Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Regression Analysis of India ‘s Gross Domestic Product per Capita and Personal Income Tax
Abstract :
When the Gross Domestic Product(per Capita) increases the common persons financial ability and his standard of living is rising. The present study covers the relation between the personal income tax and the gross domestic product per capita. It is assumed in the initial stage of the study that as the per capita GDP raises the standard of living giving a rise to more personal tax being paid. Regression and Correlation analysis is conducted to evaluate the contention of the researcher. More the income more is the spending as well as taxpaying, as the individual due to his increased income level pays more tax as he or she falls now in the taxpaying bracket. The Gross domestic Product per capita and the personal income tax seems to be rising since many years. The study proves that there is a linear relation between the Gross domestic Product per capita and the personal income tax. The study does not cover direct taxation as the study excludes corporate taxation from its scope. It also excludes the other direct taxes collected.
Keywords :
Gross Domestic Product per Capita, Personal Taxation, Regression AnalysisIntroduction:
Gross Domestic Product( per Capita ) is an important indicator of the standard of living in country. Hence it is assumed that when the Gross Domestic Product( per Capita ) increases the common persons financial ability and his standard of living is rising. A study says that if the tax on income would add to the Gross Domestic Product and thereby increase the standard of living ( Michael Busler , (2013).Gross Domestic product is the measurement of a countries growth. . The major source of revenue for any country are the taxes. As per a study the direct taxes impact and influence the growth of the gross domestic product. (Geetanjali, J., & Venugopal, P. (2017). It is observed in several studies that Gross Domestic Product and Tax revenues are positively correlated, however in some cases there is a negative relation. In the tax system there are two types of taxes:- direct taxes and indirect taxes. Direct taxes include income tax as a significant type of tax. Income tax forms an important component of revenue for the government. Income tax comprises of taxes collected on the income of corporate entities as well as individuals. The present study covers the relation between the personal income tax and the gross domestic product per capita. It is assumed in the initial stage of the study that as the per capita GDP raises the standard of living giving a rise to more personal tax being paid. Regression and Correlation analysis is conducted to evaluate the contention of the researcher.
Need and significance of study
The gross domestic product per capita is rising. It is an important indicator of the standard of living, which means that the standard of living of individuals. It must be studied as to what is the impact of rising Gross Domestic product per capita on various financial parameters. At the same time it can be noticed that the personal income tax is also rising in the same period. Tax is an important source of revenue to the government. Hence if more tax is collected more is the revenue to the government. The government utilises the revenue for various important expenditure like infrastructure, healthcare, education to name a few. Personal income tax payment happens on the income which an individual is earning. The standard of living rises if the income of the individual increases, if the income increases the tax payment by the individual to the government increases. The practical implications are that the paper tries to connect the gross domestic product per capita and the personal income tax. The paper tries to study the assumption that the rise in income and thereafter the personal income tax is an outcome of rise in standard of living, of which Gross domestic product per capita is an indicator.
Review of Literature.
