Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Study of factors influencing rural online shopping: A review of literature
Abstract :
Online shopping is booming at a phenomenal rate, and the rural market is no exception. Rural markets have risen to prominence as a result of a massive untapped market with enormous potential. Because there is a scarcity of literature on rural internet shopping, the current information, primarily on online shopping, is used to generate inferences for rural markets. This study looks at the factors that influence consumer buying behaviour, along with perceived risk and trust, and how these affect consumers' purchase and repurchase intentions. The purpose of the online shopping literature review is to gather insights for consumer decision-making and to better understand the research concerns that underpin online purchasing in rural markets. A conceptual framework is thus framed to conclude the study done in this paper.
Keywords :
Rural online shopping, consumer buying behaviour, perceived risk, trust, purchase intention.I. Introduction
Consumer attitudes and beliefs towards online buying
Literature that gives insights about shopper’s attitude and beliefs towards web based purchasing and their effect on buyer behavior has been reviewed to comprehend their capability of acceptance in rural areas.
A study led at shopping center with 435 web users chosen with convenience sampling in Beijing with two focused group interviews of 6 individuals each. With Correlation, Exploratory factor examination, and Logistic regression, the investigation reasoned that Website, Ease of using site, Variety of items, and Consumer Resources impact purchasers' choices to acknowledge internet shopping. Additionally the clients in the Higher Education Group had the most extreme likelihood to shop on the internet (Zhang Helen, 2011).
Another analysis in continuation of the previously mentioned study inspected the connection between site quality and internet shopping of E-tail stores in Nigeria. Out of 384 respondents, 369 were found a good fit to be examined utilizing Spearman's Rank Order Correlation Coefficient alongside SPSS. This uncovered that website design and aesthetics has a strong connection with perceived trust and perceived ease of use for online customers. Web based business firms should take care a greater amount of web security and they should acquire client trust as it gets most elevated positive relationship in web based shopping of clients (N. Gladson Nwokah, Sarah Walter Ntah, 2017).
An examination on "client's mentality towards internet shopping" uncovered that among the 202 respondents who shopped on the web, 89.1%were fulfilled and 96.1% fulfilled clients additionally planned to enjoy web-based shopping later on. It very well may be reasoned that the accessibility of extensive and latest information was the main factor which affected Indian clients to shop on the web. The analyst additionally uncovered that there was a critical relationship between web based shopping and per month family income, frequency of internet usage, and time used up per meeting on Internet usage (Banerjee, Dutta, and Dasgupta, 2010).
The study by Pathan (2019) discussed the rural individual's conduct towards internet shopping. The investigation was directed on a convenience sample of respondents from a variety of fields across different age groups from rural areas of the Vadodara region. An example of 100 respondents was taken into thought from the rural spaces of Karjan, Padra, Waghodia, and Sewasi. It was evident that more noteworthy choice of items played the most influencing factor. Low cost offered by online organizations additionally spurred the country clients to purchase on the web. The customers were happy with the limits and offers on online destinations. The investigation prescribed that rural buyers should be educated in terms of like usage of the product, obtaining information about the product, consumer rights, consumer law and so forth.
Suresh Kumar (2017) in his study discussed the rural consumer’s behavior towards e-shopping. The motivation behind this investigation was to examine the effect of shopper discernments concerning web based shopping. An example of 100 (63 guys and 37 females) respondents were considered about from rural regions. It was found from the research that the organizations need to lessen the risks identified with shopper ineptness by applying strategies, for example, making online sites simpler, presenting Internet kiosks and presence of computer devices and different peripherals in stores. Notwithstanding above, endeavors were to be taken to instruct the online purchasers on the means that should be attempted while making an online buy.
Mir (2014) in his paper recognized the attitude towards E-retailing of the rural consumers in India. Both the essential and optional information were utilized. The primary data was gathered through an organized poll. Secondary data was gathered from research papers, newspapers, books, magazines, diaries and sites. Samples were gathered from country buyers of 18-45 years in Haryana, Utter Pradesh, West Bengal, Karnataka and Jammu and Kashmir to know their perspective about E-retailing. The overall sample size of respondents was 200. Chi Square and Z-test was utilized to investigate the gathered information. The examination discovered that the rural purchasers felt the traditional offline shopping was extremely helpful to them than web based shopping because of less E-education rate, inaccessibility of web access and inaccessibility of product delivery to their places. Unavailability of touch and feel and trial option experience in web based purchasing was additionally a major challenge.
