Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Neuromarketing – Insights Into Consumer Behavior
Abstract :
The emergence of neuromarketing has been a game-changer in the field of marketing. This interdisciplinary field combines principles from neuroscience, psychology, and marketing to understand consumer behavior and create more effective marketing strategies. Neuromarketing uses various tools and techniques to measure the brain’s responses to marketing stimuli and gain insights into the consumer’s decision-making process. Parallel to this an eye tracking device is used, which allows the exact identification of the stimulus that produces the reaction from that moment. Also, some neuromarketing companies also use GSR (galvanic skin response) sensors to measure the electrical conductivity of the skin, which is another element that provides information about the consumer's response to various commercial messages.This paper provides an overview of neuromarketing, including its history, theoretical background, and practical applications. The paper also discusses the current state of research on neuromarketing and its potential for future developments. This paper has used the Scopus database to analyze related article between 2007 and 2018. Using neuromarketing research in digital platform and social media taking into consideration both companies purpose and customer benefits. In the paper we talk about the tools used for this purpose, which include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), brain scanners that identify brain parts that react to different stimuli, and electroencephalography (EEG), devices that measure electrical activity in the brain. The purpose of our article is to show the role played by neuromarketing in the correct understanding of consumer behavior, needs, words and emotions.
Keywords :
Neuromarketing; Neuroscience; Product sale; Advertising; Bibliometric Analysis; Scopus database; Social media ; Consumer behavior.Introduction
 Brief history of neuromarketing
Brief history of neuromarketing
The history of neuromarketing can be traced back to the 1990s when researchers began to use neuroscience techniques to study the brain’s responses to marketing stimuli. The field gained momentum in the early 2000s with the publication of several studies that demonstrated the effectiveness of neuromarketing techniques in predicting consumer behavior.
One of the earliest studies on neuromarketing was conducted by Read Montague and his colleagues at Baylor College of Medicine in 2004. In this study, participants were asked to taste two different types of cola while their brains were scanned using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The researchers found that the participants’ preferences for the two types of cola could be predicted based on the activity in their brains. This study provided evidence that neuromarketing techniques could be used to predict consumer behavior.
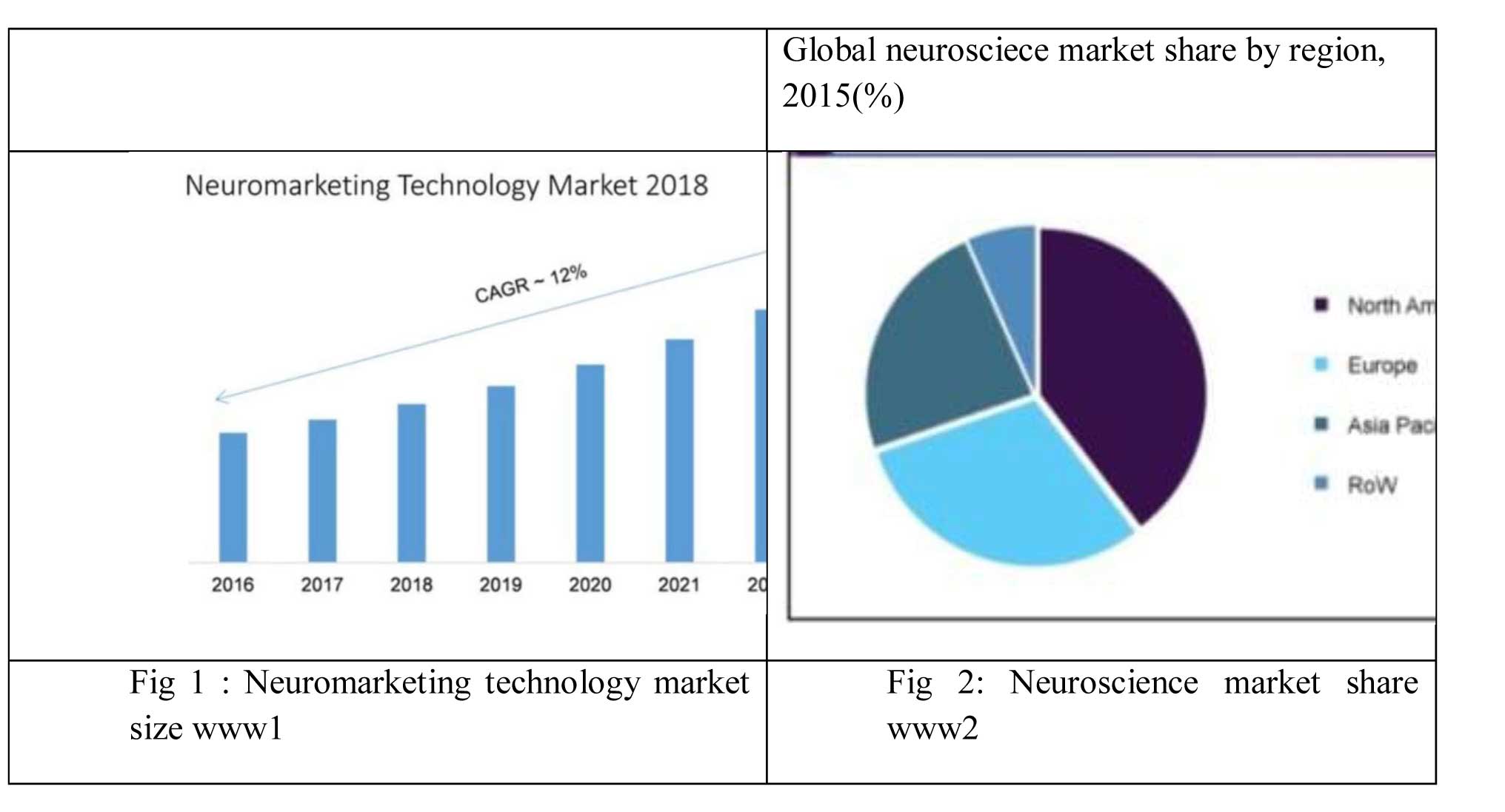
Neuromarketing Technology Market Size was constantly increasing, as international statistics shows (Figure1) especially in North America and Europe.