Further study conducted in Nigeria concluded that the direct income tax has a positive effect of 5% on the GDP . (Odum, Augustine & Chinwe Odum, Gloria & Egbunike, Chinedu. (2018). In china it was studied that if the personal income tax is improved it would lead to better economic development. (Y. Jin and X. Jia,2011) A positive relation was not found in a study between oil process and growth of energy. The study further suggested that when the growth in the energy use is positive as compared to growth in the gross domestic product. However the rise is not proportionate .(Rögnvaldur Hannesson, (2009).Similarly another study conducted revealed a positive correlation between gross domestic product and foreign direct investment, Artificial Neural networks were used to depict the relation between the two.( Liu Ying, Cui Riming, (2008). Personal income tax seems to be unproductive in Nigeria as per a study. And inorder to increase it efforts should be undertaken by government was suggested. (Nwanyanwu, Loveday. (2016).Gross domestic product is an important economic measurement which throws light on the economic health of the economy. Therefore a study conducted in Hong Kong reveals that the hotel industry was one of the contributors to the gross domestic product or GDP was affected at the time of economic crisis of 1997 in Asia, thereby impacting the GDP as well. (Wilco W. Chan Joseph C. Lam, (2000)," Gross domestic product per capita, consumption and income are correlated. The association is strong in the lower and middle income countries for income and consumption. The relation for all the three of them is strong for the same middle and low income nations. (Diacon, P., & Maha, L. (2015).In another survey the Gross domestic product per capita was inked with the human capita index with respect to the happiness (William R. Dipietro Emmanuel Anoruo, (2006).The performance of a country by its economy can be measured by the Gross domestic product per capita. It was observed in a study that there is no significant relation with unemployment and literacy rate. Though per capita GDP is positively related with literacy and negatively with unemployment.( Rahman, M. S.. (2011) A study confirms that there is a positive relationship between tariffs, consumption and gross domestic product( per capita). The study affirms that the revenues collected thorugh tariffs should be used for fruitful projects which will induce economic growth. (Metri Fayez Mdanat, Manhal Shotar, Ghazi Samawi, Jean. Mulot, Talah S. Arabiyat, Mohammed A. Alzyadat, 2016). A study revelas that the tax has a profund impact on the consumption in the lowest income group (Zhang, D.L. (2017).A paper concludes that the personal income tax has an influence on the government as it is an important component of the direct taxes. (Szarowská, Irena. (2014). In China as well as in Canada the payments of taxes are rising in case of high tax individuals. Horn‐Chern Lin, Tao Zeng, (2010).India is emerging as a significant country in the global context, but the tax system is complex. Policies for taxation can useful to induce investments. (Reji George Y V Reddy , (2015),"Reforms in trade policies can have a positive consequence on the revenue generated through tax. (Sena Kimm Gnangnon, (2017)
Statement of Problem
Different studies have shade light on the relation between taxation and the Gross Domestic Product. Studies have reiterated the fact that tax revenues lead to the increase in the Gross Domestic product. As the revenues are utilised by the governments to invest in policies which are beneficial to citizens and industries thereby leading to an improvement in the Gross Domestic Product. When the gross domestic product per capita increases it is assumed that the standard of living rises or increases. The current paper attempts to test this relation between the GDP per capita and the person’s ability to earn more income. When the standard of living rises the income earning capacity rises as there are more opportunity related to employment. More the income more is the spending as well as taxpaying, as the individual due to his increased income level pays more tax as he or she falls now in the tax paying bracket. The GDP per capita for India is rising and so is the quantum of personal tax paid. The study therefore tries to explore whether personal taxation and GDP per capita are related.
Data Description
Times series data is considered for the research of Gross Domestic Product of India in US $ and the personal income tax paid (in Crores) is in
INR. The source of the data for Gross Domestic product is the World Bank website and the source for the data on personal income tax
is - Statistical Year Book India 2017 on Direct and Indirect Taxes
Both the data sets are for a period of 18 years from 2000 to 2017
Both the dependant and the independant variables are coded as follows:-
Per Capita Gross Domestic Product in US Dollars = GDPUS$
Personal Income Taxation = PTAXRS
Methodology:
The data is for the 18years and is analysed using the Simple Regression methodology. Dependant variable is personal income tax, and the Independent variable is Gross Domestic Product per capita of India in US $. The personal income tax is in Indian Rupees(in Crores) whereas the Gross Domestic Product per capita is in US dollars
Objectives of the Study:-
After analysing the available literature one can observe that there has been studies on the influence of Direct taxation on GDP per capita. However the current study tries to throw light on the relation between personal income tax and Gross Domestic Product per capita. The government seems to be collecting more Personal Income Tax as the Gross Domestic Product per capita is increasing over the years
The objectives are:-
- To study and analyze the relation between personal Income taxation and GDP per capita.
- To ascertain growth in Gross Domestic Product has an impact on the personal income tax
Limitations of the Study
The study covers the linear relation between the per capita Gross domestic Product and the personal taxation. The study focuses on the personal taxation and not on the direct taxation. Direct taxation covers corporate taxation, personal income tax and other taxes. In the current paper the researcher specifically tries to link personal income tax and the per capita Gross domestic Product.