Another paper analyzed the impact of buyer attributes on web based shopping, product qualities and its effect on web based shopping, comparative competitive capacity of online and offline business and their impact on web based shopping and the impact of infrastructure on internet shopping. The analysis proposed that rural customers were viewed as unwilling to take risk and a lower innovative ability which brought down their activity for e-shopping. The connection between imaginativeness among rural customers and acceptance of e-shopping was another area for additional exploration and research (Velayudhan, 2019).
The four A’s of Rural marketing adding value to four P’s.
Although the 4 Ps of marketing (product, pricing, place, and promotion) have long been the gold standard by which all marketing strategies have been executed, Previously, this strategy was intended for urban markets. It is due to the uniqueness of rural markets, most suitable for them (Kashyap, 2012).
Acceptability, affordability, awareness, and availability - the four As of marketing - have emerged as a more customized alternative for developing acceptable marketing efforts for rural markets (Kashyap, 2012).
Naidu (2017) in her study concluded that to compete in rural markets, businesses must offer products that are tailored to customers' demands, are perceived as good value for money, and are functionality, incredibly simple products that meet the needs of rural customers.
Perceived risk and Consumer buying process
Normally, perceived risk is conceptualized as a common impact that is tended to during the beginning phases of the shopper purchasing measure (e.g., (Rich, 1964); (Staelin, 1994).
The customer purchasing measure is frequently portrayed as a five-stage straight interaction (R. D. Blackwell, 2001): stage one - need acknowledgment, stage two - information search, stage three - alternatives assessment, stage four – purchase choice, and stage five - post-post conduct.
In the first stage, buyers initially acknowledge perceived risk when they perceive the requirement for product or service. Within the scene of awkward degrees of perceived risk, buyers apply risk decrease methodologies during the second and third stages, like dependence on suggestions which are from personal sources (Cunningham, 1967); looking for extra information about a service or a product (Rich, 1964); an inclination for brands of national reputation and the security of guarantees and warrenties (Bettman, 1973); (Rich, 1964); (Staelin, 1994). It is generally expected that these practices are adequate for relieving risk, and risk is only occasionally concentrated past the data search stage. (Dr. Lawrence F. Cunningham, 2004).
Even though the effect perceived risk on the customer purchasing measure for services is less considered as compared with the products, the impact of perceived risk is accepted to greater affect the purchaser for services (Murray &Schlacter, 1990). Services are non-normalized, intangible and by and large sold without guarantees, and commonly should be consumed and or experienced before they can be evaluated (A. Parasuraman, 1985). Shoppers end up attempting to assess nearly identical options and their suppliers. These qualities make services harder to assess than merchandised products. Thus, service buyers during the interval of pre-purchase, depend less on loyalty of the brand and the more intensely upon individual data sources and personal suggestions. (Dr. Lawrence F. Cunningham, 2004).
Different kinds of perceived risks
(I) Financial risk
These are the risks which allude to the loss of money on account of a feeble product or service purchase decision (Linda C. Ueltschy, 2004).
(ii) Product performance risk
This kind of risk is characterized as the misfortune suffered because of an item's or a brand's actual performance isn't according to the customers’s expectations (Linda C. Ueltschy, 2004).
(iii) Physical risk
Actually this risk relates to the wellbeing and security of an individual (Linda C. Ueltschy, 2004).
(iv) Psychological risk
This kind of risk relates to a consumer's failure inside him/her if there should be an occurrence of a weak product or a poor service choice.(Linda C. Ueltschy, 2004). Psychological risk is supposed to be simply the possible loss of self image or concept about self as the after effect of the thing purchased.(Michel Laroche, 2004).
(v) Social risk
This risk relates to the mistake in the person by his companions in the event of a poor product or a poor service choice.(Linda C. Ueltschy, 2004). Michel Laroche, 2004 characterized social risk as the expected loss of respect, dignity esteem or potentially friendship accessible to the buyer by different people.
(vi) Privacy Risk
Security is identified with the individual character of the purchaser, the contact subtleties of that person, the credit card number and its passwords, the mail id and its passwords, the product or services the person consumes and purchases and so on The security risk is the danger related to divulgence of the data and information of previously mentioned things. (Fatma A. Mohamed, 2011).