The term was first used in the United States in the 1990s (Figure 2), and the first studies in the field were conducted by Gerald Zaltman, a professor from Harvard University. Several experts in this field have founded neuroscience companies, wishing to use new scientific tools outside of the academic world. (ZALTMAN, 2003). An example is offered by Gemma Calvert, who founded Neurosense in 1999, after a series of academic achievements such as obtaining a PhD in cerebral imaging at Oxford University and publishing papers in the prestigious Science and Nature journals. Revolutionizing the medical world, the pharmaceutical industry, and even the economic sciences, neuroscience have their influence much greater than world awareness (GEMMA, 2004).
Theoretical Background of Neuromarketing: Neuromarketing is based on the idea that much of human behavior, including consumer behavior, is driven by unconscious processes in the brain. These processes are difficult to measure using traditional marketing research methods such as surveys and focus groups. Neuromarketing techniques, on the other hand, allow researchers to measure the brain’s responses to marketing stimuli and gain insights into these unconscious processes. One of the key theories underlying neuromarketing is the idea of emotional decision-making. Research has shown that emotions play a significant role in decision-making, and that emotional responses to marketing stimuli can be measured using neuroscience techniques. For example, a study by Baba Shiv and his colleagues at Stanford University found that participants were more likely to make impulsive purchases when they were hungry, and that this behavior was associated with increased activity in the nucleus accumbens, a brain region associated with reward processing. Another theory that underlies neuromarketing is the idea of mirror neurons. Mirror neurons are a type of brain cell that activate when we observe someone else performing an action. Research has shown that mirror neurons are involved in empathy, social cognition, and learning. In the context of neuromarketing, mirror neurons can help us understand how consumers respond to marketing messages and how they interpret social cues in advertising. Theoretical neuromarketing is a new approach that provides us with a fresh perspective on consumer behavior and decision-making processes, particularly when it comes to purchasing products or services. It moves away from the simplified Homos Economicus model, which assumes that consumers are rational and make decisions based on a purely rational analysis of costs and benefits. The new patterns of human action explain the phases encountered by people before acting, comprising two unconscious and conscious phases:
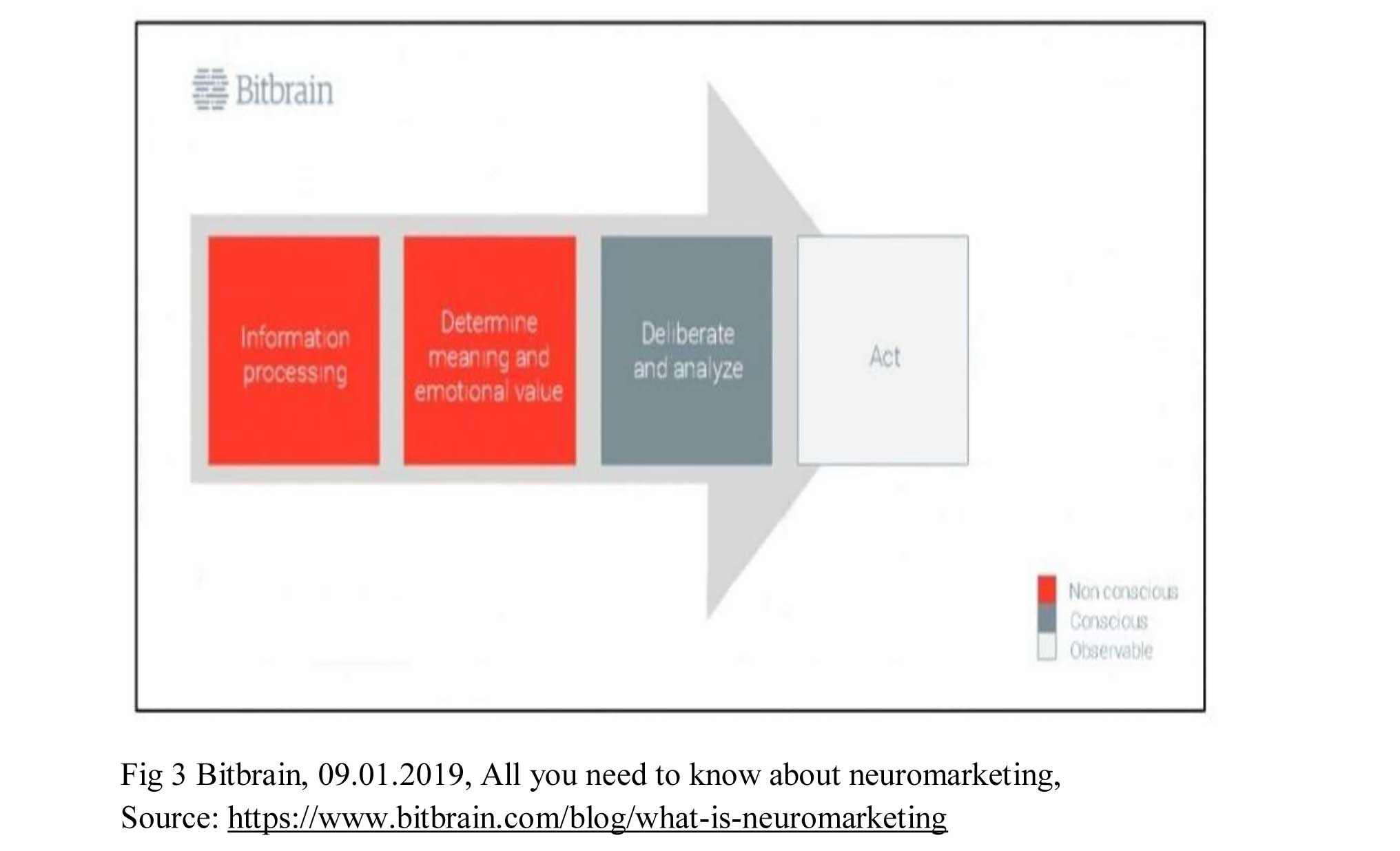
- Information Processing: Our brain engages in the processing of information through both conscious and unconscious mechanisms. Attention plays a pivotal role in determining the stimuli we prioritize. This process can be influenced by two distinct approaches: bottom-up processes, which direct attention towards stimuli that stand out from their surroundings, and top-down processes, which guide attention based on the perceived significance of the stimuli. Attention processes are crucial in decision-making as they enable us to assess available options and select the most pertinent ones.