Hypothesis Testing
For proving the linear relationship between per capita Gross domestic Product and Personal Taxation the following hypothesis is formulated. Hypothesis: There is assumed to be
a linear relationship between the per capita Gross domestic Product and Personal Income Tax.
The H0 and H1 i.e the null and alternative hypothesis are as follows:- H0: There is no significant linear relationship between the independent variable which is per
capita Gross domestic Product and the dependent variable Personal Income Tax H1: there is a significant linear relationship between the independent variable which is per
capita Gross domestic Product and the dependent variable Personal Income Tax
The ANOVA table, depicts how well the regression equation fits the data. In other the table
reveals that the regression model predicts the dependent variable significantly well. The p < 0.000, and is less than 0.05 thus indicates that, overall, the regression model
statistically significantly predicts the outcome variable and it is a good fit for the data.
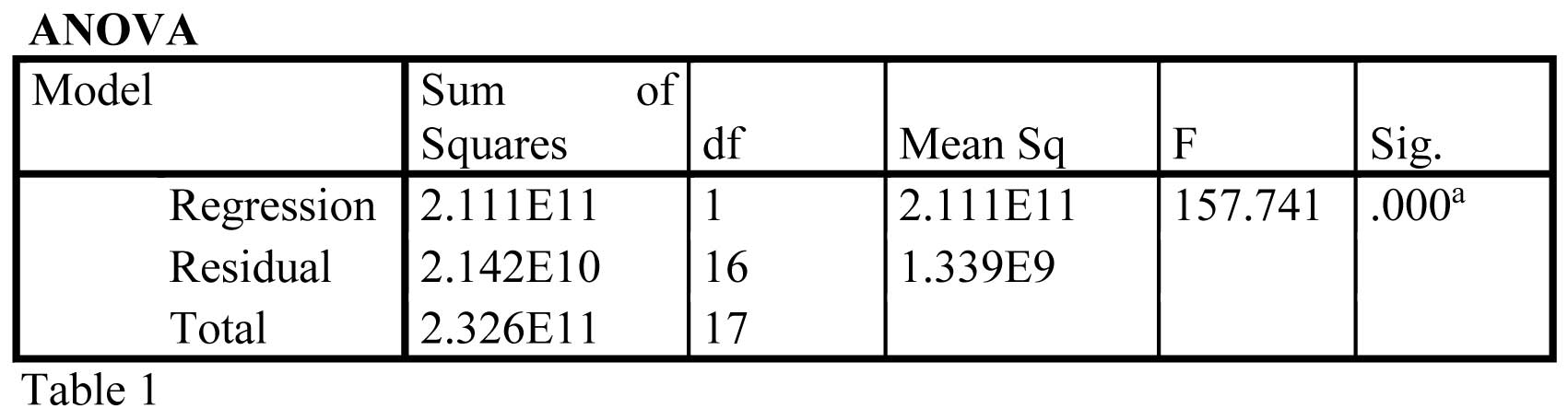
It can be observed that the P value is 0.000, which indicates that the H0 Stands rejected and the H1 is accepted.
H1: there is a significant linear relationship between the independent variable which is per capita GDP and the dependent variable Personal
Income Tax
Thus the hypothesis that there is a linear relationship between the per capita GDP per capita and Personal Income Tax stands proved.
This also suggests that as the Gross Domestic Product per capita rises or increases the Personal Income Tax also rises or increases.