Trust:
The Oxford English Dictionary describe trust as:
Confidence in or dependence on some quality or trait of an individual or things, or the reality of an assertion. The conviction that someone/something is acceptable, true, fair and so forth and won't attempt to damage or deceive you.
In the terms of marketing, trust is characterized as mental state containing goal to acknowledge weakness dependent on one's certain assumption for the expectations or practices of another party (Deshmukh, 2000), or eagerness to depend on a trade accomplice (Ganeshan, 1994). Trust has been conceptualized as a bunch of convictions about an Internet seller in electronic business research (Bhattacharjee, 2002).
As per Bhattacharjee (2002), the trust is known to have following three key measurements: trustee's capacity, altruism, and uprightness. As indicated by Patricia Beatty (2011), too trust is having three components, kindheartedness, capability and trustworthiness.
'Capability' in the investigation done by Patricia Beatty (2011) & 'capacity' in the examination done by Bhattacharjee (2002), are same. So it has been shown that the trust is a multidimensional build whose basic measurement incorporates dependability/believability, passionate solace, quality and generosity (Venkatesh Shankar, 2002).
From the above investigations it is tracked down that the trust plays its vital part while shopping on the web.
Risk perceptions and their impact on web based shopping
Gurvinder S Shergill and Zhaobin Chen (2005) in their investigation In New Zealand", found that web composition, site unwavering quality or satisfaction, site client assistance and site security or protection are the four prevailing elements which impact purchaser view of web based buying.
The examination paper "Internet Shopping Hesitation", considered four gatherings of factors i.e., buyer attributes, relevant variables, perceived vulnerability components, and medium/channel advancement factors, that anticipated three sorts of web based shopping delay i.e., in general faltering, shopping basket relinquishment, and wavering at the last installment stage. (Hoan Cho etal, 2006).
Security and unwavering quality are two basic worries that might forestall customers to shop on the web (Sin Leo and Alan Tse, 2001), Consumer Motivation and Concern Factors for Online Shopping in Turkey, discovered that when individuals have individual security concerns, they keep away from web based shopping. Customers underline more on the looking through measure instead of doing genuine shopping and consequently they partake in the investigating the shopping sites CerenTopaloglu, 2012). In Pakistan, the principle boundary during the time spent web based shopping is the security issue (Adil Bashir, 2013). . The most elevated apparent dangers with respect to internet shopping that Indian online clients have are those identified with security of charge card data, classification of individual data and confidence in e-retailers (Sita Mishra, 2013). The significant reasons that block purchasers from web based shopping incorporate installment security concerns, Delivery time, undesirable items, infection and spams, undesirable messages and innovative issues (Chayapa Katawetawaraks and Cheng Lu Wang, 2011)
Purchase and repurchase intentions of consumers
There are many variables that decide for what reason do clients get once again to a site or a store. An investigation discovered that additional time spent online by purchasers improves the probability of buyers returning to a site or becoming clients by purchasing an item. Very much like that, planning a site in such a way to acquire consumer loyalty and consideration, improves the probability of making rehashed clients and buys (Huizingh& Hoekstra, 2003).
Another examination done on 98 web clients from U.S.A which were chosen based on accommodation inspecting with the target It tracked down that the significant purposes behind customers to return to a site, do a buy, buy more articles, and willing to give input; are Free Delivery, Discounts given, shown pictures of the item, simple and free return of the things (Changchit, ChuleepornDouthit, Shawn J, Hoffmeyer, Benjamin, 2005)
A positive involvement in a site assumes an indispensable part in shaping and winning the buyers trust while doing shopping on the web and on the off chance that buyers trust the site, they will see simplicity of utilizing the site, see satisfaction and see the site to be safer which would at long last outcome into an expectation to execute with the specific site (Pooja Mordani, 2008).
