Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Impact Analysis of Covid 19 On Performance of HDFC Bank
Abstract :
The COVID-19 pandemic took the shape of a most significant public health crisis of the present
times and the biggest threat to humanity since World War II. The effects of this pandemic caused an
unprecedented socioeconomic crisis. Despite extraordinary measures taken by the regulators and the
governments, there were negative effects on social activities and economic trends.
A negative impact of COVID-19 was also felt by the Indian banking industry. In addition to financial
concerns, business continuity and operational concerns are all affected by the epidemic. NPAs grew
and demand for new loans was subdued as repaying capacity of borrowers got impacted, thus
negatively impacting profitability for Indian banks. The revenue streams got impacted but
expenditures rose. This led to a liquidity crisis. Several initiatives have been taken by the regulators
and the government to address this issue. An analysis of HDFC Bank's financial performance has
been reviewed since 2017 to 2021 so as to cover pre-Covid period and Post Covid period. Ratio
analysis is used to provide an interpretation of data such as current and cash positions, fixed assets,
debt-equity balances, and proprietary ratios. The conclusion of this article is that the bank's financial
health was adequate throughout the studied period, and it successfully managed to overcome the
challenges posed by the pandemic.
Keywords :
: HDFC Bank, Financial performance, Current ratio, Loan, Fixed asset ratio, COVID 19Introduction
HDFC Bank was incorporated in August 1994 in Mumbai, India and startedoperations in January 1995. At the end of March 2021, the Bank had 5,653 branches and 16,291 ATMs located in 2,917 cities/towns across the country.
HDFC Bank is the leading Indian bank with US $240 Billion of Assets and largest bank in terms of market capitalisation which stood at $117.21Billion as of December, 2021. This makes HDFC Bank the world's 127th most valuable company by market cap and among top 10 in India.(HDFC Bank (HDB) - Market capitalization, 2021)
The HDFC Bank operates within a highly automated environment powered by information technology and communication systems. Customers have access to online banking in all branches, enabling them to conduct transactions quickly. Bank has a diverse portfolio of products and segments, strong risk management, unmatched asset quality, a healthy balance sheet, and consistently growing revenues. HDFC Bank ranked among the world's top consumer financial services eight times on the Forbes List of 100 most valuable global brands. The Reserve Bank of India has declared the bank to be too big to fail. The bank's subsidiaries include HDFC Securities and HDB Financial Services. (HDFC Bank - ICICI Securities Limited - 17 Oct, 2021, 2021)
HDFC Bank Mission ,Vision and Values:
The mission of HDFC Bank is to be the world class Indian Bank. Both retail and wholesale customers are its primary focus, and bank wants to be their chosen supplier of banking services in both of these domains. The bank also has an objective to maintain a healthy increase in profitability that is compatible with the bank's risk tolerance. Corporate governance, regulatory compliance, and high ethical and professional standards are all top priorities for the bank. The corporate philosophy of the bank revolves around five key beliefs that form the basis of HDFC Bank's corporate philosophy. Excellence in all aspects of the company's operations; customer focus; product leadership; employee engagement; and environmental sustainability. (HDFC Bank AnnualReports, 2017-2021).
Literature Review :
Shweta Yadav & Jonghag Jang (2021) HDFC Bank's pre- and post-merger financial performance will be examined in this research, as well as the CAMEL Analysis's influence on the bank's financial performance. There are 10 years of data included in the analysis, which includes the five-year pre-merger era (2003-2008) as well as post-merger data (2009-2014). CAMEL Analysis is the research method used in this study.
Partap Singh, Rajat Mahajan (2021) In today's world, e-banking serves an important purpose. No bank can function without electronic banking. Which banks, public and private, are making use of e-banking the most? e-banking consumer happiness and employee perceptions of e-banking in the public and private sectors are the goals of the research (in relation to SBI and HDFC banks). There are main and secondary methods of investigation. The survey found that consumer happiness and staff satisfaction in online banking services were evaluated highly by customers and employees, respectively. In this study, the working style of SBI and HDFC banks is compared as a contrast between the public and private sectors.
Riya John (2020) With the use of the CAMELS Rating, this study aims to determine the health of a few of public sector banks. In this research, each of the six factors was investigated in detail. For this research, we evaluated the performance of public sector banks and chose five of them to come at a conclusion on the best performing bank. For each parameter, several ratios are being computed, and the results may be used to identify the direction of the Indian banking industry.
Anilkumar Nirmal (2020) Both HDFC Bank and SBI are from the public sector are the two biggest banks in India as of June, 2020, based on their balance sheets, reach, and client bases. For a private bank with more than 5,000 branches, HDFC Bank is India's most profitable commercial institution, with a net profit of over 21078 crores, the most in banking sector, and a gross NPA of less than 2% for the FY 2018-19.
Dudhe C. (2018) In India, the banking industry is one of the fastest-growing. The banking industry is growing more sophisticated nowadays. It's not a simple process to evaluate the Indian banking industry. There are several elements to consider while determining which banks are excellent and which are poor. An economic activity's soundness may be determined by evaluating the performance of the banking sector. Financial institutions have been subject to new regulations thanks to RBI and other policymakers.
Mihir and Annyesh Das (Mihir Dash, 2010)in their study have mentioned that Indian banking industry has gone through various complex changes and restructuring after 1991so as to make the sector more vibrant, efficientfor promoting investment, saving, and growth. They have used the CAMELS approach for analyzingthe Indian banking industry (Al Mheiri, et al., 2020).
Yadav, S., Jang, J., 2021tried to examine the impact on financial performance of HDFC Bank before and after the merger and to compare the pre and post-merger effect caused on its financial performance by CAMEL Analysis. The data used in the study is secondary data covering total time period of ten years which include five year prior merger (2003-2008) and five year of post-merger period (2009-2014). The research technique used in this study is CAMEL Analysis. Paired sample T-test has been also conducted to check the statistical significance difference between before and after merger CAMEL ratios and to measure the effect of merger on financial performance. The result showed that the financial performance of HDFC increased after the merger and positively impacted by the act of merger.
METHODOLOGY
HDFC Bank's financial statements over the previous five years are the primary focus of this research, which is quantitative in nature. The data used in this research is derived from the banks' websites and annual reports. Data is studied using various key ratios, ratio analysis, SWOT Analysis, PESTLE Analysis, CAMEL framework. The findings clearly depict bank's success over the study period which includes post COVID years also .
Objectivesofthestudy
• The purpose of this study is to examine and analyze HDFC Bank's financial performance, as well as the bank's liquidity and solvency before and after COVID.
• Trend analysis is being used to identify any shifts in the bank's patterns.
Limitationsof thestudy
• Only financial years from 2017 to 2021(five years) are included in this study's scope.
• The accuracy of the results can't be ascertained as the study is mainly undertaken on the basis of secondary sources (annual reports of the bank).
• We may not be able to include all of the ratios when assessing a bank's financial health due to limitations in word count of the punblication.
• The present study concentrates only on the Financial performance of HDFC Bank.
DataAnalysis
Examining some of the most important statistics may help shed light on the bank's financial health before and after COVID. SWOT Analysis, PESTLE Analysis, CAMEL Analysis and Ratio Analysis is used to study the performance trend.
