Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Socio –Economic Impact Assessment of Covid 19 on Various Sectors
Abstract :
The ongoing pandemic ‘COVID-19’ has with no doubt, shown some good time to 7.8 billion people that inhabit this earth. A year has passed and we have witnessed a great loss of resources within just a span of few months. This research article summarizes on the adverse affects on several sectors; right from the manufacturing corporate to the hospitality industry. Majority or say all the companies have restructured their target charts in order to mitigate the risks that just keeps on increasing day by day. In the start, the essence of living definitely came down and everyone, individually is looking forward to surviving this unfortunate catastrophic event which has befallen on them. The usage and budgets even on a family level has reduced and policies of adjustments and self-sustaining notions have come in practice. These times have called upon a more better organizations that can remain operative even in such dark times. With most of us going through a tuff time, strategies and policies require amendments. However, amidst all this mess and uncountable adaptations that came into effect such as ; remote learning, work from home, telemedicine etc, many of us have come to know the true meaning of life and we all have gained good experience on how to handle the unpredicted challenges like that of one we are currently facing. Self-centricity and chaotic schedules are gradually getting demolished and people are collectively coming together to overcome all this. The lockdown periods have given rise to attachments and care for the loved ones which might have been almost somewhat forgotten from our day-to-day busy life.
Keywords :
industrial revolution, Psychology, remote work, Consumer Anxiety, Sense of Unity1. Introduction
The Covid -19 pandemic is the biggest test the world has faced since the Second World War. There is a natural tendency in the face of crisis to take care of Ones’ own first. But true leadership understands that there are times to think big and more generously. Such thinking was behind the Marshall plan and the formation of nation after the Second World War. This is also such a moment. We must work together as societies, and as an international community to save lives, ease suffering and lessen the shattering economic and social consequences of Covid -19.
1.2 Definition
When the Covid -19 pandemic first broke out in Wuhan early this year, the impact of it is immediate and dreadful. We must now act togetherto address another urgent global emergency that we must not sight off. The pandemic has also underpinned the need for business to be agile to remain competitive.
The undeniable truth is that we need to be more responsible and stand united. In a world after Covid -19, our tried and tested ideas, approaches and outlook will be redundant, calling for organizations to place agility at the heart of their operations. The Covid-19 crisis has been impacting every aspect of life and work. The pandemic has accelerated transformation in many industries by condensing several years’ worth of disruption into a few months. It also compounded problems on sectors already reeling under the impact of new tech and the fourth industrial revolution.
Review Of Literature
2.1 Public Relations Industry
The pandemic has been particularly unforgiving for the print media, ushering in a further reduction in ad revenues and in some cases the discontinuation of print editions as part of measures taken by governments to curb the spread of the virus, thus shaving off the vital income in the form of retail sales and subscription renewals. Native, branded or sponsored content and other forms of paid for masked editorial coverage started becoming the norm, combining different types of static video content getting published on news websites and their affiliated social media channels. More recently, some of the Middle East’s most prestigious news media started introducing pay walls for their online editions generating revenue streams, in line with internationally acclaimed titles such as Financial Times, Bloomberg and Wall Street Journal. Whether this strategy proves successful and sustainable for the regions,publishers remains to be seen.
The resilience as first showcased early on during the digital revolution when publishers created appealing subscription only or open to all portals. Various gradients of content from premium to exclusive and from podcasts to videos gave rise to different subscription models thus keeping up with the changing habits of hard core news consumers.
2.2 Psychology Elements of Remote Working
Research suggests that working is generally related to positive health for an individual. However as noted due to the spread of coronavirus millions around the world have been forced into self-isolation and other forms of social distancing. Such measures are critical to halting the spread of the virus in hard hot countries. The sudden change to the normal flow of everyday life is jarring but there are some significant opportunities to this shift. Remote working is one of them. We have explored the benefits of a remote work setup for our group of companies. With tools lie slack messaging platform, Dropbox file sharing and the Google suite of productivity software, we found that remote work streamlines the impact of our workflow. We get more done in an efficient manner.
