Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Study on Growth and Opportunity of Agropreneurship In India
Abstract :
India is predominantly a rural country with 2/3(two third) population and 70% workforce residing in rural areas. Rural economy constitutes 46 per cent of national income. Traditionally, agriculture is the prime sector of rural economy and rural employment. The transition in composition of output and occupation from agriculture to more productive non-farm sectors are considered as an important source of economic growth. Economic studies on rural India have focused mainly on changes in rural employment, by sectoral aggregation between agriculture and non-agriculture. In India there needs to have planning and implementation for development of entrepreneurial programs are essential because of over-dependence on agriculture for employment. Entrepreneurship development in rural industries appears to be the best potential alternative to find employment avenues for the rural population. Since Entrepreneurship is one of the key driver for economic development of any country, promotion for agriculture entrepreneurship is key element to turn agricultural more productive and profitable for rural people. The present study examines long-term changes in Employment and Future Growth in Rural area, Modern Agriculture as output growth and employment and Adaptation of new agriculture model to overcome basic challenges in Indian Agriculture. Also the Study analyses the changing behavior in Agriculture sector in recent year in India. For this study, Secondary data has been considered for analysis. The findings of the study may be used to suggest strategy for future development of India's rural economy.
Keywords :
Rural economy, Agriculture, Employment, Entrepreneurship, Rural industries, Economic development.Introduction:-
The 'Make in India' Strategy adopted by the Prime
Minister Shri Narendra Modi aims to facilitate
investment, foster innovation, entrepreneurship,
enhance skill development in the country. Mahatma
Gandhi has rightly pointed out that “India lives in
villages”. Villages comprise the core of Indian society
and represent the real India. Rural entrepreneurs are
those who carry out entrepreneurial activities by
establishing industrial and business units in the rural
sector of the economy. In other words, establishing
industrial and business units in the rural areas refers to
rural entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship can play an
important role in rural development. Agriculture
continues to be the backbone of rural society. 70 Percent
farmers held by small & marginal farmers are resulting
in overcrowding on the agricultural land and
diminishing farm produce. This results in migration of
farm worker in large numbers to the urban areas. Land
being limited and unable to absorb the labor force in
agriculture, there is a need to develop rural industries
to solve rural unemployment and rural migration to
cities.
Growth and development of rural economy is an
essential pre-condition to the development of the
country as a whole. The gap between rural and urban
disparities should be lessened. The standard of living
of the rural population is not up to mark and need to
improve. Entrepreneurship in rural sector considering
available sources may provide an answer to the above
problems.
Indian rural sector is no longer primitive and isolated.
Therefore, if entrepreneurships encouraged in rural
and tribal areas looms large to solve the problems of
poverty, unemployment, and economic disparity, poor
utilization of rural capacity, low level of standard of
living and backwardness of Indian economy. Rural
industrialization is viewed as an effective means of
accelerating the process of rural development.
Government of India has been continuously assigning
increasing importance and support for the promotion
and growth of rural entrepreneurship.
According to latest definition of Government of India,
"Any industry located in rural area, village or town
with a population of 20,000 and below and an
investment of Rs. 3 crores in plant and machinery is
classified as a village industry." Rural entrepreneurship
is a new field in the area of entrepreneurship research. It
has become one of the supportive factors for rural
economic development and agribusiness. In this
backdrop, the present paper addresses the problems
and challenges for development of entrepreneurship in
the context of rural India.
Agriculture as Entrepreneur boon for Rural Area
In context of Indian scenario where large scale of people are living in rural area, it becomes necessary to develop the economic environment for rural people to make the rising India. Although there are so many promotional schemes are governing by the government but due to various factors like illiteracy, non-availability of facilities, life-style challenges, lack of knowledge about the new farming system, lack of resources etc. people from rural area still not moving to advance farming.
Concept of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the act of being an entrepreneur, who starts any economic activity for being selfemployed. The entrepreneurial activity is governed by varying combination of socio-economic, psychological, cultural and other factors: Caste/religion, Family background, Level of education, perception, Occupational background, Migratory character, Entry into entrepreneurship, Nature of enterprise, Investment capacity and Ambition.
Entrepreneurship in Agriculture
Considering the growing unemployment in rural areas and slow growth of the agricultural sector, it is necessary to tap the opportunities for promoting entrepreneurship in agriculture, which in turn can address the present problems related to agricultural production and profitability. An “agricultural entrepreneur” is an individual or group with the right to use or exploit the land or other related elements required to carry out agricultural, forestry or mixed activities. (Suarez,1972)
In a simple word, we can define Agri-entrepreneur as “People who is developing the employment using agriculture as a business.Objective:
- To find out the Growth in agriculture in India
- To find out the entrepreneurial opportunity in agriculture.
- To explore government schemes for rural entrepreneur in India.
- To find out challenges in agricultural entrepreneurships
Review of Literature:
Piore and Sable (1984), they concluded in their book, “The second industrial Divide” that rural economy will be more effective if government try to improve business condition in rural areas. Petrin (1994) in article found that entrepreneurship can play an important role in development of rural area to a greater extant. It works as vehicle to increase personal satisfaction for people and families of rural areas. Gavian et al. (2002), in their study , that have find that SMEs are plat well poised to react the increased demand by creating job. Sherief, (2005) focused on factors of rural entrepreneurship will helpful for its improvement . in this study they found that development of entrepreneurship in rural area is most essential to accelerating economy development. Mehta, (2011), in this study, he found that many Indian origination including MNCs creating business opportunity in rural area of India. The study will be supportive for the different organizations to figure arrangements and approaches so as to help the rural entrepreneurship in India. This may make the Indian rural business sector as a basic power in the worldwide e conomy. In hor t i cul tur e , ut i l i z ing new entrepreneurial exercises is moderately simple since agriculturists for the most part have numerous valuable assets available to them, for example, land, structures, apparatus, work, systems, and so on. Sharma, Swati, Vyas and Divya (2011) demonstrated that different social, financial, political and environmental issues in provincial regions in creating nations like India make challenges in livelihood, diminishing rural generation and expanding nourishment lack. This has come about a colossal effect on the residential generation, livelihood and so forth. To a specific degree, these issues can be understood by creating entrepreneurship in rural India.
