Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Liquidity of funds: Deciding factor in choosing investment plan for children education
Abstract :
Liquidity of investment is one of the criteria in investment decisions. Systematic investment plans and insurance are short or long term investment plans. The amount will be due only after all these instalments are paid. The children education is one of the future investments and fulfilment of life commitments. But, an investment like bank deposits get interest but has liquidity, higher than SIP and insurance. The investment in children education insurance depends income, saving, number of children, level of education, course and fees structure, etc. The study was conducted in Bangalore and found that the investment in children education is a personal choice and depends on how the parents plan education and interest of students. The career planning is influenced by financial potential of the respondents.
Keywords :
children education, investment, education insurance.Introduction
Children Investment schemes are a specific investment scheme to ensure adequate fund for the children's career development and life plans. The academic process is a dynamic segment in which new courses and domains arise along with changing economic, technological, and political changes. Hence, it is the responsibility of parents to plan and manage the life and career of the children with the changing environment. The child investment plans is an investment avenue in which the future of next generation is financed with the current saving of parents
Importance of Children investment
A model citizen is nurtured through a systematic process of education , parenting, lifestyle and opportunities for further career development. Providing the best education, training, and opportunities, every parent has to plan the savings such that the priority will be given for the career of children. At the same time, every family has to give importance for other needs like, shelter, health, fitness and hygiene as well. The cost of medical treatments, shelter and education are increasing continuously and these expenses in future has to be planned though systematic investment plans.
A few challenges in planning children plan are, inadequate and inconsistent income, inadequate saving, lack of awareness on different investment avenues and lack of financial literacy. Being the resources are limited, the families have to maintain liquidity of funds for immediate financial needs and systematic saving as well without compromising return but at a low risk. In education funding, the student's educational loan such that they can pay after course and placed while another option is to use family funds. The investments for children fund can be fixed deposits, mutual funds for children growth fund, Insurance schemes or directly invest in stock market. The risk-return combination changes with investment avenue. The utility of educational loan and systematic loan are same except in only one thing, utility is solved at first in education loan while it will be at last for systematic investment plan. The education loans will be supported by guarantees or mortgages while in systematic investment, there is no guarantee from the financier but a trust that there is no option to offload the risk of investor. Only credit rating or long history or past performance are the factors that give confidence.
The liquidity has a benefit and a problem as well. The liquid funds will be consumed in need and may not be available for the planned purpose as they are readily available. But in systematic investment plans, the fund will be locked during the plan that diversion of fund may not happen.
Child investment Plans and family income
Maslow's need theory and investor's attitude are the deciding factors in choosing an appropriate investment plan. In the case of fundingchildren education, there a two levels of effects occur, child level and parent level. In the child's level, there is a systemic growth trajectory from, physical needs, safety needs, belonging and love needs, esteem needs, cognitive needs, aesthetic needs, self-actualization, and transcendence. But, the role of the parent is to ensure these in different ages in life and to achieve self-actualization in fulfilling the commitment to educate, and place the children in right position in career and their life attains transcendence as the children take care of them from physiological, safety and belonging and love needs(McLeod, 2018). Hence, the investor's attitude towards the children is also affective ( to avail the best education), cognitive (plan career) and behavioural ( choose right course) (Jain, 2014). Liquidity factor of investment is the easiness convert to cash and whenever the money is needed for children, it can be made available for it, Multiple term deposits or SIPs can help in this regard.
Theoretical Background
The career perspective has been changed from a linear relation of employer skill and organizational needs to 'a flexible career planningbased on value, flexibility and growth' which needs a tremendous personal development in achieving set unique goals. The Digital world had helped the individuals to select a profession according to own interest. This need focussed training and involvement. It demands a deviation from traditional education system to vocational and creative career management and it needs dynamism is updating the skills and profession (Sullivan & Baruch, 2013)
The Keyson's theory explained average propensity to consume (APC) and marginal propensity to consume (MPC) to explain the average consumption per income and marginal increase in consumption per unit increase in income. This measure is important in managing our consumption and saving for a specific purpose. Financial literacy and family budgeting are the requirements in managing consumption according to income. Life Cycle Model says the potential life of a person to earn so that the propensity to consume can be improved through wealth creation (Parker, 2010).