The most impactful lesson we have learned is not about which application or platform is best, but rather how to manage the psychology of remote work. There are plenty of online tools that facilitate easy communication and collaboration but they don’t replace the human element of office culture. Our challenge is trust. In a physical office environment, trust is hard wired into the space. If an employee is not at his or her desk, productivity alarms go off by themselves.
Actually what happens when employees are at home? The targets and deliverables mitigate the challenge, but can only go so far. Employers need to go extra mile in fostering a work culture based on empathy. Supporting partners and employees must be a company’s core value. This people centric approach is reinforced by a commitment of sustainable growth and practical measures designed to prepare for the future. Ironically, remote work embodies this core value.
The incredible technology that enables these interactions is a powerful vehicle that allows these relationships to flourish. The additional effort of making these experiences possible is invaluable for promoting a vibrant office culture, wherever the office to be. Covid 19 is that test and that’s why this moment can be viewed as an opportunity. As more business embrace technology as part of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, remote work will become the norm instead of the outlier. Hence we should see this as a valuable trial instead of hindrance.
Ensuring employees valued and appreciated during rough remote work transitions is critical to keeping them engaged. While digital norms might enjoy the solitude of working from home, others need social engagement in the office. Nevertheless, we create a sense of unity that fights away the loneliness and build trust.
Productivity Analysis Of Workforce
So far workforce productivity has decreased during the pandemic. The productivity picture isn’t all that rosy right now. The facts contradict what employees say. In the past few months, office doors are shut and the mass exodus of workers began employers and employees feared that the distractions of home would act as a drag on productivity. Survey statistics say, executives can’t help but feel that that something which is not quite right ad they lack the tools and insight of pinpoint the problem. Companies need productivity to increase margins and boost profitability.
Manage Perceptions: Even if company productivity concerns are misplaced and employees are working from home, it doesn’t matter. As economies on the brink of recession, it is the time to plunge into the world of Quantitative productivity score and emerge from Covid-19 with deeper insights as this new world of ours is full of unknowns but the productivity of workforce does not have to be one of them
2.3 Job Redundancies
Sectors such as the aviation and hospitality have already gone in for significant downsizing of operations and with it, reductions in staff salaries/allowances.Hotels too have been letting go of all non-essential staff, for what looks like an extended period until demand returns to some normalcy. The retail sector, for now, has not had any major lay-offs, but the ceasing of commercial activity is telling heavily on their bottom-line.
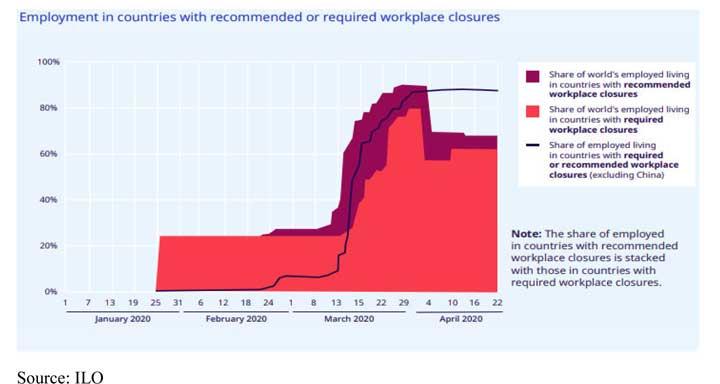
The banks, insurance, automotive outlets, healthcare are already restructuring and downsizing or wanting to cut down their wage-related expenses should make things clear with their workforce. Many industries have halted the recruitments to cope with current pandemic situation. The restrictions on movements and people contact required businesses to allow their staff to work remotely. Some of the multinationals already had contingency plans in place well ahead of the virus crisis, but local businesses have to go through a steep learning curve. And with no clue as yet as to what could be on the other side.