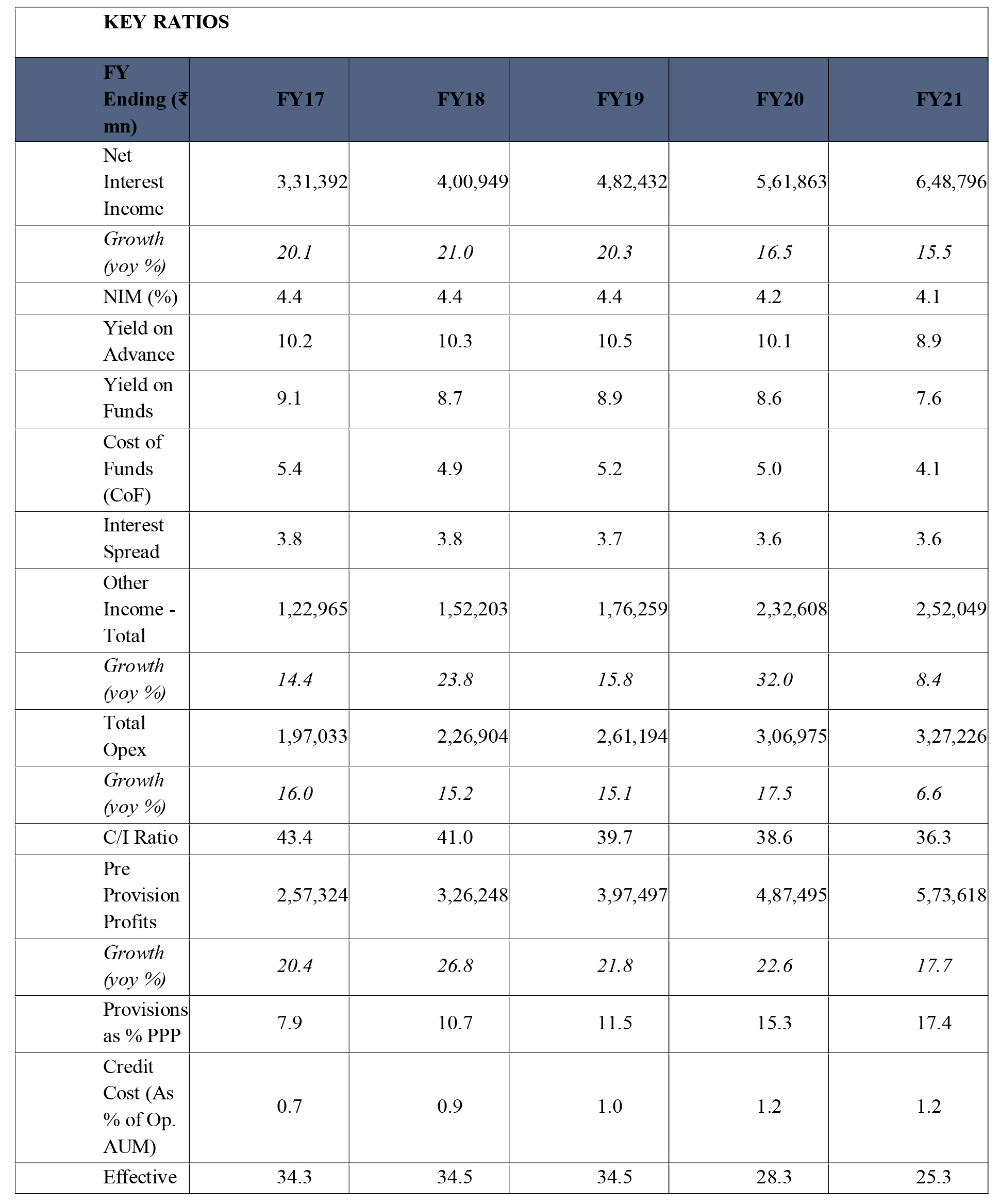
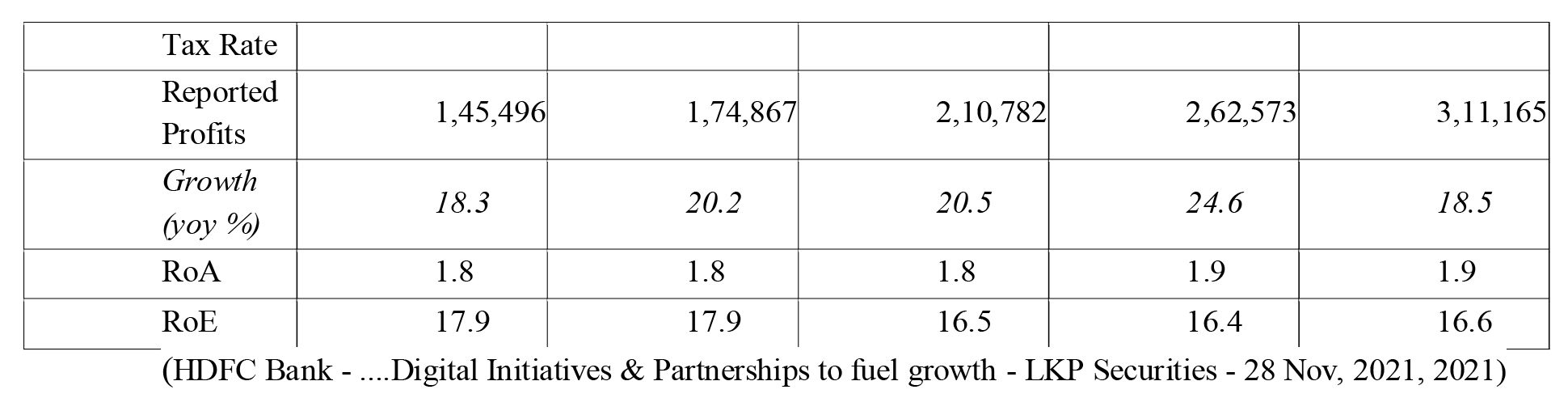
From above key parameters, HDFC Bank is maintaining a year-on-year healthy growth and only some stress is seen towards 2020 & 2021 primarily due to COVID factor.Net interest income has a consistent and healthy growth 20% in 2017, 21% in 2018, 20% in 2019. The growth has marginally declined to 16.5% in 2020 and to 15.5% in 2021. Net Interest margin (NIM) is important indicator of a bank's profitability and growth. It is the difference between interest earned on loans and interest paid on deposits.The higher the margin, the higher the profitability and leverage for the bank to fix its pricing for loan products. In case of HDFC Bank, the NIM is consistent at around 4% which is very healthy when margins are shrinking across industry in India. Yield on advances for HDFC Bank from 2017 to 2020 has been steady at 10% and marginally reduced to 8.9% in 2021primarily due to COVID impact when credit offtake was restricted. Cost Income Ratio which is the indicator of how efficiently bank manages its costs and profitability. The lower ratio is good. Although 60% in considered as a good ratio but HDFC Bank has managed it at 43% in 2017 and reduced to 36% in 2021 which means the bank is efficient in managing costs and improving profitability. Both operating profit and Net profit have shown a healthy Year on year growth. Operating profit grew by healthy 2o% in 2017, 26.8% in 2018, 21.8% in 2019, 22.6% in 2020 and 17.7% in 2021. AT the same time Net Profit has grown by 18% in 2017, 20% in 2018, 20% in 2019, 24.6% in 2020 and 18.5% in 2021, a very healthy and satisfying trend and consistency in performance. Return on Assets which indicates that how profitable bank is in relation to its employed assets is at around 2% which is comparable to the bank's peer groups. ROE is a measure to know the company's ability to generate income from capital. 15-20% is considered a healthy ratio. HDFC Bank has shown ROE of 17.9% in 2017 and 16.6% in 2021 which is quite good.


- Having entered new markets and made a successful transition, HDFC Bank has a considerable amount of experience. By expanding into new markets, the organization has built new revenue streams and diversified risks associated with economic cycles in the markets it serves.
- Having built a reliable distribution network over the years, HDFC Bank Limited is able to reach most of its markets including the deeper geography of rural India.
- HDFC Bank Limited has strong free cash flows that enable the company to expand into new areas.
- HDFC Bank Limited has been able to scale up and scale down according to the demand conditions in the market by automating activities. As a result, HDFC Bank Limited's products have a consistent quality.
- Successful learning and training programs lead to a skilled workforce. As a result of HDFC Bank Limited's substantial investment in training and development of its employees, the bank has a highly skilled and motivated workforce.
- Low response time and high customer satisfaction.The challenges HDFC Bank faces on a number of fronts besides COVID 19 include Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental. The bank is fully prepared to manage these challenges. In addition, there are a variety of external and internal challenges in the form of customers, regulators, investors, and also competitors. For the bank to remain strong, it also needs to improve internal processes and management controls.
The challenges HDFC Bank faces on a number of fronts besides COVID 19 include Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental. The bank is fully prepared to manage these challenges. In addition, there are a variety of external and internal challenges in the form of customers, regulators, investors, and also competitors. For the bank to remain strong, it also needs to improve internal processes and management controls.
SHORT-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOS :
CURRENTRATIO
A current ratio relates current assets to current liabilities. In other words, current assets are assets that can be converted into cash in the next year or so. The term "current liabilities" refers to obligations that must be resolved or repaid within a year.
CurrentRatio=CurrentAssets/CurrentLiabilities.
In terms of current ratio, 2:1 is the most commonly used benchmark or guideline. If the current ratio is high, the liquidity of a bank is good.
