Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
A Study on Consumer Preference towards Branded luxury Car in Chhattisgarh
Abstract :
In the past few years post-LPG (Liberalization, Privatization, Globalization) India has emerged as one of the largest market for Luxury goods since there has been a huge growth in IT industry after globalization consequently giving rise to the purchasing power of the people. The materialism has increased with change in disposable income and there has been a significant increase in luxury consumption. Car has always been a luxury for Indians but with growing transportation needs the demand has increased in every household. A car has now become status symbol in the society and is a matter of envy. A car is common man’s dream which has converted into want due to easily availability of finance/loans facilities. But with time there has been a paradigm shift from buying budget cars to buying high end/luxury cars. With development in roads and infrastructure people are now switching to luxury high-end expensive foreign brands who offer more features like power, performance, off-roading etc. A few years back Indian market was not prepared for expensive cars but with increasing number of millionaires the sales of brands like Mercedes, Audi, BMW, Jaguar, and Land Rover has increased. These brands are not only owned by celebrities, sportsmen, business tycoons/industrialists but even upper middle class families and middle class consumers are buying luxury cars to add esteem and show their status in society. This study is aimed at finding more factors responsible for this kind of consumer behavior and to analyze the sudden shift from necessities to luxury lifestyle. This behavior of luxury consumption is not only limited up to urban areas or metropolitan cities but the rural areas or cosmopolitan people are also aiming high on their esteem and are investing more money for lavish lifestyles. The consumption of luxury products like air-conditioner and cars have no boundaries.
Keywords :
Consumer Preference, Consumer Behavior, Luxury Brands, Lifestyle Brands, Automobile Sector, Purchase Decision, Luxury Car SegmentIntroduction
As India is growing rapidly in this era of globalization the growth of consumerism and materialism is at its peak due to the rise in purchasing power of people. In India the consumers have moved beyond their needs due to growing aspirations of luxury andpeople are engaged in lavish lifestyles following the western counterparts by possessing branded products. This new mass interest fueled the growth of luxury consumption in India which is an indication of the changing Indian consumers. Nowadays in India showing off status & prestige has become integral part of society and hence the people are busy in raising their standards and every individual wants to live lavish lifestyle. Hence growing up from food, shelter and clothing the people are fulfilling their desires by using expensive products. The researcher identifies and proposes to test the relationship between factors of luxury consumption and Indian consumers. The scope of the study is themed towards consumption of luxury car brands. The researcher applied descriptive research design involving survey through questionnaire for data collections. Researcher took Raipur region being the capital city of Chhattisgarh and highly populated city for the research. The researcher revealed that the brand, price, built quality, family size, durability, availability of service, fuel economy, cost of maintenance, roads, performance, safety, space, design, technology, resale value and features of car are the most critical factors towards purchase intentions of luxury cars. Findings suggest most of upper middle class and upper class consumers purchase the luxury brands of car to fulfill esteem needs. The Brand consciousness provides consumers a common expression to signify their status by position of the luxury brands. The results also show that brand consciousness have a commendable relationship between income and luxury consumption. India in 2019 became the 4th-largest auto market in passenger and commercial vehicle overtaking Germany. The two-wheeler segment is dominating the industry in terms of production because of an increasing middle-class community and a younger demographic. India is a giant car exporter and this export will increase in the immediate future. India has already become a world leader in car markets in2020.
In India, the two-wheeler, four-wheeler and commercial vehicles contribute huge in domestic automotive industry. Consumption of cars in every segment has increased be it Compact car, Mid-size hatchback, Sedan, Vans, Multi utility vehicles (MUV), Compact SUV, Sport Utility Vehicles (SUV) has increased with increase in income. The commercial vehicles such as pick-ups, buses and trucks contribute to 40% of total vehicles sales, and play a significant role in transportation/logistics and hence contribute to the GDP. Indian government is planning to switch to electric vehicles (EV) by 2030.Many companies have already launched e-scooters & e-rickshaws looking forward to future technological change. The premium car (BMW, Audi, Mercedes etc) sales in India have increased drastically in past few years with increase in purchasing power and lifestyle of the population. Since globalization there has been a significant change in the consumption pattern of the population. People have become brand conscious and prefer imported brands more than national brands which is a symbol of prestige
The market in Chhattisgarh is also mixed with potential buyers from rural and urban areas. Chhattisgarh being agriculture based state which is also known as ‘Bowl of Rice’. The capital of Chhattisgarh, Raipur has been developing rapidly since Chhattisgarh came into existence in the year 2000. Since then there has been a lot of infrastructural development as well as opportunities in Raipur. It has become a hub for business as well for various activities. Although Raipur is not of a Metropolitan nature it has developed as a Cosmopolitan city. But there has been development in tourism and places of amusements like Malls and super-markets. In this chain various global brands have reported their presence which includes Dominoes, Pizza Hut, KFC, Subway, PVR, Shoppers Stop, Westside, Mc Donald’s, D-Mart, Big-Bazaar, Vishal Mega Mart, Best Price, Café-Coffee Day, Lotus etc have already marked their presence and penetrated in various segments. As far as car brands is concerned most global brands like Mercedes, BMW, Audi, Jaguar-Land Rover, Volvo, have also entered the market since a few years and are also finding customers to sell their products. The buyers of the foreign(imported) brands are not limited upto cosmopolitans like Raipur, Bilaspur or Bhilai, but the consumption in rural areas or towns has also increased significantly. In recent years the trend of diffusion has neutralized among urban-rural areas. That means the rural areas are not isolated and are equally exposed to imported goods as urban areas, due to e-commerce rural areas are also equally exposed to the products consumed worldwide.
This research is based on secondary data. This study only focuses on urban buying behavior of customers. The study does not say anything about rural buying behavior of customer because rural norms/status/attitude & acceptance of the rural customers differs with urban customers. The scope of research is limited for Chhattisgarh area. It provides help to understand consumer behavior towards lifestyle products/brands. The research is also important to identify Market size, growth and Market Potential of Lifestyle car brands.
LITERATURE REVIEW –
The three authors Sukhdial, Chakraborty and Steger (1995) developed a List of Values (LOV) which includes self-respect, sense of accomplishment, being well respected, security, warm relationship with others, sense of belonging, fun and employment in life and excitement.
It is said that the values mentioned influence the people’s daily lives and that luxury products “may be mainly purchased for value expressive reasons” (Aaker et al., 1992).