Research Methodology:
All data have been collected through articles, journals, magazines, books, and website etc. the objective of this paper is to bring out the growth, Opportunity and Prospective of Agropreneurship in India.
Growth in Agriculture in India
India has the 10th largest arable land resources in the
world. With 20 agri-climatic regions, all 15 major
climates in the world exist in India. The country also
possesses 46 of the 60 soil types in the world. Growth in
Gross Value Added (GVA) by agriculture and allied
sectors is estimated at 3 per cent in 2017-18**. Strategic
geographic location and proximity to food importing
nations favor India in terms of exporting processed
foods. During 2017-18* crop year, food grain
production is estimated at record 284.83 million tones.
In 2018-19, Government of India is targeting food grain
production of 285.2 million tones. India is the largest
producer of spices, pulses, milk, tea, cashew and jute;
and the second largest producer of wheat, rice, fruits
and vegetables, sugarcane, cotton and oilseeds. India is
currently the world's fourth largest producer of
agrochemicals. India has the largest livestock
population of around 512 million.
Also India is one of the largest manufacturers of farm
equipment such as tractors, harvesters and tillers. India
accounts for nearly one-third of the overall tractor
production, globally.
Tractor sales in the country are expected to increase 11-
13 per cent in FY19, while the tractor industry is
expected grow at 8-10 per cent between FY17-22.
Note: *as per 4th advance estimates,
** as per 2nd advance estimates
Source: Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India,
MOSPI, BCG, Crisil
Gross Value Added by Agriculture and Allied Sectors
As per Report of 'India Brand Equity Foundation', Indian agriculture sector has made significant progress in Agriculture and Allied Sector, below progress chart has been shown the progress per year in US $ billion: Source: Ministry of Agriculture, Print Release, RBI, Aranca Research, MOSPI, Central Statistics Office (CSO)
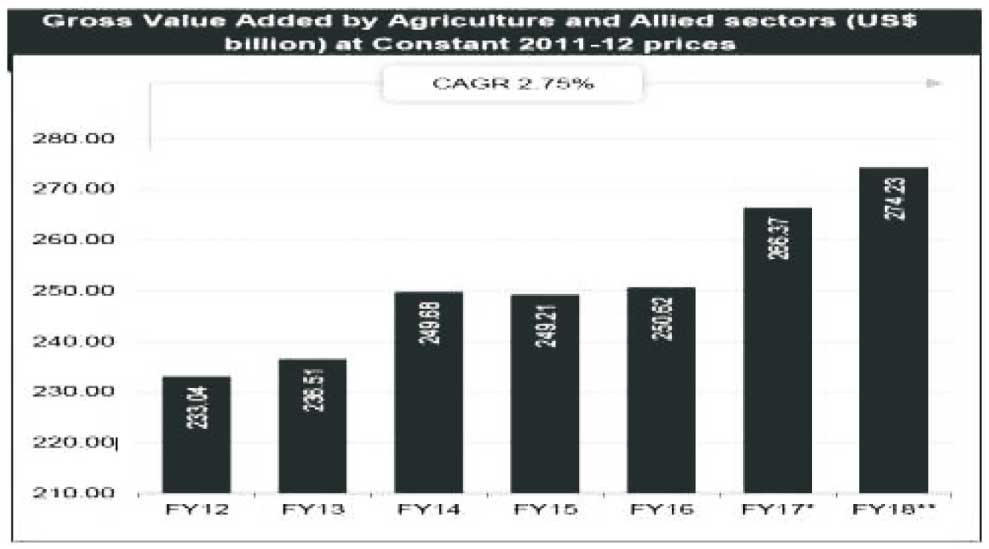
Key Highlights on Agriculture and Allied Sectors
- Agriculture is the primary source of livelihood for about 58 per cent of India's population.
- Gross Value Added by agriculture, forestry and fishing is Rs 17.67 trillion (US$ 274.23 billion) inFY18.
- Agriculture and allied sector's GVA at constant 2011- 12 prices grew a CAGR of 2.75 per cent between FY12-18.
- As per Union Budget 2018-19, allocation of Rs 57,600 crore (US$ 8.9 billion) was made for The Agriculture Ministry.