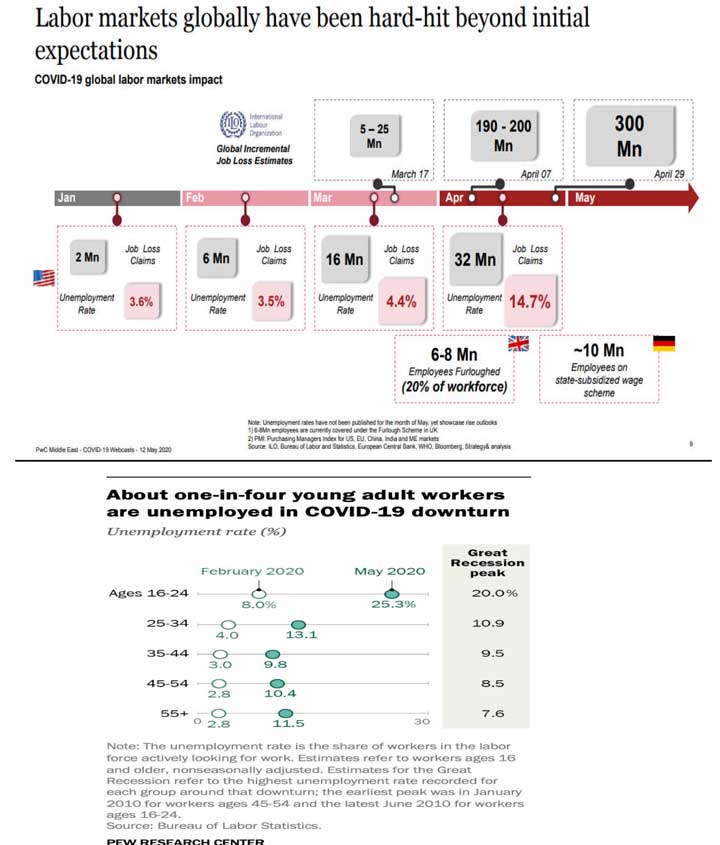 Chapter 3 – Research Methodology
Chapter 3 – Research Methodology3.1 Scope and Coverage Of Research Study
The scope of the research would be covering the impact of Covid 19 pandemic affected in different industries and reflection in the overall business. 3.2 Objectives of Research Study The objectives of the study are:
- To find out the kind and level of changes in the usual routine function of industries
- To identify the impact of business outcomes and depreciation
- To find out reasons that cause changes in the work force at office environment
- To identify expectations of employees during work at home scenario
- To suggest the techniques to overcome the downturn and reducing managerial problems
Research Methodology & Details of Tools
Discuss the research design, research problems, important of the study, scope and significance of the study, source of data, statistically techniques used and objective of the study and limitations of the study.
3.3 Research Design And Reliability
A research design is an arrangement of conditions for collection and analysis of data in a manner that aims to combine relevance to the research. The purpose of the study is providing an observation and changes from routine work environment due to Covid 19 pandemic.
3.4 Nature & Source Of Data/Information
The relevant data has been collected from newspaper, journals, websites, magazines, etc.
3.5 Impact In Oil Industry
Demand for oil continues to fall sharply as more countries enforce stay at home policies due to current pandemic situation, planes are grounded and major industries shut down or partially functioning amid a global campaign to contain the coronavirus. And as the pricewar between major oil producers continues crude prices are expected to plunge further into all-time lows, even below operational cost levels.
Goldman Sachs analysts said in a note by analyzing the current situation to the investment bank’s client that Brent, the international benchmark, “could dip as low as $20per barrel and test operational stress levels”. “This is what the world of oil is facing as demand temporarily collapses and prices fall near lows not seen since the late 1990s. This is an emergency situation for the oil industry given the extreme speed at which it is unfolding,” Jim Burkhard, Vice President and Head of HIS Markit Crude Oil Research and Energy and Mobility Research conveyed.