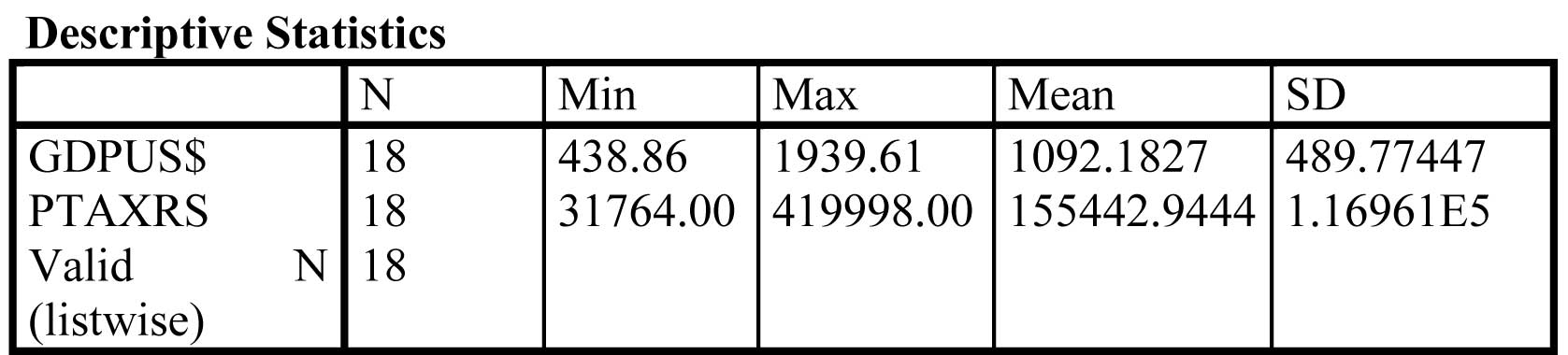
Descriptive Statistics
The Mean GDP in US$ is 1092.1827 whereas the Personal tax in Rupees is 155442.944.
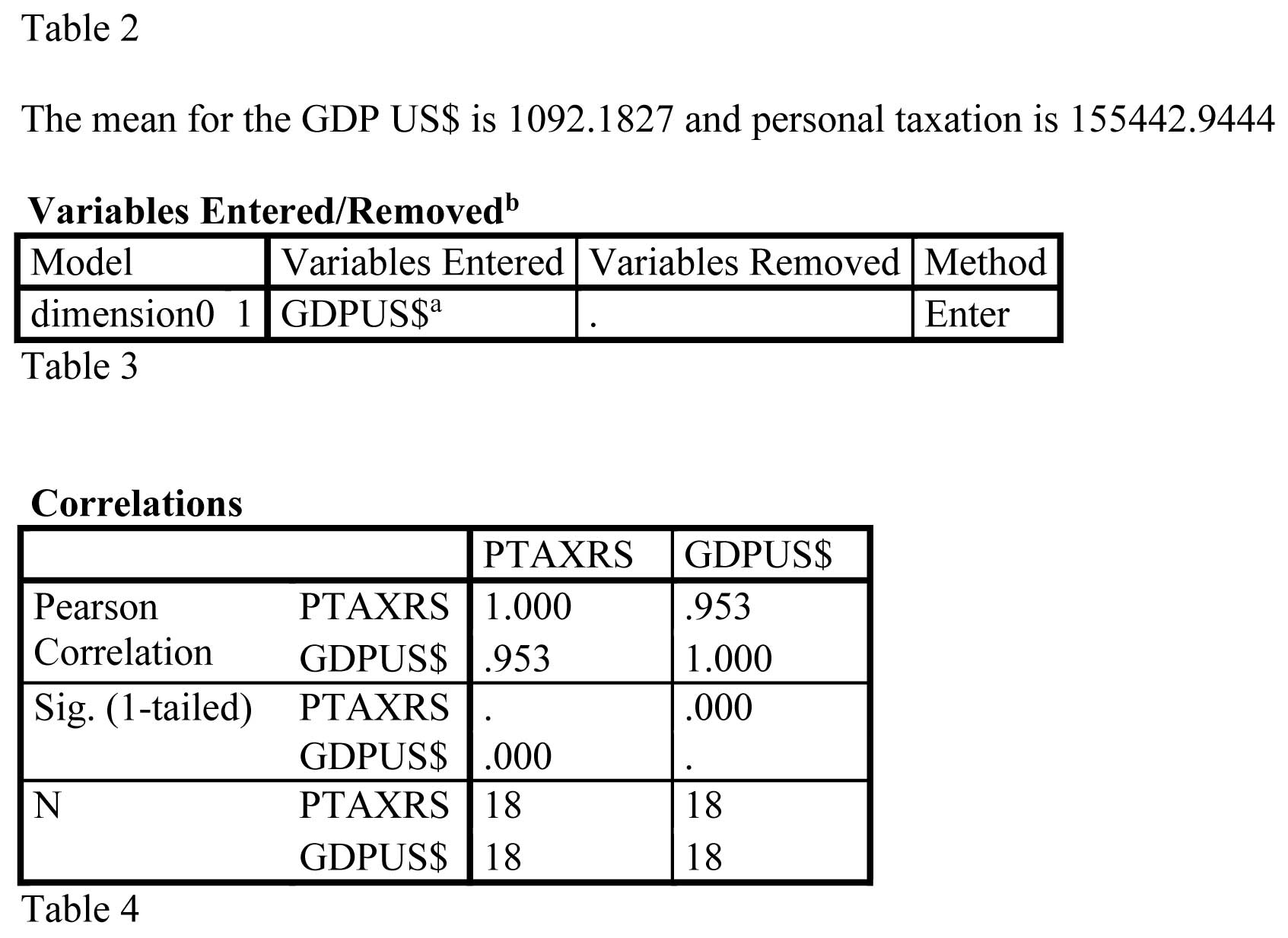
The Table shows a P value= 0.000, P value is less than 0.05. This indicates a correlation between the Gross Domestic Product per capita and the Personal Taxation.