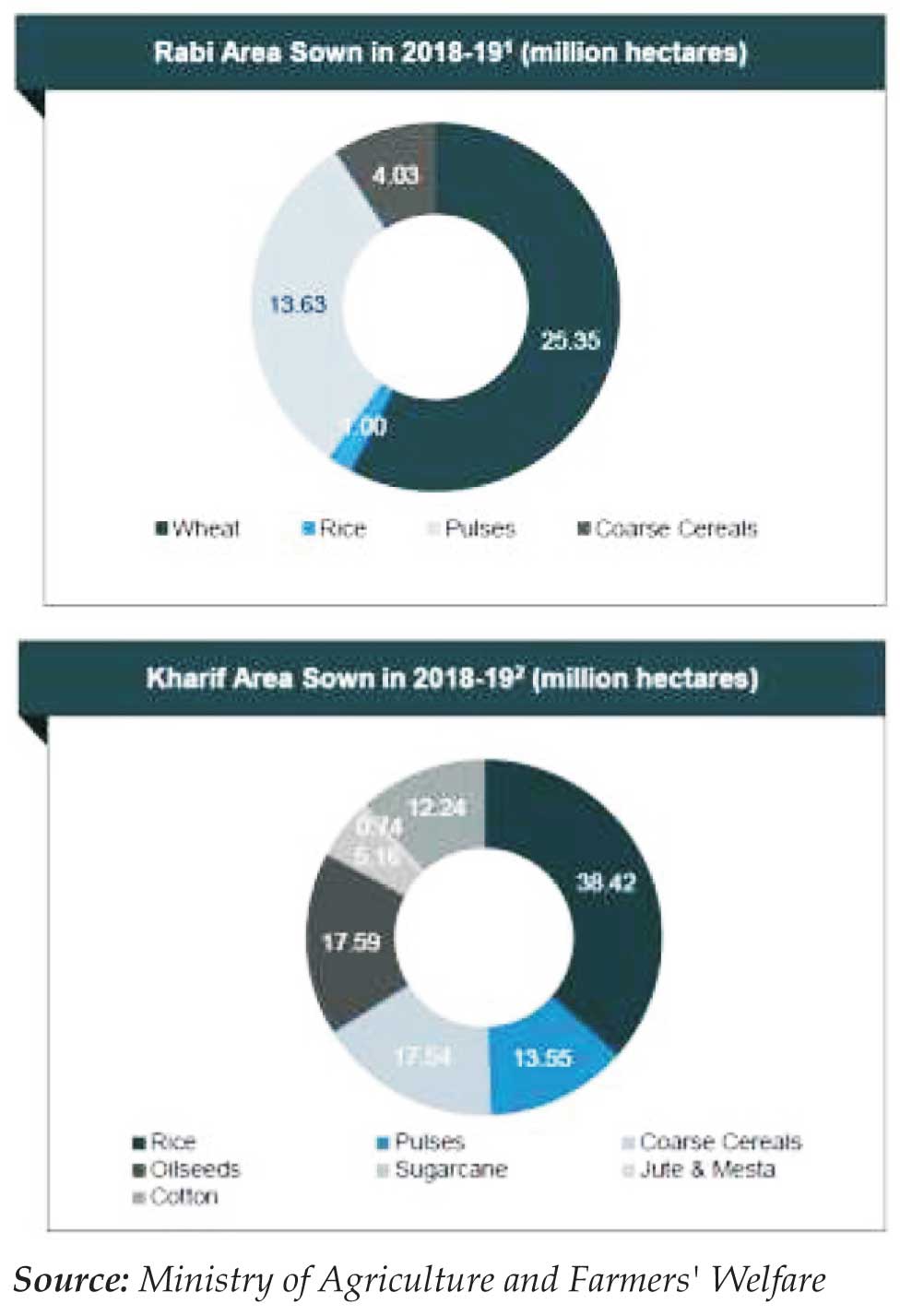
Production of KHARIF AND RABI Corps
There are two major agricultural seasons in India:
Kharif and Rabi. Kharif season lasts from April to
September (summer); rice (paddy) is the season's main
crop. Rabi season lasts from October to March (winter);
wheat is the season's main crop. As of October1 2018,
total area sown with kharif crops in India reached
105.24 million hectares .
Progress of Kharif and RABI corps are shown in below
graph:
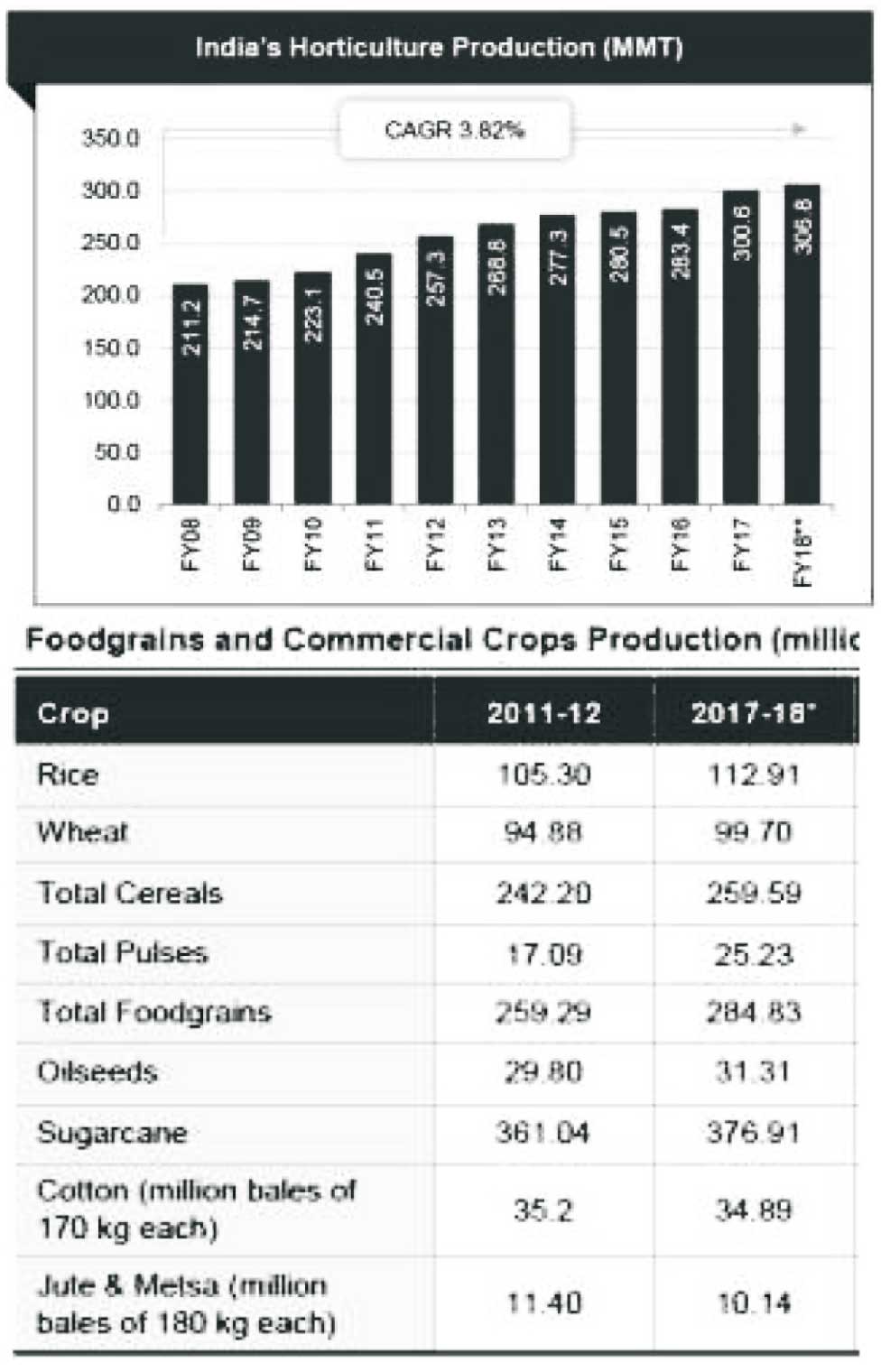
Increasing Production in Food grains and Commercial Corps
Since 2010, production as well as yield of both major
crops - rice and wheat has increased significantly. As
per fourth advance estimates, production of rice is
estimated at record 112.91 million tons while
production of wheat is estimated at 98.70 million tons in
2017-18 crop year.