Referring to Sukhdial, Chakraborty and Steger (1995) people who desire a luxury car to use it as a symbol of their achievements are an example for people who value a sense of accomplishment. However people who value fun, enjoyment and excitement desire a luxury car which embodies fun and is exciting to drive (Sukhdial, Chakraborty & Steger, 1995). An example for the desire for security is that some consumers think that German cars are well engineered. They are safe in case of an accident (Sukhdial, Chakraborty & Steger, 1995).
In the research of the three authors about “examining owner’s personal values in addition to their evaluations of car attributes” (Sukhdial, Chakraborty & Steger, 1995) they found out that fun-enjoyment-excitement is important for owners of German luxury cars.
& Steger, 1995). Furthermore comfort and low maintenance cost were not that important related to a luxury car. Whereas safety, power and speed were relevant attributes of a car (see appendix: Exhibit 1 and 2).
Sagar, Ambuj, D. & Chandra & Pankaj (Research Entitled: Technological Change in the Indian Passenger Car Industry)
Sagar et al. (2004), discussed, as to how the Indian car industry has advanced technologically driven by a confluence of factors such as intense competition, demanding consumer preferences,
Government policies (especially tightening emission standards), and the global strategies of the various players. They elaborated that car manufacturers in India are based on designs, incorporating advanced technologies, that are often comparable with those available globally
and Indian car exports are also growing rapidly.
Mandeep Kaur and Sandhu H.S. (Research Entitled: A Study on Factors Influencing Buying Behaviour of Passenger Car Market)- Mandeep Kaur and Sandhu (2006), attempts to find out the important features which a customer considers while going to purchase a new car. The premium car owners perceive that safety and comfort are the most important features of the passenger car followed by luxuriousness.
Dr. S. Subadra, Dr. K. M. Murugesan, Dr. R. Ganapathi (Research Entitled: Consumer Perceptions and Behaviour: A study with reference to car owners in Namakkal District)
S. Subadra et al. (2007),postulates the changing perceptions and behaviour of the consumers with special reference to the car owners. Through this research paper the authors discussed how India is witnessing a change in consumerism. Market has now become predominantly consumer-driven. The focus has now been shifted from product based marketing to the need based marketing. Consumer is given many options to choose. This paper discussed the consumer perceptions and behaviour of the car owners which was supposed to give a feedback on how marketing strategies work. This study throws light on various features that the manufacturers should concentrate on to attract the prospective buyers. The authors trace the factor-analysis – factors influencing purchase. The general purpose of this is to find a method of summarizing the information contained in a number of original variables into a smaller set of new composite dimensions with minimum loss of information. It derives out of several variables which
are identified as the influencer in purchase decision and satisfying the consumers. Some 14 variables under the sub-head „factors influencing purchase‟ have been discussed.Hence, an understanding of the consumer behaviour enables a marketer to take marketing decisions which are compatible with its consumer needs. There are four main classes of consumer behaviour
determinants and expectations i.e., cultural, socio-economic, personal and psychological. The manufacturers and marketers who study the behaviour of consumers and cater to their needs will be successful.
Shyamala Mathan Sankar (Research Entitled: Consumer Perception of Global vs. Local Brands: The Indian Car Industry) Shyamala Mathan Sankar (2006), through this research study examines consumer perception of global brands vs. local brands in the Indian car industry. Consumer brand perception is having substantial implications in Marketing. This study explores and helps in understanding consumer perceptions of global and local car brands in India by accomplishing the secondary objectives. The secondary objectives were achieved by highlighting the factors that affect consumer preferences for global brands, by examining the effects of
country of origin on consumer perception for global brands and local brands, and by studying the effects of consumer ethnocentrism towards global brands. The findings of this particular study advised that the consumers who possessed global car brands preferred their car brands due to
factors such as global presence, worldwide reputation, and quality of being a foreign make. It was found the prestige of status had a very little or no influence in their preference for global car brands consumers made favourable perceptions of the country, wherein they tend to associate factors such as superior quality, technical advancements modernization etc., to the country from which the brand had taken its origin. Consumers who owned a local car brand evaluated the local brand in a favourable manner, wherein they tend to associate the brand to India‟s strong automobile sector that makes quality and technically efficient cars. The study found to have both
non-ethnocentric consumers and consumers who were low on CET.Most of the study results show, the local brands to be good in India,but not as good as the global ones in quality, technical expertise and designs of the cars.
Dr. M. Akber, P. Ashok Kumar (Research Entitled: “A Study on Attributes of Car Buyers in Vellore District”) M. Akber and P. Ashok Kumar (2012), presents this study of
consumer buying behaviour , that has proved that many factors like price, income, distribution of income, competition with alternatives, utility, consumer preference (economic factors) and factors like culture, attitude, social values, lifestyles, personality, size of family, education, health standards etc., play a major role in buying behavior of customers. The scientific study on the purchase decision towards the purchasing of cars has revealed fruitful findings and recommendations, which could be used for enhancing the products to meet the requirements of car buyers. This study explores aspects like:
i. To investigate the reason for the time gap between intention and actual purchase of a car.
ii. To identify the attribute sources of information for purchasing a car.
iii. And to measure the significant motivating factors that contribute for the preferences of the cars.
The overall analysis that contributes for the preference of any car has
come with five significant factors:
- Economy in fuel
- Economy in maintenance
- Purchase price
- Warranty
- Style
Pick-up, durability and size of the cars have been preferred very less by the respondents. Resale value, company reputation, after sale value, and prestige are the attributes which were not at all preferred by any consumer using any brand of car. The study has brought out the attributes of buyer of market and different brand of a given market. If the Marketing Management of respective car companies lesser the car as per the aspiration of buyer revealed through the perfect study they would stand to benefit both in intern of volume and value of turnover.
Dr. K. Singaravelu (Research Entitled: “Consumer Behaviour: A study of influence of special features of passenger cars in Coimbatore”)
This research is an attempt to assess the buying behaviour of passenger cars. And to examine the pre-purchase behaviour of passenger car buyers, study gives an analysis of influence of special features of passenger cars. It is illustrated that Government employees have got their salary increment after introduction of sixth pay commission, which make them shift from two wheelers to four wheelers. Hence, rising per capita income and changing demographic distribution are conducive for growth of automotive industry. In this research paper influence of the sources of information and influence of special feature of passenger cars have been discussed. Sources of information are classified into three categories, i.e., personal sources,commercial sources and public sources. It is concluded that family members, friends and relatives are the main motivators to purchase the passenger cars. Likewise the factor analysis condensed and simplified the influence of twenty seven features of passenger car and grouped into five factors explaining 62.585 percent of the variability of all the 27 features of the passenger cars. The manufacturers should put in more efforts to increase the market share in terms of introducing more innovative colours and new models. Since, most of the customers feel that maintenance cost is pretty high. The management should take efforts in reducing and create awareness among customers by showing them how cheap it is to maintain their passenger cars when compared to its competitors.
