Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
A conceptual study on the various factors affecting the career choices of Generation Z
Abstract :
Career isthe sequence of employment positions that a person has held over his or her life. However, it very much depends on initial choices made by students during their studies or while opting for first job. Therefore, it becomes essential to understand factors which influence a student while choosing first career choice. Although considerable research has been conducted in this area world over however new factors keep emerging on the horizon with advancement in technology, way of living, apparitional changes. This paper intends to provide systematic literature review on the topic of factors influencing first career choices of graduate students in India focusing on southern parts of the country. This paper also intends to provide the gap for future research including new factors emerging on the horizon such as social media, education loan, aspiration of settling in abroad among many others. Study of impact of new factors will have short-term and long-lasting benefits for students and society at large. Students will know realistically what to expect from job and it will also mature society at large by giving them an empirical idea, beyond any presumption, that how gen Z thinks about career.
Keywords :
Career, Factors Influencing Career Choice, Occupational Preferences, Generation Z, Career Choice TheoryIntroduction
Demographically, India is one of the youngest Nation. Our 50% population is less than 25 years of age. Many of the young Indians are studying in colleges and universities with a dream of having a good future ahead.A lot of it depends on what kind of education they get followed by the career choices they make right after the college.
Right after class 10th exam career choices are partially decided when a student opts for science, commerce, or arts. Science has its own set of occupations to offer so has commerce and arts. However, choices are entirely based on academic excellence of students and not his area of interest. A student doing very good in maths may want to pursue a career in History or archaeology. Sadly, our education ecosystem is not flexible enough to merge various courses so that student can create career of his own choice. This at times lead to unwarranted academic choices opted by students which later becomes their occupation.
Kumaraswamy, N. (2013) have suggested 10-20% of college students suffer from depression, stress, or anxiety due to variety of reasons. Academic excellence, and fear of future are one of the reasons of stress. Study also concludes that counselling would help students to great extent in dealing with and overcoming that stress. Generations senior to GenZ need to understand the ever-evolving dynamics of world and it’s utmost important for them to understanding that the environment in which they made similar choices are not same for their sons/daughter.
Looking beyond metal pressure a student undergoes we need to acknowledge that world is changing dynamically so is the preferences and choices of people. With each generation preference for job also differs. Šnýdrová, M., Depoo, L., &Šnýdrová, I. (2021) argues that generation along with university education has significant impact on the attitude of students towards job.
Sokro, E., Osei-Bonsu, N., Agbola, R. M., &Ankrah, E. (2011)suggests that individuals who make right career choices perform well in job and remain satisfied with their job. Hence it becomes essentialfor graduates to understand the choices available in the job market vis a vis their personality and other preferences. Not only this is important for employee, it is also important for employers to attract right set of talent so that better employee productivity can be achieved.
There are a number of factors which influences decision makingDietrich, C. (2010). He further suggests that decision making process is shaped by past experiences, cognitive biases, individual differences, including age and socioeconomic status, and a belief in personal relevance. Hence, it can be conveniently concluded that minds of young college going Indians are also evaluating career options using such factors. This paper will focus on relevant factors which are into play while choosing career options.
Nobel Laureate Richard Thaler in his book Nudge has introduced the concept of “ChoiceArchitects”.It’s important for us to understand whatbecomes the choice architect for students when they make career decisions. For example, high valuation tech start-ups and their frequent reporting in all the media platforms would encourage a graduate more towards high paying job in technology sector as compared to any other sector.
Career Choice Theories
Career choices and development had been an interesting area of research sincethe last century. There are close to a dozen theories available in this topic. Frank parson was the first person to provide a conceptual framework to career choices in the very beginning of 20thcenturyLeung, S. A. (2008). He propounded three step formula also called trait-and-factor model.
1. Understanding of yourself (aptitude, ambition, knowledge that one has, interest)
2. Knowledge about the requirement (compensation, success factors, opportunities, and different prospects)
3. Relationship between first two groups
Further Leung, S. A. (2008), suggests that big five theories of career choice were written and developed in USA, hence they might be needing indigenous version in case one wants to apply them in different cultural set up.