- Sensory Perception and Emotional Evaluation: Our brain receives sensory information and assigns meaning and emotional significance to it, often without conscious awareness. This implies that even when we reach a decision unconsciously, we already have a preferred choice based on past experiences and emotional associations.
- Deliberation and Analysis: During this stage, conscious cognitive tasks come into play, including memory retrieval, interpreting past events, anticipating the future, planning, forming intentions, evaluating and judging alternatives, simulating outcomes, problem-solving, and reasoning. This phase allows us to consider multiple possibilities and weigh their advantages and disadvantages, ultimately leading to a decision that may not necessarily align with our unconscious preferences. Overall, these three phases work together to influence our decision-making process. While unconscious processes play a significant role in determining our preferences and emotional associations, conscious analysis allows us to weigh our options and make informed decisions. Understanding the interplay between these phases is essential in designing effective marketing strategies that appeal to both unconscious and conscious decision-making processes.
Importance of neuromarketing in marketing research
- Understanding consumer behavior: Neuromarketing provides insights into the subconscious and emotional responses of consumers to marketing messages. This can help marketers understand consumer behavior better and design more effective marketing campaigns.
- Identifying effective advertising: Neuromarketing can help identify the most effective advertising by analyzing consumer responses to different ads. This can help marketers save time and money by avoiding ineffective ads and focusing on the ones that work.
- Improving product design: Neuromarketing can also help improve product design by analyzing consumer responses to different product features. This can help marketers create products that are more appealing to consumers.
- Testing packaging: Neuromarketing can help test different packaging designs to see which ones are more likely to catch the attention of consumers and influence their buying decisions.
- Predicting consumer behavior: Neuromarketing can help predict consumer behavior by analyzing neural responses to marketing messages. This can help marketers anticipate how consumers will respond to different marketing strategies and adjust their campaigns accordingly.
Objective of the research paper
The objective of neuromarketing research is to understand how the human brain responds to marketing stimuli such as advertisements, product packaging, pricing, and brand messages. Neuromarketing uses various techniques such as EEG, fMRI, eye-tracking, and biometric measurements to measure and analyze brain activity and physiological responses to marketing stimuli.
The ultimate goal of neuromarketing research is to gain insights into consumer behavior and decision-making processes, which can help companies design more effective marketing strategies and improve their products and services to better meet the needs and preferences of their target audience. By understanding how the brain processes and responds to marketing stimuli, companies can create more engaging and persuasive marketing campaigns that are more likely to resonate with their customers and drive sales.
Neuroscience and marketing
Neuroscience and marketing are linked because marketing is about understanding consumer behavior, decision-making, and motivation, while neuroscience is the study of the brain and how it functions. Neuroscience can help marketers understand the emotional and cognitive processes that underlie consumer behavior. For example, neuroimaging studies have shown that emotional responses play a crucial role in decision-making and that the brain responds differently to different types of marketing messages. By using neuroscience techniques to measure these responses, marketers can design more effective marketing campaigns that elicit the desired emotional and cognitive reactions from consumers. Neuroscience can also help marketers understand how different factors such as product packaging, pricing, and brand messages impact consumer decision-making. By measuring brain activity and physiological responses, marketers can gain insights into what aspects of marketing are most appealing to consumers and use that knowledge to improve their marketing strategies.
Overall, the link between neuroscience and marketing is about using the latest scientific insights into the human brain to create more effective marketing campaigns that resonate with consumers and drive sales.
