Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Impact of Diagnosis, Treatments, and Precaution in Primary Health Centre during Covid 2019
Abstract :
This study examines COVID – 20i9 impact of diagnosis, treatments, and precaution in Thoothukudi district. The primary data and secondary data were used. Most of the data collected through questionnaires and interview schedules and secondary data collected through published articles, journals, magazines, books, newspapers, and websites. The data collected from about 144 respondents selected using a random sampling method covering the villages Arumuganeri, Authur, Eral, Kalugumalai, Karungulam, Mappilaiyurani, Pudukottai, Sivakalai, Thenthiruperai, Vallanadu, Veppalodai, and Vembar. Version 21.0 Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) was used to analyze the data. The collected data were analyzed by using appropriate statistical tools like percentage, rank test, and chi-square test for arriving at conclusions. The findings of the study are to define the patient shows various symptoms usually fever/headache, running nose/cold, cough, breathing trouble, wheezing, etc and to identify the possible causes of COVID-19, to prevent the prospective transmission of diseases to other patients and health care staff.
Keywords :
Corona virus disease-2019, Diagnosis, Treatment and Precaution1. Introduction
Health wellness is a very basic requirement for all individuals. If individuals are sound in health they could discharge their best for the society at the micro-level and nation and globe at the macro-level. Health wellness is a measure of the energy and productive capacity of any country. When health is missing, knowledge cannot disclose itself, the ability cannot manifest, power cannot emanate, and prosperity becomes ineffective. Today the concept of development has shifted from economic improvement to human resources. Human development has been accepted as an important goal of the Eighth Five Year Plan as well as. The economic survey also stresses the same and makes it crucial for the long-term success of economic reforms. Thus the long-term development of social sectors such as education and health is vital for sustaining high rates of overall economic growth.
Primary Health Care (PHC) services substantially affect the general health of the population. However, many other factors also influence the quality and efficiency of PHC services in developing countries. The World Health Organization (WHO) particularly points out that to some extent, the decline in the health status of developing countries is attributed to inadequacies in PHC implementation and neglecting responsible factors such as commitment, allocation of financial resources to PHC, and community participation.
Prevent infection and slow transmission of COVID-19.
· Wash hands regularly with soap and water, and clean with alcohol-based hand rub.
· Maintain 1 metre distance between people coughing and sneezing.
· Keep away from touching the face.
· Cover the mask with face when coughing or sneezing.
· Stay at home
Objectives of the Study:
1. To analyze the demographic profile of the respondents in Thoothukudi Primary Health Centres.
2. To evaluate the impact of diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of COVID – 19 in Thoothukudi District.
Methodology
The primary data and secondary data were used. Most of the data collected through questionnaires and interview schedules and secondary data collected through published articles, journals, magazines, books, newspapers, and websites. The data collected from about 144 respondents selected using a random sampling method covering the villages Arumuganeri, Authur, Eral, Kalugumalai, Karungulam, Mappilaiyurani, Pudukottai, Sivakalai, Thenthiruperai, Vallanadu, Veppalodai, and Vembar. Version 21.0 Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) was used to analyze the data. The collected data were analyzed by using appropriate statistical tools like percentage, rank test, and chi-square test for arriving at conclusions.
Review of Literature
Adepeju. M. Lateef & Euphemia. M. Mhlongo (2020) in his paper entitled “A Literature Review on people-centered Care and Nursing Practice in Primary Health Care Setting”. The study has been found that the deliveries of nurses with people-centered care concept in primary healthcare centers. Nurses’ job in delivering PCC and gauging their information and understanding is becoming essential and crucial. In primary health centre environments, staff plays a significant role in understanding a patient's culture of quality and efficient health care.
Anthony Rahul Golden S. & S. Bulomine Regi (2019) examines the research study investigates various problems that are faced by patients in Private Hospitals, Tirunelveli city. The objective of the study is to identify the lack of services in private hospitals that adversely affect a patient’s physical and mental health. A comprehensive survey was made in the hospitals situated in the research area through a structured interview schedule to record the problems faced by the patients regarding private healthcare hospitals. 75 percent of the respondents were randomly selected from four Private hospitals situated in Tirunelveli City. The study has been found that the problem faced by patients in private hospitals based on facilities and treatment provided by the health sector. This study suggests that the proper attention of provision on sound infrastructure, usage of medical equipment, and cost consumed by the private hospitals. The results of this review highlighted evidence of the relationship between quality health care.