Piplai (Research Entitled: Automobile Industry: Shifting Strategic Focus) Piplai (2001) examines the effects of liberalization on the Indian vehicle industry in terms of production, marketing, export, technology tie-up, product up-gradation and profitability. Till the 1940s, the Indian auto industry was non-existent, since automobile were imported from General Motors and Ford. In early 1940s, Hindustan Motors and Premier Auto started by importing Know-How from General Motors and Fiat respectively. Since the 1950s, a few other companies entered the market for two wheelers and commercial vehicles (CVs). However most of them either imported or indigenously produced auto components till the mid-1950s, when India had launched import substitution programme, thereby resulting in a distinctly separate auto component sector. Due to the high degree of regulation and protection in the 1970s and 1980s, the reforms in the early 1990s had led a boom in the auto industry till 1996, but the response of the industry in terms of massive expansion of capacities and entry of multinationals led to an acute over capacity. Intense competition had led to price wars and aggressive cost-cutting measures including layoffs and large scale retrenchments. Indian companies have started focusing on the price-sensitive consumer. Utility Vehicles, foreign companies continues utilising their expertise on technology-intensive vehicles for individual and corporate usage. Thus, Piplai (2001) concludes that vehicle industry in India has not gained much from the reforms, other than being thrusted upon a high degree of unsustainable competition.
Balakrishnan Menon, Dr. Jagathy Raj V. P. (Research Entitled: “Determinant Mean percentage score factors of the consumer purchase behaviour of passenger cars”) Through this paper the researchers discuss the main purpose hat is to come up with the identification of possible parameters and a framework development, that influence the consumer purchase behaviour patterns of passenger car owners in the state of Kerala, so that further research could be done, based on the framework and the identified parameters. With the multiple choices available to the Indian passenger car buyers, it drastically changed the way, the car purchase scenario in India. It transformed the automobile scenario from a sellers‟ market to buyers‟ market. Passenger car customers started developing their own personal preferences and purchasing patterns, which were hitherto unknown in the Indian automobile segment. Researchers conceptualized a consumer purchase behaviour model with major parameters influencing the behavioural patterns of the passenger car owners. In this model it is represented that the consumer behaviour is a blend of Economic, technological, political, cultural, demographic, and natural factors as well as his own characteristics which is reflected by his attitude, motivation, perception, personality, knowledge and lifestyle. The study benefits the stakeholders of car manufacturers, dealers, financing agencies, to formalize and sterilize their policies towards an effective marketing strategy. All the parameters developed in this paper and the model which has been conceptualized was tested through an extensive research and quantitative analysis to establish its acceptability. It is concluded that marketers can rationalize their existence only when they are able to understand consumer behavior.
The principal contribution of this study lies in extending our understanding of consumer behaviour through an empirical examination of the contribution of group and social influences on consumer behaviour towards the purchase of new luxury cars. This thesis under study demonstrates the significance of the contribution of group and social influences on consumer behaviour of luxury products as exemplified are luxury cars in two main markets, the UK and Thailand. Theoretical contributions of this thesis are as under: - This paper confirms Fishbein‟s behavioural model that there can be different types of beliefs held by an individual. - The theoretical contribution of this thesis lies in an extension of Maslow‟s hierarchy of needs and motivation. - This thesis develops links between culture and consumer behaviour by linking branding and consumer needs using brand components, i.e. - functional, social and experimental images.
Badri Narayan G., Pankaj Vashisht (Research Entitled: “Determinants of competitiveness of the Indian Auto Industry”) As in all other countries, the Indian automobile industry is also one of the key drivers of industrial growth and employment, which will further gain in importance in the coming years. Its‟ recent records of rapid growth of output, productivity improvements and expanding share in global market has perhaps not been so well documented. This study fills that gap. The study helps us understand how the industry‟s success is quite directly linked to the trade and industrial policy reforms initiated in the early 1990s. more importantly, this study identifies the critical constraints that prevent the industry from further expansion in the global share and emerge as one of the major production and export hubs in the coming years. According to this study, the major advantage of the Indian economy is educated and skilled workforce with knowledge of English language. So, our disadvantages include poor infrastructure, complicated tax structure, inflexible labour laws, interstate policy differences and inconsistencies. This study analyses the determinants of competitiveness in the Indian automobile industry. The effective rate of protection on automobiles is much higher than on components. With the higher countervailing duty and other cesses/levies, the effective rate of protection for automobile sector would be even higher. The differential rate of effective protection distorts resource allocation and investment pattern in the industry. The import tariff for the assembled vehicles is 60%. Given the low level of protection both for the auto components and CKD/SKD kits, this reflects a policy bias in favour of auto assembles. These are few of the recommendations provided by the authors. It has been emphasised to work out for the several constraints, e.g. to strengthen R&D and design capacity, skill shortages, India‟s current levels of tariff on capital goods, higher material goods, infrastructure deficit, for strengthening of the anti-dumping mechanism and lack of credit availability etc. At last, the authors opine that, the recommendations provided in this paper, if accepted and implemented, could contribute to India‟s emergence as one of the major automobile producing economics in the world. Given our domestic demand and the entrepreneurial talent, this would be a natural outcome.
Mahipat Ranawat, Rajnish Tiwari (Research Entitled: “Influence of Government Policies on Industry Development: The case of India’s Automotive Industry”) According to this research, the evolution of India‟s automobile industry is identified to have occurred in four phases. In the first (1947-1965) and second phase (1966-1979), the important policies identified were related to protection, indigenisation and regulation of the automotive industry. On the one-hand, these policies helped India to build an indigenous automotive industry. While on the other it led to unsatisfactory industry performance. In the third phase (1980- 1990), the single most important policy identified was the one with regard to relaxation in the means of technology acquisition. The foreign competition inducted into the industry transformed its dynamics. Lastly, in the fourth phase (1991 onwards), the liberalization with regard to foreign investment had a significant influence on the Indian automotive industry as we see it today. This work traces the evolution of the automotive industry from its inception to present day and identifies the important policies made by the Indian Government. This work also studies the influence of important policies on the development of the industry. It is also of interest to understand the considerations made on the part of the Indian Government that underlie such policies and to explore the role played by the Government in the development of the industry. With every major shift in policies made by the Indian Government, the automotive industry has come out stronger and better. While the shift in policies seems to have mostly been brought by choice events, the Indian Government has at least to be credited for making the right decisions and implementing them correctly. It‟s paradoxical that the Indian middle class, the most attractive features for foreign investment in the liberalization phase, was a outcome of the statist ideologies in the regulatory phase. Author has made a detailed historical account to provide the context and considerations under which the policies were formulated by the Indian Government.