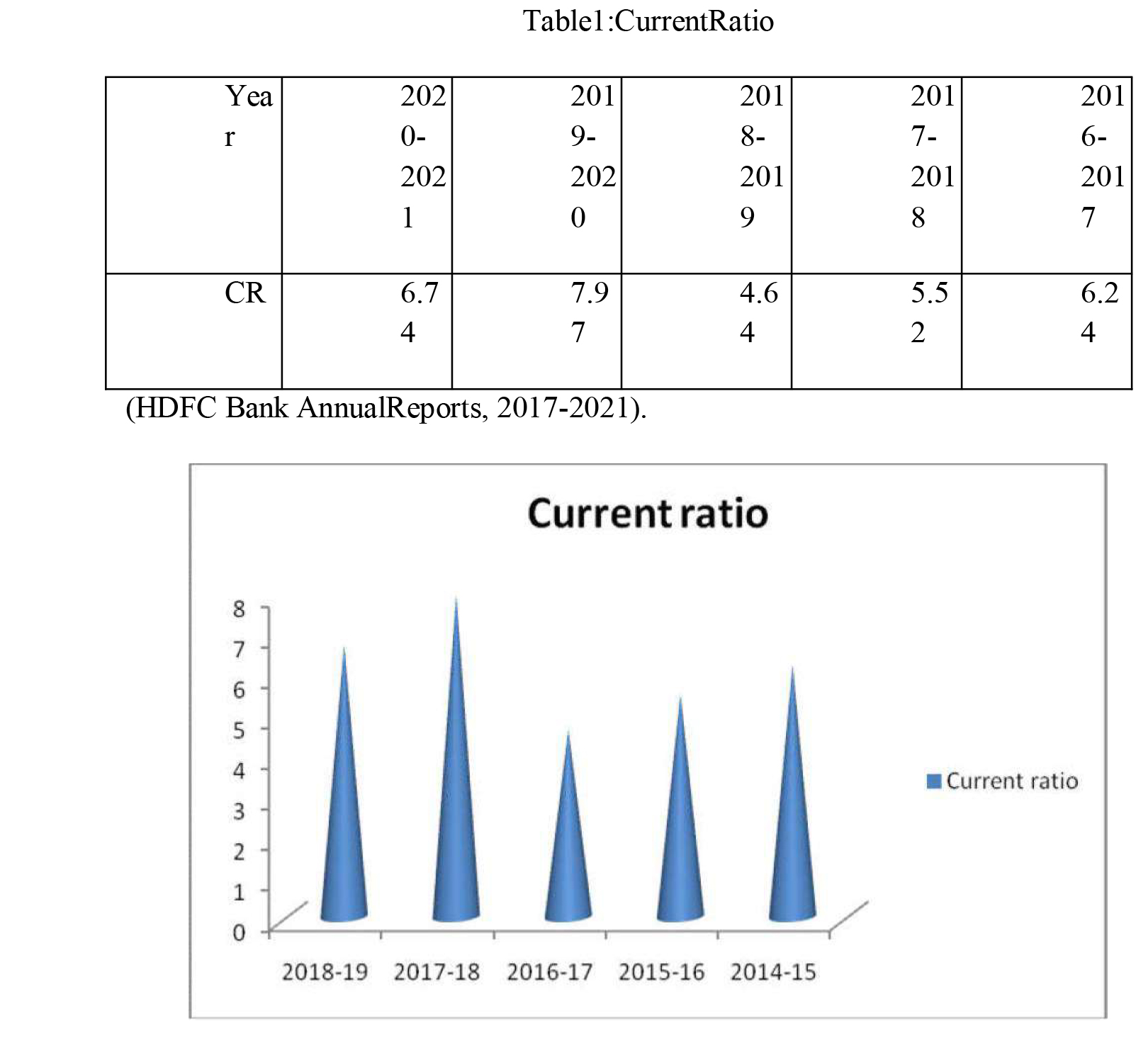
From a current ratio of 6.24 in 2016-2017, it has risen to 5.52, then 4.64 in 2017-18 and 2018-19, as shown in Table 1. A 7.97 percentage point gain was seen from 2019-2020 to 2020-2021. During the time of the assessment, banks' liquidity and ability to repay loans was found to be sound.
LONG-TERM SOLVENCY RATIOS:
FIXEDASSETSRATIO
The fixed asset ratio is a ratio between fixed assets and long-term funds ratio and takes into account the interaction between the two. Among its major objectives is to determine how much capital a company has invested in long-term assets.
FixedAssetsRatio=FixedAssets/Long-TermFunds
Anidealfixedassetsratiois0.67.Theratiomustnotbemorethan1,iftheratioislessthan1itindicatesthat aportion ofworkingcapital hadfinancedbylong-term funds.
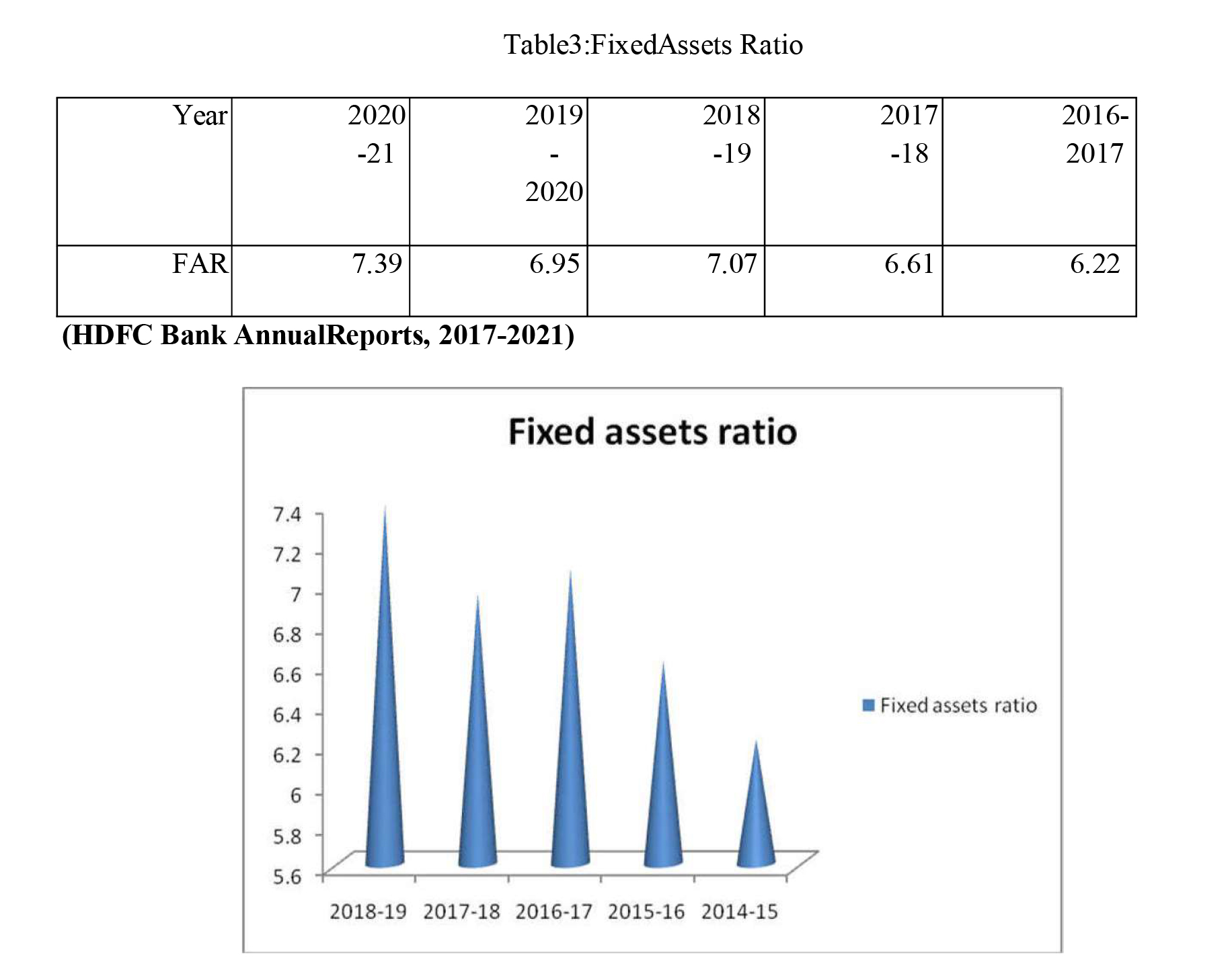
Fixed assets and long-term funds may be seen in Table 3. In 2016-2017, the fixed assets ratio was 6.22, while in 2017-2018 it was 6.61. There was a decline from 7.07 in 2018-19 to 6.95 in 2019-2020 in the ratio. The ratio was raised to 7.39 in 2020-21. These ratios, when compared to the usual, are very high. Consequently, throughout the research period, some of the company's operating capital was funded by long-term funds.