The Veblen Effect may be defined as the interest of people to buy expensive products as their income increases. In the career development also, a similar trend is visible that unique and new generation courses are expensive but rewarding in placement. Availing education in developed counties also become common for affordable parents or potential students to pay off the loan from their earning. It can be termed as a conspicuousconsumption as a wealth accumulation is needed to meet the investment in it, depending on propensity to save and accumulate the saving (Bagwell & Bernheim, 1996)
Social Media and Career Choice
Social Media has both constructive and destructive effect on young generation due to the high possibility of indulging in different websites with good and bad intentions. The high degree of collaborations with sites and social groups that provide new trends in career, income, etc as well as the groups in which the youth can participate in programs in online helps to redefine their career perspective. Even, a few parents are also vigilant on career development of their kids. The real utility is attained only if the children are in right track of career development to ensure the benefit of investment.
Statement of Problem
The propensity to save is the fundamental for investment and investment is the process of using available saving for future use for higher return and specific utility. Children Investment is one of such investments to ensure fund availability at the time of need. Hence , the investor's attitude towards the investments are important in deciding the type of investment along with career selection of the child which intern depends on interest, capability and fitness of the child
Objectives
• To analyse the effect of life cycle on choosing investment for child investment
• To analyse the effect of life cycle on factors in choosing children career plan and investment on career
Research Methodology
The population of this research are the employed respondents in Bengaluru city of Karnataka State and the data was collected using a structured questionnaire, with reliability of Cronbach alpha of 0.72 and improved consistency through test and re test method.
The sample size is 432.
Crosstab is used to test the hypothesis using chi quare .