Dr. H. S. Adithya (Research Entitled: “Customer Perception and Behaviour of car-owners- an Empirical study in Bangalore city”) Like previous ones this study also attempts to analyse the variable that affect the buyer behaviour today. It throws light on various features that the manufacturers should concentrate on to attract the prospective buyers. It concludes the consumer behaviour plays a vital role in marketing cars. Consumer behaviour consists of the human behaviour that goes in making purchase decisions.
Understanding of the consumer behaviour enables a marketer to take marketing decisions which are compatible with its customer needs. Four major classes of consumer behaviour determinants and expectations are cultural, socio-economic, personal and psychological. The socio-economic determinants of consumer behaviour consists of age, marital status, occupation, education, income, family size, realizing the importance of passenger car industry in the present economic situation, the researcher has analysed the perceptions and behaviour of consumer related to the product. From the discussion made in the paper, there are certain product attributes which are identified in the study as influencing the purchase decision and satisfying the consumers. Manufacturers show concentrate on the product attributes as they influence the choice of more prospective buyers. The population growth in India and the increasing number of middle class consumers have attracted the attention of car manufacturers and marketers. Those manufacturers and marketers who study the behaviour of consumers and cater to their needs will be successful. It is concluded that consumer behaviour has a greater role to play in the LPG era of economic activities.
Dr. K. Singaravelu (Research Entitled: “Consumer Behaviour: A study of influence of special features of passenger cars in Coimbatore”) This research is an attempt to assess the buying behaviour of passenger cars. And to examine the pre-purchase behaviour of passenger car buyers, study gives an analysis of influence of special features of passenger cars. It is illustrated that Government employees have got their salary increment after introduction of sixth pay commission, which make them shift from two wheelers to four wheelers. Hence, rising per capita income and changing demographic distribution are conducive for growth of automotive industry. In this research paper influence of the sources of information and influence of special feature of passenger cars have been discussed. Sources of information are classified into three categories, i.e., personal sources, commercial sources and public sources. It is concluded that family members, friends and relatives are the main motivators to purchase the passenger cars. Likewise the factor analysis condensed and simplified the influence of twenty seven features of passenger car and grouped into five factors explaining 62.585 percent of the variability of all the 27 features of the passenger cars. The manufacturers should put in more efforts to increase the market share in terms of introducing more innovative colours and new models. Since, most of the customers feel that maintenance cost is pretty high. The management should take efforts in reducing and create awareness among customers by showing them how cheap it is to maintain their passenger cars when compared to its competitors.
Ms. A. Josephine Stella, Dr. K. Rajeshwari (Research Entitled: “Consumer Behaviour towards passenger cars- A study with reference to Virudhnagar District of Tamilnadu”) The research focuses on the consumer behaviour towards passenger car and involves the critical analysis of factors influence the purchase behaviour. The research is conducted for better understanding of the relationship between the consumer satisfaction, brand image and information from mass media towards the purchase evaluation at various stages of purchase decision. By understanding the consumer‟s satisfaction of the product will help the automobile manufacturers in developing their product to meet customer‟s needs and designing the proper Marketing programs and strategies. The researcher has found out that the most important factor that influences the consumers to use passenger cars is the price of the cars followed by low maintenance, better quality and durability. Further, there is significant relationship between demographic characteristics towards various features of passenger cars. It is concluded from the following study that customer satisfaction is the important factor which affects the financial position and goodwill of the company. Relationship Marketing is an influential asset for consumer behaviour analysis at it has a keen interest in the rediscovery of the true meaning of Marketing through the re-affirmation of the importance of the customer or buyer. A greater importance is also placed on consumer retention, customer relationship management, personalization, customization and one-to-one Marketing.
Types of cars in India-
Compact Cars: These cars have engines capacity of 800-1000 cc, and seating capacity of 4-5 passengers. Compact cars are very popular in India, because of low budget. Cars like Maruti-800,Wagon-R,Hyundai Santro, Maruti Alto/Alto 800,Hyumdai Eon and Renault Kwid are very popular in this segment because they come in a frugal budget of 3-5 lakhs and are in easy reach of middle class people specially first time buyers. They fulfill the necessary crieterias and needs of the buyers and doesn’t offer too many features and comfort.Tata nano was also designed with the same philosophy abut failed in the Indian market.
Mid-size Hatchback: The size of a hatchback car will be more than a compact car, but has greater engine displacement around 1200cc and seating capacity of 4-5 persons. These are cars with better safety standards and better comfort as well performance. Maruti Swift/Baleno,Hyundai i10 grand,i20 elite, Tata indica/Tiago/Altroz etc are some popular cars in this segment. These cars are extremely successful because they offer many features which are desirable by the demanding customers.
Sedan:-A sedan car is a lengthy car which is more than 4 meters. Its a luxury car and is extremely comfortable for 4-5 adults and has a large boot space. Engines are more powerful than hatchbacks and offer more features like powerful AC and sun-roof. These cars make the owner feel luxury. Honda City, Hyundai Verna, Maruti Dzire/Ciaz, Tata Tigor etc are extremely popular in Indian market.
MPV(Multi-purpose vehicle):- MPV’s refers to estate cars with a sitting capacity of 7-10 persons. They are approximately 4+ meters and usually have engines capacity between 1500cc to 2200cc, but some have engines of up to 2500 cc as well. These are the most popular vehicles in taxi segment and are preferred by families with bigger family size. Mahindra Bolero,Marazzo,Scorpio,Maruti Ertiga/XL6, Toyota Innova etc are some very popular MUV’s in the Indian Market.
Van-A van is a vehicle which is of multi-purpose use and has a seating capacity of 6-7 people usually preferred by taxi operators and joint families. Examples of van are Maruti Omni/Eeco,Tata Winger,Mahindra Voyeger,Nissan Evalia,Kia Carnival etc.
Crossover SUV: Crossover SUVs are derived from an Automobile Platform with light off-road capability and lower ground clearance than SUVs. They may be styled similar to conventional "off-roaders", or may be look similar to an estate car or station wagon..Examples of crossover SUVs are Maruti S-cross/ Ignis, Polo cross, Toyota Etios cross, Honda W-RV, Renault Captur, Hyundai i20 Active, Skoda yeti, Ford Freestyle, Fiat Aventura, Nissan Magnite etc.