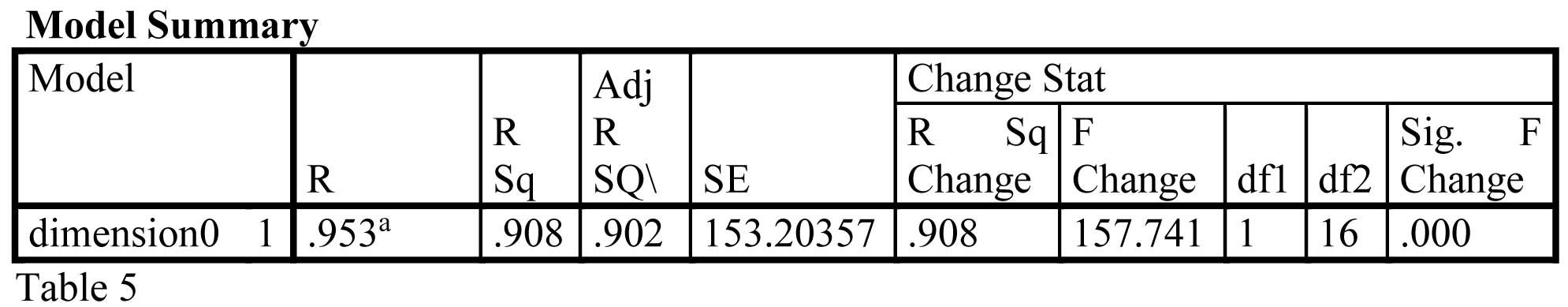
There is a high degree of correlation as the R value is 0.953. The R square is high as it is 90.8% which indicates how much of the total variation in the dependent variable personal income tax can be explained by the independent variable per Capita Gross Domestic Product.
