Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Development of Emotional Intelligence to manage self and others for Effective Performance
Abstract :
Several research studies have shown that Emotional Intelligence (EI) is essential for accomplishment in family, groups, sports, study, works place and other social settings. Daniel Goleman has rightly mentioned that "If your emotional abilities aren't in your own hands, if you don't have self-awareness, if you are not able to manage your distressing emotions, if you can't have empathy and have effective relationships, then no matter how smart you are, you are not going to get very far." He also mentioned that "One needs to have 20 percent IQ and 80 EQ to be successful in life." Emotional Intelligence (EI) is a multi-dimensional concept which has a significant influence on the behaviour of human beings. EI is a person's capacity to manage his emotions and the emotions of others in a particular setting. EI can help individuals to develop stronger relationships at home, educational institutes, workplace and social settings, feel better about themselves, and do better in many parts of their lives. Emotional Intelligence can be learned and improved through practice and experience. Although some people may have a natural propensity toward high emotional intelligence, yet it is still a set of skills that can be cultivated by anyone.
Keywords :
Emotional Intelligence, Workplace, Behavioural Change, AdaptabilityIntroduction
The world is becoming VUCA (volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous) with demographic changes, globalization, technological advancement (the digital era), and climate change. There is hyper-competition, frequent change, conflicting demands from stakeholders, technological disruption, knowledge-based intervention, and customer-driven processes among organisations. Human capital has become a scarce resource. Workplace adaptation, productivity, collaboration, and job satisfaction for an employee in an organisations have become more complex. Managers and executives are facing tremendous challenges in running the business.
Since 2019, the global pandemic (Covid-19) caused by the SARS-Cov2 virus and its mutations has resulted in a hybrid workplace. Working from home, that is, remotely, via the use of the internet and mobile technology, has become the new standard. This has presented additional challenges for a large number of employees particularly the older generation, which has less experience with technology.
According to a study by World Economic Forum "Skills on-demand would be complex problem-solving, critical thinking, creativity, people management, coordinating with others, emotional intelligence, judgement and decision making, service orientation, negotiation and cognitive flexibility. It specifies Emotional Intelligence (EI) as one of the many vital competencies.
Several research studies have shown that Emotional Intelligence (EI) is essential for accomplishment in family, groups, sports, study, works place and other social settings. Daniel Goleman has rightly mentioned that "If your emotional abilities aren't in your own hands, if you don't have self-awareness, if you are not able to manage your distressing emotions, if you can't have empathy and have effective relationships, then no matter how smart you are, you are not going to get very far." He also mentioned that "One needs to have 20 percent IQ and 80 EQ to be successful in life" One needs learn to perform. "All learning has an emotional base." - Plato
Concept of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (EI) is a multi-dimensional concept which has a significant influence on the behaviour of human beings. EI is a person's capacity to manage his emotions and the emotions of others in a particular setting. It includes recognising emotions, comprehending emotions, monitoring emotions, controlling or regulating emotions, and taking the proper actions.
There are several definitions of Emotional Intelligence (EI) given by different researchers and academicians. Some of these are
I. Salovy & Mayer (1990): "Emotional Intelligence is the subset of social intelligence that involves the ability to monitor one's own and other's feeling and emotions to discriminate among them and to use this information to guide one's thinking and actions."
II. Salovy and Mayer also mentioned that "Emotional Intelligence is the ability to perceive emotions, to access and generate emotions to assist thoughts, to understand emotions and emotional knowledge and to reflectively regulate emotions to promote emotional and intellectual growth."
III. Daniel Goleman: "Emotional Intelligence is the ability to sense, understand, value, and effectively apply the power of emotions as a source human energy, information, trust, creativity and influence"
IV. Palmer & Stough: "Emotional Intelligence is the ability to sense, express, understand, and manage one's own and other people's emotions in a suitable, professional, and effective manner at work."
V. Jeanne Segal: "Emotional Intelligence is a different types of intelligence. It is about being heart smart not just book smart."
VI. Bar – on: "Emotional Intelligence measures a person's ability to recognize and regulate their personal competence and social competence."
VII. Ajay K Jain: "Emotional Intelligence, in contrast to cognitive intelligence is an ability to perform under the stressful conditions through cognitively controlled affective process."
Oxford English Dictionary defines Emotion as "any agitation or disturbance of mind, feeling, passion; any vehement or excited mental state"
Emotion is a neural impulse that moves an organism to action. Emotions are specific and intense and are a reaction to a particular event.