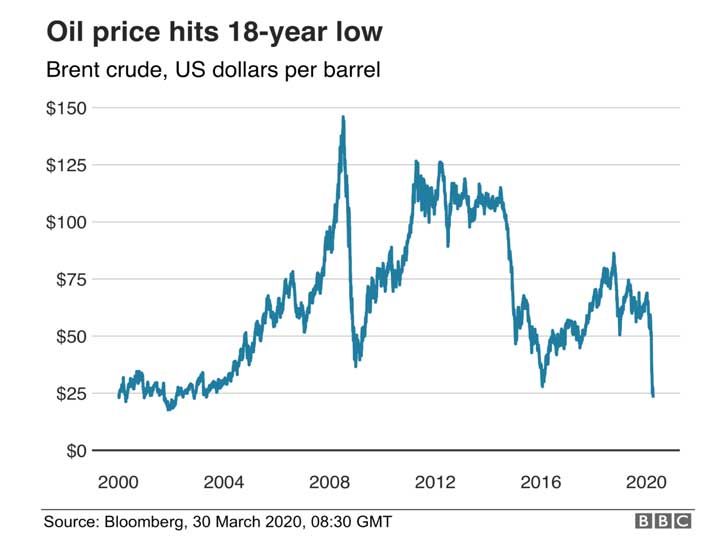 The oil prices are likely to slip further said Andrea de Vries a GCC based strategy consultant in the energy industry. Because as far as coronavirus mitigation is concerned, it is affected drastically in European countries like Germany, UK, France, US and Canada. It is likely that they will introduce more stringent measures to combat the spread of the virus over time. This means global economy will slow down further. The current oil supply levels are already above global demand. These additional barrels are going into storage. As storage gets filled closer to capacity, this will further depress oil price.
The oil prices are likely to slip further said Andrea de Vries a GCC based strategy consultant in the energy industry. Because as far as coronavirus mitigation is concerned, it is affected drastically in European countries like Germany, UK, France, US and Canada. It is likely that they will introduce more stringent measures to combat the spread of the virus over time. This means global economy will slow down further. The current oil supply levels are already above global demand. These additional barrels are going into storage. As storage gets filled closer to capacity, this will further depress oil price.
3.6 Healthcare Marketing
The Covid 19 crisis impacts everywhere it also add a complication for healthcare brands and their communication teams. They are required to adjust their brand and communications strategy to be thematic in light of the virus crisis. The healthcare marketing needs to deploy the trust and empathy mechanisms to spread the message, by establishing their voice as a frontline leader. The key points for enhancing the market presence, brand awareness and position in alignment with the shift in focus:
Deploy Empathy: Communicate exactly to reach the consumers. Awareness short clips to educate community in challenging times
Apply appropriate tone: Message to convey appropriately as per the moment. Consider many ways the coronavirus outbreak is affectingpatients
Showcase and emphasize: Highlight how we are helping the crisis like donating medicines, testing labour camps, additional healthcare services.
Communicate Authority: Audience should know the organization can be trusted and ready to provide information. Keep authorities informed timely and accurate
It is an opportunity for all healthcare teams to rise to the occasion. During pandemic uncertainty, extend the community with a better quality services.
Data Analysis & Interpretation
4.1. Economy Depression
The Corona virus Pandemic officially snapped economic growth streak in the past six months of the year. The question is how deep the damage will get – and how long will it take to recover. The widespread layoffs and business closings, economists expect the figures from past quarters, which will capture the shutdown’s impact more fully, to show that GDP contracted at an annual rate of 30 percent or more.