Production of horticulture crops in India is estimated at
record 306.82 million metric tons (MMT) in 2017-18,
implying a CAGR of 3.82 per cent between FY08-18.
Below Graph shows the ratio of Increasing Production
Note: * As per 4th advance estimates, **as per 3rd advance
estimates, 1as of September 26, 2018, *** estimate as per the
Indian Cotton Federation
211.2
Source: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare
ØIncreasing Production in Fruits from 2007-08 to
2017-18
As per the First Advance Estimate the area under fruit
crops during 2017-18 is 6.4 m. ha with a total production of 94.8m. MT. During the period (2007-08 to 2017-18),
production of fruits increased by about 44.6% while the
area increased by about 9.7%. (2007-08 to 2017-18)
Comparative details of area, production and
productivity of fruit crops are given are in Figure 1.
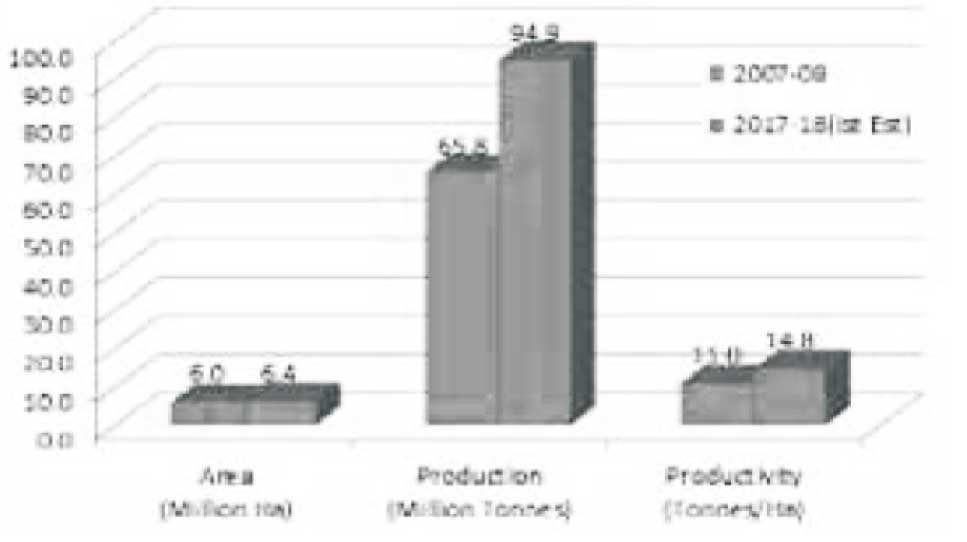
Sources http://www.dowrorissa.gov.in/Training Programme/2018/FEBRUARY/ICAR/materials/dy3 /Overview%20of%20Organic%20Farming.pdf India has retained its status as the second largest producer of fruits in the world.The country is first in the production of fruits like mango, banana, sapota, pomegranate and aonla. India ranks second in global production of fruits and vegetables and are a leading exporter of mangoes and bananas.
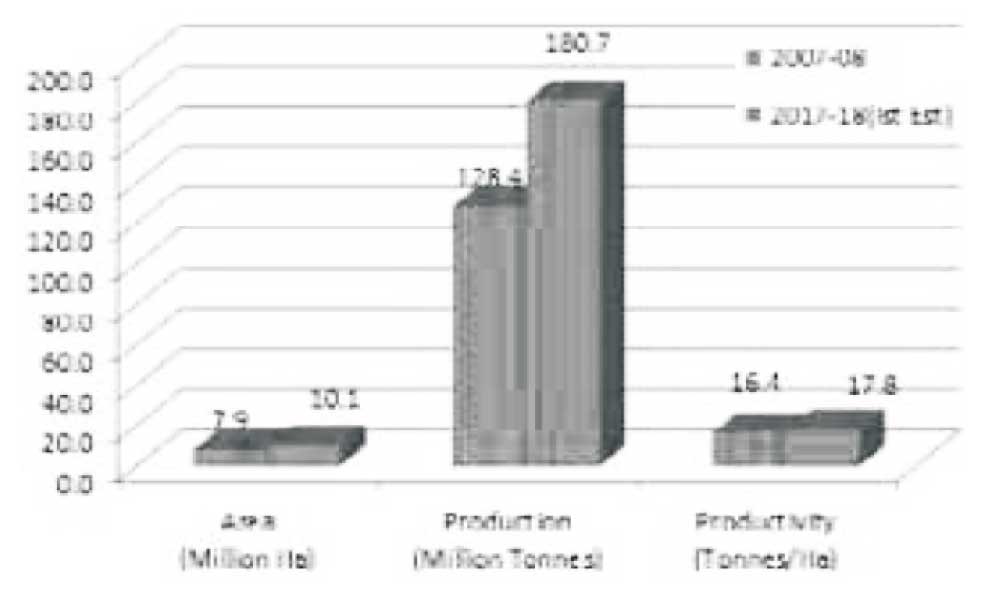
Increasing Production in Vegetables from 2007-08 to 2017-18
Vegetables are an important crop in horticulture sector,
occupying an area of 10.1 million a during 2017-18 (1st
Estimate) with a total production of 180.7 million
tonnes with average productivity of 17.8 tonnes/ha. In
fact vegetables constitute about 59% of horticulture
production. During the period (2007-08 to 2017-18),
area and production of vegetables increased by 30%
and 41% respectively. The comparative details are
depicted in the Figure 2.
