Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Impact of Brand Awareness and Brand Loyalty on Consumer Purchase decision: A study on FMCG products
Abstract :
As a result of globalization, the local and the international competition have increased and in order to survive this extensive competition, organizations need certain distinguishing elements that will cause their consumers to keep buying their products. In this era of enormous competition some of the traditional ways of attaining a competitive advantage such as price differentiation and product quality is no longer sufficient to ensure the success of a product. Corporates are now realizing that the worth of any organization is tied to its brands which are competent to satisfy the needs of the consumers. This study analyses the impact of brand awareness and brand loyalty on the consumer purchase decision for the FMCG products. The sample size for this study is 160 FMCG consumers of Bangalore city. A self-prepared questionnaire based on the literature was used for the study. Cronbach alpha coefficient was used for measuring the reliability of the questionnaire. Certain statistical techniques such as Correlation and Multiple Regression analysis were used to test the different hypotheses.
Keywords :
Globalization, FMCG, Brand Awareness, Brand Loyalty, Consumer Purchase Decision.1. Introduction
As per the American Marketing Association (AMA), a brand could be considered as a “name, term, sign, symbol, or design or could be a combination of any of them, intended to identify the goods and services of one seller or groups of sellers and to differentiate them from those of the competitors.” The word “Brand” has become an important and strategic factor for the business organizations and provides competitive advantage, wealth creation, delivering value to the stakeholders and ensuring social wellness. Marketing in today’s world of Internet and media outburst is all about creation, communication and value delivering to the end consumers (Keller& Lehmann, 2003).Indian consumers in this era of globalization are bombarded with hundreds and hundreds of national and international brands with newer features and better quality and hence there are several factors which influence the consumer decision making towards the purchase of certain brands of products (SamudhraRajakumar and Sritharan, 2004).Marketers try to create a unique position in the consumer’s minds by developing their products into brands.
Whenever a brand attains superiority, it leads to great sales and hence the companies have the power to charge greater premiums on their products and also to resist distribution strength. For instance, whenever someone refers to soft drink, the two brands that come in the consumer’s mind is Pepsi and Coke, whenever someone thinks of antiseptic for treating basic wounds, the first brand that comes to the consumers’ mind is Dettol followed by Savlon. Whenever any consumer remembers chocolate, the brand that comes to his or her mind is Cadbury’s chocolates. All these examples tend to signify the role of brands in consumer buying behaviour. Some brands such as Cadbury’s, Dettol, Pond’s, Lakme remain in the consumers’ minds forever. Nowadays brands are created by supplementing a particular product with distinguishing values in order to create a distinct identity for the product resulting in brand personality (Shekhar, Acharya, Roy & Nguyen, 2019).Understanding the core values of a brand becomes the responsibility of everyone in the organization because a brand is considered as the soul of an organization (Adamson, 2003). Creating a memorable brand name in the minds of the consumers is highly essential if a company wants to succeed in business.
LITERATURE REVIEW
The heart of any business and marketing strategy constitutes a brand (Baltas& Doyle, 1998). A lot of significant work has been carried out by researchers and academicians in the field of branding. Branded products build a much more sustainable as well as profitable relationship with the consumers as compared to products which are unbranded (De Chernatony, L, 2010). When a brand is strong enough for a consumer to be able to recollect a particular brand under different conditions and leaves a trace in his or her memory, it is called as brand awareness. It is the extent to which consumers are aware about the life and the availability of a particular product and his or her desire to buy the same (Santoki & Parekh, 2017). Brand could be considered as a “perception” that a consumer has which he associates with the product.
Literature on brand awareness suggests that when brands are presented to the customers, it is more like a stimulus – response approach and the consumers are able to relate and recognize and be fully aware of the brands. Constant brand reinforcement techniques are used by companies to build on their brand awareness programmes. The consumer buying behaviour or buying decision is influenced by the product brand as a consumer always considers a brand when he goes to buy a product. Consumers always make an economic decision, and when a consumer has more information pertaining to a particular brand, there will be more chances of him or her buying that brand. There could be several factors that influence a consumer’s brand awareness such as the name of the brand, an effective advertisement that increases the awareness about a particular brand, the sales and promotions pertaining to a particular brand etc. (Shahid, Hussain, aZafar, 2017).