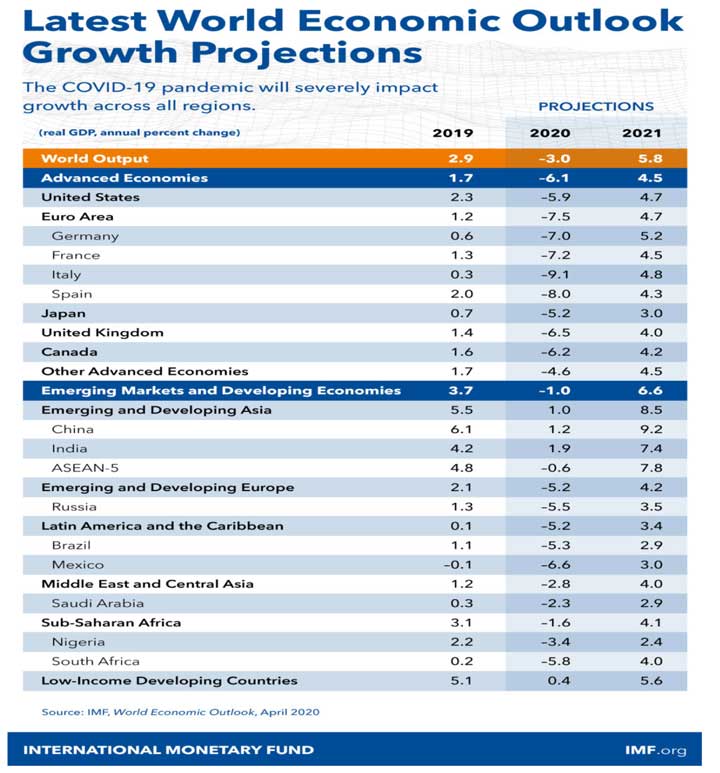 The world economy could shrink by $9 trillion due to the coronavirus pandemic – the worst economic downturn since the great depression according to the IMF World Economic Outlook. The Consumer spending, bedrock of the decade-long economic expansion fell at 7.6per cent rate. Business investment which had already been struggling in part because of the trade war fell for the fourth straight quarter. Imports and exports both declined sharply. The pandemic has hit the service sector particularly hard: Restaurants are closed, flights are nearly empty, stadiums and hospitality industry are not utilized for weeks.
The world economy could shrink by $9 trillion due to the coronavirus pandemic – the worst economic downturn since the great depression according to the IMF World Economic Outlook. The Consumer spending, bedrock of the decade-long economic expansion fell at 7.6per cent rate. Business investment which had already been struggling in part because of the trade war fell for the fourth straight quarter. Imports and exports both declined sharply. The pandemic has hit the service sector particularly hard: Restaurants are closed, flights are nearly empty, stadiums and hospitality industry are not utilized for weeks.
4.2 Public Fears
Doctors have allayed public fears over the possible dangers of wearing face masks for longer periods of time as business activities resume and residents begin to return to their work places. Though the guidelines are declared by government authorities, the public are still skeptical to follow the norms. However, not all offices goers are comfortable wearing a mask continuously for nine to ten hours while they function from their workplaces after weeks of operating from home.
Three layered surgical masks can be worn by all and N95 should be reserved for employees working high risk area.
Change masks every four to five hours. Reusable masks too are washed every day.
People who exercise outdoors can wear dust masks. Ensure social distancing.
Avoid touching mask or adjusting repeatedly. Make sure it is disposed of safely.
Maintain respiratory hygiene and hand washing on a frequent basis. Adequate social distancing to be followed.
4.3 Consumer Anxiety
In the first couple of months when the pandemic struck, anxious customers stocked up on cleaning supplies, frozen foods, etc. but the last few months have seen changes in the spending habits of consumers. According to the management consultant McKinsey & Company, two-third of consumers experienced a decline in savings and income in June.
Shopping locally: Half of the consumers around the world have started to buy more locally sourced products – neighborhood stores and restaurants, according to an Accenture conducted survey of 8800 people across 20 countries.
Reduction in bulk purchasing: Change mindset to buy smaller pack sizes which they are forced to afford. The shopping basket is coming down from peak Covid-19 levels.
Food ordered-in: Customers are ordering delivery from restaurants as dining across country is forced to close or work in limited capacity. In UAE there was a 69 per cent increase in people shopping for groceries online during Covid-19.
DIY Mentality: A “do-it-yourself” mentality has found its way into many homes such as cleaning, cooking, gardening and other recreation. Embraced behavior of consumers will lead to interest in creative, cost-conscious and safe consumption.
4.4 Inflation
The fight against Covid-19 has out developed economies on course for rising prices on a scale they haven’t seen in decades. This has been lead to question in economies right now, than inflation is on the way back. The debate touches every area of policy, from trade rivalries to unemployment benefits. Workers and consumers will see the impact in wage packets and household bills. The scenarios that can result in price increases:
Money Supply: Unlike a decade ago when a similar infusion of money never moved much beyond banks’ balance sheets. The cash is making its way into the pockets of consumers and companies. Today’s policy measures are injecting cash flows that will directly raise the broader measures of money.