Sources http://www.dowrorissa.gov.in/Training
Programme/2018/FEBRUARY/ICAR/materials/dy3
/Overview%20of%20Organic%20Farming.pdf
Sampling technique/sample size determination:
Simple random sampling was used to survey ten
manufacturing companies in Port Harcourt, Rivers State
from Manufacturers Association of Nigeria
(http://phmanufacturersnigeria.org/members.html).
Sample size of seventy (70) was determined using
Krejcie and Morgan (1970).
India continued to be second largest producer of
vegetables after China. India is a leader in production of
vegetables like peas and okra. Besides, India occupies
the second position in production of brinjal, cabbage,
cauliflower and onion and third in potato and tomato in
the world. Vegetables such as potato, tomato, okra and
cucurbits are produced abundantly in the country.
Increasing Production in Flowers Market across India
India is on the 18th rank with contributing 0.6 percent
share in global floriculture trade. During the last
decade, export increased at a CAGR of 4.33 percent. The
domestic Indian market is growing at the rate of 25 per
cent per year in the country as a whole. About 249
thousand hectares area was under cultivation in
floriculture in 2014-15. The states like Karnataka, Tamil
Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Maharashtra,
Rajasthan, Delhi and Haryana have emerged as major
floriculture centres in recent times.
Flowers are categorized into cut flowers and loose
flowers as followings:
- Cut flowers:
Cut flowers are fresh flower harvested in clusters / spike or in single along with their stem. like, Rose, Carnation, Gerbera, Tuberose, Gladiolus and Orchid. West Bengal is number one in cut flower production. - Loose Flowers:
The flowers which are usually harvested without stalk and used for Gajara, Veni and Garland like Jasmine, Crossandra, Marigold, Gaillardia and Chrysanthemum. Tamilnadu is number one among the states in Loose Flower productions may be due to aesthetic preferences of women for their hair.
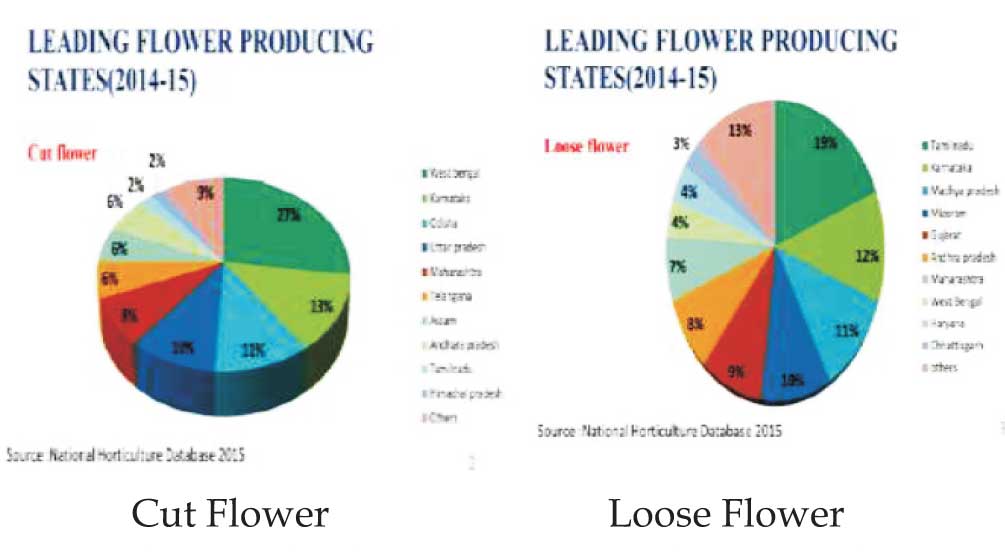
Fig.1 : Showing leading states in Cut Flower Production
and Loose Flower Production in India
Entrepreneurial Opportunity in Agriculture
Nowadays, Easy access to technology, emergence of
micro financing, liberalized government rules,
awareness and training programs on agri and allied
sectors and finally changing mindset of the highly
qualified people to go for self-employment in the field of
agriculture have contributed significantly in enhancing
the potentiality for entrepreneurship in India.
Agriculture have several areas of entrepreneurship
which include the activities like Dairying, Goat earing,
Rabbit rearing, Floriculture, Fisheries, Shrimp
Farming, Sheep rearing, vegetable cultivation, nursery
farming, farm forestry.
The possible areas of entrepreneurship in agriculture
are:
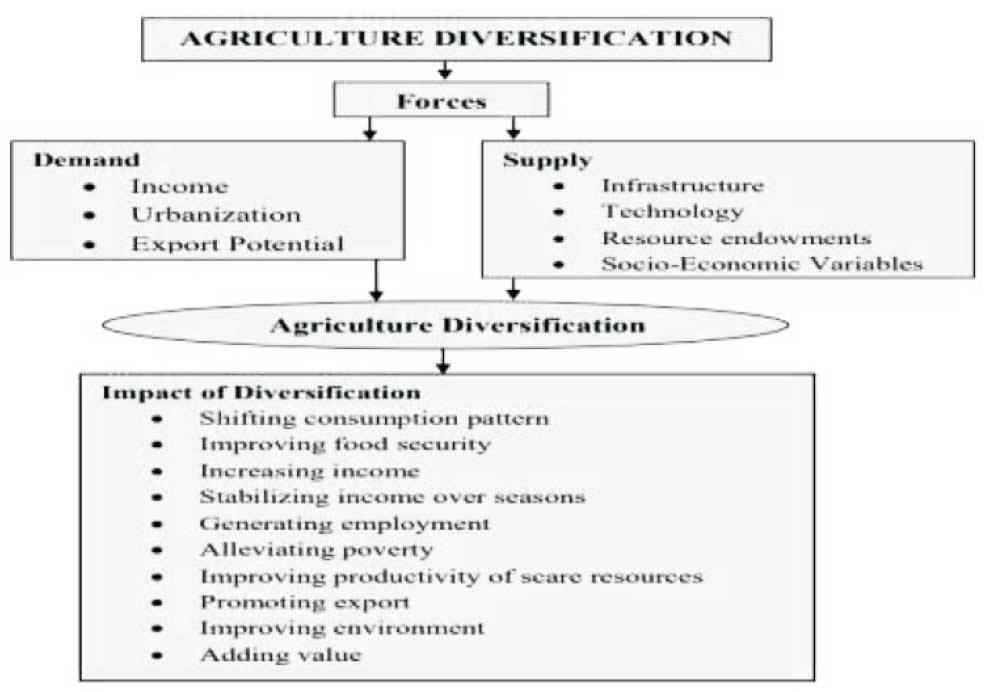
Diversification
Diversification in agriculture involve shift in cropping
pattern from traditionally grown crops to more
remunerative crops like oilseeds, pulses, fodder crops,
horticulture, medicinal and aromatic plants,
floriculture etc.