DEBT-EQUITYRATIO
Most of the time, debt equity ratios are used to evaluate the long-term viability of policies and to determine the percentage of outsiders and stackholders. This ratio shows how debt and equity are linked. (Karthika., 2021)
Debt-EquityRatio=ShareholdersFunds/TotalLong-TermFunds
Debt-equity ratios indicate that creditors own more of a company's assets than its shareholders. High debt-equity ratios are indicative of a company's poor financial state. Low debt-to-equity ratios increase margins of safety for creditors and reduce the risk of a claim. It is recommended that the standard ratio be 2:1.
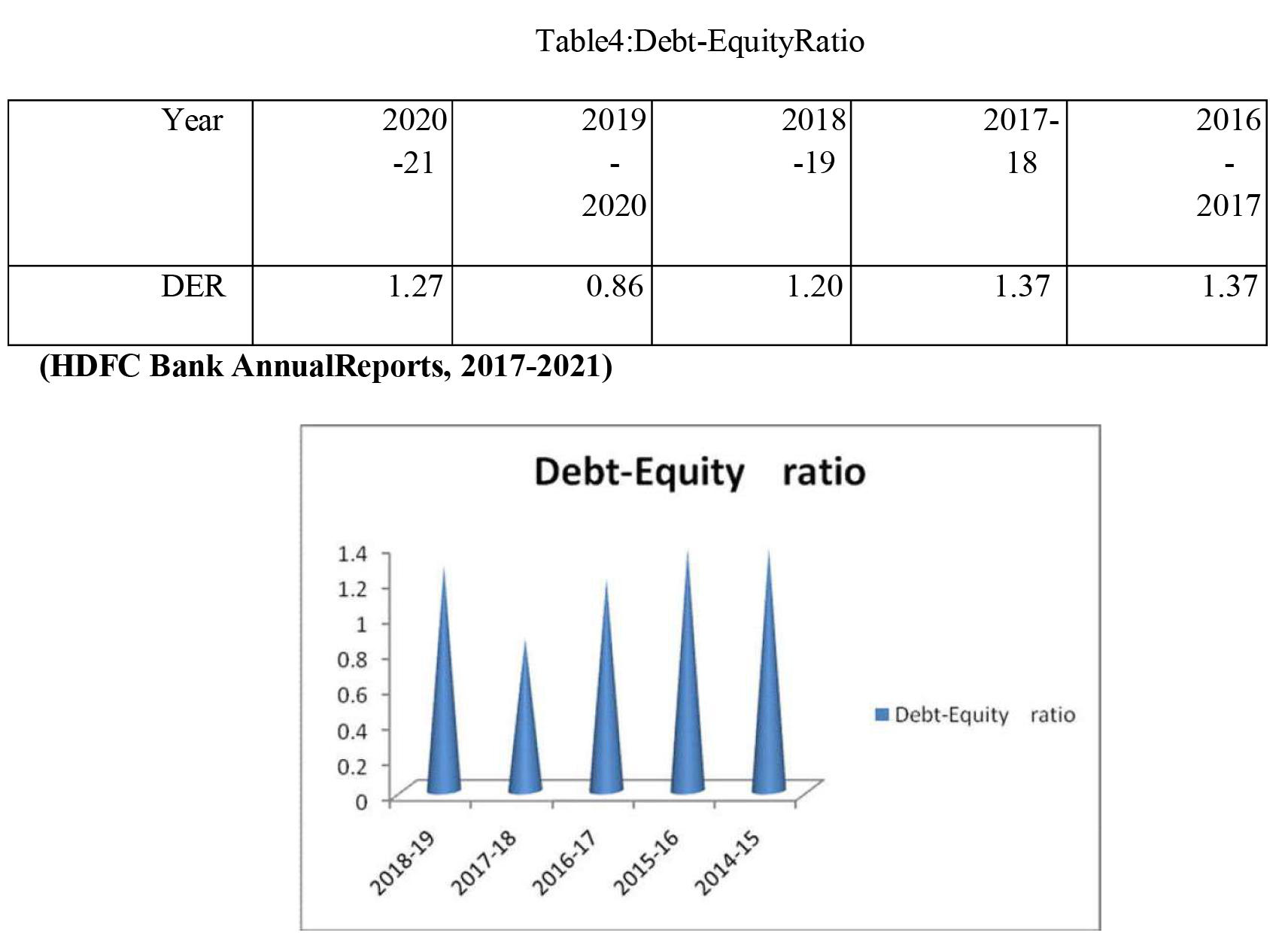
Table 4 shows the link between debt and equity. As of 2016-2017, the ratio was 1.37; in 2017-2018, it remained the same; and finally, in 2018-19, it fell by 1.20. While it was down by 0.86 in 2019-2018, it was up by 1.27 in 2020-21. These ratios are lower than the typical 2:1 standard. As a result, creditors are protected during the study period.
PROPRIETARYRATIO
Owners fund ratios or net worth ratios are terms for this ratio. An analysis of this ratio shows the relationship between the total tangible assets and the stakeholder's funds.
ProprietaryRatio=Shareholdersfunds/Totaltangibleassets
In assessing the long-term viability of a company, this ratio is very useful. A creditor needs to know how much of the company's assets are invested in shareholder funds. The ratio must be at least 0.5 or creditors may suffer significant losses if the company goes bankrupt.(Karthika., 2021)
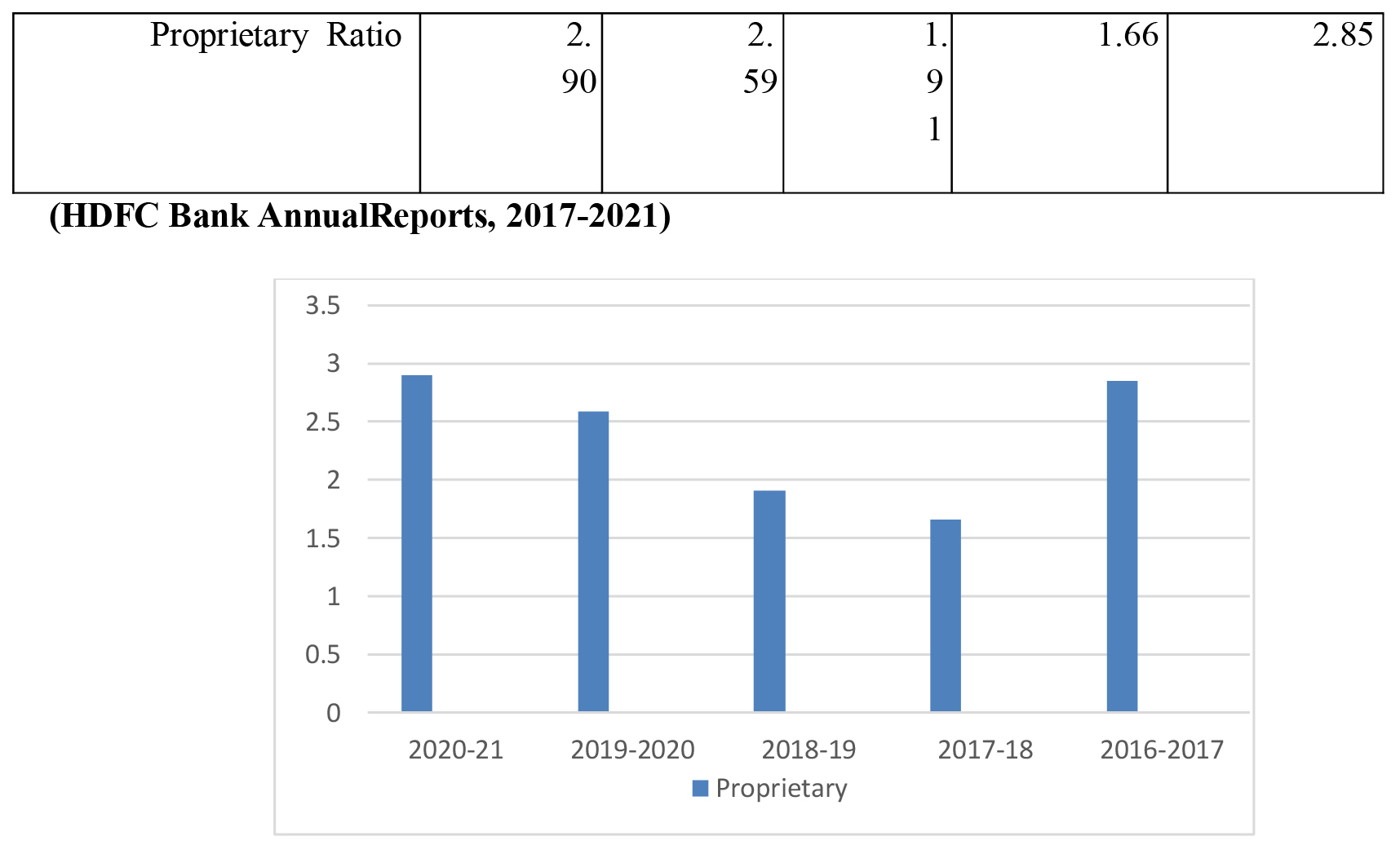
Table 5 clearly demonstrates the company's long-term viability. There was a decline of 1.66 percentage points in the ratio between 2016-2017 and 2017-2018. It was raised to 1.91 in the 2018-19 fiscal year. This was followed by a rise to 2.59 in 2019-2020 and 2.90 in 2020-21. These ratios are higher than the typical 0.5. During the research time, it is apparent that the banks' safety is unquestionable.