There are seven stages that a consumer goes through while making any purchase decision namely need identification, information search, pre-purchase evaluation of the product, product purchase, product consumption, evaluation post-product consumption and divestment. These seven stages act as a roadmap for the marketers to determine the reasons why consumers are buying or not buying a particular product. However, there are studies that prove that purchase of all products do not involve all of the seven stages of decision making. For expensive products which are infrequently purchased such as washing machines, the consumer goes through all the above mentioned stages of purchase decision, however for inexpensive products which are frequently purchased such as Fast Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) which involves a concept of trial purchase as the products tend to be purchased for a considerable short period not all the above stages are considered for by the consumers for making a purchase. In FMCG products, if the consumer finds the product or brand performance to be satisfying after the trial period, then the consumer is more likely to repeat the purchase of those brands of products (Sarangapani& Mamatha, 2008).
There are normally two purchasing patterns that are identified in the fourth stage of consumer purchase decision i.e. product purchase stage. The two purchasing patterns are the degree to which consumers develop repeat purchasing patterns and the degree to which purchases are unplanned or purchase happens on the basis of an impulse. The repeat purchase behaviour is linked to brand loyalty. Literature indicates that when consumers are being exclusively loyal to a specific brand then it is called as Brand Loyalty. However, due to globalization, consumer has access to a wide variety of products and brands and markets are becoming more and more fragmented and this has resulted in a decline in the number of consumers being exclusively loyal to one particular brand. Consumers are constantly on the watch out for those brands which meet their requirement rather than being loyal to any one brand. Some of the studies have defined brand loyalty as recognition of true loyal consumers who not only show repeat purchase behaviour of certain brands but also show a favourable attitude towards the purchased brand (Loudan and Della Bitta, 2009).
There are many factors that influence the brand loyalty of the consumers. Consumers tend to remember famous brand names much better than the non-famous ones (Keller& Lehmann, 2003). Even though there are many alternative brands in the market, consumers have more faith and trust in famous brand names and these reputed brand names cause them to demonstrate repeat purchase behaviour irrespective of the product price (Cadogan and Foster, 2000). The product quality could be another factor that influences the repeat purchase or re-buying behaviour of consumers. It could be the material quality or the colour of the product, the hand feel, the texture etc. that causes the re-buying behaviour of the consumers (Sproles &Sproles, 1990). A factor that does not influence the brand loyalty of consumers towards certain products is the price of the brand. Consumers with high loyalty towards a certain brand are willing to pay a premium price due to their preference towards a certain brand. The consumer purchase intention towards a particular brand of product is not very easily affected by the brand price (Yoon and Kim, 2000). The brand design also influences the consumer attraction towards a particular brand. Brands which have an attractive packaging tend to influence the consumer buying behaviour (Singh &Pattanayak, 2014). As per a study carried out by Omar &Sawmong (2007) the store environment was a single significant element in the success of retail marketing. Some of the store elements such as its location, layout, and in-store stimuli impact the brand loyalty of the consumers. The accessibility of the store and the store attractiveness and services may cause the consumers to be loyal towards it (Khan, 2013).