According to Goleman (1995), "emotion refers to a feeling and its distinctive thoughts, psychological and biological states and range of propensities to act" There are hundreds of emotions, along with their blends, variations, mutants and nuances.
Some of the primary emotions are Anger, Sadness, Fear, Enjoyment, Love, Surprise, Disgust and Shame.
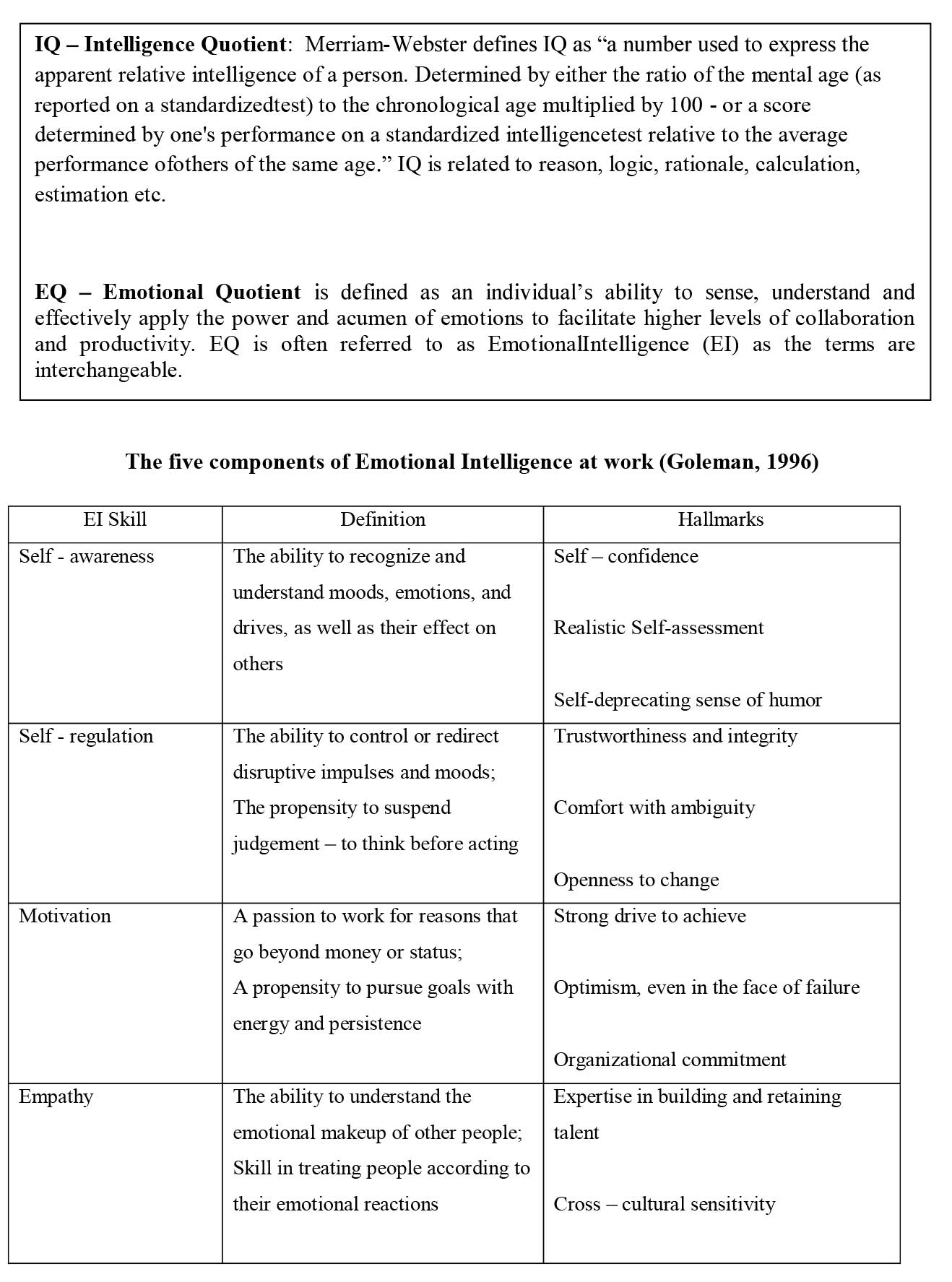
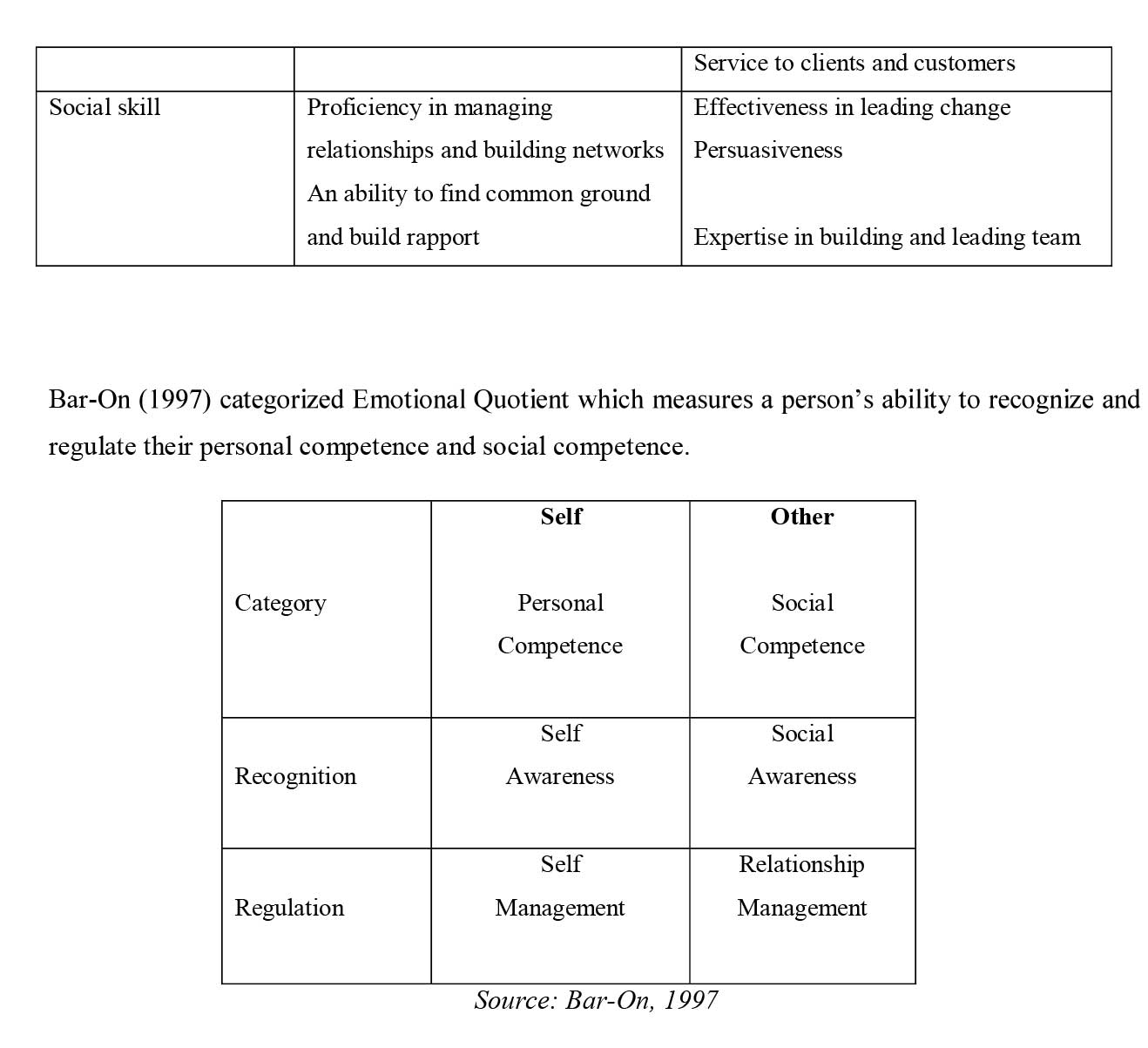
Emotional intelligence is the product of two main skills: Personal and Social competence. Personal Competence focuses on as an individual and is divided into self-awareness and self – management. Social competence focuses more on how one behaves with other people and is divided into social awareness and relationship management.
Emotional Intelligence and Human Personality
Cognition
Cognition refers to an implicit process of knowing the real world and it is related to our rational and logical thinking, learning and remembering, analysis and prediction etc. The concept of intelligence belongs to cognitive aspects of human personality, wherein "Intelligence is the aggregate or global capacity of the individual to act purposefully, to think rationally and to deal effectively with the environment.
Affect
Affect refers to the emotional interpretation of perceptions, information or knowledge. It is generally associated with one's attachment (positive or negative) to people, objects, ideas etc. Mood and feelings are related to affective aspects of human personality. In several social psychological experiments, it is confirmed that mood or emotions directly affect the cognitive skills or functioning of the memory. For example, people tend to forget things quickly when they are exposed to highly irritating or depressive situations while remembering things better under positive mood conditions. It means there is a complex interrelationship between cognitive and affective processes.