Return on Total Assets Ratio
ROI measures a company's profitability as a percentage of its total assets. Profitability as a measure of how well a company's management makes use of its resources, ROA is useful to managers, investors, and analysts. A percentage represents the return on investment.
It's all about efficiency in business: getting the most out of your limited resources. Even if comparing earnings to revenue is a good way to assess operational efficiency, doing so in relation to the resources used by the firm in achieving those profits is problematic. The easiest way to gauge a company's value for money is to look at its return on assets (ROA). It might be stated mathematically as follows:
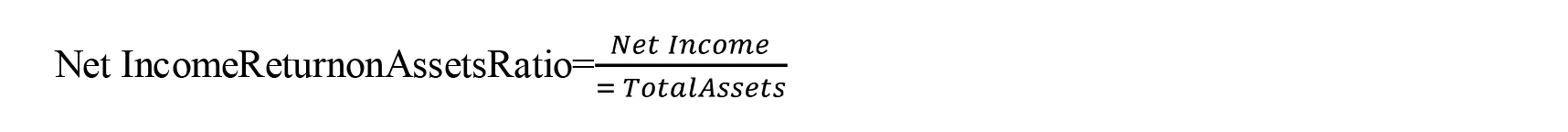
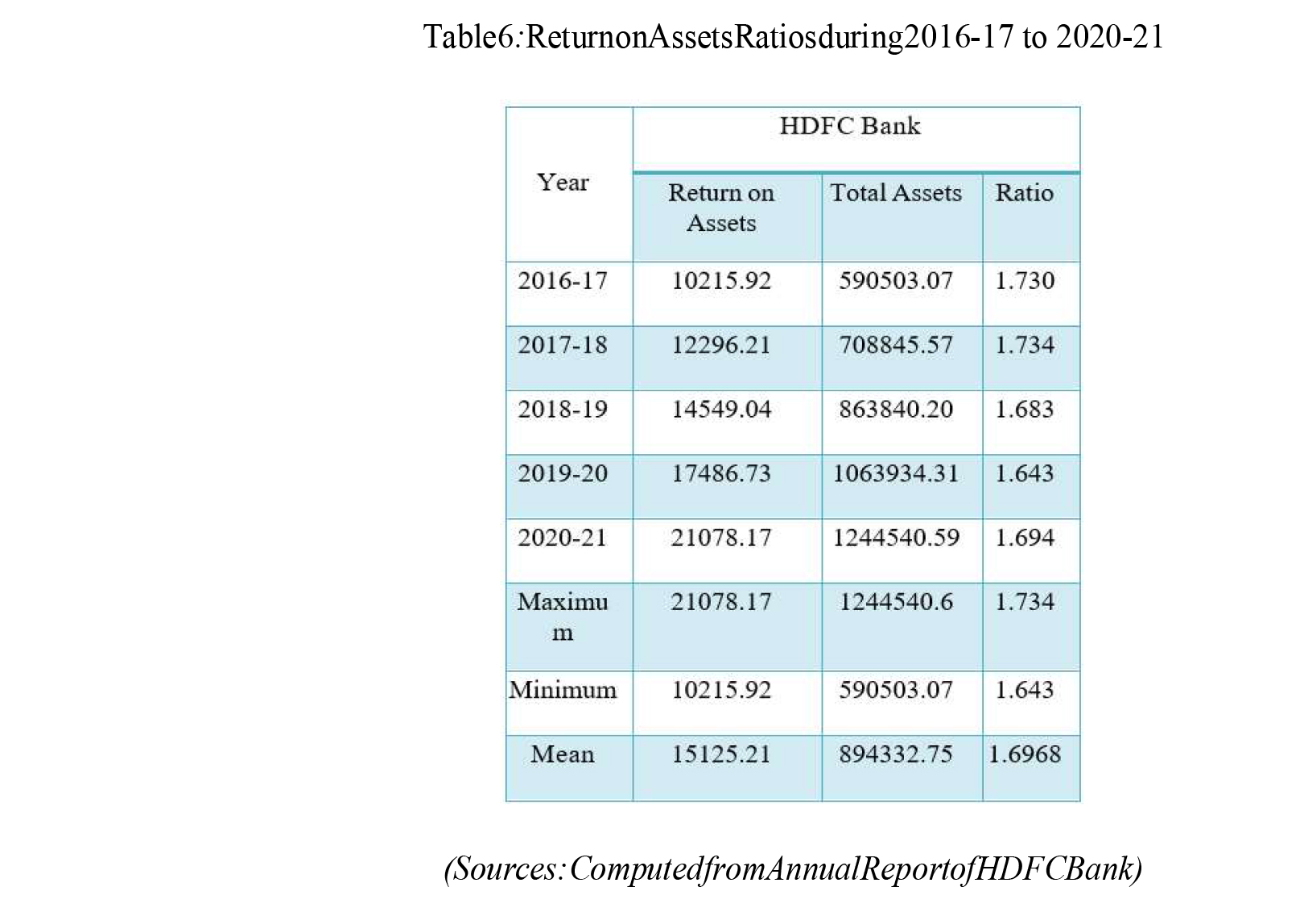
Table 6 shows the HDFC's Return on Assets Ratio from 2016-17 to 2020-21, as seen above. The HDFC Bank's average Profit Ratio over the research period was 1.69. In 2017-18, the ratio was greater, at 1.73, than in 2019-20, at 1.643.
Hypothesis
H0=ThereisnosignificancedifferenceofReturnonassetsratioinselectedHDFCBank.