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
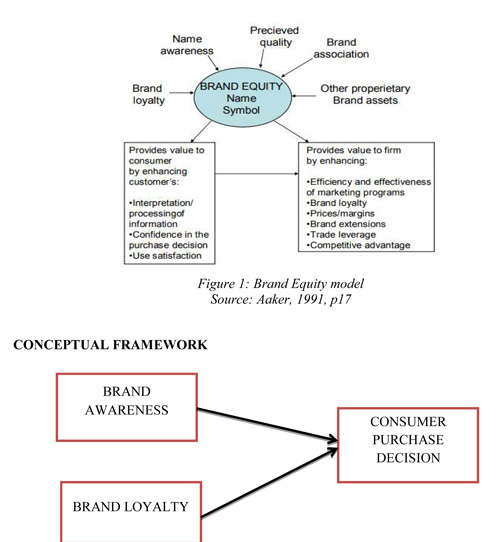
Aaker’s (1991) brand equity model is one of the most frequently used and practiced model comprising of brand awareness, perceived brand quality, brand associations and brand loyalty. However, in this study, only brand awareness and brand loyalty are considered. Aaker (1991) defined brand awareness as the consumers’ familiarity with a certain brand and the strength of a brand’s existence in the consumer’s minds.The four levels of brand awareness as proposed by Aaker (1991) are”top of the mind, brand recall, brand recognition and brand awareness”. The very first step in communicating with the consumers is through brand awareness. Aaker (1991) has mentioned some of the ways brand awareness can be attained which are to be memorable and to be different, to include a slogan or a jingle, to have a known symbol or a logo, to publicize the product, to consider brand extensions, to build recognition and recalls through repetitions. The second most fundamental dimension of brand equity is brand loyalty which is the core of brand value. Aaker had stated in his study that no other dimension of brand equity is as effective as brand loyalty (Aaker, 1991). When consumers become loyal to a certain brand they buy that particular brand on a regular basis. Aaker (1991) describes brand loyalty as a consumer’s emotional involvement with the brand. It shows whether or not there is consumers’ willingness to shift over to another brand on the basis of feature or price differentiation. Hence, the two main dimensions of Aaker’s Brand Equity model i.e. Brand Awareness and Brand Loyalty were considered for this study in order to understand their impact on Consumer Purchase Decision.
RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
1. To study the level of Brand Awareness and Brand Loyalty of FMCG products chosen for the study.
2. To study the association of Brand Awareness and Brand Loyalty with Consumer Purchase Decision.
3. To study the influence of Brand Awareness and Brand Loyalty on Consumer Purchase Decision.
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODOLOGY
The nature of the study is descriptive and empirical. A quantitative research design has been chosen for the study as the variables are continuous in nature. In this study the authors intend to determine the extent to which brand awareness and brand loyalty influence the consumer purchase decision. Self-developed questionnaire based on the literature was used to measure brand awareness, brand loyalty and consumer purchase decision of FMCG consumers across Bangalore city. The questionnaire was filled by 160 respondents from different areas across the city. A convenient and judgmental sampling method was adopted to collect the data from the respondents. The data that was collected was analysed using the SPSS software and few statistical techniques like Correlation Analysis & Regression Analysis.
HYPOTHESES OF THE STUDY
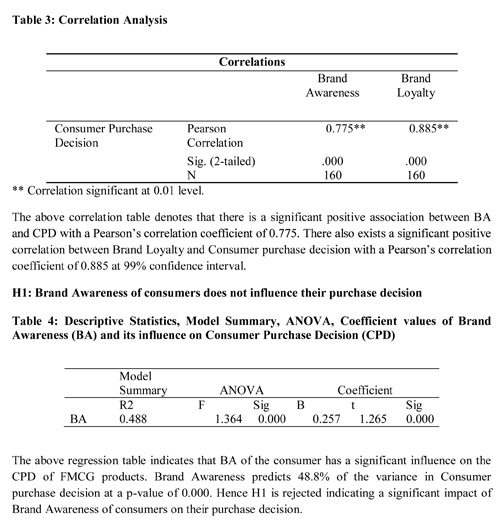
H1: Brand Awareness of consumers does not influence their purchase decision
H2: Brand Loyalty of consumers does not influence their purchase decision
PROFILE OF THE RESPONDENTS
Out of the 160 samples collected from respondents, 60% were females and 40% were males. Around 50% of the respondents were between the age group of 25 to 45 years. More than 45% of the respondents were employees from the private sector while 35% of them were homemakers. Majority of the respondents had an annual income between five to ten lakhs per annum.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Reliability of the instrument used
The questionnaire developed to measure Brand Awareness comprising of 11 items had a Cronbach alpha value of 0.877 while that of Brand Loyalty comprising of 19 items had a Cronbach alpha value of 0.898. The 10 item questionnaire measuring Consumer Purchase Decision had a Cronbach alpha value of 0.901.