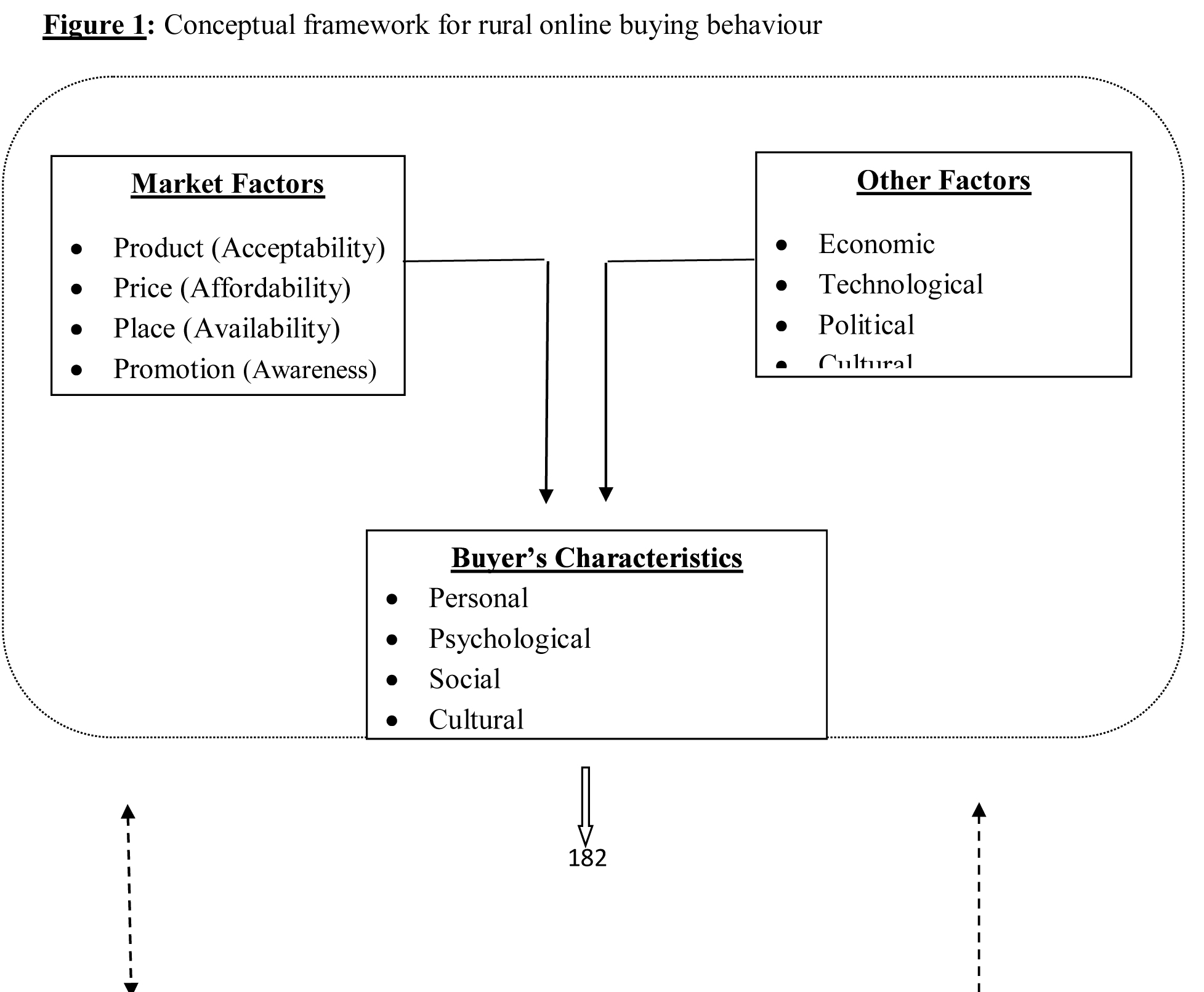
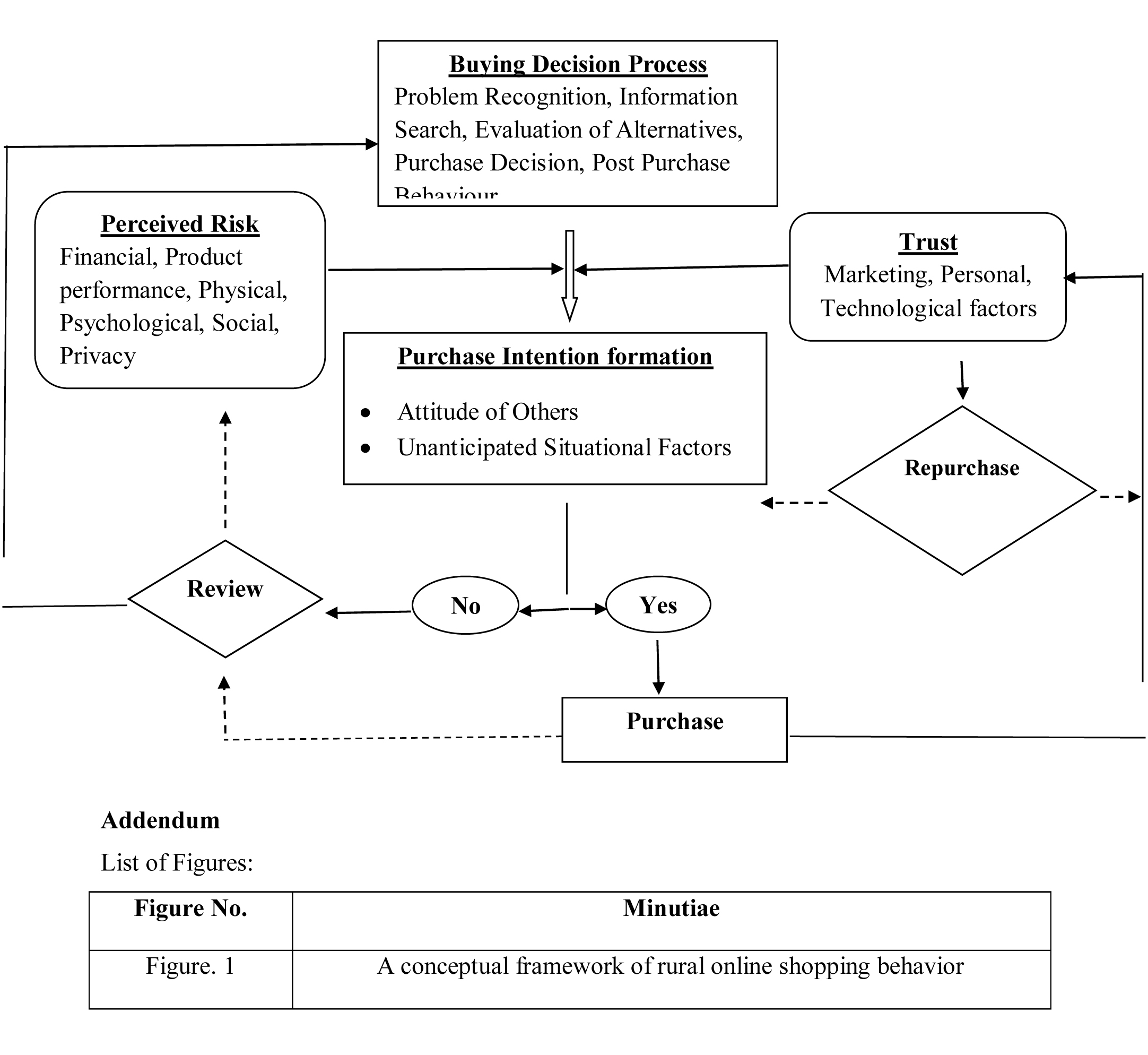
Concluding Conceptual framework based on literature review
In this review paper this conceptual framework is a vibrant model outlined based on accessible literature. The structure portrays that Consumer purchasing conduct is impacted by Market factors viz. 4p's, Product, Price Place and Promotion alongside other components viz. Economic, Technological, Political and Cultural variables. And furthermore the Buyer's attributes viz. Individual, Psychological and Socio-Cultural. Which further prompts development of Purchase Intention which depends on the Attitude of others and Unanticipated Situational Factors. The online buy intention in rural is significantly affected by Perceived risk which has a few variables like Financial, Product execution, Physical, Psychological, Social and Privacy included into it. These risks could be offset by Trust which can be capitalized by Marketing, Consumer's personal and Technological factors. Which further prompts actual purchases and intentions to repurchase. Otherwise, this requires a rewind of the purchase decision process alongside the variables of perceived risks, assuming any, related with the purchasing decision process. Furthermore, the perceived risk and trust, to a great extent, are again affected by Market factors, Other factors and Buyer's characteristics.
References
- Banerjee,N., Dutta, A & Dasgupta, T(2010). A Study on Customers Attitude Towards Online Shopping – An Indian Perspective.”Indian Journal of marketing 40(11), 43-52.