Money Velocity: The fell off in 2008 financial crisis never really recovered and has collapsed to unprecedented loss now.
Household Wealth: Spending may bounce back faster than it did. An aggressive policy response has cushioned the blow to household finances.
Household fear: Income may have held up thru the recession.
Loose Central Banks:Analysts expects higher inflation because central banks, guardians of price stability in the low inflation area, are more willing than ever to let it rise.
Loose Labour markets: Policy makers have worked with a thumb rule that assumes some kind of tradeoff between inflation and unemployment, known as Philips Curve. The concept is that prices will only face sustained upward pressure when the economy is using all its resources including labour.
Supply shocks: There is already evidence that disruptions to supply chains are pushing prices up.
4.5 Crunch In Healthcare Industry
It became impossible for hospitals to function normally, and almost simultaneously these institutions decided to stop elective procedures, outpatient services and non-urgent services. This was for mainly two reasons – to save healthy people from the highly contagious infection, and to keep the hospital beds available for any eventually. Healthcare delivery encompasses four kinds of patients: those who visit hospitals for elective surgeries, those who come for emergencies, the out-patients and in-patients.
This left the global healthcare industry financially crippled. Due to pandemic, when a large chunk decided to stay away it automatically translated into a major cash crunch. Senior Consultants and super specialist became practicallyredundant for four months because of Covid-19 management do not require them. It is generally managed by GPs, Intensivists and Physicians. Resultantly hospitals and medical specialty centers took a huge hit.
On the other side healthcare industry learned a few valuable lessons, which will prove to have long term dividends. One of the most important was the need for a proper telemedicine platform, which has remained under-utilized now.
Healthcare Procurement System
For over the two decades the entire world relied almost exclusively on China for its every healthcare procurement need, given the Asian giants’ sheer manufacturing capabilities, cost advantage and dependability; all of which resulting in a nicely humming global supply chain scenario. Realizing how lucrative it was to be the world’s leading manufacturing base, China also greatly enhanced its manufacturing capabilities, quality and making it irresistible to the $105 billion global healthcare procurement sector. When the Covid-19 hits, they shuttered all production facilities across the country to mitigate the spread of the deadly disease.
Around the world proclaimed the glaring shortage of face masks, PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) for front-line workers, penicillin, antibiotics, painkillers and other bulk drugs and the alarm bells kept on ringing for months as the manufacturing was kept in lockdown.
Though, Indonesia and Malaysia are quickly emerging as key alternative healthcare production suppliers to meet global demand, at one point there was a global shortage of medical ventilators the bulk where being produced in China. Germany ramped up their own production of ventilators when supplies drape up at the height of pandemic. The pandemic has put the global healthcare supplies procurement system under the microscope with several important take-away.
4.6 Nail in Exhibitions And Tourism Sector
The pandemic has affected all sectors like never before, the exhibitions and conference industry was also got an impact, owning to the cancellations and postponement of thousands of scheduled events. The damage is getting greater causing the global economy to slow down in a way never seen before, which has led to cutting down the spending and consumption habits. This explains the challenges facing in the tourism and travel industry. The global economy is going through a period of forced restructuring, when the concept of digital transformation is dominating all economic and social activities.
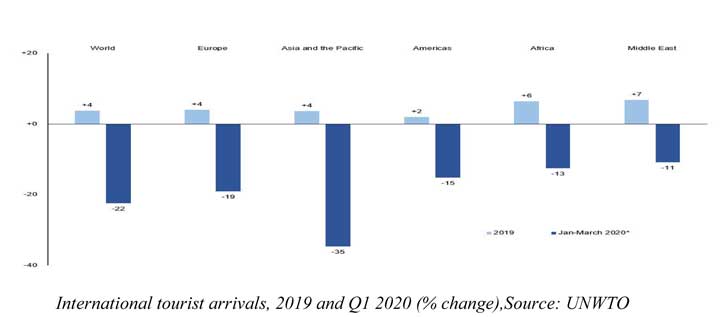
Available data reported by tourism destinations point to a 22% decline in arrivals in the first three months of the year, according to the latest UNWTO World Tourism Barometer. Arrivals in March dropped sharply by 57% following the start of a lockdown in many countries, as well as the widespread introduction of travel restrictions and the closure of airports and national borders. This translates into a loss of 67 million international arrivals and about US$80 billion in receipts (exports from tourism).Although Asia and the Pacific shows the highest impact in relative and absolute terms (-33 million arrivals), the impact in Europe, though lower in percentage, is quite high in volume (-22 million).Tourism has been hit hard, with millions of jobs at risk in one of the most labour-intensive sectors of the economy.