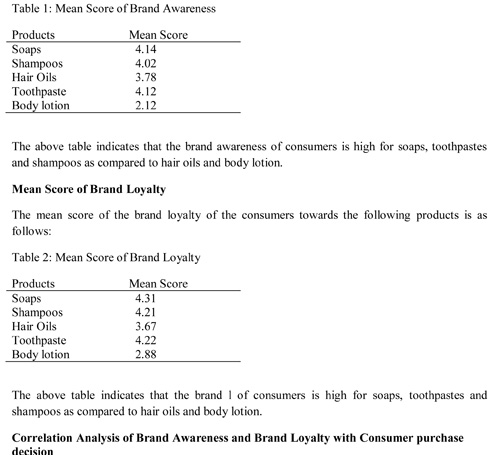
Mean Score of Brand Awareness
The mean score of the brand awareness of the following products is as follows:
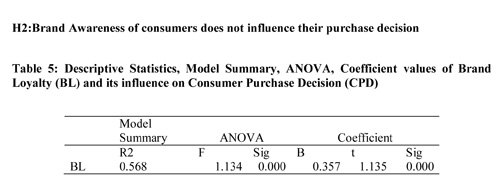
The above regression table indicates that BL of the consumer has a significant influence on the CPD of FMCG products. Brand Loyalty predicts 56.8% of the variance in Consumer purchase decision at a p-value of 0.000. Hence H2 is rejected indicating a significant impact of Brand Loyalty of consumers on their purchase decision.
DISCUSSION
This study examined the relationship and impact of Brand Awareness and Brand Loyalty on Consumer Purchase decision of FMCG consumers in Bangalore city. The findings indicate that there is a significant positive correlation and impact of brand awareness and brand loyalty on consumer purchase decision. Similar studies were carried out by various researchers in India and also in different parts of the world. As per a study conducted by Venkateswaran, Muthukrishnan, Ananthi& Geetha (2013), the consumers tend to remain loyal to the brands mainly for the reasons of emotions and objectivity. There exists an emotional bond between the consumer and the brand which the consumer tends to believe is his best option which reflects his emotions for the brand. This emotion mainly influences the consumer’s purchase decision. Researchers have found a significant increase in brand loyalty of consumers since 2001 despite the entry of new products and new brands into the market and the main reason for this is the consumer awareness of the benefits of well-known brands and also saving time searching for products based on consumer requirements (Daye and Van Auken, 2009). A study by Keller (2009) has found that for certain products, an increase in customer loyalty towards brands can enhance the brand awareness of such products. Judith and Richard (2002) have indicated that both brand awareness and brand loyalty are significantly connected to each other and has a certain influence on the consumer purchase decision. Another study carried out by Karam and Saydam (2015) in the fast food sector too have found similar results wherein the researchers have found that consumers’ brand awareness leads to a good brand image which in turn enhances the consumers’ brand loyalty towards the fast food sellers.
LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE RESEARCH
A lot of work has been done on brand equity and its various dimensions. This study focuses on the two main dimensions of brand equity namely brand awareness and brand loyalty. The author was unable to cover all the regions of Bangalore city due to time and cost constraints. Only some of the FMCG products such as soaps, shampoos, hair oils, toothpastes and body lotions were covered in this study. Certain other products such as cosmetics, food products, face-wash and washing machine powders etc. could be carried out in the future research. Even though brand awareness and brand loyalty were considered for this study, other variable of brand equity such as perceived quality and brand association could be considered for future studies.