It also includes livestock and fishery enterprises and
small scale agro-based industries. Diversification
increases the employment opportunities, optimum use
of resources and profitability.In above graph Importance of Agriculture
Diversification has been explained as Forces to
Impacting the diversification
Organic Farming
India has a lot of potencial in the field of Organic Farming, this is started mostly as a small farm agriculture system with operation also being farm less than 1 acre in size. Form Farms under 10 acres in size, farming is mostly labor intensive and requires lesser mechanization. Also Organic Farming tends to reduce the cost as it removes the extra cost of synthetic fertilizers used in conventional farming method. Organic farming results in clean very good quality products. Given the current state of Indian agriculture, Organic Farming seems to have a lot of scope in Uplifting the condition of Indian Farmers. The importance of organic farming is growing very fast particularly in international market. This sector provides great business opportunities to agro-based entrepreneur. Area under organic farming is increasing but unable to meet the demand of organic produce.
Floriculture
Floriculture is the growing of cut flowers, potted flowering and foliage plants, and bedding plants in greenhouses and/or in fields. There are several thousand different species of flowers and plants that are grown as commercial crops. Cut flowers include such crops as roses, freesia, alstromeria and snapdragons. Some of the favourite flowering potted plants that are available year-round are African violets, orchids, cyclamen and potmums (potted Chrysanthemums). Some seasonal flowering plants are an important part of our traditions, for example, poinsettias for Christmas and Easter lilies for Easter. Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Tamil Nadu , Rajasthan , West Bengal have emerged as major floriculture centers.
India facts & Figure for Floriculture
About 249 thousand hectares area was under Cultivation in floriculture in 2015-16. Production of flowers are estimated to be 1659 thousand tons loose flowers and 484 thousand tons cut flowers in 2015-16.
Exports
The country has exported 20703.46 MT of floriculture products to the world for the worth of Rs. 507.31 crores/78.73 USD Millions in 2017-18. U S A, Netherland, U K, Germany and United Arab Emirates were major importing countries of Indian floriculture during the same period.

Fruits & Vegetable Seed
Fruits & Vegetable Seed in India is being viewed as a high growth Industry. Most seeds normally remain viable for 2 or 3 years if stored under good conditions. Therefore, buy only from seed firm of known integrity. High yielding, high price seeds should have 90% germination. For germination of seeds adequate moisture, temperature and aeration are essential. The requirement of temperature for various fruits and vegetable seeds varies markedly. Some seeds do not germinate at low temperature while some others at high. Usually germination is optimum in between 400 F and 600 F.
Varieties:
The major seeds which are grown in India are Beet Seeds, Cabbage Seeds, Cauliflower seeds, Fruit Seeds, Onion seeds, Pea Seeds, Pomegranate seeds, Radish Seeds, Tamarind Seeds and Other Seeds etc.
Areas of Cultivation :
Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Uttar Pardesh, Orissa have emerged as major areas of cultivationIndia Facts and Figures for Foods and Vegetables Seeds
The country has exported 14463.14 MT of Fruits and Vegetables Seeds to the world for the worth of Rs. 670.9 crores/ 104.03 USD Millions during the year 2017-18.
Major Export Destinations (2017-18):
U S A, Netherland, Pakistan Ireland, Bangladesh and Thailand were major importing countries of Indian seeds during the same period.
 http://apeda.gov.in/apedawebsite/SubHead_Products/Floric
ulture.htm
http://apeda.gov.in/apedawebsite/SubHead_Products/Fruits
_and_Vegetable_Seeds.htm
http://apeda.gov.in/apedawebsite/SubHead_Products/Floric
ulture.htm
http://apeda.gov.in/apedawebsite/SubHead_Products/Fruits
_and_Vegetable_Seeds.htm
Government Schemes for Rural Entrepreneur In India
The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is
an autonomous organization under the Department of
Agricultural Research and Education (DARE), Ministry
of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of
India.
The Council is the apex body for coordinating, guiding
and managing research and education in agriculture
including horticulture, fisheries and animal sciences in
the entire country. With 101 ICAR, institutes and 71
agricultural universities spread across the country this
is one of the largest national agricultural systems in the
world.
The ICAR has played a pioneering role in ushering
Green Revolution and subsequent development in
agriculture in India. Through its research and
technology development that has enabled the country
to increase the production of foodgrains by 5.4 times,
horticultural crops by 10.1 times, fish by 15.2 times,
milk 9.7 times and eggs 48.1 times since 1951 to 2017. It
has played a major role in promoting excellence in
higher education in agriculture. It is engaged in
innovative areas of science and technology
development and its scientists are internationally
acknowledged in their fields.
There are several schemes available to promote new
startups, facilitating training to farmers on agrientrepreneur.
Listed below some of the major schemes
operated in India to boost the Agriculture as an
entrepreneur.
- AGRI-UDAAN Program - In an attempt to promote innovation and entrepreneurship in agriculture, the government is launching a new AGRI-UDAAN program that will mentor startups and help them connect with potential investors
- Training programme - The National Institute of Agricultural Extension Management (MANAGE), Hyderabad is implementing the Scheme of Agri-clinics and Agri-Business centers initiated by the Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India. The Scheme aims at supplementing existing extension network to accelerate process of technology transfer in agriculture and strengthening input supply and services. Agri-graduates and Post graduates. Diploma holders in agriculture and allied fields can set up their Agri-Clinics and Agri-Business Centers and offer professional/consultancy extension services to farmers. The scheme enumerates availability of better methods of farming to farmers and better opportunities for self-employment to the Agricultural Graduates.