The role of the brain in decision-making
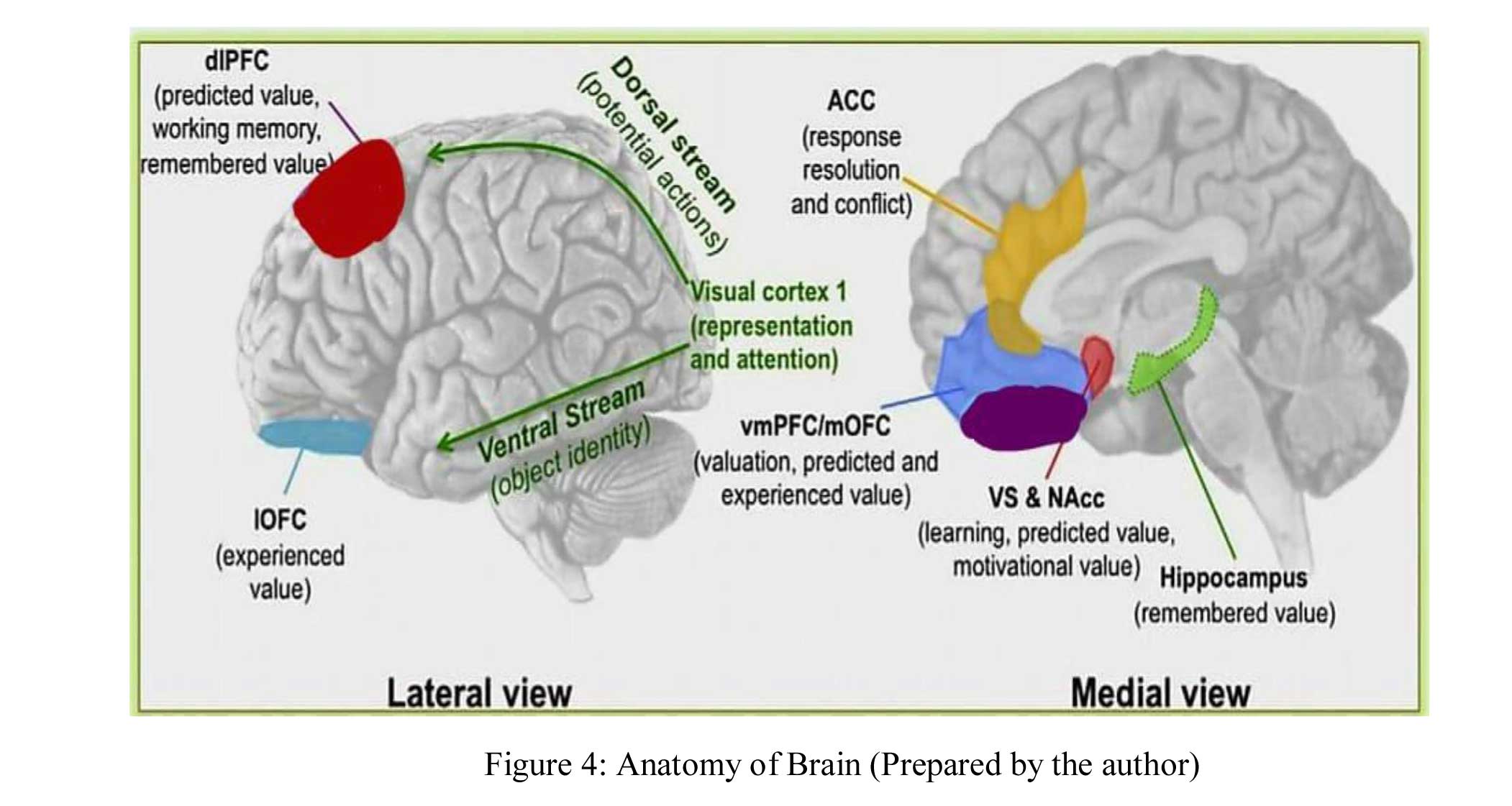 The brain is made up of four regions, each with a specific function. The occipital lobe processes visual information, while the temporal lobe is responsible for object recognition, object memory, and spatial movements like hearing. The parietal lobe contains sensory strips that process spatial changes related to actions, and the prefrontal cortex, located in the frontal lobe, helps with working memory, preference, and decision making.
Research has shown that when a product is displayed for four seconds, it triggers strong activation in the Nucleus Accumbens, a region associated with reward and pleasure. On the other hand, displaying the price for the same duration activates the insula, which is linked to emotional responses. The medial prefrontal cortex is activated when a person makes a decision between yes and no. Learning occurs in the Ventral Stratum, located in the left part of the brain. The sense of smell is connected to emotions, and EEG can be used to record brain activity while exposed to different fragrances.
The sense of smell, or olfactory function, can influence consumer behavior in retail settings (Video of Per Meller, Associate Professor, Copenhagen Business School). Emotions are non conscious and occur in subcortical regions and the neocortex of the brain. Joy is an emotion, while happiness is a feeling. The responses create biochemical and electrical reactions in the body that alter its physical state – emotions are neurological reactions to an emotional stimulus. The amygdala plays a crucial role in arousing emotions and consolidating memories. Feelings prompt bodily reactions that can be objectively measured through eye-tracking, GSR, EEG, fMRI, ECG, and facial expressions.