Materials and Methods
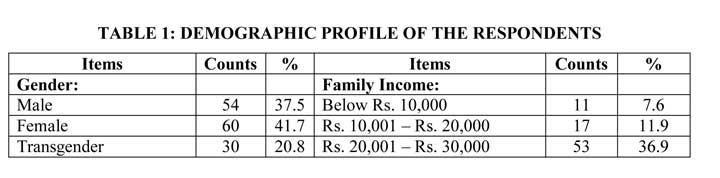
The demographic characterized of the sample are analyzed and found that among the total respondents of 144, 37.5 percent of the respondents are male, 41.7 percent of the respondents are female and 20.8 percent of the respondents are transgender. About 29.8 percent of the respondents fall under the age group of above 60 years, 21.6 percent of the respondents fall under the age group of 21 years - 30 years, 15.9 percent of the respondents fall under the age group of 51 years - 60 years, 12.6 percent of the respondents fall under the age group of 31 years – 40 years, 11.8 percent of the respondents fall under the age group of 41 years – 50 years and 8.3 percent of the respondents fall under the age group of below 20 years. About, 15.9 percent of the respondents are illiterates, 11.1 percent of the respondents are undergraduate level, 25.7 percent of the respondents are diploma, 31.3 percent of the respondents are undergraduate level, 9.1 percent of the respondents are postgraduate level and 6.9 percent of the respondents are professionals. The majority of the respondents are working in private as large as 22.9 percent, 15.9 percent of the respondents are agriculturist, 8.3 percent of the respondents are working in government employee, 6.9 percent of the respondents are working in the company, 6.3 percent of the respondents are doing businessman, 11.9 percent of the respondents are working in teaching and 7.7 percent of the respondents are others i.e. housewife. While 7.6 percent of the respondents are monthly income falls under the category of below Rs. 10,000, 11.9 percent of the respondents are monthly income falls under the category of Rs. 10,001 – Rs. 20,000, 36.9 percent of the respondents are monthly income falls under the category of Rs. 20,001 – Rs. 30,000, 21.5 percent of the respondents are monthly income falls under the category of Rs. 30,001 – Rs. 40,000, 13.8 percent of the respondents are monthly income falls under the category of Rs. 40,001 – Rs. 50,000 and 8.3 percent of the respondents are monthly income falls under the category of below Rs. 5,000. About 63.1 percent of the respondents are married, 23.7 percent of the respondents are unmarried, 5.5 percent of the respondents are a divorcee and 7.7 percent of the respondents are a widow. Most of the respondents are having above five members in their family as large as 43.8 percent, 6.9 percent of the respondents are having 2 members in their family, 4.8 percent of the respondents are having three members in their family and 31.3 percent of the respondents are having five members in their family. About 15.9 percent of the respondents are having one male child, 13.3 percent of the respondents are having two male children, 36.8 percent of the respondents are having three male children, 22.2 percent of the respondents are having four male children and 11.8 percent of the respondents are having above four male children. While 25 percent of the respondents are having one female child, 10.4 percent of the respondents are having two female children, 26.4 percent of the respondents are having three female children, 25.7 percent of the respondents are having four female children and 12.5 percent of the respondents are having above female children. The majority of the respondents are nuclear families as large as 57.6 percent and 42.4 percent of the respondents are joint families.
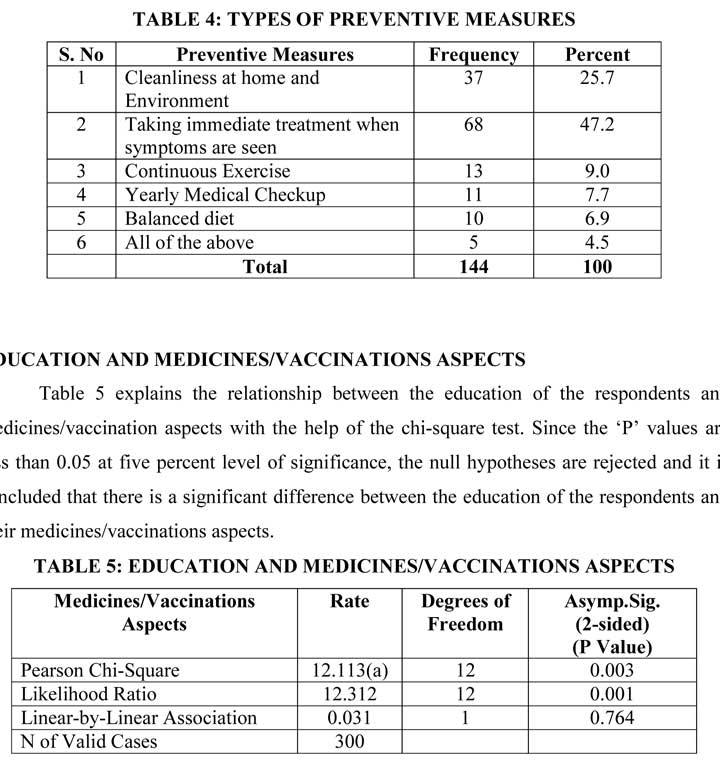
In applying the measures stated above (Table 4) to prevent diseases, among the 144 respondents, 25.7 percent of the respondents are cleanliness at home and environment to prevent diseases, 47.2 percent of the respondents are taking immediate treatment when symptoms are seen, felt that continuous exercise is the best preventive measures to prevent diseases. 9 percent of the respondents felt that continuous exercise. When symptoms are seen the other preventive measures to be taken immediately is 7.7 percent, balanced diet is 6.9 percent. However, 4.5 percent of the respondents take all the above preventive measures to prevent diseases.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
From this article, it is understandable that health care services provided to the people in Thoothukudi district village is considerably good as revealed in the sample respondents who widely use primary health centres for treating almost all diseases. Again the basic need indicators such as health and education are closely related to each other. The government rules should guarantee an improved level of health status, which will definitely achieve the goal of “Health for all” and it will go a long way in meeting the social needs of people.
References
- Anthony Rahul Golden S. & S. Bulomine Regi, Problems faced by Patients in Private Hospitals with special reference to Hospitals in Tirunelveli City, Research Review International journal of Multidisciplinary, Volume: 04, Issue: 02, February 2019.
- Adepeju. M. Lateef & Euphemia. M. Mhlongo, A Literature Review on People-Centered Care and Nursing Practice in Primary Health Care Setting, Global Journal of Health Science, Volume: 12, Number: 2, January 2020.
- Sivasubrahmanian, B, Growth and Equity in Health Care Services in the Union Territory of Pondicherry, Department of Economics, Pondicherry University, 27 October, 2010.
- www.google.com
- www.inflibnet.ac.in