Compact/Mini SUV(Sports utility vehicle): -These cars are a mixture of a car and jeep resembles to mid-size hatchback car with high ground clearance and powerful engine capable of off-roading. This segment has become favorite for car lovers with a minimum budget of 10lacs and is usually extensive user of cars with frequent travelling history. Examples- Renault Duster,Hyundai Creta/Venue,Maruti Vitara Brezza, Tata Nexon,Mahindra Thar/XUV 300, Kia Sonet/Seltos,etc. This segment is the hottest in India since Renault launched its Duster.
SUV (Sports Utility Vehicles): - Sports utility vehicles are Off-Roaders, with four-wheel drive(4x4) and true off-road capability. The common feature is high ground clearance and an upright body design with powerful engine of 2500-3000cc. Sport Utilities are typically defined by a body on frame construction which offers more off-road capability but reduced on-road ride comfort and handling compared to a cross-over or car based utility vehicle. Toyota Fortuner, Tata Harrier Safari, XUV 500/700,Mitsubishi Pajero, Honda C-RV, Ford Endeavour, Jeep Compass, Chevrolet Captiva, Citroen C5 Aircross etc are SUV’s in India.
Executive/Business class Saloons:- An executive/business class saloon car is described as full length sedans with large boot and powerful engines and are extremely luxurious and spacious with a lot of luxury features like panoramic sunroof, recliner seats, champagne holders in rear seats, rear AC vents, wooden finish interiors, automated curtains etc. Examples of executive cars are Nissan Teana,Jaguar XJ/XF, Mercedes Benz E class/ S Class, Audi A8, BMW 3 & 5 series etc.
Business class SUV’s:- An executive/business class SUV is described as a luxurious SUV with powerful engines(4x4)and are extremely luxurious and spacious with a lot of luxury features like panoramic sunroof, recliner seats, champagne holders in rear seats, rear AC vents, wooden finish interiors, automated curtains etc. Examples are Range Rover, Jaguar f-pace, Mercedes GLA class, BMW X1/X3/X6 Audi Q3/Q5/Q7 etc.
Premium Car Brands in Raipur City:-
MERCEDES- Mercedes is a German Based company but when one thinks about luxury cars Mercedes is the first brand that comes to their mind. It is a matter of pride to own a Mercedes in India.
BMW- BMW, like Mercedes, is considered to be one of the most high-end brands used by top officials.BMW was also used by the President and the PM of India. Again, like Mercedes, it is also a German Based Brand, but it's still regarded as one notch below Mercedes in India.
Audi- Audi is also a German luxury car manufacturer subsidiary of its parent company Volkswagen Group. Audi is very famous among youth and celebrities.
Jaguar-Land Rover- Jaguar is a luxury vehicle brand of British multinational car manufacturer which was acquired by the TATA group in 2008. Jaguar is famous for making luxury sedan cars and Land Rover is a very famous SUV manufacturer with ultra modern safety and security features.
Volvo- Volvo has been a giant in bus segment with very high performance and quality products and is well known player.They also make premium cars with high quality and safety deatures and are present in Raipur as well.
Luxury Car Brands in Raipur city-
Maruti NEXA- Nexa is the one-stop destination for Maruti Suzuki’s Luxury and Premium cars. Maruti is a household brand in India and the people of this country have utmost faith in this brand. Maruti has been the market leader for several years. It is known for its easy availability of after-sales services.
Hyundai- Hyundai is a Korean brand which started its operations in India in the year 1996 with a very popular product named Santro. Hyundai is the second largest selling brand in India after Maruti. Hyundai has its presence in almost all segments and is known for its technological refinement.
KIA- Kia is a South Korean Company (a subsidiary of Hyundai) that entered the Indian market only recently, but it has been a great market player since its entry in 2019.
MG- Morris Garages(MG) entered India looking at the huge demand in SUV segment in 2019 and now is a market leader in electric vehicle segment now.
Toyota- Toyota is Japanese Company that is highly preferred by Indian Consumers. Toyota is a leading MUV/SUV manufacturer who has change the definition of luxury and comfort in India with its products like Qualis, Innova and Fortuner. It also produced legendry cars like Corolla in D-segment.
Honda- Honda the Japanese manufacturer introduced itself to the Indian market in 1995 in the Sedan sement with the most successful brand Honda city. Honda introduced many models which were extremely successful in Indian market and set new standards of luxury. Honda cars proved to be extremely reliable and are well known for their quality and durability.
TATA- Tata the biggest conglomerate in India has been a truck manufacturer since past but started manufacturing vehicles of taxi segment soon like Tata indica & Tata Sumo. Tata’s Safari has been an important member of VIP’s convoy after HM Ambassador shut down. Tata is also supplying vehicles in the Indian army.
Mahindra- Mahindra & Mahindra is one of the oldest careers in India which supplied jeeps to India’s Police department. Later they expanded in making vehicles for taxi segment and presently the largest MUV(Multi-utility segment) manufacturer. Mahindra’s Bolero & Scorpio is among the most successful vehicles among the segment.
Renault- Renault the French automaker has also been a player in the Indian Market since a decade and is continuously trying to penetrate the market by offering the products as per need of the India households. Renault has been well known for introducing a new category of product i.e compact SUV segment in India with Renault Duster.
Jeep/Fiat- Fiat has been a player in India since decades but after globalization the Italian brand struggled a lot to keep up with the pace of the market and due to cut-throat competition it exited the market and introduced its another brand Jeep which specializes in SUV’s,which is quite a hot segment in the India market with changed needs.
Skoda- Skoda a subsidiary of the Volkswagen group has been selling cars in India since two decades and specializes in sedan products and is continuously changing with the changing needs of customers in India.
Volkswagen- Volkswagen the German giant is also present in the Indian market with a very small market share and very limited products.
Nissan Motors- Nissan has presence in India since long with a frugal market share. It has also introduced their cheaper flagship brand Datsun in India as per the demographics of India. Nissan has been selling cars like Kicks, Magnite, Terrrano, Sunny, Micra, Teana (D-Segment),X-trail etc. Datsun has Go,Go+ and Ready Go models for sale but are not successful.
Research Methodology- The research paper is based on secondary data and conclusions are drawn from the very basic concepts of consumer behavior with the help of literature reviews. Descriptive research is done with the help of the consumer buying process and Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Factors have been identified which influence the consumer behavior towards luxury car purchase in India as well the intrinsic factors have also been discussed.