Hypothesis Testing
• There is no significant effect of life cycle on choosing investment avenues
• There is no significant effect of life cycle on child investment plan
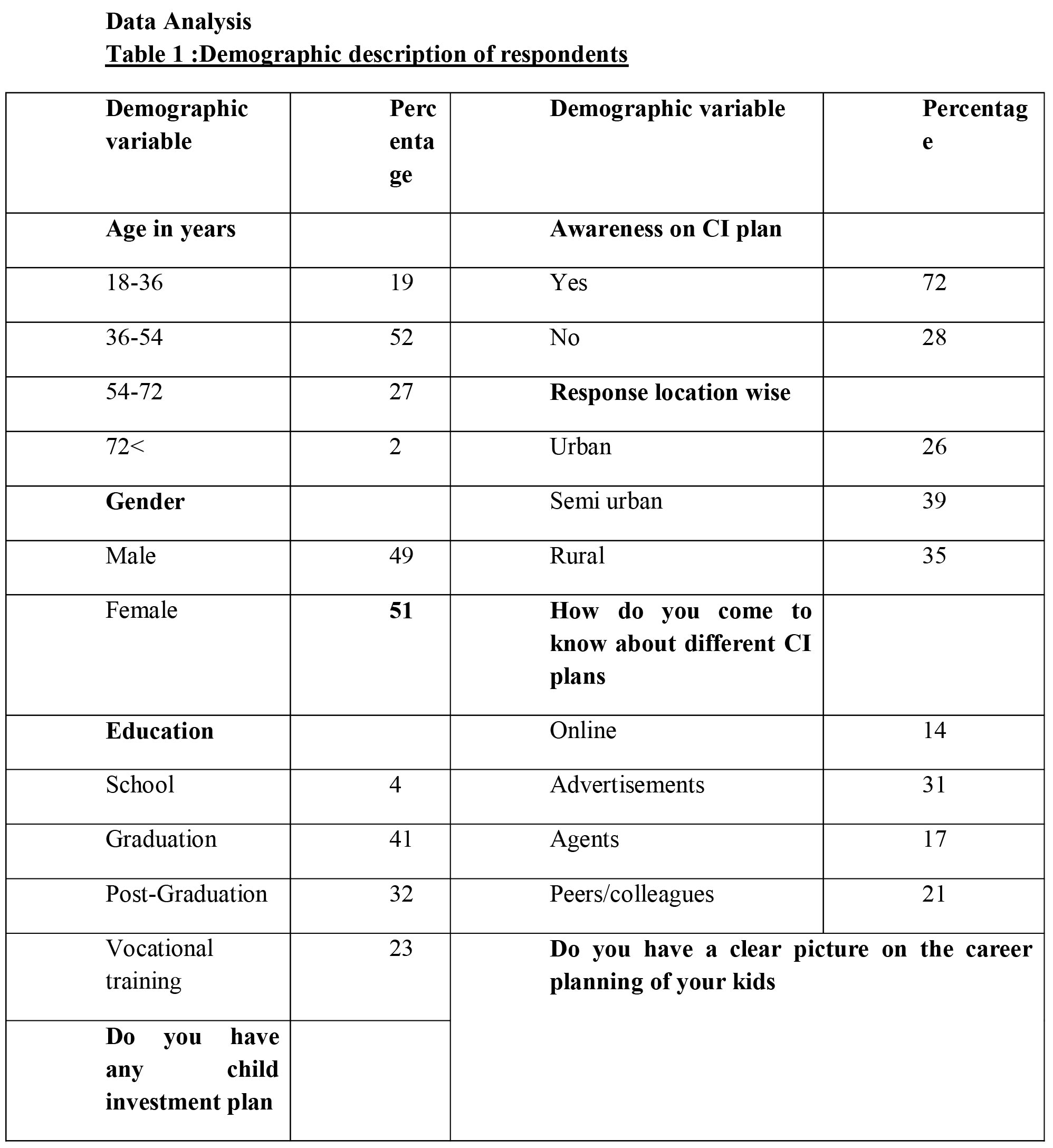
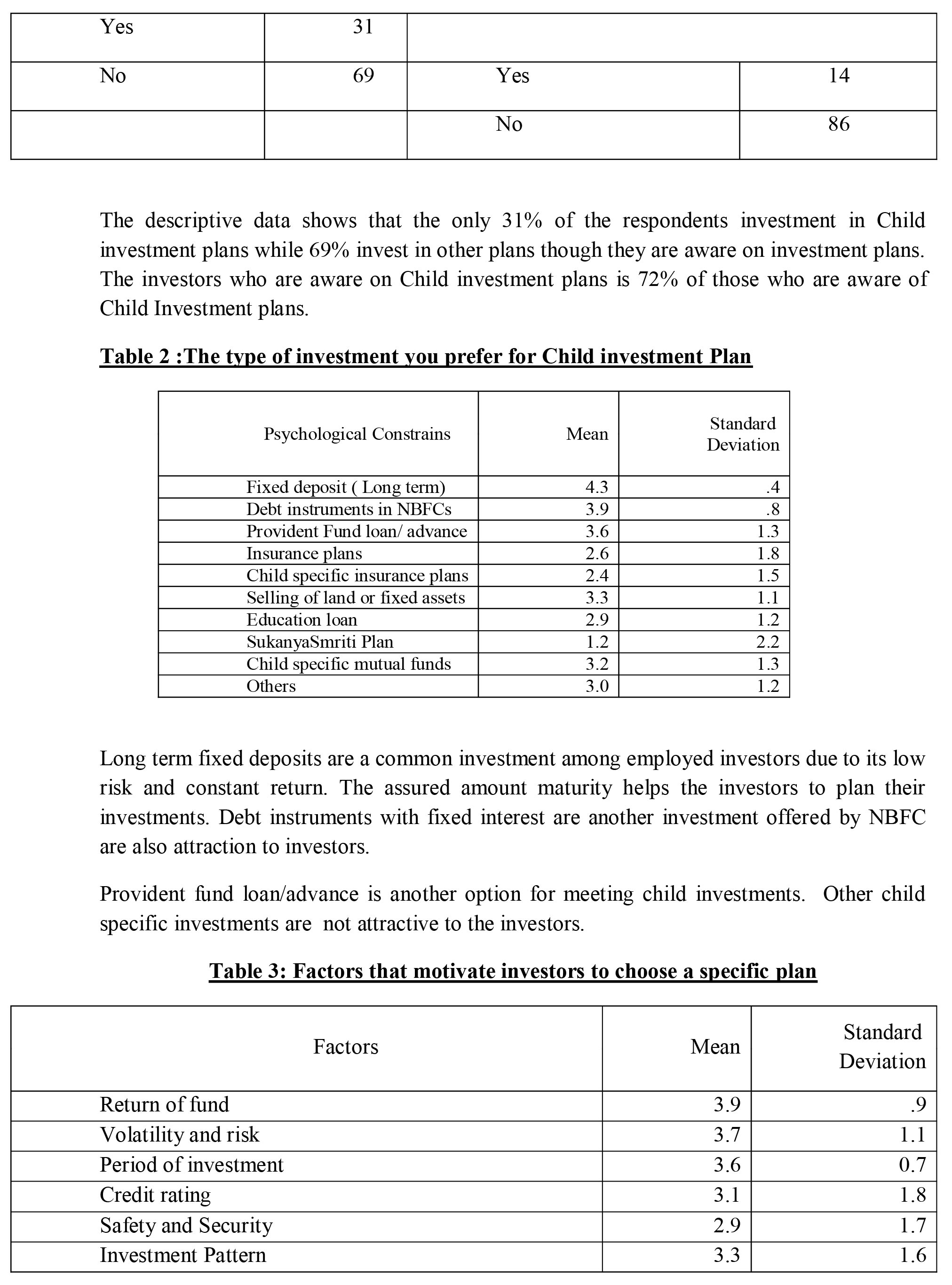
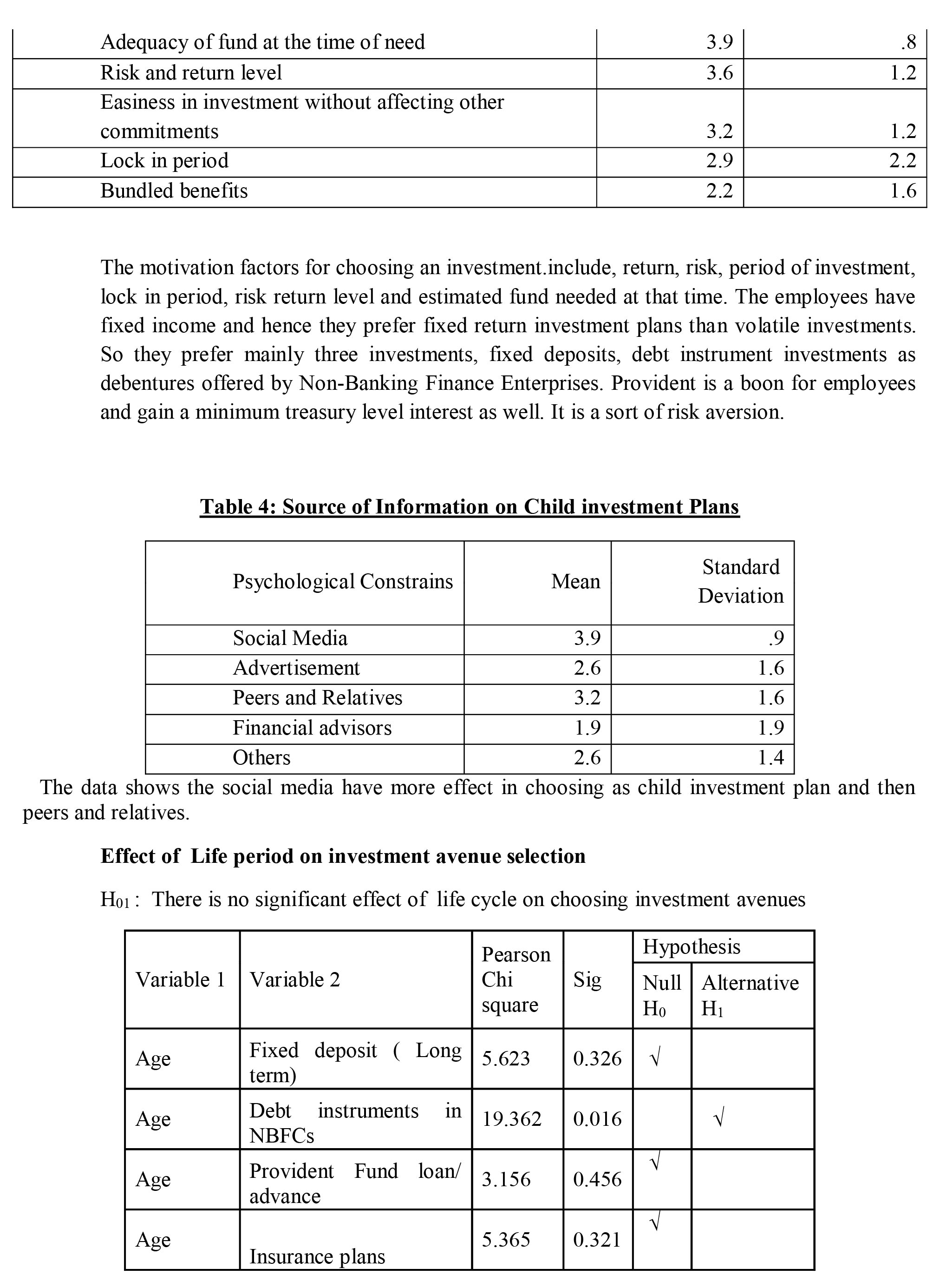
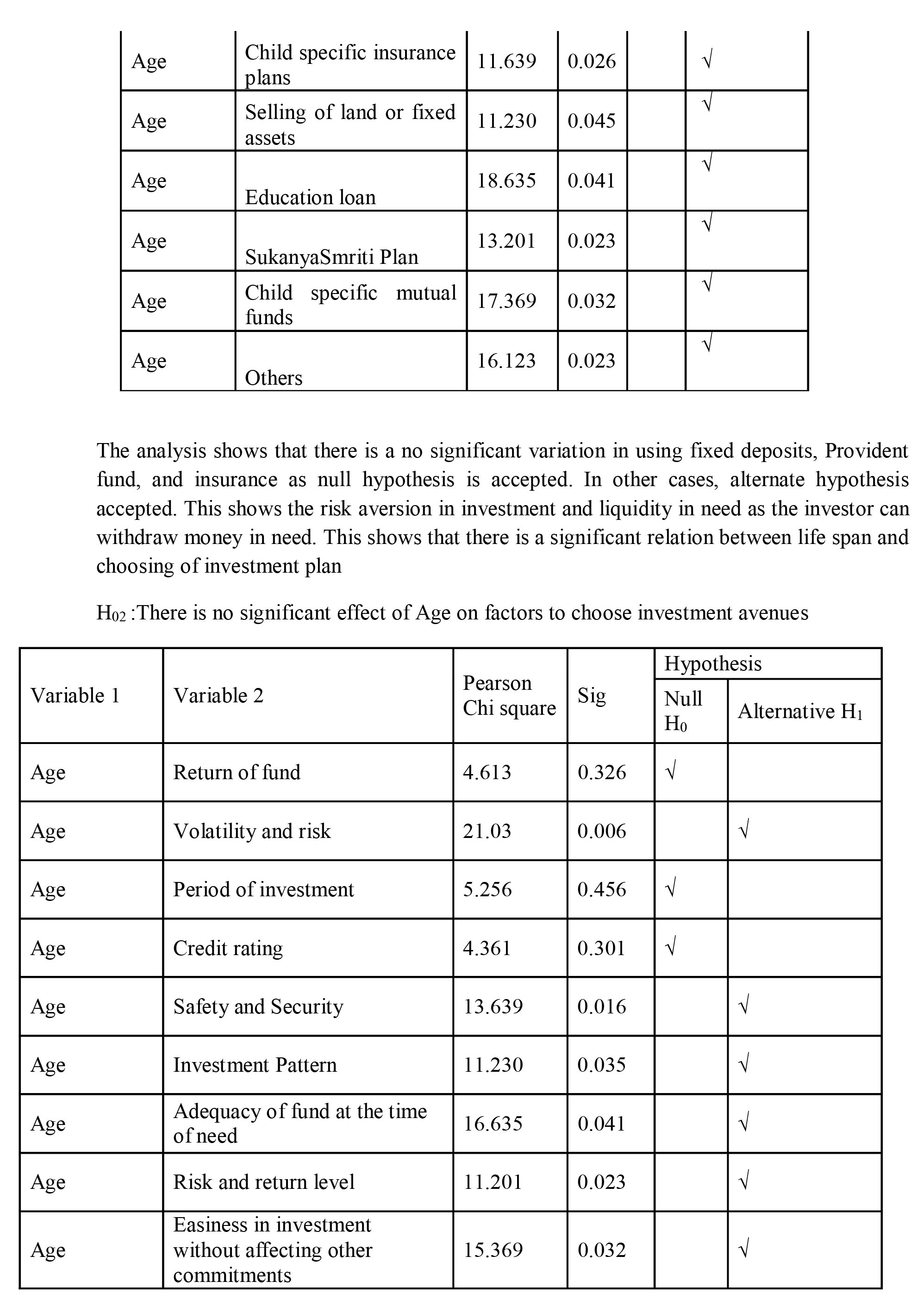
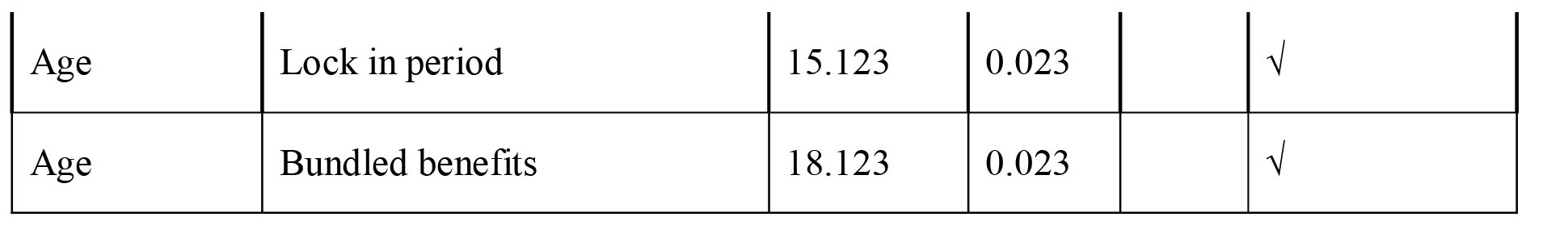
The data shows that there is no significant effect on three factors , return, period of investment and credit rating. In other cases alternative hypothesis is selected. There is a significant effect of life on choosing child investment plan
Conclusion
The results shows that the child investment plans are not so popular among employees as they focus more on fixed deposits, insurance and fixed investment plans of NBFCs. In other cases the perception towards the investment avenues differs with age or life cycle. The fixed deposits have high rate of return. Similarly, perception on Return on investment, period of investment and credit remain same irrespective of age while perception towards other attributes changes. This supports effect of life cycle model on investment pattern