Conative
Conative (or motivation) refers to the personal, intentional, planned, deliberate, goal-oriented or striving component of motivation, the proactive (as opposed to reactive or habitual) aspects of behaviour.
Cognitive, affective and conative aspects interact with each other in any situation, but one may dominate the other in some cases. Cognitive aspects were emphasized more because of its link with IQ and decision-making.
Benefits of Emotional Intelligence
- Better Communication: People with high emotional intelligence communicate better with others because it makes them better able to understand and respond to the feelings of others.
- Improved relationships: People with high emotional intelligence tend to have better relationships with others, as they are better able to understand and communicate with others and to manage conflicts effectively.
- Dealing with Stress: Emotional Intelligence can help people deal with stress and problems because it makes them better able to understand and control their own emotions and ask for help when they need it.
- Better decision-making: People with high emotional intelligence are better able to consider the emotions of others and to think about the long-term consequences of their actions, which can lead to more effective decision-making.
- Leadership skills: Emotional intelligence is often seen as an important leadership skill, as it can help leaders build strong teams and create a positive work culture.
Overall, emotional intelligence can help individuals to develop stronger relationships at home, educational institutes, workplace and social settings, feel better about themselves, and do better in many parts of their lives.
Emotional intelligence (EI) in Team
Team members with high EI are able to understand and control their own emotions as well as the emotions of others. This makes for better relationships. This can help people get along better and make the team work better as a whole.
Team members with high emotional intelligence are better at actively listening, showing empathy, and avoiding misunderstandings. This can help people have better and more useful conversations.
People on a team with high EI are more likely to trust and help each other, which makes the team work better together and feel more like a whole. Teams with members who are emotionally intelligent are better able to deal with conflicts and find solutions that are good for the team as a whole.
Emotional intelligence and workplace adaptability
EI can help improve an employee's ability to adapt at work. EI can help employees deal with change and uncertainty at work better because they are more aware of how their emotions affect them and can control their responses in a positive way.
EI also includes empathy and good communication skills, which can help employees better understand the points of view of others and work together well when things change. Also, employees are more likely to get support and resources to help them adjust to new situations if they have good relationships with their coworkers and manager.
Improving an employee's emotional intelligence can help them be more flexible and adaptable at work, which can lead to greater job satisfaction and success.