Objectives of the Study:
(i) To study the dynamics in the pre-purchase behavior of the buyers of luxury cars in Raipur.
(ii) To explore the factors influencing and deciding the brand of luxury car purchase.
(iii)To study the Demographic characteristics of the buyers of luxury cars.
(iv) To understand the brand preferences of luxury/premium car buyers.
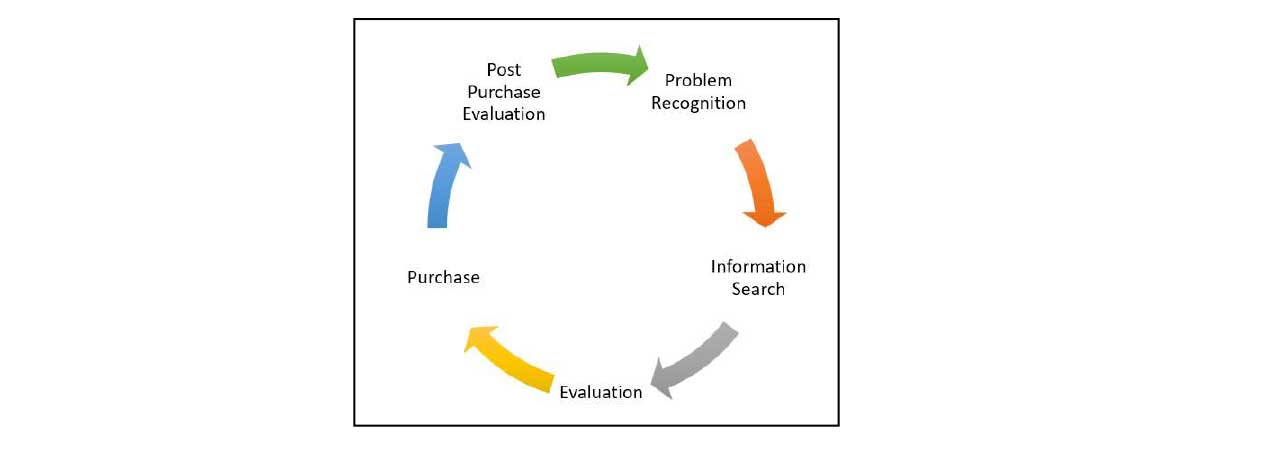
Theoretical Background - The Buying process (Five stage model)-A consumer usually experiences 5 purchasing decision stages. The process begins well before and long after the actual purchase. Consumers might not always be skipping or modifying the fivesteps.
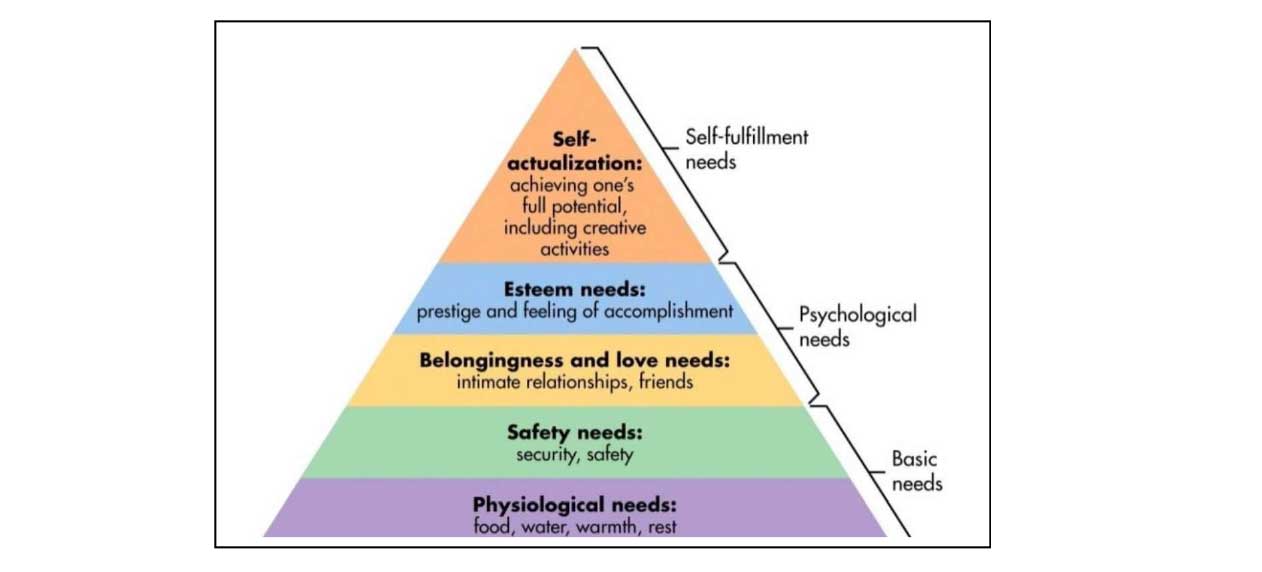
Base of the Study-Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs -
Abraham Maslow formulated a widely accepted need hierarchy theory. He identified five stages in need theory. This theory shows that it is necessary to reach lower levels before higher levels are required. Here are the different human needs levels-
- Physiological Needs − they are known as necessities or primary needs. Shelter, food and clothing are some of the basic needs. If these needs are not fulfilled the human cannot function properly. Basic needs are the most important needs as all the other needs can be accomplished only after these needs aremet.
- Safety needs - The need for protection and safety comes when the physiological needs are met. People want to remain in order, predictable, and regulated for a longer time in t heir lives. The family and culture follow these conditions in theory. Financial protection as well as law and order, fear-free, social harmony, health, and education,etc.
- Love and belongingness needs - The third necessity is a sense of belonging. This is important to motivate behavior in interpersonal relationships. Examples include friendship, confidence, acceptance, love, andaffection.
- Esteem needs are the – It is the fourth need which is divided into categories: Self-esteemand the desire for respect fromothers.
- Self-actualization is the highest level of need, and it refers to the realization of a person's fullest ability, seeking personal growth, self-fulfillment. Maslow termed this level “the desire to accomplish everything that one can, to become the most that one canbe”.