- Institutional Support for Agri-business - RBI started in July 1982 NABARD to give full attention to the rural sector in areas of agriculture, small –scale and cottage industries and agro-based industries. Since its formation NABARD hold the responsibility of managing all the activates of the RBI pertaining to rural development and agro based activities
- Panchayatmandi (Agri-Mandi) - The concept of self-governance has gone to the level of marketing of village produce through village markets and fairs. The concept of Panchayat mandi is to reduce the influence of middlemen and traders. This is possible only if functioning of the District Panchayat is effective in coordination with state marketing boards and APMC (Agriculture produce market committee)
- State Agricultural marketing banks (SAMB) - State agricultural marketing banks are set up to actively regulate markets for food crops and oilseed in bigger markets of towns and cities
- NCOSAMB (The national council for state marketing board) - An agro based country like India needs training centers with modern facilities throughout the country. The government of India provides grants in aid to state to set up such training facilities. NCOSAMB is the body to coordinate the programmes of such training
- State Trading Corporation (STC) - The state trading corporation of India ltd is premier international trading house owned by the government of India having been set up in 1956; the corporation has developed vast expertise in handling bulk international trade international trade.
- In September 2018, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) approved a Rs 5,500 crore (US$ 820.41 million) assistance package for the sugar industry in India
- In March 2018, the Government of India extended the urea subsidy to the farmers till 2020 with the aim of ensuring supply of urea at statutory controlled prices. Urea subsidy for 2018-19 is estimated at Rs 45,000 crore (US$ 6.95 billion).
Challenges in Agriculture Entrepreneurship
Although there are so many schemes available for the farmers in respect of Agriculture, Rural development. But still there are some challenges which cannot be ignore and all the responsible body like Central Govt., State Govt., Local Authorities and Corporate leaders need to overcome with some solutions. There are some 125 IUJ Journal of Management Vol. 7, No. 2, Dec. 2019 basic challenges has been highlighted below as following:
Financial Challenges
Shortage of Funds - Lack of finance available to Agri
entrepreneurs is one of the biggest problems. Major
sources of finance in rural areas are loans from
regional rural banks or from zamindary but their rate
of interest are usually very high.
Lack of infrastructural facilities -
The growth of Agri
entrepreneurs is not very healthy in spite of efforts
made by government due to lack of proper and
adequate infrastructural facilities.
Risk element - Agri. entrepreneurs have less risk
bearing capacity due to lack of financial resources and
external support
Marketing Challenges
Competition - Major problems faced by marketers are
the problem of standardization and competition from
large scale units
Mediators (Distribution Channel) - The Agriculture
entrepreneurs are heavily dependent on distribution
channel for marketing of their products who pocket
large amount of profit.
Management Challenges
Lack of Advance technology - Information technology is not very common in rural areas. Legal formalities Agri-entrepreneurs find it extremely difficult in complying with various legal formalities in obtaining licenses due to illiteracy and ignorance Lack of Modern Machinery – The growth of agriculture is based on advance supporting machinery and tools. In Indian context farmers is not having such capability to cultivate the farms with modern machinery which result as time taken processing for agriculture.
Finding
Gross values added by agriculture and allied sectors are
attending satisfactory growth. India rank 2 nd in global
production of fruits and vegetable continuous to be a
leading exporter of mangoes and banana; along with
producing potato, brinjal extra in abundant quantity.
India is rank significantly on the promotion of global
floriculture trade. There are numerous opportunity of
agropreneurship by means of diversification, organic
farming, and floriculture with the development of
hybrid seeds of fruits and vegetables.
There are several government schemes to promote new
startups in the field of agropreneurship like agri-udaan
program, state agriculture marketing bank, NCOSAMB
besides providing adequate subsides to the player in
this field.
After this study , it can also be found that besides the
positives being under taken to cater there are several
challenges like financial, marketing, and management
challenges in order to make a prolific statement in the
sector.
Conclusion & Recommendation Conclusion:
Agricultural entrepreneurship shares many
characteristics of "generic" entrepreneurship, but also
has its distinct features due to the specific context of the
agricultural sector. With better industrial and
entrepreneurial education discipline, entrepreneurs
will naturally take advantage of the vast human
resource availability. It is clear that there is a great
scope for entrepreneurship in agriculture, only
effective management of agri elements an individual
can tap this potentiality with risk bearing capacity, and
a quest for latest knowledge in agriculture sector can
prove to be right agriculture entrepreneurs.
The agriculture sector has a large potential to
contribute to the national income while at the same
time providing direct employment and income to the
numerically larger and vulnerable section of the
society. Agriculture entrepreneurship is not only an
opportunity but also a necessity for improving the
production and profitability in agriculture sector.
Floriculture production and market is booming now
days due to increase in demand both in national and
international market. USA and United Kingdom are
two best markets for India floral export, but national
market is very much fragmented, that gives emerging
of many associations. Understanding of major market
at both brick and click way, gives the stakeholders a
better way of understanding of floral market.
A shift from 'agriculture' to 'Agroepreneurship' is an
essential pathway to refresh Indian agriculture. While
the share of pure agriculture in GDP may decline, the
share of Agri Entrepreneurship is bound to go up with
the demand for value added products continuously
increasing.
Agri entrepreneurship is also the answer to removal of
rural poverty in India. Therefore, there should be more
stress on integrated rural development programs. The
problem is that most of the rural youth do not think of
entrepreneurship as the career option. Therefore, the
rural youth need to be motivated to take up Agri based
entrepreneurship as a career, with training and
sustaining support systems providing all necessary
assistance. There should be efficient regulated market
and government should lend its helping hand in this
context.