D. Brown & Associates, 2002 have summarised the various available theories into following categories.
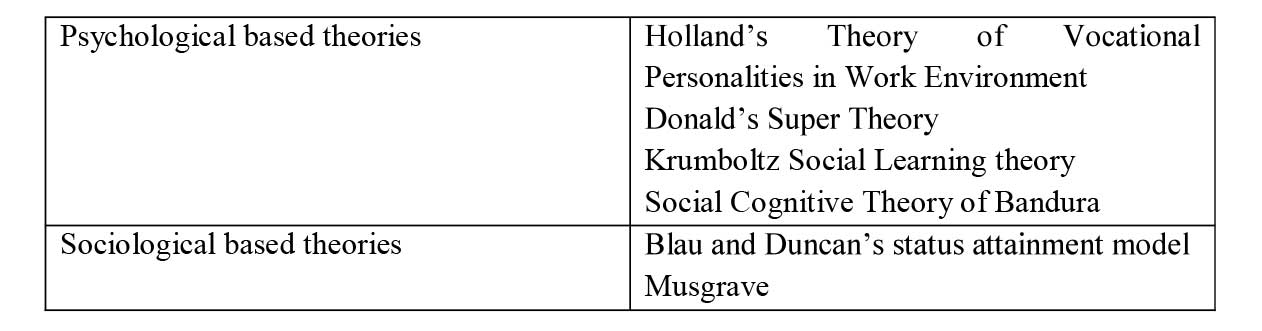
Psychology based theorist focus on personal traits, environmental factors, and cultural aspects on occupational choices whereas sociological theorists focus on perceived social status attached to an occupation.
Psychologists have also related the occupational choices with Maslow’s hierarchical needs theory.
Literature Review
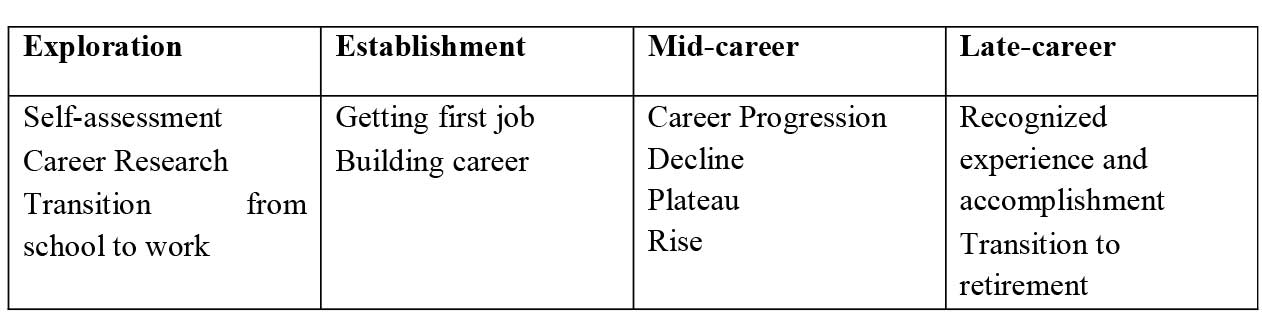
According to Robins, career means “The sequence of employment positions that a person has held over his or her life”. Book further categorises career into four parts as mentioned below. However, this study is limited to first two stages of career progressions.
Generation Z
Karl Mannheim first proposed the idea of generation cohort. Mannheim, K. (1952) in his theory proposed similar experience and time as two criteria for formation of a generation. However, later theorist categorised generations based on the year of birth.
Gen X – consists of people born during 1965-79 (Berkup, S. B. 2014).
Gen Y - consists of people born during 1980- (Berkup, S. B. 2014).
Generation Z -consists of people who are born after 1995 (Lanier, 2017).
Šnýdrová, M., Depoo, L., &Šnýdrová, I. (2021) have concluded that generation X, Y and Z have different attitude towards job. From the above age split it is now clear that Generation Z has started joining the Indian workforce as some of them have already graduated. However, there is a long list of students who will keep on joining the workforce in the years to come.