Re-scripting Emotions of Employee (Purushothaman (2021)
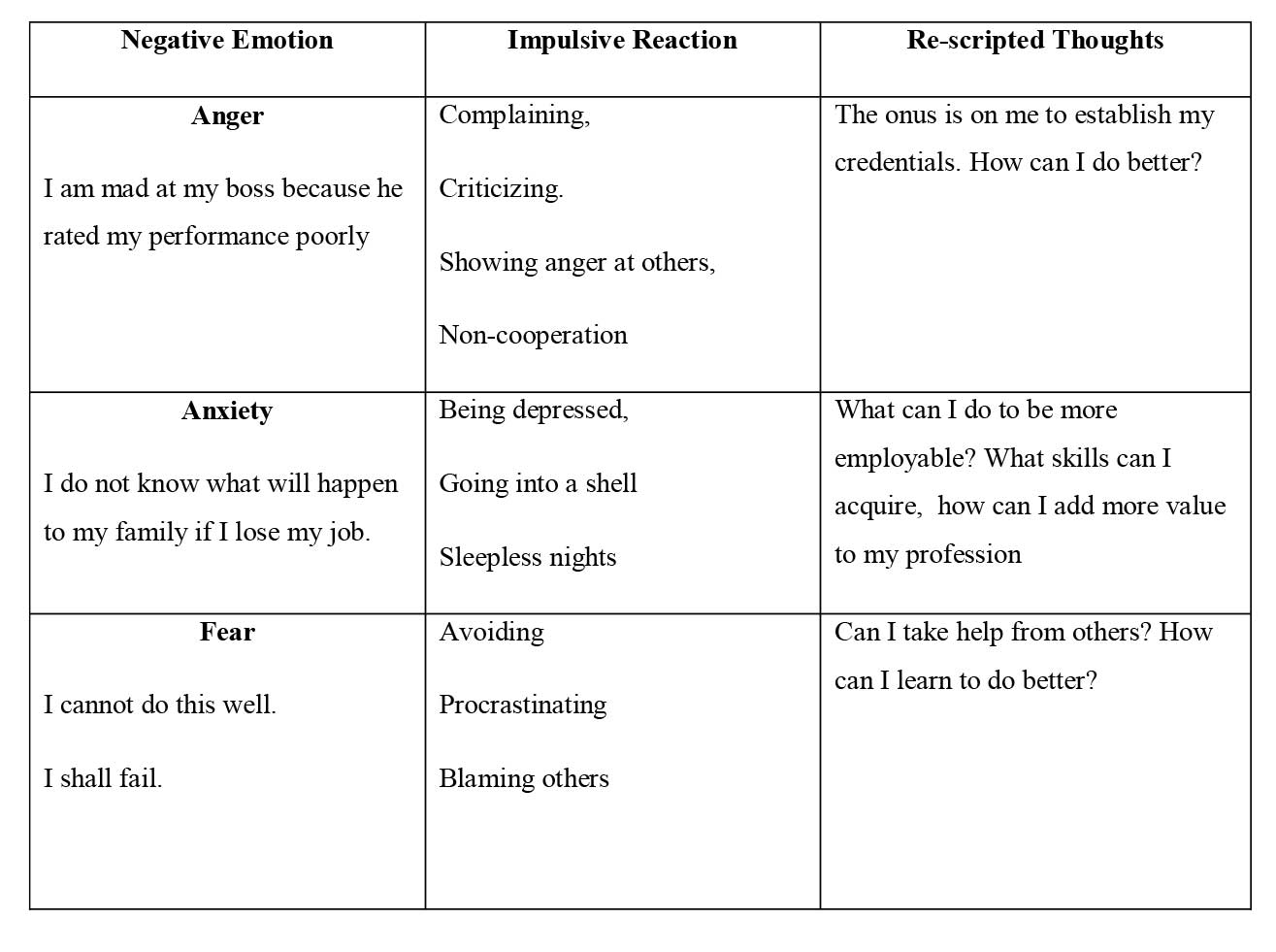
Managers may improve organizational performance, foster a healthy work environment, and increase employee engagement and happiness by using their emotional intelligence (EI). Manager should understanding one's own feelings, ideas, and behaviours, as well as how they impact others. Managers should be being responsive to the feelings and viewpoints of others, especially coworkers and customers. They may be able to manage stress and ambiguity more effectively and come to wise conclusions that are good for the organisations as a whole.
Ways to improve Emotional Intelligence
World-wide research have proved that Emotional Intelligence can be learned and improved through practice and experience. Although some people may have a natural propensity toward high emotional intelligence, it is still a set of skills that can be cultivated by anyone.
I. Practice of Mindfulness
Mindfulness is a state of mind that can be reached by keeping one's attention on the present moment while calmly noticing and accepting one's feelings, thoughts, and body sensations. It is a way to focus on the present moment without making any judgements about it. People often call it a type of meditation, but one can practice mindfulness in daily life i.e. Mindfulness sitting, mindfulness listening, mindfulness eating, mindfulness walking, mindfulness working etc. The goal of mindfulness is to help people become more aware of their thoughts and feelings so they can better control them.
II. Behavioural Change
Breaking old habits and establishing new ones i.e. from prompt reaction to patience listening, delaying response, redirecting or controlling disruptive impulses, from quick expression or suppression of emotions to experiencing the emotions with patience.
III. Developing Compassion
Compassion is triggered by empathy. Compassion is being sensitive to the distress and pain of others, with a commitment to try to do something about it. Compassion demands action from us. Just feeling for somebody in suffering can be pity or sympathy, but compassion is a higher level of emotion. Attributes that help us act with compassion include distress tolerance, non-judgment, sensitivity and interest. When all four attributes come together, the chance of being compassionate is enhanced.
IV. Accepting Feedback from others
Accepting feedback and suggestions from others i.e. family members, friends, co-workers, coaches about one's way of listening, responding, behaving, working etc. and improving with persistence and practice.
Driving Emotional Intelligence (EI)
According to Purushothaman (2021)
Driving Emotional Intelligence (EI) is about implementing EI while dealing with real-life situations and people. In order to gain a common understanding of the steps that helps that help us drive EI here is an analogy of driving a car. Brake, mirrors, gears, rules and steer help us to navigate through traffic. Similarly, driving EI help us navigate through difficult and challenging life situations.
These are sequential and need to be practiced, especially when faced with challenging situations and people. The more we practice these steps the more EI will be manifested in us.