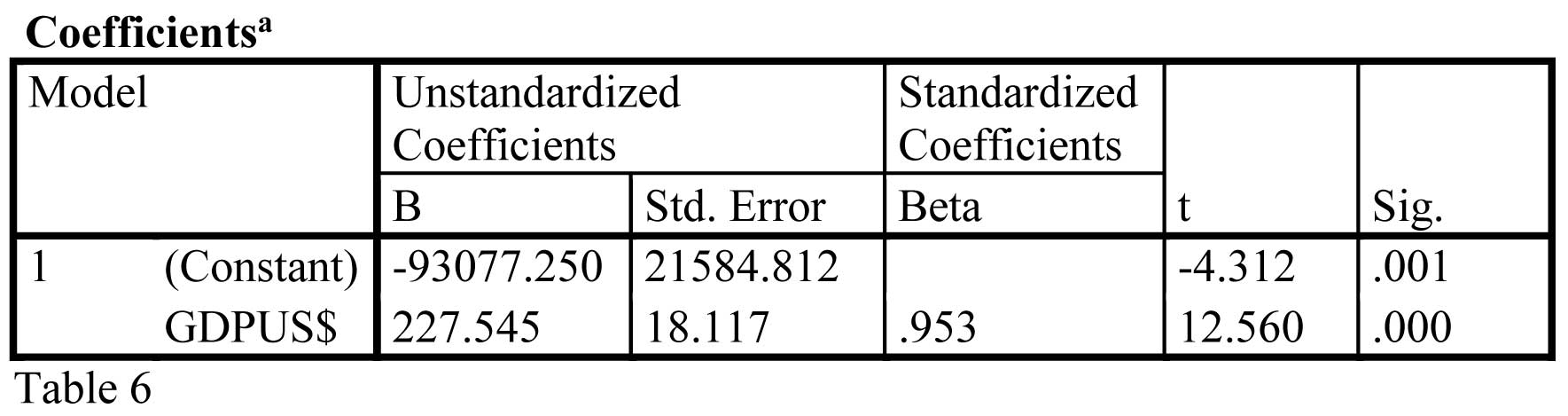
Hence the equation can be written as follows:-
PTAXRS = 227.45 (GDPUS$) - 93077.250. The Personal Income Tax is dependant variable and Gross Domestic Product per capita is the independent variable.
Findings:
There is a correlation between the Gross Domestic Product per capita and the Personal Income Tax. The ANOVAs table proves the hypothesis that there
is a linear relationship between the per capita GDP per capita and Personal Income Tax. The R value is 0.953 showing that the degree of correlation
is high. The R square is high as it is 90.8% . The high R-Square value depicts how much of the total variation in the dependent variable which is
personal income tax can be explained by the independent variable per Capita Gross domestic product.
As the Gross Domestic Product seems to be increasing so is the personal income tax. This shows that as the standard of living is increasing so is
the ability of individuals to pay taxes. If the individuals standard of living increases their ability to pay tax increases. Does this signify that
the rise in the standard of living can result in more collection of tax from the government’s point of view? Is the question to be asked and pondered
up on. From the review of literature and other studies it can be observed that rise in the Gross Domestic product is influenced by the rise in direct
taxes. And in the current paper the it can be concluded that the personal income tax collections are rising as a result of the rise in the per capita
Gross Domestic Product
The practical aspects of such a study are that as the gross domestic product per capita is the measure of the standard of
living. If the gross domestic product rises it can be inferred that the standard of living is also rising. This in turn means that the individual
citizen’s standard of living is rising. Thus since the personal taxes are rising which indicates that the income level and the tax paid is also
increases or rises. More taxes means more revenue to the government, which can be used for better government expenditure on healthcare, education.
A study like the present one can help in formulation of the better tax related policies as well.
Conclusion :
Gross Domestic Product per capita is an important measure in the economy. It throws light on the general standard of living. Regression analysis was carried to establish a linear relationship between Gross Domestic Product per capita and the Personal Income Tax Both the parameters have been raising. Hence was analysed to find whether any linear relation exists between the two. Many studies have thrown light on the impact or the influence of the Gross Domestic Product per Capita (GDP per capita) on various other sectors and parameters. Studied have commented on the influence on the direct taxation. Personal Income Tax is a component of direct taxes and in the current study corporate direct taxes are excluded. It can be concluded that the as the per capita GDP rises the Personal Income Tax also increases as per the regression analysis. It can be observed that when the standard of living increases the income earning capacity rises as there is more opportunity related to employment. Some studies have indicated that the more the revenue is earned trough taxation better policy formulation from the government, leading to more employment opportunities leading to more personal income. More the income more is the spending as well as taxpaying, as the individual due to his increased income level pays more tax as he or she falls now in the taxpaying bracket.
References:
- Michael Busler , (2013),"Income tax policy: is a single rate tax optimum for long-term economic growth?", World Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development, Vol. 9 Iss 4 pp. 246 – 254 Permanent link to this document: http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/WJEMSD-01-2013-0008
- Geetanjali, J., & Venugopal, P. (2017). Impact of Direct Taxes on GDP: A Study. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM),21-24.