Chillakuri, B., &Mahanandia, R. (2018) suggested that generation Z are mostly children of millennials hence they posses’ certain qualities of millennials, however, they are different in various aspects from their parents.
Berkup, S. B. (2014) have also suggested that use of technology by Gen Z is different than their GenX parents.
According to Eisenfuhr, F. (2011) decision making is all about selecting the best choice from available alternatives to achieve a desired result. Similarly,university or college graduates also need to evaluate plenty of factors before arriving at a career choice decision.
Sharif, N., Ahmad, N., &Sarwar, S. (2019) have also suggested that there are multiple influencing factors.Study suggests that there are varieties of intrinsic and extrinsic factor which affect the choice of college courses and then the future career.However, students themselves don’t understand the impact of these factors while taking the decision. It considers five influencers Mother, father, tutor, social status and future income. It concludes that father has greater influence as compared to mother when it comes to making future occupational choices.
Bhattacharya, S. (2013)studied the impact of parents along with their income status asinfluencing factor. Parental upbringing has lot to do with the way child view the world. Yes, generational factors do come into play, but till students become financially independent. However, this study was limited to engineering students. Study also highlights the gender factor. Girls are influenced more by parental social and income status as compared to boys.
Agarwala, T. (2008) also made similar observations related to father playing a pivotal role for management graduates. Cultural values also play an important role.
Sarwar, A., &Azmat, A. (2013) have categorised items into five following categories:
Family – It suggests that along with father and mother, siblings also have a role to play.
Socializers- It covers the aspect of social capital which essentially means people with whom an individual interactson a daily basis. The interaction of media, peers and significant others such as teachers, role model strengthens certain beliefs about a profession.
Environmental factors – Gender, job opportunities, family financial condition constitutes environmental factors. Awareness about the profession and prevailing economic condition plays equally important role.
Personality–Individual personality has a very pivotal role to play in shaping the occupational choices. Personality itself is formed by combined influence of family, environment, and society.
Career Itself – Traits of job could be one of the reasons which might attract. Incentives, health benefits, appraisal etc are affecting the decision taken by students.
It concludes that interplay of above factors come to play when students make occupational choices, and no factor alone influences the decision of career choice.
Theresa, L. D. (2015) emphasized on career information students have when they are in college. The information is very limited and which becomes reason for incorrect choices.
Research Gap
Going through a number of papers it has been evident that factors across the world have not been relooked into with a fresh perspective. Given the new elements have emerged following research gap has been identified
- Studying the impact of career counsellor in Indian universities in vocational choices made by students
- Impact of social media(LinkedIn Influencers, Blogs) onGeneration Z.
- Start-up Vs MNCs – what influences graduates to choose one over the other.
- Incubation centre or entrepreneurship cell have on career choices students are having.
- Internship as an influencing factor
Conclusion
Various research paper has been written on the influencing elements on career choice of students. Some of them are static such as family, however some of the factors such as environmental factors are dynamic. Hence the study of this nature will be relevant with changing social, economicscenario of a country or region. Moreover, generational attitude also differs in a decade or two, hence, it becomes essential for us to re-evaluate factors which make decisive impact on the newer generation.
Multiple research projects have been conducted on Gen Z buying behaviour however, very little has been done on the first job preference. Given that last few years have seen a monumental shift in technological penetration and rise in data consumption, gen Z being largest consumer of this data would certainly be affected by many new ways. In order to make a satisfied, productive workforce along with employers, students must also know what elements causes career choice decision which are not irreversible but hard to change.
Study of emerging factors would keep us abreast with needs and perception of youngest workforce of country. It would prepare educational institutions better in addressing the knowledge gap of students about the industry they want to be part of. Additionally, it would motivate organizations to make a hiring process such that they clarify misconceptions about job, which would lead to satisfied employee.
References
- Snydrova, M., Depoo, L., &Snydrova, I. (2021). How University Graduation Shapes Attitudes Toward Employment in Different Generations Operating at Job Market?. Journal on Efficiency and Responsibility in Education and Science, 14(3), 143-153.