Table 7:With equal variance, the two-sample Return on Assets Ratio
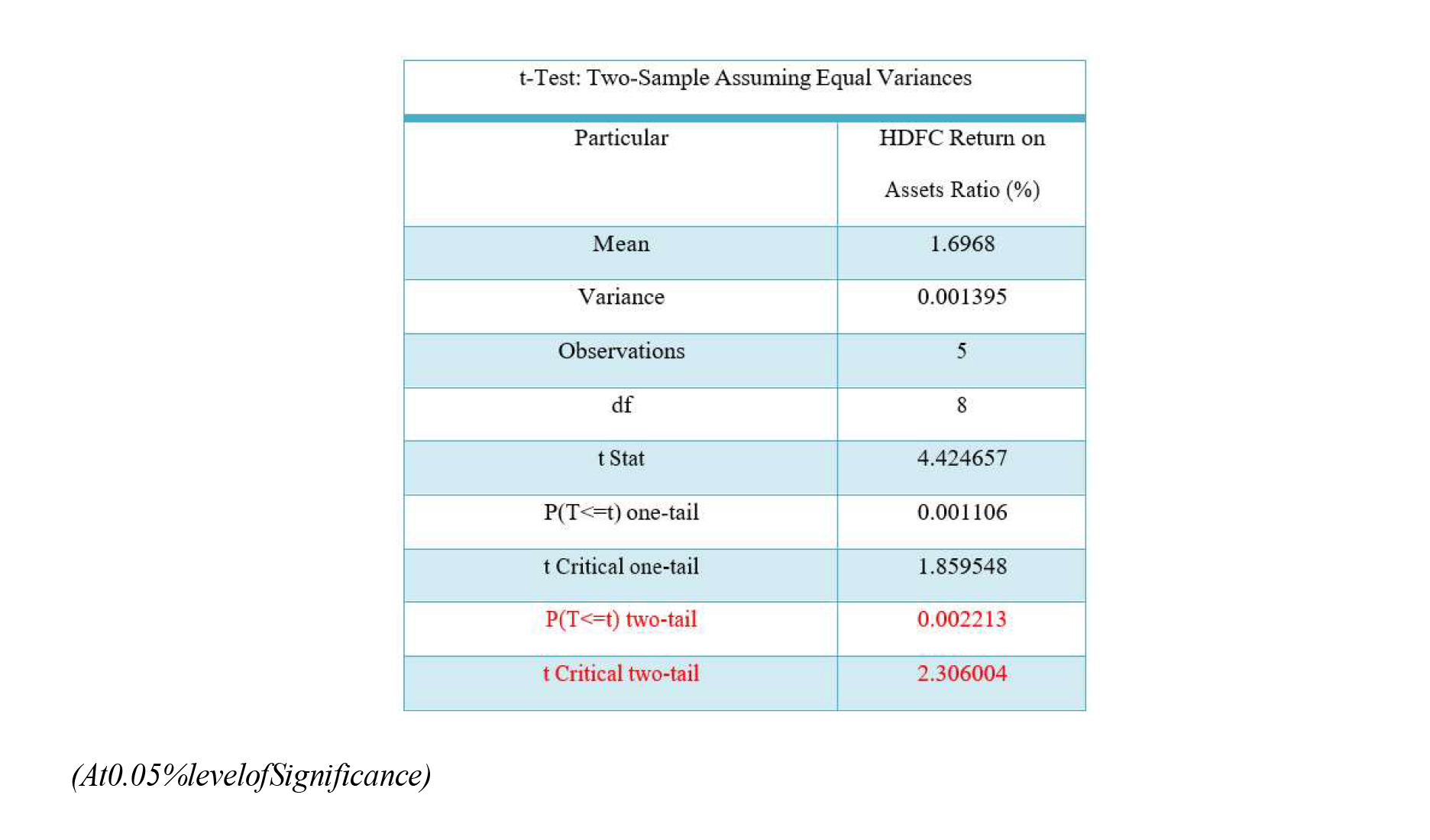
Table 7 displays the t-test results based on the computed value of 't', which is 4.424, and the table value of 't', which is 2.306. Consequently, at a level of significance of 5 percent, we reject the null hypothesis and adopt the alternative hypothesis. Excluding a bank loan, current assets + current liabilities plus current liabilities equals a meaningful amount. The capital employed is equal to the sum of one's net worth and one's entire debt

Significance:
This ratio is used to assess a company's overall performance.
From a managerial perspective, it's perhaps the most critical ratio.
Return on Capital Employed
Businesses use this ratio to measure their success. From a managerial perspective, it is of greatest importance.
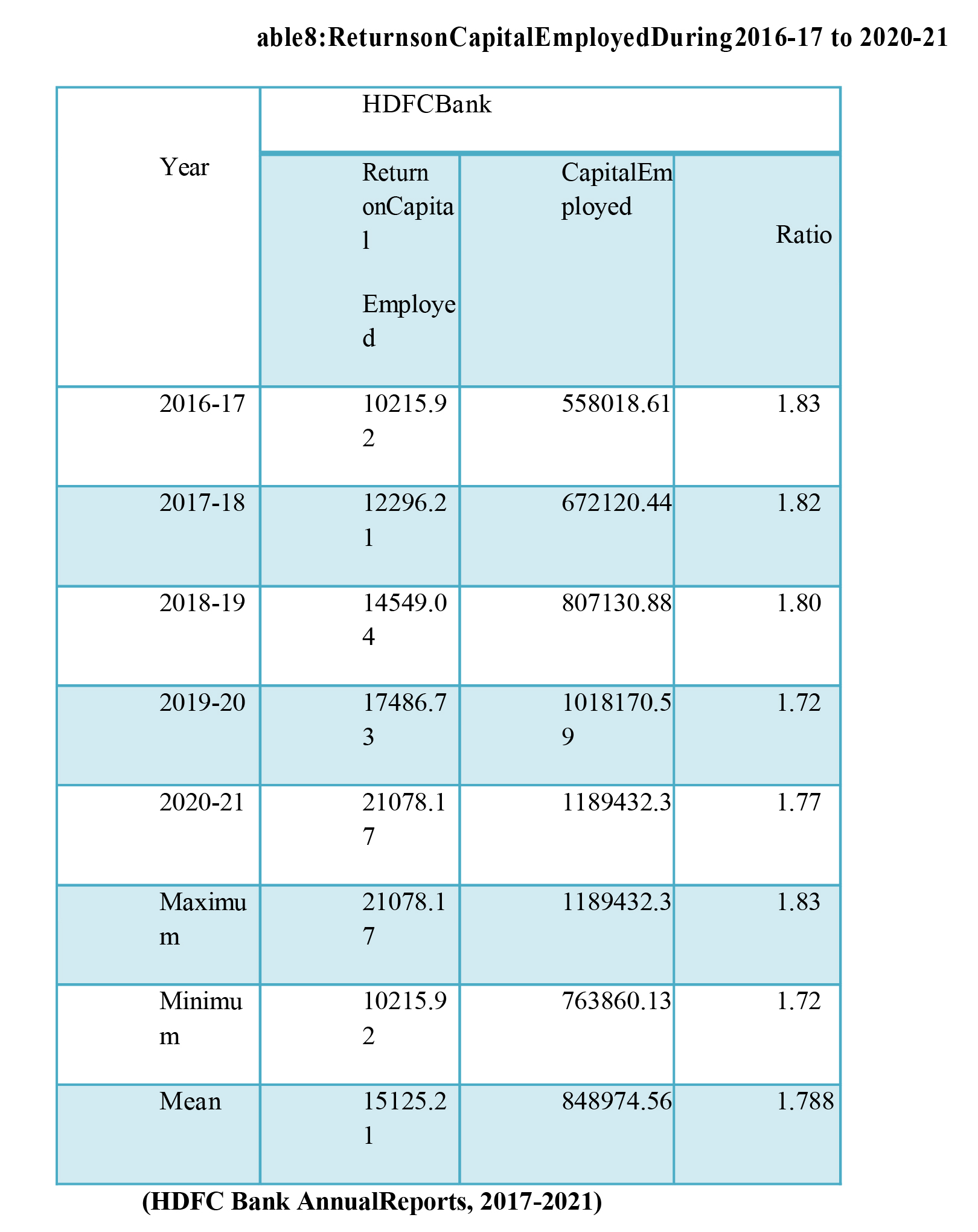
In the table 8 above, the HDFC's Capital Employed Ratio from 2016-17 to 2020-21 is shown. The Ratio fluctuates at HDFC Bank. During the time of the research, HDFC Bank's profit ratio averaged 1.788. In 2017-18, the ratio was 1.83, but in 2018-19, it was 1.72, the lowest of the two years. In 2017-18, it was 0.171, which dropped to 0.289 in 2020-21. Over the research period, the Ratio was higher in HDFC Bank..
Hypothesis:
H0= There is no significance difference of Return oncapitalemployedratioinselectedHDFCBank.
H1= There is a significance difference of Return oncapitalemployedratioinselectedHDFCBank.