- Odum, Augustine & Chinwe Odum, Gloria & Egbunike, Chinedu. (2018). Effect of Direct Income Tax on Gross Domestic Product: Evidence from the Nigeria Fiscal PolicyFramework. 1. 59-66.
- Y. Jin and X. Jia, "Research on Personal Income Tax System Reform from the Perspectives of Equity and Efficiency in China," 2011 International Conference on Management and Service Science, Wuhan, 2011, pp. 1-4. doi: 10.1109/ICMSS.2011.5998454
- Rögnvaldur Hannesson, (2009) "Energy and GDP growth", International Journal of Energy Sector Management, Vol. 3 Issue: 2, pp.157-170, https://doi.org/10.1108/17506220910970560Permanent link to this document:
- https://doi.org/10.1108/17506220910970560
- Liu Ying, Cui Riming, (2008) "Function simulation of FDI, foreign trade and regional GDP in China",
- Journal of Chinese Economic and Foreign Trade Studies, Vol. 1 Issue: 3, pp.232-243, https://doi.org/10.1108/17544400810912383 Permanent link to this document: https://doi.org/10.1108/17544400810912383
- Nwanyanwu, Loveday. (2016). Assessing the Productivity of Personal Income Tax System in Nigeria.. Account and Financial Management Journal. 10.18535/afmj/v1i7.04.
- Wilco W. Chan Joseph C. Lam, (2000),"The lodging industry’s contribution to Hong Kong’s gross domestic product", International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, Vol. 12 Iss 2 pp. 86 – 98 Permanent link to this document:http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/09596110010307314
- Diacon, P., & Maha, L. (2015). The Relationship between Income, Consumption and GDP: A Time Series, Cross-Country Analysis. Procedia Economics and Finance,23, 1535-1543. doi:10.1016/s2212-5671(15)00374-3
- William R. Dipietro Emmanuel Anoruo, (2006),"GDP per capita and its challengers as measures ofhappiness", International Journal of Social Economics, Vol. 33 Iss 10 pp.698–709 o Permanentlink to this document:http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/03068290610689732
- Metri Fayez Mdanat, Manhal Shotar, Ghazi Samawi, Jean. Mulot, Talah S. Arabiyat, Mohammed A. Alzyadat, "Tax structure and economic growth in Jordan, 1980–2015", EuroMed Journal of Business, https://doi.org/10.1108/EMJB-11-2016-0030 o Permanent link to this document: https://doi.org/10.1108/EMJB-11-2016-0030
- Rahman, M. S.. (2011). Relationship among GDP, Per Capita GDP, Literacy Rate and Unemployment Rate.
- Zhang, D.L. (2017) Research on Personal Income Tax Affecting Structure of Resident Consumption Expenditure in China. Modern Economy, 8, 161-171.
- Szarowská, Irena. (2014). Personal Income Taxation in a Context of a Tax Structure (WOS:000345439100078). Procedia Economics and Finance. 12. 662-669. 10.1016/S2212-5671(14)00391-8.
- Horn-Chern Lin, Tao Zeng, (2010) "The distributional impact of income tax in Canada and China: 1997-2005", Journal of Chinese Economic and Foreign Trade Studies, Vol. 3 Issue: 2, pp.132-145, https://doi.org/10.1108/17544401011052276
- Permanent link to this document: https://doi.org/10.1108/17544401011052276
- Reji George Y V Reddy , (2015),"Corporate tax in emerging countries: some aspects of India", International Journal of Law and Management, Vol. 57 Iss 5 pp. 357 - 366
- Permanent link to this document:http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/IJLMA-03-2014-0023
- Sena Kimm Gnangnon, (2017) "Impact of trade facilitation reforms on tax revenue", Journal of Economic Studies, Vol. 44 Issue: 5, pp.765-780, https://doi.org/10.1108/JES-03-2016-0054 Permanent link to this document: https://doi.org/10.1108/JES-03-2016-0054
- http://www.mospi.gov.in/statistical-year-book-india/2017/175