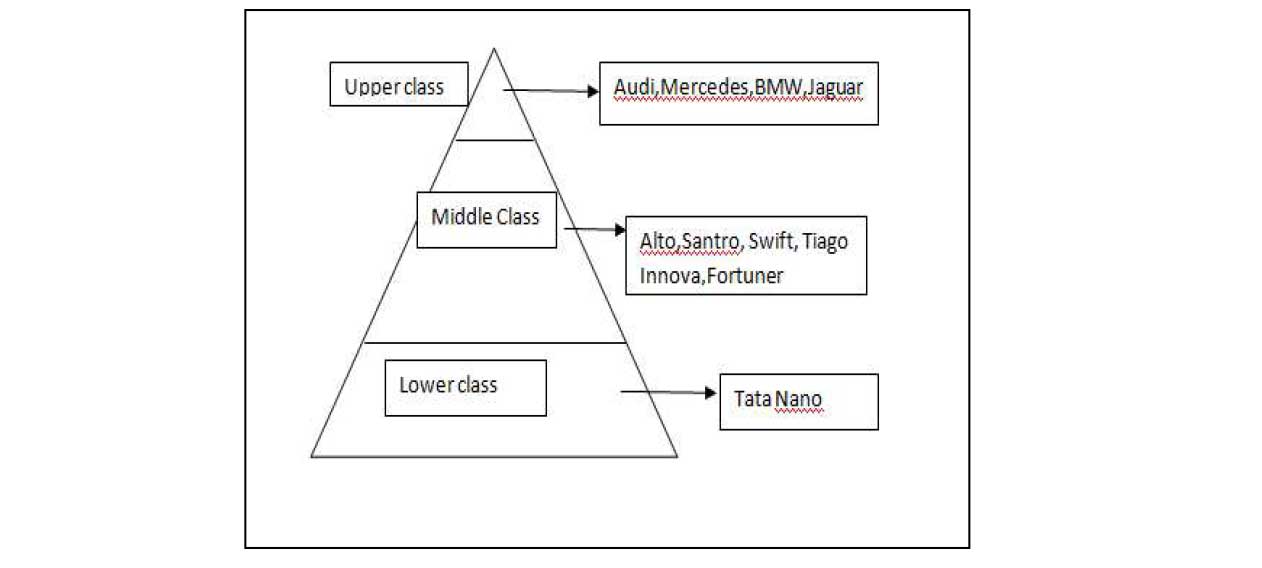
Classes in India based on the Maslow’s Need Hierarchy-
Upper Class- This is the elite class of people who are the celebrities, business tycoons, industrialists, politicians, high class government officials, sportsmen, etc. These people are mostly from high income group and earn in crores and hence can afford high end premium brands like Audi, Mercedes, BMW, Jaguar,Lexus, Range Rover, Mini Cooper, Mustang, Maserati, Nissan GT-R, ultra luxury like Rolls Royce, Bentley even super cars like Lamborghini, Ferrari, Porche, Aston Martin, Bugatti, etc.
Middle Class – The strength of the Indian economy is the Indian middle class who are the most dynamic and the potential class who are the tax-payers and savers who are capable of handling the market alone and are in maximum in numbers. This middle class is considered the most powerful when it comes to savings and investments. They can manipulate the market as well as politics with their dynamics. They are further divided into upper middle class and lower middle class people. Upper middle class are into business and lower middle class people are in either government or private jobs. These people have a huge range and can afford a car of economy segment to high end SUV’s that ranges from 3-5 lakhs to 25-35 lakhs.
Lower Class- This class is the poor people who are farmers, auto/taxi drivers, labours,beggers, servants or into self employment like cobblers, sweepers,etc who fall in low income group. They are further categorized into Above poverty line(APL) and Below poverty line(BPL) by the Indian government. These people survive in frugal income and get subsidies/support from the government. These people can hardly afford to have a two-wheeler. But Tata nano was launched by Tata group looking the lower class in mind with 1 lakh rupees budget.
Demographic factors of Consumers in India- The most important of all the factors which determines consumer behavior in India is demographic factors that decides how a consumer will behave in the market in a huge country like India. Demographic factors vary from country to country. The demographic factors are as follows-
Age- Age is an important factor which decides the consumption pattern of individuals in India. At different stages of life an individual has different needs i.e the needs changes with age and family life-cycle. India has most varied age groups and the most number of youth hence the consumption pattern is also very different in India.
Gender- Gender is an important factor which decides the product categories of consumption hence there are different product categories for gender. However both genders may have different preferences for buying a car.
Income- Income is the most important ingredient for consumption. The greater the income the more the consumption of products. The income is directly proportional to the cost of car that means the higher the income the costlier the car.
Education- Educated people take buying decision after a lot of analysis and it is an important factor for car purchase. Education decides the level of knowledge and analytical power. Educations supports the decision making process and is an important aspect.
Family size- Family size is the most important factor for deciding a car purchase, the bigger the family size the bigger the size of car.
Marital Status- Marital status is also an important factor which decides consumption of various products. But it has nothing to do with a car. But it is a part of couple dreams which includes food, clothing and shelter to home, car and servants.
Occupation- Occupation plays an important role on deciding consumption of an individual specially occupations like celebrities, sportsmen and business tycoons buy most luxury cars in India.
Socio-Economic Status- According to the individual status in society the people choose to buy a car accordingly.
Hence it is clear from the demographic factors as well as Maslow’s Need Hierarchy that on the basis of their needs the consumers buy a car. A car is a luxury for lower class, need/necessity for middle class and a prestige issue for upper class people. A lower class person can afford to buy a cheapest car like Tata Nano, middle class can buy Maruti ,Hyundai, and other cars of non-premium segment according to their budget, Upper class people may but cars from the premium segment i.e BMW,Audi, Mercedes so as to flaunt their status in the society
-
Factors influencing a consumer’s purchase decision
- Brand: A brand is termed as a logo, name, term, sign, symbol (or a combination of these) that identifies the maker or seller of the product" brand plays a vital role for a consumer while deciding which car to buy and when it comes to buying a luxury car, it becomes extremely important. Nowadays in India people also categorize brands on the basis of country of origin like USA, U.K, Italy, Germany, France, Japan etc.
- Prestige: A car has become a status symbol hence criteria’s such as the society standards, education, profession, friends & relatives, neighbors, locality(rural/urban), lifestyle, vehicle usage,etc are considered before buying a car.
- Price: In a country like India price is an important factor which decides the potential of buyers and every individual has a budget. The budget in most cases is flexible and expands from 2-3 lakhs to 10 lakhs for middle class and for upper class car budget may reach upto 50 lakhs.
- Design: Although the word “design” is extremely subjective and what might be appealing to one might be opposite to the other. Today, people make statements by using cars to flaunt and status. Cars are meant to be a personality extension, therefore people want to buy the best.