CONCLUSION
Brand Loyalty of consumers tend to be showing an increasing trend due to many benefits such as saving time evaluating the alternate products, sophisticated advertising appeals, sales promotion tactics etc. which cause the consumers to show the re-buying behaviour or repeat behaviour. In a highly competitive and a conscious brand market such as today consumers tend to rely more on brands rather than products, hence building brand awareness and brand loyalty for FMCG products is very essential. This has been proved by the present study as both brand awareness and brand loyalty have found to have a significant impact on the purchase decision behaviour of consumers.
REREFENCES
- Aaker. D. A. (1991). Managing Brand Equity, The Free Press, New York.
- Adamson, A. (2003). See the Brand The traditional tools of brand positioning are of little use in a rooftop environment. Here's why. BRANDWEEK-NEW YORK-, 44(42), 38-39.
- Baltas, G., & Doyle, P. (1998). An empirical analysis of private brand demand recognising heterogeneous preferences and choice dynamics. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 49(8), 790-798.
- De Chernatony, L. (2010). Creating powerful brands. Routledge.
- Daye, D., & Van Auken, B. (2009). The benefits of corporate brands.
- Foster, B. D., & Cadogan, J. W. (2000). Relationship selling and customer loyalty: an empirical investigation. Marketing intelligence & planning.
- Khan, S. (2013). The Effect of Brand Characteristics on Brand Loyalty A Study of Cosmetics Products in Peshawar Pakistan.
- Karam, A. A., &Saydam, S. (2015). An analysis study of improving brand awareness and its impact on consumer behavior via media in North Cyprus (A case study of fast food restaurants). International Journal of Business and Social Science, 6(1).
- Keller, K.L & Lehmann, D.R.(2003), How do brands create value?, Marketing Management, 12(3),26.
- Keller, K. L. (2009). Building strong brands in a modern marketing communications environment. Journal of marketing communications, 15(2-3), 139-155.
- Loudon, D. L., Della Bitta, A. J., Consumer Behaviour, T. M. H., & Edition, F. TEXT BOOK. JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD, 48.
- Omar, O., &Sawmong, S. (2007). Customer satisfaction and loyalty to British supermarkets. Journal of Food Products Marketing, 13(2), 19-32.
- Rajakumar, S. Sritharan,(2004)," Brands Building strategies", Innovation in Marketing Management, Edited by Dr. V. Balakrishnan and Dr. C. SamudhraRajakumar.
- Sarangapani, A & Mamatha, T.(2008). Rural consumer behaviour with regard to selected FMCGs consumption patterns and brand usage: a study, The Icfai University Journal of Brand Management, 5(3), 22-61.
- Santoki, A. A., & Parekh, M. H. (2017). Brand Awareness and Consumer Buying Behaviour of selected FMCG’s Products among Rural Consumer in Dang Area of Gujarat. liInternational Journal of Applied Research, ISSN Print, 2394-7500.
- Shahid, Z., Hussain, T., & Zafar, F. (2017). The impact of brand awareness on the consumers’ purchase intention. Journal of Marketing and Consumer Research, 33(3), 34-38.
- Shekhar, V., Acharya, A., Roy, S. K., & Nguyen, B. (2019). CONSUMER-BRAND RELATIONSHIP. Contemporary Issues in Branding.
- Singh, P. K., &Pattanayak, J. K. (2014). The Impact of Brand Loyalty on Consumers' Sportswear Brand Purchase. IUP Journal of Brand Management, 11(4), 40.
- Sproles, E. K., & Sproles, G. B. (1990). Consumer decision‐making styles as a function of individual learning styles. Journal of Consumer Affairs, 24(1), 134-147.
- Venkateswaran, P. S., Muthukrishnan, K. B., Ananthi, N., & Geetha, U. (2013). Factors Influencing Brand Loyalty: A Study on Shaving Cream Brands. IPE Journal of Management, 3(1), 89.
- Yoon, S. J., & Kim, J. H. (2000). An empirical validation of a loyalty model based on expectation disconfirmation. Journal of consumer marketing.