- Bauer, R. A. (1960). Conceptualization and measurement of perceived risk in shopping. Marketing Management Journal. , 138-147.
- Bettman, J. R. (1973). Perceived risk and its components. Journal of Consumer Research , 184- 190.
- Changchit, C., Douthit, S. J., &Hoffmeyer, B. (2005). Online shopping; Company business management. Journal of Academy of Business and Economics, 5(3).
- Cunningham, S. M. (1967). The Major Dimensions of Perceived Risk. In D. F. E. Cox (Ed.), Risk Taking and Information Handling in Consumer Behavior. Boston: MA: Division of Research, Graduate School of Business Administration.
- Hardikkumar V desai and Marolia Jamshid R (2012) E-commerce and the Rural Sector, International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Engineering & Technology (IJARCET) Volume 1, Issue 9, November 2012
- Hoan Cho etal (2006). “Online Shopping Hesitation”, Cyber Psychology &Behaviour, Volume 9, Number 3, 2006.
- Huizingh, E. K., & Hoekstra, J. C. (2003). Why do consumers like websites?. Journal of Targeting, Measurement and Analysis for Marketing, 11(4), 350-361.
- Irshad Ahmad Mir (2014). Anticipation of e-retailing in rural India and rural consumers attitude towards e-retailing; Research journali’s journal of management, Vol. 2 | No. 3 April | 2014 ISSN 2347-8217.
- Kashyap, P. (2012). Rural marketing (2 ed.). Dorling Kindersey (India) Pvt Ltd., Pearson, New Delhi.
- Katawetawaraks, Chayapa& Wang, Cheng. (2011). Online Shopper Behavior: Influences of Online Shopping Decision. Asian Journal of Business Research. 1. 10.14707/ajbr.110012.
- Leo Sin & Alan Tse (2002). “Profiling Internet Shoppers in Hong Kong”, 10.1300/J046v15n01_02, pages 7-29
- Linda C. Ueltschy, R. F. (2004). A Cross-National Study Of Perceived Consumer Risk Towards Online (Internet) Purchasing. The Multinational Business Review.
- Michel Laroche, G. H. (2004). Exploring How Intangibility Affects Perceived Risk. Journal of Service Research.
- Mishra S. (2013). “Analyzing Perceived Risks and Website Attributes in E-Retailing: A Study from India”, Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, August 2013, vol. 18, no.2
- Mordani Pooja (2008): Investigation of consumer perception towards internet based Eshopping; Proceedings of the 4th National Conference on managing customer loyalty, Maharishi Markendshwar University, 28-50.
- N. GladsonNwokah, Sarah Walter Ntah (2017). Website Quality and Online Shopping of E-Tail Stores in Nigeria, Journal of Service Science and Management, Vol.10 No.6, December 15, 2017
- Naidu Aditi (2017)Strategies for Marketing to the Rural Customer in India: The 4 As Model of Rural Marketing, Journal of Rural and Industrial Development, Volume 5, Issue 1, pp 35-39.
- Nidhi, Dr. B.M. Singh, Dr. Manoj Mishra (2016). Online market: Analysis of factors responsible for buying. International journal of Business Quantitative Economics and applied Management Research. Vol -3.Issue-3.
- R. D. Blackwell, P. W. (2001). Consumer Behavior (9th Edition). Ohio: South Western: The Dryden Press
- R. Sureshkumar (2017) Rural consumer attitude towards online shopping: an empirical study of rural area, International Journal of Innovative Research in Management Studies (IJIRMS) Volume 1, Issue 12, January 2017, pp.1-5.
- Rich, D. F. (1964). Perceived risk and consumer decision making-the case of telephone shopping. Journal of Marketing Research. , 32-49.
- S. Gupta, Ruchi Nayyar. (2011). Determinants of Internet Buying Behavior in India. Asian Journal of Business Research, Vol. 1, No. 2, 2011.
- Samuel, S. &Janardhanan, KottayathumVeedu. (2016). Online shopping -A strategy need for rural customer. 9, 2082-2085.
- Staelin, G. R. (1994). A model of perceived risk and intended risk –handling activity. Journal of Consumer Research , pp 119-134.
- Zeenat Pathan (2019). Rural Consumer Behaviour Towards Online Shopping in Vadodara District, International journal of Management Technology and engineering, Vol. IX, Issue I, Page (1929-1938).