- Fuel Economy: The most demanding feature in India for car buyers is fuel efficiency, because India is very price sensitive and Indians have a mentality of savings but buyers nowadays want both performance andquality.
- Space & Comfort: The bigger the car the greater the prestige. India has a high demand for compact cars but nowadays people prefer spacious cars and . For consumers for the first time. Their decision to purchase is based on the space the carprovides.
- Safety features- Safety features like Airbags, anti-lock breaking(ABS),electronic break force distribution(EBD), traction control etc plays a key role. The bigger the features list, the greater the sales, because it not only increases the value of the car,but they are life saving features.
- Availability of Service: The ownership starts after the purchase of a vehicle. If we start to wear and tear, some of the pieces must be replaced at long last. So availability of service is important for car buyers.
- Resale Value: Customers look for the resale value of almost every asset including acar.
- Performance: Performance of car in India roads is now an important factor due to development of world-classroads and infrastructure the buyers want high performance cars with powerful engines so as to reduce journey time.
- Quality & Durability- Quality has become a major issue for car buyers and the consider as important aspects. Japanese and German cars are considered better quality nowadays.
- Technology- The technology is important factors which is preferable like diesel, petrol, CNG or electric technology or manual or automatic transmission is also important factors nowadays.
- Cost of Maintenance- In India people prefer cars with less cost of maintenanceas there are already a lot of expenses attached with a car like insurance, road tax, fuel cost etc.
- Features- Luxury features are more preferred nowadays like sunroof, 4x4 ,projector headlamps with LED DRL’s, automatic transmission, UV cut glass, wireless mobile charging, touch screen infotainment system, reverse parking camera/sensors, driving modes(city/sports/eco) automatic parking, voice recognition, GPS & navigation, smartphone integration, automatic tailgates, cruise control, ventilated seats, keyless entry, push button start/stop, automatic emergency braking system, automatic climate control a/c, automatic wipers etc
-
Conclusion
- This study revealed that price has always been a constraint for buying cars but nowadays the buyers extend their budget for feature packed luxury cars.
- The study says that brand is an important factor for consumers and imported cars are always preferred over local brands.
- The study says that a car is now a status symbol in the Indian society and people buy foreign brands for getting the feel of prestige which is associated with the brand/product.
- The study says that the consumers prefer to buy fuel efficient cars, but they ignore it when it comes to luxury cars and their focus is on performance, safety and build quality.
- The study says that resale value and technology (petrol/diesel/CNG/EV/Automatic transmission et) is an important factor for car buyers nowadays.
- The study shows that the consumers are now brand conscious as well quality conscious.
- The rise in disposable income, wide choice of car models and easy availability of finance has boosted sales in premium/luxury car segment in India.
- The increased usage of vehicles in households and business has increased the consumption of cars i.e passenger/commercial vehicles.
- Due to growth in roads and infrastructure need for safety features have been felt to avoid causalities during travel.
-
References:-
- Ajzen, I & Fishbein, M 1980, Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior, Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- Allsop, J 2005, 'Premium pricing: understanding the value of premium', Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 185-94.
- Anurit, J, Newman, K & Chansarkar, B 1999, Consumer behaviour of luxury automobiles: a comparative study between Thai and UK customers' perspective, Hendon, UK.
- Ariely, D 2008, Predictably irrational: the hidden forces that shape our decisions, Harper Collins, London.
- Audi 2010, Efficiency: standard in every Audi, Audi AG, viewed 06.10.2010 .
- BMW Group 2010a, BMW EfficientDynamics, Bayerische Motorenwerke AG, viewed 10.05.2010 . ---- 2010b, Joy is BMW,
- Bayerische Motorenwerke AG, viewed 04.06.2010 . ---- 2011, BMW Group Dow Jones Sustainability Index leader for 6th consecutive year.,
- BMW AG, viewed 30.03.2011 .
- Dubois, B & Czellar, S 2002, 'Prestige Brands or Luxury Brands? An Exploratory Inquiry on Consumer Perceptions', Brand Management Track.
- Firat, FA, Sherry, JFJ & Venkatesh, A 1994, 'Postmodernism, marketing and the consumer', International Journal of Research in Marketing, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 311-6.
- Flick, U 2002, An introduction to qualitative research, 2 edn, Sage Publications, London.
- Fournier, S 1998, 'Consumers and their brands: developing relationship theory in consumer research', Journal of Consumer Research, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 343- 73. ----
- 2007, 'Make a case for your brand', Advertising Age, vol. 78, no. 47, p. 4/5.
- Fraj, E & Martinez, E 2007, 'Ecological consumer behaviour: an empirical analysis', International Journal of Consumer Studies, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 26-33.
- Holt, DB 2004, How brands become icons, Harvard Business School Press, Boston.
- Holt, DB, Quelch, JA & Taylor, EL 2004, 'How global brands compete', Harvard Business Review, vol. 82, no. 9, pp. 68-75.
- Honda 2011, Eco Assist, viewed 30.03.2011 . Hooley, G, Saunders, J, Piercy, NF & Nicoulaud, B 2008, Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning, vol. 4, Pearson Education, London.
- Interbrand 2009, Best global brands, www.interbrand.com, viewed 15.05.2009.
- Keller, K 2003, Strategic brand management: building, measuring and managing brand equity, 2 edn, Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
- Kotler, P 2003, Marketing management, 11 edn, Pearson Education, New Jersey. Kotler, P & Armstrong, G 2009, Principles of marketing, 13 edn, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
- Land Rover 2011, Our plan for a sustainable future., viewed 30.03.2011 . Lexus 2010, Environment and Technology,
- Maslow, A 1943, 'A theory of human motivation', Psychological Review, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 370-96.
- Mercedes 2010, Mercedes BlueEfficiency, Mercedes AG, viewed 05.10.2010 .
- Schiffman, L, Bendall, D, O'Cass, A, Paladino, A & Kanuk, L 2005, Consumer behaviour, 3 edn, Pearson, Prentice Hall International, London.
- Solomon, MR 2004, Consumer behaviour: buying, having and being, vol. 6, Pearson Prentice Hall, New Jersey.
- Silverstein, MJ & Fiske, N 2003, 'Luxury for the masses', Harvard Business Review, vol. 81, no. 4, pp. 48-57.
- ---- 2005, Trading up: why consumers want new luxury goods and how companies create them, Penguin Group, New York.
- Volkswagen 2011,
- BlueMotionTechnologies., viewed 30.03.2011 .
- Williams, TG 2002, 'Social class influences on purchase evaluation criteria', The Journal of Consumer Marketing, vol. 19, no. 2/3, p. 249.