The use of brain imaging techniques in marketing research
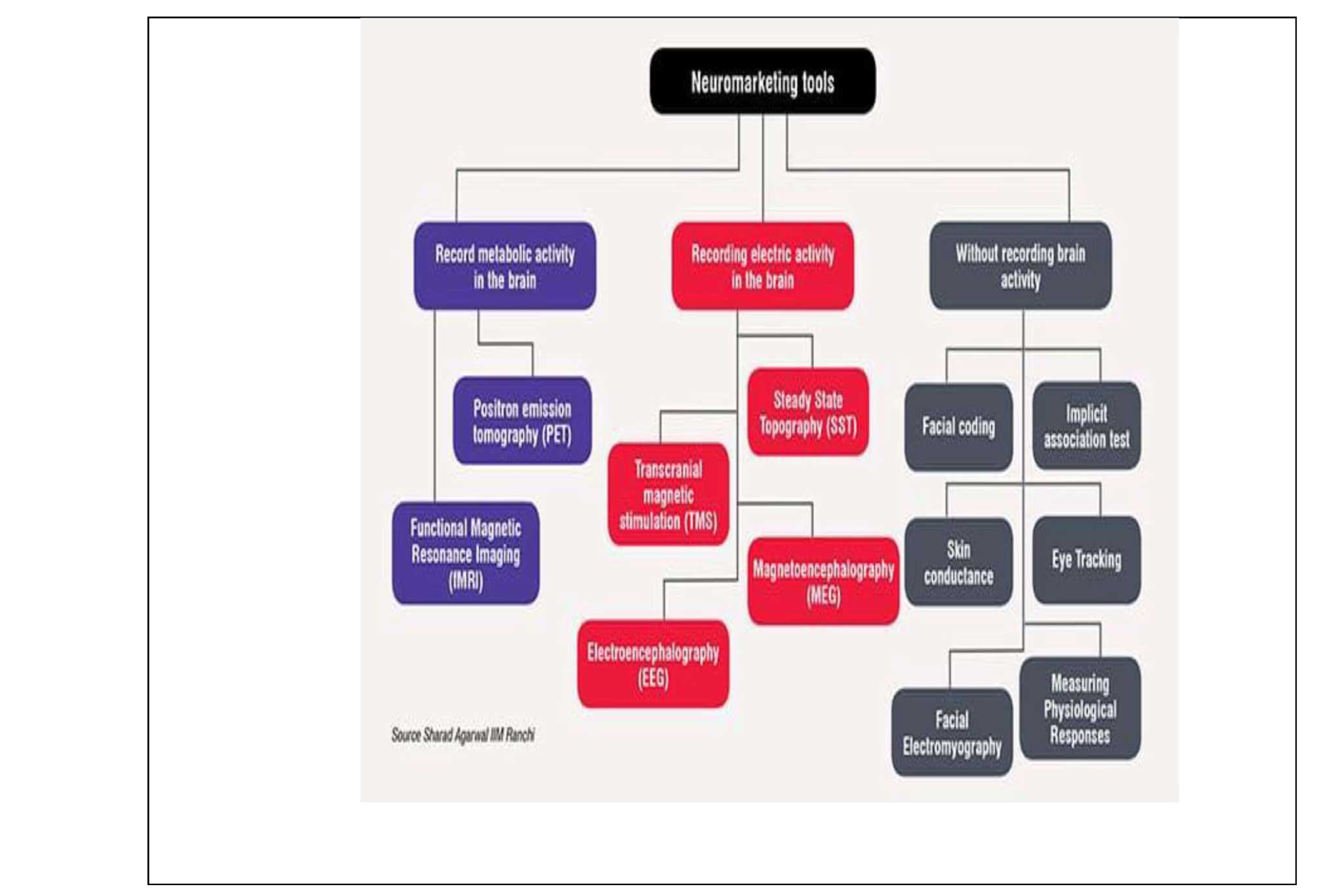
Neuromarketing is a field that studies how consumers respond to marketing stimuli using neuroimaging techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalography (EEG), magneto-encephalography or brain topography (SST). These techniques require subjects to carry out experiential tasks and control tasks while being wired to various neuroimaging devices. The devices generate instant, colorful images of the brain at work, and researchers can compare the differences in the images produced during those tasks to identify which parts of the brain have responded to the stimuli. This helps to identify certain parts of the brain that react differently to certain stimuli and the reactions that can lead to the desire to buy. Furthermore, eye-tracking devices and galvanic skin response (GSR) sensors are also used in major research to analyze exactly where the viewer's eye is located and to indicate the electrical conductivity of the skin, respectively. Therefore, through measuring brain activity in certain areas of the brain, neuromarketing seeks to investigate how consumers make decisions and the link between decision-making and human brain areas. (SHARMA, 2016)
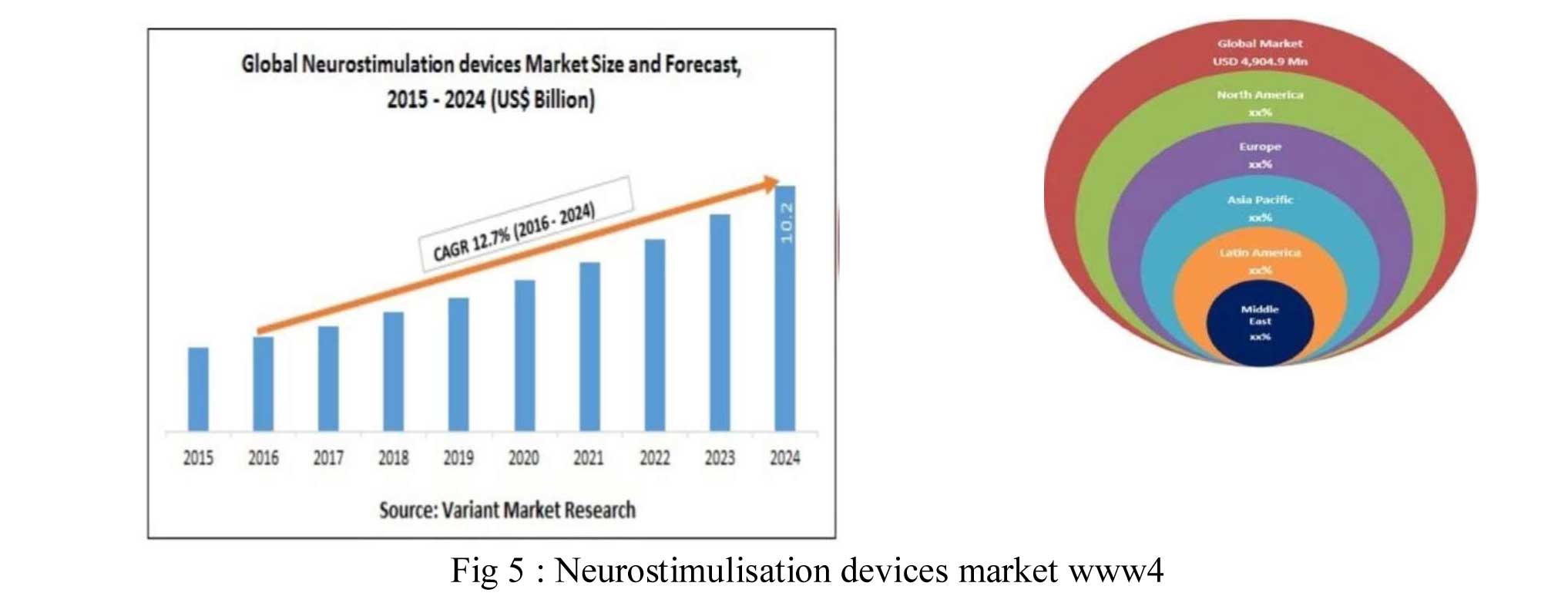
Neuro stimulation Devices Market is dominated by North and is increasing continously.