Recommendation:
Following are the recommendation has been
underlined to make new India as Agri India:
-
Change in Traditional Agriculture - as per current
position of the agriculture in India especially in States
like Bihar, Jharkhand, Punjab, Maharashtra, West
Bengal, Odisha and Northeast, where maximum
population is dependent on Agriculture. People need
to change the scope of farming from traditional
farming to advance farming like organic farming,
Floriculture, Fruits and seeds farming and even crop
farming with advance machinery to avoid the flood
and Dry-land issues.
Technology - Improvement in the production technologies. Apart from the production technologies, the extension worker now, have to get equipped with market information which requires further training for skill upgradation in the field of agricultural marketing.
Network Building - Strong network of marketing e x t e n s i o n i s v e r y mu c h n e c e s s a r y a t District/block/Village level to effectively advise farmers on various aspects of marketing, advice on product planning, marketing information, securing market for farmers, advice on improved market practices and advice on post-harvest management practices.
lMarketing of Production - Marketing is the necessary element of any production activity to mobilize the product in global Market. Officers of Agriculture, Horticulture and Agricultural Marketing departments should be given training on various aspects of Agricultural Marketing for the purpose of carrying out extension works effectively and efficiently. This will help in minimizing the postharvest losses to a considerable extent.
lDevelopment of Cooperative Society - Cooperative market should be formed. To set up mandi of nearest block so that they may could direct contact with the customers.
lEnhancement of Communication Skills of Farmers – Since we are moving into global market and to compete with global competition the communication skill is playing major role to promote the products, explore the markets and grabs the global markets eas i ly. Enhanc ing the int e rac t ive and communication skills of the farmers to exchange their views with customers and other market forces (middlemen) for getting feedback and gain the bargaining during direct marketing.
Training Center - Educating the farming community to treat agriculture as an entrepreneurial activity and accordingly plan various phases of crop production and marketing. Training also require to develop the skill to cultivate organic corps, floriculture, Fruits and vegetables etc.
Facility of Resources - Providing the facility of resources like advance machinery, proper water facility etc. to enable the farmers to produce and cultivate the corps in any form.
References:
- Abraham, Vinoj (2013), “Missing Labour or Consistent 'De-Feminisation'?”, Economic and Political Weekly, 48 (31).
- Anderson D. Small industry in developing countries: A discussion of issues. World Development, 1982;
- Anyon J. Social class and the hidden curriculum of work. Journal of education, 1980, 67-92.
- Bairwa SL, Lakra K, Kushwaha S, Meena LK, Kumar P. Agripreneurship Development as a Tool to Upliftment of Agriculture.
- Himanshu (2011), 'Employment Trends in India: A Re-examination', Economic and Political Weekly,46(37): 43-59.
- Hirway, Indira (2012), 'Missing Labour Force: An Explanation', Economic and Political Weekly, 47(37): 67–71.
- International Journal of Applied Research 2015; 1(9): 1063-1066
- Kular IK, Brar AS. Transforming Indian Agriculture through Agripreneurs. Indian Journal of Marketing.2011; 42(3).
- McCombie JS, Thirlwall AP, Thompson P. Economic growth and the balance-of-payments constraint. New
- McElwee G. Farmers as entrepreneurs: developing competitive skills. Journal of. 2006.
- McElwee G. Farmers as entrepreneurs: developing competitive skills. Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship. 2006; 11(03):187-206.
- Mehrotra, Santosh, Parida, J, Sinha, S and Gandhi, A (2014), 'Explaining Employment Trends in the Indian Economy: 1993–94 to 2011–12', Economic and Political Weekly, 49(32): 49–57.
- Pradhan, Kanhu Charan (2013), Unacknowledged Urbanisation: New Census Towns of India, Economic and Political Weekly, 48 (36), Sep 7, pp. 43-51.
- Pertin, T (1997), "Entrepreneurship as an economic force in rural development", in " Rural Development through Entrepreneurship”, Compiled and edited by Tea, REU Technical Series 41, FAO RegionalOffice for Europe, FAO of the United Nations, Rome. Rangarajan, C, Kaul, P I and Seema (2011), 'Where is 127 IUJ Journal of Management Vol. 7, No. 2, Dec. 2019 the Missing Labour Force?', Economic and Political Weekly, 46(39): 68–72.
- Rawal, Vikas and Saha, Partha (2015), 'Women's Employment in India: What do Recent NSS Surveys of Employment and Unemployment Show?', Statistics on Indian Economy and Society, Jan 28, Rustagi, Preet (2010), Employment Trends for Women in India, ILO Asia-Pacific
- Saini JS, Bhatia BS. Impact of entrepreneurship d e v e l o pme n t p r o g r amme s . J o u r n a l o f Entrepreneurship.1996; 5(1):65-80.
- Sancho. F. year (2010) Agricultural and rural Entrepreneurship: concepts for modeling development. Year-5 , Jan- July page 64-65.
- Sandeep S. (2012) Problems Faced By Agri Entrepreneurs and Remedies to Solve it. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSRJBM) ISSN: 2278-487X V olume 3, Issue 1 (July-Aug. 2012), PP 23-29
- Suryvanci. S. year (2012) Opportunities for Agri. Entrepreneurship. ISAP. lThomas, Jayan Jose (2012), 'India's Labour Market during the 2000s: Surveying the Changes', Economic and Political Weekly, 47(51): 39-51.
- Umali-Deininger D. Public and private agricultural extension: Partners or rivals. The World Bank Research Observer. 1997; 12(2):203-224.
- Working Paper Series, ILO Subregional Office for South Asia, New Delhi. lYork: St. Martin's press, 1994.
- h t t p : / / a p e d a . g o v . i n / a p e d a w e b s i t e / S u b Head_Products/Floriculture.htm
- h t t p : / / a p e d a . g o v . i n / a p e d awe b s i t e / S u bHe a d Products/Fruits_and_Vegetable_Seeds.htm
- http://www.scribd.com/doc/26661470/Agri. Entrepreneurshipin-India on 26-04-14
- http://www.studymode.com/essays/Agri.- Entrepreneurship-Opportunities-And-Challenges- 383504.html on 30-04-14
- https://ibef.org
- https://icar.org.in/content/about-us