 4.7 Challenges In The Real Estate
4.7 Challenges In The Real Estate
The industry currently faces sustained cost pressures, ongoing labour shortages that are effecting productivity, and emerging trends in fixed bid project that often demand a level of pricing and operation precision difficult to obtain with traditional systems. Amid all the challenges borne out of the Covid-19 outbreak companies are trying hard to survive. Industry leaders are also looking at defining a new vision as well as mapping a comprehensive digital blueprint to realign business and operational process to reflect the opportunities. Engineering and construction is a sector that depends on time and money. If the virus outbreaks continue to create problems,time and money will get effected and hence industry will suffer.
4.8 Findings and Suggestions
The finding of the present revealed on the following:
• Most of the data showing a depression in the business due to pandemic across the globe.
• Salary reinstatements may not happen until business feel they have turned corner.
• The following dimensions of reducing the head counts, working at home, reduced business turnover and overall impact lead to imbalance in routine process.
• The pandemic went through its own share of critical times and every industry is gone through a disruption.
• There is significant drop in entire economy and each industry is adapting different cost saving methodologies to sustain in the market.
4.9 Recommendations
The coronavirus pandemic has brought about unprecedented challenges for business around the world. It has reinforced the basic principles and an eye opener. There has been the biggest lesson of the pandemic:
• Importance of efficient cash flow management
• Positive outlook towards works / responsibilities
• Controlled leveraging and risk management through proper management decisions
• Soft infrastructure should prioritize survival security and practical approach
• Quickly respond to the unprecedented challenges and adapt to a new reality
• Emotional Intelligence and Quotient are vital while taking decisions during critical moments
• Realigning resources in line with changing market conditions and embraced digital transformation
• Remain united to face the uncertain situation and share responsibilities
5.0 Conclusion
As global lockdowns are lifted, business and regulations are rushing to re-adjust to a different economic situation. The pandemic has demonstrated the higher comparative importance of traditional industries such as agriculture and healthcare in extreme situations. Low oil prices, global change in supply chain partners and fundamental self-sufficiency have been the main concern for the GCC nations in recent months. Logistics got complicated and national priorities differed in these stressful situations. Domestic production in such industry is of strategic and shared interest for the GCC.
Organizations need to develop, intimate empathy for their customers. It requires pushing analytics beyond their head office to front lines before, during and after the customer interactions while being able to rapidly predict and identify patterns and analyze potential scenarios.Our goal should be to create exceptional experiences and to infuse core concepts of resiliency throughout the lifecycle of planning and design. This pandemic has given us is a sense of unity on a global scale. People are coming together, to collectively look for ways to create impactful solutions.
References
- https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-tips-for-health-and-safety-at-the-workplace-in-the-context-of-covid-19
- https://www.accenture.com/ae-en/about/company/coronavirus-business-economic-impact
- D. E. Altig et al., COVID-19 caused 3 new hires for every 10 layoffs. macroblog (2020). https://www.frbatlanta.org/blogs/macroblog/2020/05/01/covid-19-caused-3-new-hires-for-every-10-layoffs. Accessed 1 July 2020.
- Asad A. Aburumman, COVID-19 impact and survival strategy in business tourism market: the example of the UAE MICE industry, Published: 05 November 2020
- https://www.rotary.org/en/rotary-and-coronavirus-impact-frequently-asked-questions
- Roger A. Strickland Jr, Malta: COVID-19 Business Impact Survey, Published 17June 2020