- Sokro, E., Osei-Bonsu, N., Agbola, R. M., &Ankrah, E. (2011). The impact of career choice on job satisfaction among employees in Ghana. Indian Journal of Commerce and Management Studies, 2(6), 83-88.
- Mount, M. K. (2002). Five-Factor Model of Personality and Job Satisfaction: A Meta-Analysis Timothy A. Judge Department of Management University of Florida Daniel Heller Department of Psychology University of Iowa. Journal of Applied Psychology, 87(3), 530-541.
- Sriprom, C., Rungswang, A., Sukwitthayakul, C., &Chansri, N. (2019). Personality Traits of Thai Gen Z Undergraduates: Challenges in the EFL Classroom?. PASAA: Journal of Language Teaching and Learning in Thailand, 57, 165-190.
- Career chapter of Book Robins
- Mannheim, K. (1952). The problem of generations. In P. Kecskemeti (Ed.), Karl Mannheim: Essays (pp. 276–322). New York: Routledge.
- Career choice and development, Duane Brown and Associates fourth edition (2002) https://www.google.co.in/books/edition/Career_Choice_and_Development/U0SZRvNz4S8C?hl=en&gbpv=1&dq=what+is+career&pg=PR9&printsec=frontcover
- Leung, S. A. (2008). The big five career theories. In International handbook of career guidance (pp. 115-132). Springer, Dordrecht.
- Chillakuri, B., &Mahanandia, R. (2018). Generation Z entering the workforce: the need for sustainable strategies in maximizing their talent. Human Resource Management International Digest.
- Lanier, K. (2017), “5 Things HR professionals need to know about generation Z: thought leaders share their views on the HR profession and its direction for the future”, Strategic HR Review, Vol. 16 No. 6, pp. 288-290
- Dietrich, C. (2010). Decision making: Factors that influence decision making, heuristics used, and decision outcomes. Inquiries Journal, 2(02).
- Eisenfuhr, F. (2011). Decision making. New York, NY: Springer.
- Sharif, N., Ahmad, N., &Sarwar, S. (2019). Factors influencing career choices. IBT Journal of Business Studies, 15(1), 33-46
- Bhattacharya, S. (2013). A study on parental and social influence on career choice as engineer. Voice of Research, 2(1), 13-16.
- Agarwala, T. (2008). Factors influencing career choice of management students in India. Career Development International.
- Sarwar, A., &Azmat, A. (2013). Factors having impact on the career decisions: Study of business graduates in Pakistan. Business Management Dynamics, 2(7), 9.
- Barhate, B., &Dirani, K. M. (2021). Career aspirations of generation Z: a systematic literature review. European Journal of Training and Development.
- Iorgulescu, M. C. (2016). Generation Z and its perception of work. Cross-Cultural Management Journal, 18(01), 47-54
- Theresa, L. D. (2015). Factors That Inform Students' Choice of Study and Career. Journal of Education and Practice, 6(27), 43-49.
- Gokuladas, V. K. (2010). Factors that influence first‐career choice of undergraduate engineers in software services companies: A south Indian experience. Career Development International.
- Berkup, S. B. (2014). Working with generations X and Y in generation Z period: Management of different generations in business life. Mediterranean journal of social Sciences, 5(19), 218-218.
- Arno, A., & Thomas, S. (2016). The efficacy of nudge theory strategies in influencing adult dietary behaviour: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC public health, 16(1), 1-11.
- Leonard, T. C. (2008). Richard H. Thaler, Cass R. Sunstein, Nudge: Improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness.
- Poddar, S. K. (2008). Organizational employment vs entrepreneurship: a study of career choice of Indian engineering and management students (Doctoral dissertation, IIT Delhi).
- Kumaraswamy, N. (2013). Academic stress, anxiety and depression among college students: A brief review. International review of social sciences and humanities, 5(1), 135-143.
- Abdo, A. A. (2016). Factors affecting career choice among undergraduate students in Univeritas Indonesia. International Journal of Economic Perspectives, 10(1), 630-644.