Bibliography
- Aydin, G., Uray, N., & Silahtaroglu, G. (2021). How to Engage Consumers through Effective Social Media Use-Guidelines for Consumer Goods Companies from an Emerging Market. Journal Theoretical Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16, 768-790. Retrieved from . https://doi.org/10.3390/jtaer16040044
- Bagwell, L. S., & Bernheim, B. D. (1996). Veblen effects in a theory of conspicuous consumption. The American Economic Review, 349-375.
- Busenna, P., & Reddy, A. A. (2021). KHADI & VILLAGE INDUSTRY : A CASE STUDY OF KHADI INSTITUTIONS IN INDIA. Journal of Rural Development, 273-291.
- Cipolla, C. M. (1956). Money, Prices and Civilization in the Mediterranean World, Fifth to Seven teenth Century, New York: Gordian Press.
- Deepti Sharma, D. A. (2019). A Study Of Consumer Perception Towards M Wallets. NTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & TECHNOLOGY .
- Jain, V. (2014). 3D MODEL OF ATTITUDE. nternational Journal of Advanced Research in Management and Social Sciences.
- McLeod, S. A. (2018). Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Retrieved from https://www.simplypsychology.org/maslow.html
- Parker, J. (2010). Economics 314 Course work.
- Sadek, H., & Elwy, S. (2018, January). The impact of social media brand communication on consumer-based brand equity dimensions through Facebook in fast moving consumer goods: The case of Egypt. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 12(2).
- Siddiqui, S., & Singh, T. (2016). Social Media its Impact with Positive and Negative Aspects. International Journal of Computer Applications Technology and Research, 5(2), 71-75.
- Sullivan, S. E., & Baruch, Y. (2013). Advances in Career Theory and Research: A Critical Review and Agenda for Future Exploration. Journal of Management. doi:DOI: 10.1177/0149206309350082
- Yapa, U. A. (2017). The Impact of Social Media on Brand Awareness (With Special Reference to Facebook Use in Fast Moving Consumer Goods in Sri Lanka). International Journal of Engineering and Management Research, 7(5), 262-272.
- Ye, X., Zhao, B., Nguyen, T. H., & Wang, S. (2019). Social Media and Social Awareness. In Manual of Digital Earth (pp. 425-440). Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9915-3_12