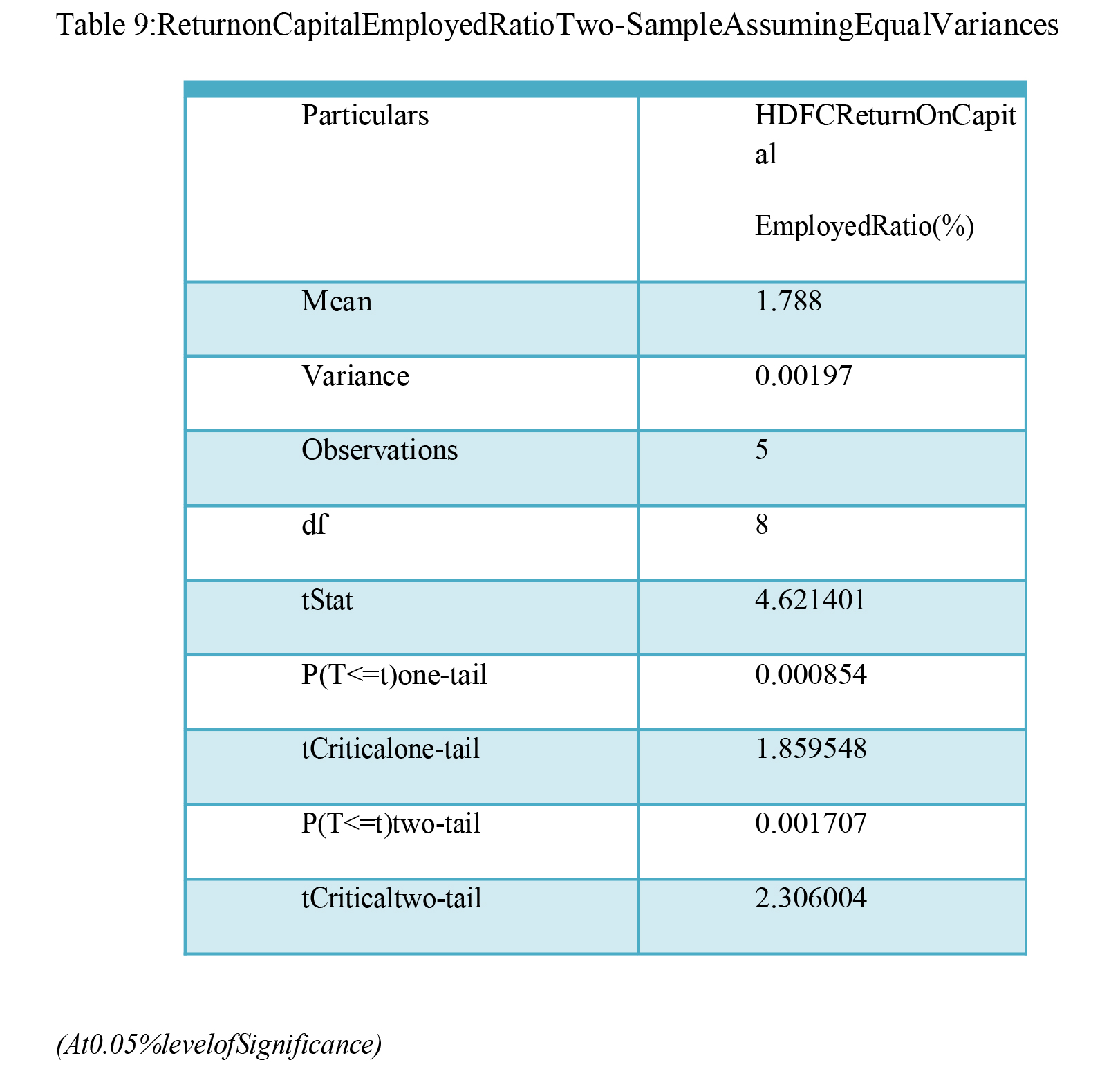
T-test results in table 9 reveal that the computed 't' value is 4.621, while the calculated value. Because the discrepancy between HDFC Bank's Return on Capital Employed and the null hypothesis is less than 5%, the alternative hypothesis is accepted.
CAMELS approach
"CAMELS" referring to Capital adequacy, Asset quality, Management, Earnings, Liquidity and Sensitivity is used in the study to measure the performance and health of HDFC Bank in these critical factors.This approach has been used by regulators and rating agencies to assess health of banks. This is a risk-based regulation that has gained popularity among bankers and regulators since the financial crisis (Mihir Dash, 2010).
The Capital Adequacy Ratio of HDFC Bank was 14.55% in 2017, 14.82% in 2018, 17% in 2019, 18.5% in 2020 and 18.8% in 2021. The ratio has been strengthening YOY basis and much above the regulatory stipulation of 9% indicating adequate Capital cushion in case of any eventuality. This establishes that banks have enough capital on reserve to handle a certain number of lossesand more likely will be able to withstand a financial downturn or other unforeseen losses.
Asset Quality: HDFC Bank's assets are examined in this component of CAMEL as they are exposed to various investment policies and various risks. A quality investment or asset is important to examine both the current status as well as potential future deterioration. The advances of Bank have increase from 8,19,401crores in 2018-19 to 9,93,703crores in 2019-20 and 11,32,837crores in 2020-21. Despite having a healthy growth of 21% in 2019-20 and 14% in 2020-21, the Gross NPA remained in the range of 1.30 % which indicates that quality of Assets has remained very good.
Management Quality:
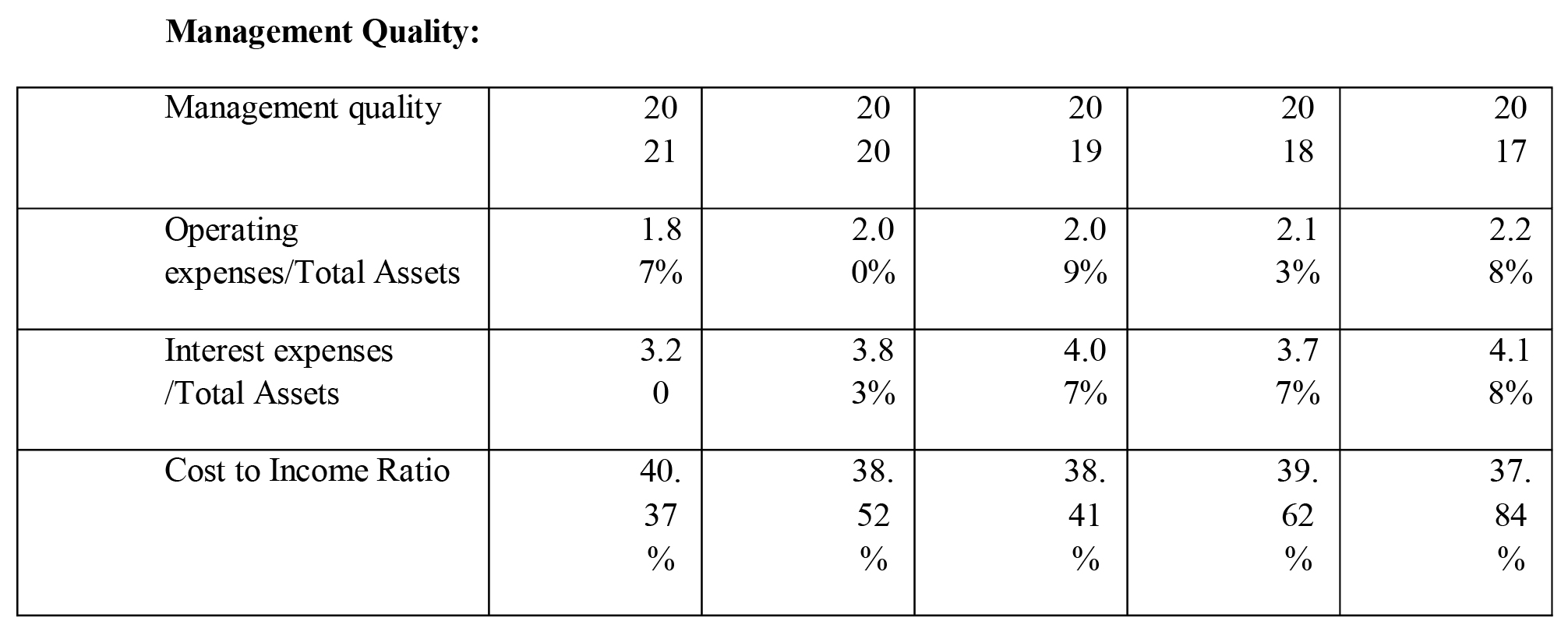
The above tables show few of the ratios which help to understand the quality of operations and management. These ratios over the five year period indicate thatbank is in safe hands and management at the bank is good and able to manage banking operations efficiently despite challenging operating environment.