The brain is made up of four regions, each with a specific function. The occipital lobe processes visual information, while the temporal lobe is responsible for object recognition, object memory, and spatial movements like hearing. The parietal lobe contains sensory strips that process spatial changes related to actions, and the prefrontal cortex, located in the frontal lobe, helps with working memory, preference, and decision making.
Research has shown that when a product is displayed for four seconds, it triggers strong activation in the Nucleus Accumbens, a region associated with reward and pleasure. On the other hand, displaying the price for the same duration activates the insula, which is linked to emotional responses. The medial prefrontal cortex is activated when a person makes a decision between yes and no. Learning occurs in the Ventral Stratum, located in the left part of the brain. The sense of smell is connected to emotions, and EEG can be used to record brain activity while exposed to different fragrances.
The sense of smell, or olfactory function, can influence consumer behavior in retail settings (Video of Per Meller, Associate Professor, Copenhagen Business School). Emotions are non conscious and occur in subcortical regions and the neocortex of the brain. Joy is an emotion, while happiness is a feeling. The responses create biochemical and electrical reactions in the body that alter its physical state – emotions are neurological reactions to an emotional stimulus. The amygdala plays a crucial role in arousing emotions and consolidating memories. Feelings prompt bodily reactions that can be objectively measured through eye-tracking, GSR, EEG, fMRI, ECG, and facial expressions.
The use of brain imaging techniques in marketing research
Neuromarketing is a field that studies how consumers respond to marketing stimuli using neuroimaging techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), electroencephalography (EEG), magneto-encephalography or brain topography (SST). These techniques require subjects to carry out experiential tasks and control tasks while being wired to various neuroimaging devices. The devices generate instant, colorful images of the brain at work, and researchers can compare the differences in the images produced during those tasks to identify which parts of the brain have responded to the stimuli. This helps to identify certain parts of the brain that react differently to certain stimuli and the reactions that can lead to the desire to buy. Furthermore, eye-tracking devices and galvanic skin response (GSR) sensors are also used in major research to analyze exactly where the viewer's eye is located and to indicate the electrical conductivity of the skin, respectively. Therefore, through measuring brain activity in certain areas of the brain, neuromarketing seeks to investigate how consumers make decisions and the link between decision-making and human brain areas. (SHARMA, 2016)
Neuro stimulation Devices Market is dominated by North and is increasing continously.
 Neuromarketing has emerged as a means to fill the informational gap in understanding human behavior and consumer preferences. It utilizes tools such as EEG, eye-tracking, and IAT, which are valuable and untapped resources for any company, regardless of industry. The use of these techniques has led to the creation of graphic collages that can stimulate different emotions, and many renowned companies such as Coca Cola, Nestle, Procter & Gamble, and General Motors have quickly embraced these new techniques. Other well-known brands such as Campbell, Frito-Lay, PayPal, Walmart, Home Depot, and IKEA have also recognized the importance of neuromarketing in keeping up with consumer behavior (NOTCH, 2015). With the emergence of new decision-making models, it has become imperative to gain insight into human behavior, particularly consumer behavior, in each phase of the decision-making process.
Neuromarketing has emerged as a means to fill the informational gap in understanding human behavior and consumer preferences. It utilizes tools such as EEG, eye-tracking, and IAT, which are valuable and untapped resources for any company, regardless of industry. The use of these techniques has led to the creation of graphic collages that can stimulate different emotions, and many renowned companies such as Coca Cola, Nestle, Procter & Gamble, and General Motors have quickly embraced these new techniques. Other well-known brands such as Campbell, Frito-Lay, PayPal, Walmart, Home Depot, and IKEA have also recognized the importance of neuromarketing in keeping up with consumer behavior (NOTCH, 2015). With the emergence of new decision-making models, it has become imperative to gain insight into human behavior, particularly consumer behavior, in each phase of the decision-making process.
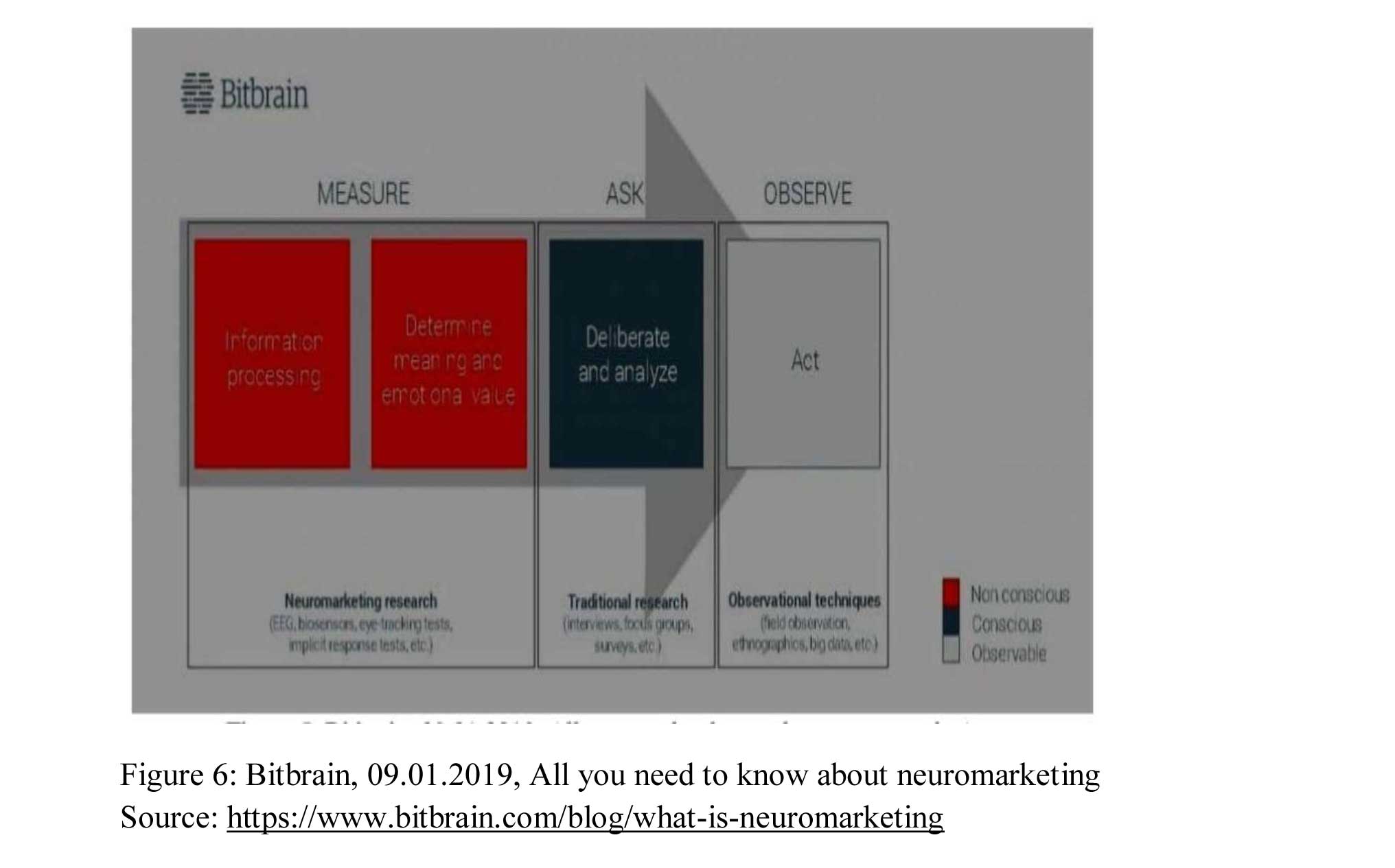
- Observing the way the consumers act: There are various methods in market research to observe consumer behavior, such as field observation, ethnography, digital behavior analysis using big data, and even big data from the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Understanding the consumer’s way of deliberate and analyze: To understand how consumers deliberate and analyze, companies can directly ask the consumer as this phase is conscious. Surveys, interviews, and focus groups are the most common techniques used to comprehend a consumer's decision.