Brake
Pause to reactive stress and reduce it
- I shall take a pause.
- I shall calm down my emotions
- I shall try to understand the emotions that I am experiencing.
- I shall try to understand the emotions experienced by others.
- I shall collect my thoughts
- I shall choose to respond and not be driven by my emotions.
- I shall focus the challenges posed.
- I shall not give up easily
- I shall try my very best to overcome the challenges.
- I shall use homour and playfulness appropriately to ease my nerves.
Communicate with respect
- I shall be careful in choice of words.
- I shall use positive body language.
- I shall not fall prey to negative emotions.
Attract attention of others and influence
- I shall try my best to influence people.
- I shall maintain relationships with people.
- I shall be a role model in monitoring emotions.
"Between stimulus and response there is a space" In that space is our power to choose our response. In our response lie our growth and freedom" - Viktor Frank
(Holocaust survivor and author of the book Man's search for meaning)

Few Videos on Emotional Intelligence
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LgUCyWhJf6s
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FKjj1tNcbtM
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sfT55TZV-20
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D6_J7FfgWVc
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=auXNnTmhHsk
-
Websites on Emotional Intelligence
- https://www.eiconsortium.org/
- https://www.danielgoleman.info/biography/
- https://positivepsychology.com/category/emotional-intelligence/
- https://medicine.yale.edu/childstudy/services/community-and-schools-programs/center-foremotional-intelligence/about/
- https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/basics/emotional-intelligence
Case Study
A new CEO joined a medium size company in the closing of the financial year i.e. in 2nd week of March. Health insurance and Group accident insurance policies of employees were going to lapsed on 31st March. There was urgent need to renew the policies by retaining the same insurance service provider and pay the premium to continue the coverage of employee. The new CEO is a process oriented person who examines rules, provisions, and contracts thoroughly and takes his own time for approval. The head of HR department approached CEO and requested for approval for insurance related things. The CEO read the file notes and renewal proposal of HR head and put several queries in the file related cost norms, procurement process, benefit to employees, insurance practices in other companies etc. HR head replied the queries point by point. But the CEO was not satisfied on the responses of HR head and put further queries in the file. HR argued strongly with CEO about the urgent need insurance policy for employees. Meanwhile new financial year started. Insurance policies of the employees lapsed. Few employees got admitted in hospitals but could not get insurance benefits like previous years. They were calling desperately to the HR head for support. HR head highlighted the issue to the CEO but could not get positive response. She was under tremendous pressure from the employees undergoing hospitalization and other employees for insurance policies. She tried to convince both CEO and employees about the issue and bottleneck in the official process. In the month of May she resigned from the company as she could not regulate her emotion and manage emotions of employees and CEO. The second in-command in the HR department took the charge HR. He was a self-motivating person and good in inter-personal and social skills. With his self-confidence and good communication abilities he built good rapport and convinced the CEO about the renewal of insurance policies of employees. Same time he organized several meeting of employees both on-site and online and defuse the tension by practice of attentive listening and empathy. He worked hard with help of his HR team members and put additional notes in the insurance file. He completed the process of hiring of new insurance service provider collaborating with procurement manager. Finally CEO gave the approval of new insurance policy of the company. Premium paid. Employees who hospitalized get the benefit of insurance policy of the company.
References
- Bar-On, R (1997). Bar-On emotional quotient inventory: A measure of emotional intelligence: Technical manual, Toronto, Canada; Multi-Health System.
- Bradberry, T. and Greaves, J. (2005), The Emotional Intelligence Quick Book, New York, A Fireside Book (Published by Simon & Schuster)
- Goleman, D. (1995), Emotional Intelligence: Why it can matter more than IQ, New York, Bantam Book.
- HBR's 10 Most Reads (2015), On Emotional Intelligence, Boston, Harvard Business Review Press.
- Mayer, J.D., & Salovey, P. (1993). The intelligence of emotional intelligence. Intelligence, 17 (4), 433 -442.
- Mayer, J.D., Salovey, P., & Caruso, D. R. (2004). Emotional intelligence: Theory, findings, and implications. Psychology Inquiry, 15 (3), 197 – 215.
- Palmer, B. & Stough, C. (2001). Workplace SUEIT: Swinburne University Emotional Intelligence Test – Interim Technical manual. Au: Organizational Psychology Research Unity, Swinburne University.
- Pareek, U. & Khanna, S. (2011). Understanding Organizational Behaviour, New Delhi, Oxford University Press.
- Purushothaman, R. (2021). Emotional intelligence, Sage Publication.