Earnings:
The below table shows the ROA ,ROE, NPM, NIM which are the few of the ratios sindicating the earnings of the bank.
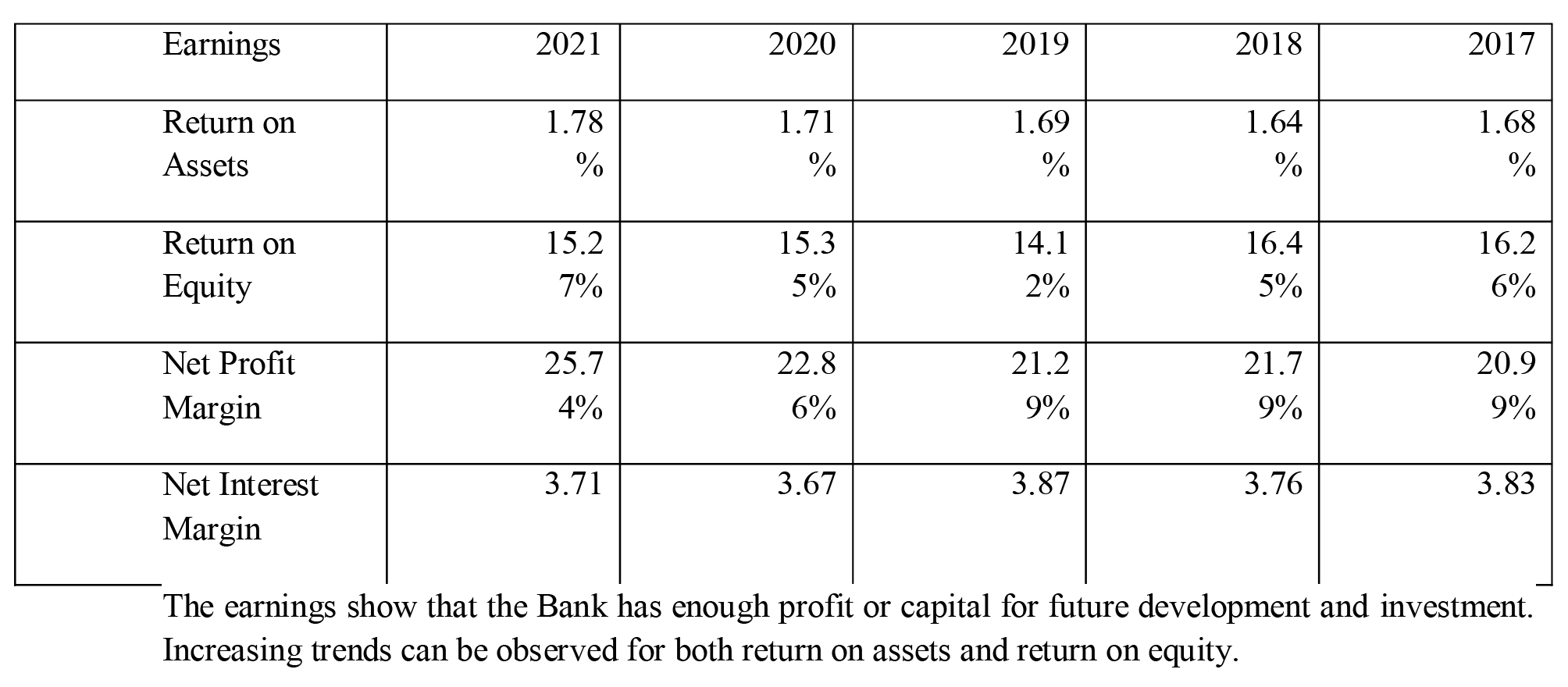
The earnings show that the Bank has enough profit or capital for future development and investment. Increasing trends can be observed for both return on assets and return on equity.
Liquidity: The CAMELs looks at liquidity from a broader perspective, which is an important aspect of the framework. This focuses on two aspects of financial risk: the risk of interest rates and the risk of liquidity. A CAMLE framework analyses the risk of adverse changes in interest rates and their impact on earnings (Albeshr and Nobanee, 2020). An analysis of the bank's balance sheet, interest rate exposure, and level of risk management is performed. In addition to liquidity management, banks' balance sheets are evaluated, as well as their ability to manage excess liquidity and cash flows. The liquidity ratios discussed in earlier paras clearly indicate that Bank liquidity is in excellent shape according to the Absolute Liquidity Ratio or Cash Position Ratio.
Sensitivity to the market:
The CAMEL framework concludes with this element. In this element assessment of how sensitive the bank's investment and other assets are to market fluctuations. To assess the impact of unexpected and abrupt changes in interest rates on the bank's earnings, this is added to the CAMLE. As well as price changes involving equity FX and commodities, the paper examines the sensitivity to these factors (Al-Blooshi and Nobanee, 2020).Beta is a good way to measure the risk of a market. HDFC Bank has a Beta of 0.89, which indicates that it is less volatile and sensitive to market risk. As a major part of its portfolio, the bank is exposed to credit risk, and exposed to derivatives as well. They diversify their lending portfolio and offer various global products to ensure that growth is not dependent on a single region.
FINDINGS:
- Capital Adequacy at 18.8% is much higher than RBI stipulation.
- Asset quality is robust.
- There is a strong correlation between current ratio and the bank's liquidity and ability to repay its loans.
- Bank liquidity is in excellent shape according to the Absolute Liquidity Ratio or Cash Position Ratio.
- During the time period under consideration, a significant proportion (or fixed assets ratio) of working capital was funded by long-term debt.
- During the research period, the debt equity ratio shows that creditors are secure.
- In the research period, the bank's long-term solvency is shown by the bank's proprietary ratio.
- Higher specific provision & contingency buffer of 77 bps provide comfort .
- Credit demand near pre-Covid level; MSME & retail segment to drive growth.
- Strategy to identify and expand segment & geography to aid momentum.
- Building up of physical/ digital infra to drive growth led by competitive edge.
- Strong liabilities franchise, adequate capitalisation and healthy provision buffer to aid business growth as well as earnings trajectory
- Superior underwriting process
- Asset quality concerns are behind but provision buffers likely to stay
CONCLUSION
The emergence of COVID-19 has affected banking operations in India and the financial industry as a whole. It has had a devastating impact on every industry on the planet, not just the financial sector. Due to COVID-19, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and government of India need to make periodic interventionsso as to keep the financial system and all of its parts liquid. The biggest bank in India's private sector , HDFC Bank was analyzed for financial performance from 2016-2017 through 2020-21 The major information was obtained from the bank's annual reports and its website. The ratios used to examine the data. In conclusion, this analysis indicated that HDFC bank's financial performance was good throughout the study period. HDFC Bank is expected to outperform the sector on the back of the following characteristics: 1) Strong balance sheet growth, 2) Strong operating income growth reflected in higher yielding credit cards,3) exceeding regulatory provisions on the balance sheet4) significant capital cushion at 17.9% and 5) outstanding underwriting practices and risk management.
The CAMELS analysis also shows that HDFC is more stable in terms of capital adequacy, earnings, quality of assets, and market sensitivity.
Given these strengths we can safely conclude that HDFC Bank will remain one of the best among all the banking institutions. However, bank doesn't need to be complacent and keep an eye on the competition, political and economic environment coupled with disruptions caused by technology and Fintech revolution. India's banking industry is undergoing a transformation, and digital banking is taking center stage. The digital banking channel is being considered as another means of differentiating from competitors and engaging customers. This is seen as an opportunity by banks to engage with their customers, which could lead to both increased income and customer retention and loyalty. Fintech companies also pose a threat to banks, as they are steadily eating market share from them. In the wake of recent recurring technology outages that led to the RBI banning HDFC Bank from issuing new credit cards and delaying its new Digital 2.0 initiative, HDFC Bank needs to learn from the mistakes it made. In his annual report for 2020-21, HDFC Bank MD and CEO Sashi Jagdishan also acknowledged deficiencies in compliance, coupled with technology issues that led to regulatory actions. As a result of HDFC Bank's failure to comply with regulatory requirements regarding its auto loan portfolio, the Reserve Bank has imposed a penalty of Rs 10 crore on the bank.(Redoubled efforts to fix issue': HDFC Bank CEO apologises for tech outages, 2021)
References :