- Analyzing the consumers’ unconscious reactions: When consumers have unconscious reactions to stimuli, such as physiological changes like sweaty hands when feeling nervous, traditional market research techniques like surveys or observation are not effective in analyzing them. However, with the help of neuromarketing, it is possible to measure these physiological changes using neurological instruments such as EEG or biosensors. Complex decoding algorithms can then be used to determine the emotional or cognitive response that caused these changes. Companies can utilize this method to monitor the physiological changes that occur in consumers while they are exposed to certain stimuli, like an advertising campaign, and deduce the emotions that caused those changes.
The field evolves precisely from the need to better understand the consumer's decisions(identifying the cause and effect), measuring the moment-by-moment interaction for any type of stimulus, and reaching where traditional marketing has no access: in the subconscious. The market, as well as the individual behavior of consumers, is being analyzed using technologies that measure brain activity and a close connection is established between the exact reactions and the stimuli to which consumers have been exposed.
Neuromarketing can confirm, reconfigure, or improve the conventional theories of marketing theory. The classical methodology of market research that we are already familiar with is incomplete because it can only probe the consumer's consciousness, but not his subconscious. Some might say that such studies are also made in the forms of classic marketing, but the tools used in neuromarketing are brain scanners that use magnetic resonance imaging. All this is done in order to determine the exact reactions of the potential consumers.
Practical Applications of Neuromarketing:
Neuromarketing has several practical applications in the field of marketing. One of the most common applications is using neuroscience techniques to test the effectiveness of marketing materials such as advertisements and product packaging. By measuring the brain’s responses to these stimuli, marketers can gain insights into what works and what doesn’t.
For example, a study by Vinod Venkatraman and his colleagues at Temple University found that consumers were more likely to choose products with rounded edges over products with sharp edges, and that this preference was associated with increased activity in the brain’s insula, a region associated with the perception of pain. This finding has important implications for product design and packaging.
Neuromarketing can also be used to understand consumer preferences and motivations. For example, a study by Martin Lindstrom and his colleagues at the Buyology Inc. used fMRI to study the brain’s responses to different brands of cigarettes. The study found that the brain’s responses to the brands were associated with specific emotions and personal experiences, and that these responses were not always consistent with the participants’ stated preferences.
In addition to testing marketing materials and understanding consumer preferences, neuromarketing can also be used to optimize pricing and promotional strategies. For example, a study by Ana Carolina Maldonado and her colleagues at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul found that the brain’s responses to price discount varied depending on the type of product being sold. The study also found that consumers were more likely to respond positively to discounts that were framed in terms of absolute savings rather than percentage savings.
Methodologies used in neuromarketing research
This study was developed through an integrative literature review which is a rather useful method in integrating and analysing research results on emerging issues, collecting and analysing the state of the literature relating to the subject, and identifying challenges to the development of future studies. Another method, used in this paper, is the descriptive method, through which consumer behavior, neuromarketing, and its use are described. Data sources: Secondary data sources were used. The quantitative method of data collection was used, whereas the questionnaire was used for data collection. Ismajli, A., Ziberi, B., & Metushi, A. (2022).
Overall, the methodology for neuromarketing research involves a multi-disciplinary approach that combines neuroscience and marketing techniques.
Techniques for neuromarketing research
- Electroencephalography (EEG) is a technique that measures the electrical activity of the brain. It is used in neuromarketing to understand the emotional responses of consumers to different stimuli. It measures attention, engagement, boredom, excitement, emotional valance, cognition, memory encoding, recognition, and approach/withdrawal. It is used for testing and developing advertisements, for testing new campaigns, for testing movie trailers, for testing websites designs and usability, for testing in-store experience and testing taglines.
