2019). Managerial Decision Uncertainties In VUCA Spectrum, Proceedings of National Seminar on Issues and Challenges in VUCA World, 23 Mar 2019, ICBM - School of Business Excellence, Hyderabad, Telengana, India (Adjudged as Outstanding Research Paper) (National).
- Satpathy, J. and Hejmadi, A. (2019). Neuro - Optometric Decision Estimates in Managing Creative Organisation, Proceedings of National Seminar on Managing Resource through Creativity for Generating Opportunities in 21st Century, Pp: 30 - 55, ISBN Number: 978 - 81 - 922746 - 9 - 0, S B Patil Institute of Management, Pune University, 18 -19 Jan 2019, Pune, India (National). Reprinted under the title NEURO - OCULAR DECISION GUESTIMATES in Odisha Journal of Social Science, Vol 6. (1), January Edition, Pp: 103 - 115, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India. (National).
- Satpathy, J. and Hejmadi, A. (2019). Electrodermal Traces in Decision Making, Proceedings of National Seminar on Technology, Innovation, Policy Initiatives and Entrepreneurship Development (NSTIPED - 2019), 30th - 31st Jan 2019, Parala Maharaja Engineering College, BPUT University, Berhampur, Odisha, India (National).
- Satpathy, J., Hejmadi, A. and Padmaja, B. (2019), Cardio - Peep Into Organisational Decision Foundation, Proceedings of National Seminar on 'Human Dimension In Information Age', 21 - 22 Feb 2019, Acharya Nagarjuna University, Ongole, Andhra Pradesh, India(National).
- Satpathy, J. (2019). Neuro - Optometric Decision Estimates in Managing Creative Organization (Poster), 4th Coller Conference on Behavioral Economics (CCBE), 19 - 20 June 2019, Center for Behavior Change, Tel Aviv University, Israel (International).
- Satpathy, J. and Gohain, A. (2018). Socio - Genetic Matrices in Decision Diminuendos (Case Study in North - East India), Proceedings of UGC - Sponsored National Seminar on Development of Marginalized Sections in North East India: Its Problems and Prospects, Department of Sociology, 10 - 11 Jan 2018, Khowang College, Dibrugarh, India(National).
- Karmakar, S. and Satpathy, J. (2018).Human Capital: Neuro - Based Analysis of Three Indian States, Proceedings of Golden Jubilee Conference (OEA Journal), 50th Annual Conference, Orissa Economics Association, 10 Feb 2018, Nabakrushna Choudhury Centre for Development Studies, Bhubaneswar, India (National).
- Satpathy, J. and Shukla, O.P. (2018). Anthology on Economics of Spirituality, Journal of Business Economics, Vol. 31 Jan, 2018, Pp: 59 - 60, Kolkata, India (National).
- Satpathy, J., Hejmadi, A., Mishra, D. and Singh, S. (2018). Managerial Eyes for Business Decisions, FMU Journal of Management, Department of Business Management, Vol. 5 and 6, March 2018, Balasore, India (National).
- Satpathy, J. (2018). Neuro - Based Decisions in Global Business Undercurrents, IMS International Conference on Indian Trade and Commerce: Past, Present and Future, March 18, Bhubaneswar, India (International).
- Satpathy, J. and Shukla, O.P. ( 2018 ). Neuroreductionist Approaches to Development (Case Study on Uttar Pradesh, Proceedings of International Seminar on Developmental Challenges of India after Twenty Five Years of Economic Reforms, 16 - 18 March, 2018, Department of Economics, Banaras Hindu University, Banaras, India (International).
- Satpathy, J. and et. al. (2018). Thoughts on Managerial Skills, National Institute of Personnel Management, Utkal Chapter, Vol. 14, Issue No. 1, ISSN No. 2229 - 6506, Pp: 01 - 06, January 2018, Bhubaneswar, India (National).
- Satpathy, J. and Hejmadi, A. (2018). Decision Signatures in Managerial Brain Architecture (Poster), Proceedings of Neuro Psycho Economics Conference, Pp: 61, May 24 - 25, Zurich, Switzerland. (International).
- Satpathy, J. and Hejmadi, A., Subhashree P. and Mishra,S. , (2018). Decision Monikers in Managerial Eyes, Proceedings of International Conference on Contemporary Issues in Business Innovation, Technology and Social Sciences, Gautam Buddha University, 01 - 02 June 2018, June 2018, Noida (UP), India (International).
- Rajpurohit, J.S. and Satpathy, J. (2018). Anthology on Triguna in Contemporary Humanity, Journal of Pune Research Discovery, ISSN. 2455 - 9202, Vol 3, Issue 2, May - July 2018, Pp: 01 - 17, Pune, India (International).
- Satpathy, J. and Mishra,S. (2018). Cognitive Competence 'Agent' in Organisational Decisions, Proceedings of National Conference on Business Transformation Through Strategy And Innovation (BTTSI-2018), BIITM Institute, Biju Patnaik University of Technology, 11 July 2018, Bhubaneswar (Odisha), India (National).
- Mishra, S. and Satpathy, J. (2018). Reflections on Neuro - Competency in Power Sector, Odisha Journal of Social Science, Vol 5. (2), July Edition, Pp: 05 - 30, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India. (National). lSatpathy, J. and Rajpurohit, J. S. (2018). Triguna Geometry in Effective Economic Behaviour, National Seminar on Relevance of Triguna Theory in Contemporary World, 03 - 04 Oct 2018, Indian Institute of Advanced Study, Shimla, India. (National).
- Deo, M. and Satpathy, J. (2018). Hematological Insight into Entrepreneurial Decision, 71st All India Commerce Conference, 20-22 Dec, Department of Commerce, Osmania University, Hyderabad, India. (National).
- Satpathy, J. and Mallik, B. (2018). Hematological Judgement in Entrepreneurial Decision, Proceedings of International Conference on Management, Sciences, Engineering and Applications (ICMSEA - 2018), Dept. of Mathematics, Centurion University, Odisha; Kaziranga University, Assam and University of Perpetual Help, Philippines, 20 - 22 Dec 2018, Vishakhapatnam, India(International). Reprinted in International Journal of Management, Technology and Engineering, ISSN No: 2249-7455, Volume 8, Issue XII, Pp: 2849 - 2863, December, India (International).
- Satpathy, J. and Mallik, B. (2018). Mathematical Exposition on Eye Movements in Decision Dynamics, Proceedings of International Conference on Mathematical Sciences in Engineering Applications (ICMSEA - 2017), Dept. of Mathematics, Centurion, University, 22 - 24 Dec 2017, Vishakhapatnam, India (International). Reprinted in International Journal of Management, Technology and Engineering, ISSN No: 2249-7455, Volume 8, Issue XII, Pp: 3245 - 3254, December, India (International).