- Facial Coding: Facial coding is a technique that uses software to analyze facial expressions. It is used in neuromarketing to understand the emotional responses of consumers to different stimuli.
- fMRI: functional magnetic resonance imaging is a technique that uses magnetic fields to measure changes in blood flow in the brain. It is commonly used in neuromarketing to understand how the brain responds to different stimuli, such as product packaging, advertising, and pricing. It measures memory encoding, sensory perception, valence of emotions, craving, trust, brand loyalty, brand preference, brand recall. It is used for testing new products, testing new campaigns, testing and developing advertisements, identifying the key moments of an advertisement or video material, for testing packaging design, testing prices, repositioning a brand, predicting choices, identifying needs, sensory testing, celebrity endorsement.
- Eye-tracking: Eye-tracking is a technique that uses cameras and software to track the eye movements of consumers. It is used in neuromarketing to understand which parts of an advertisement or product packaging attract the most attention from consumers. It measures visual fixation, search, eye movement patterns, spatial resolution, excitement, attention and pupil dilation. It is used for testing websites and user-interface effectiveness, testing in-store reactions, testing packaging design, testing advertisements and video materials, testing prints and images design, testing how the consumer filters information, determining hierarchy of perceptions of stimulus material (which things are perceived first, which last, and which remain unnoticed), testing shelf layout, testing product placement.
- Stimulus presentation: During neuromarketing experiments, participants are typically exposed to a range of marketing stimuli, such as advertisements, product packaging, or website designs. The stimuli may be presented using various methods, such as a computer screen or virtual reality headset.
- Data analysis: Neuromarketing data is typically analyzed using specialized software and statistical methods. The data may be analyzed on multiple levels, such as individual brain activity, group-level responses, and correlations with consumer behavior.
- Ethical considerations: Ethical considerations are an important part of neuromarketing methodology. Researchers must obtain informed consent from participants, ensure that data is collected and used responsibly, and consider the potential impact of their research on consumer behavior and privacy.
- Biometric measures (e.g., heart rate variability, skin conductance) It measures arousal and is used for predicting market performance.
- Neuropsychological testing is a type of assessment that measures cognitive and behavioral functions, such as attention, memory, language, and executive functioning. Neuropsychological testing can be used to understand how different stimuli, such as product packaging or advertising, affect cognitive processing and decision-making. It measures emotions and emotional engagement during choice processes. It is used when testing advertisements, testing movie trailers, testing websites design, identifying in-store reactions and when identifying consumer behavior in its natural environment
- MEG: Magnetoencephalography is a neuroimaging technique that measures the magnetic fields generated by the electrical activity of neurons in the brain. In neuromarketing, MEG is used to understand the neural responses of consumers to different stimuli, such as product packaging, advertising, and pricing. MEG provides high temporal and spatial resolution, allowing researchers to identify the specific brain regions and neural networks involved in the processing of different stimuli. It measures perception, attention and memory. It is used when testing new products, testing advertisements, testing packaging design, identifying needs and for sensory testing.
- Steady State Topography (SST): SST is a technique utilized in cognitive neuroscience and neuromarketing research for rapid observation and measurement of human brain activity. Developed by Richard Silberstein it involves recording brain electrical activity (EEG) while presenting a sinusoidal visual flicker in the visual periphery, which induces an oscillatory brain electrical response called the Steady State Visually Evoked Potential (SSVEP). Changes in brain activity related to a particular task can then be determined from the SSVEP measurements. It measures consumer behavior, effectiveness of video materials, long term memory encoding, engagement, emotional intensity, emotional valence, processed visual and olfactory input and attention. It is used when testing advertisements, testing movie trailers, testing prints and images, testing brand communication.
- Transcranial magnetic stimulation: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive technique that utilizes magnetic fields to influence specific areas of brain activity located approximately 1-2 centimeters beneath the skull, without reaching the neocortex. TMS now has the capability to target lower brain regions and effectively monitor population neural activity. Notably, this method is more cost-effective compared to other brain imaging techniques such as PET or fMRI scanners. It measures attention, cognition, changes in behavior. It is used when testing new products, testing advertisements, testing packaging design and testing other marketing stimuli.
- Implicit association test: IAT is a technique used to measure an individual's behavior and experiences, allowing for the identification of product hierarchies through comparisons. According to Houwer and Bruycker (2007), implicit measures may be less biased by deliberate attempts to conceal attitudes, and may even reflect attitudes of which the respondent is not aware. The IAT measures the underlying attitudes or evaluations of subjects by assessing their reaction times on two cognitive tasks. Specifically, the IAT measures the speed with which individuals can associate two different concepts, such as advertisements, brands, or concepts, with two different evaluative anchors or attributes.It measures reaction time and underlying attitudes / evaluations. It is used when celebrity endorsement (for choosing the right option), category segmentation salient packaging features and brand positioning.
THE IMPACT OF NEUROMARKETING ON CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR
Study conducted by Ismajli, A.,Ziberi, B., &Metushi, A. (2022)(Corporate Governance and Organizational Behavior Review, 6(2), 95–103.https://doi.org/10.22495/cgobrv6i2p9) on the impact of neuromarketing on consumer behavior on various aspects are shown in the graph in fig 7 below. This study raised the following hypotheses:
H1: Consumers demand and buy products that meet their needs, desires, and requirements based on the quality of that product and where the quality of the products directly affects the decision to buy.
H2: In the decision-making process to buy a specific product, a consumer preference is influenced by the importance of obtaining information about that product.
H3: The application of neuromarketing influences and helps companies to modify and select their advertisements that are relevant and have an effect on the choice of a product by the consumer.
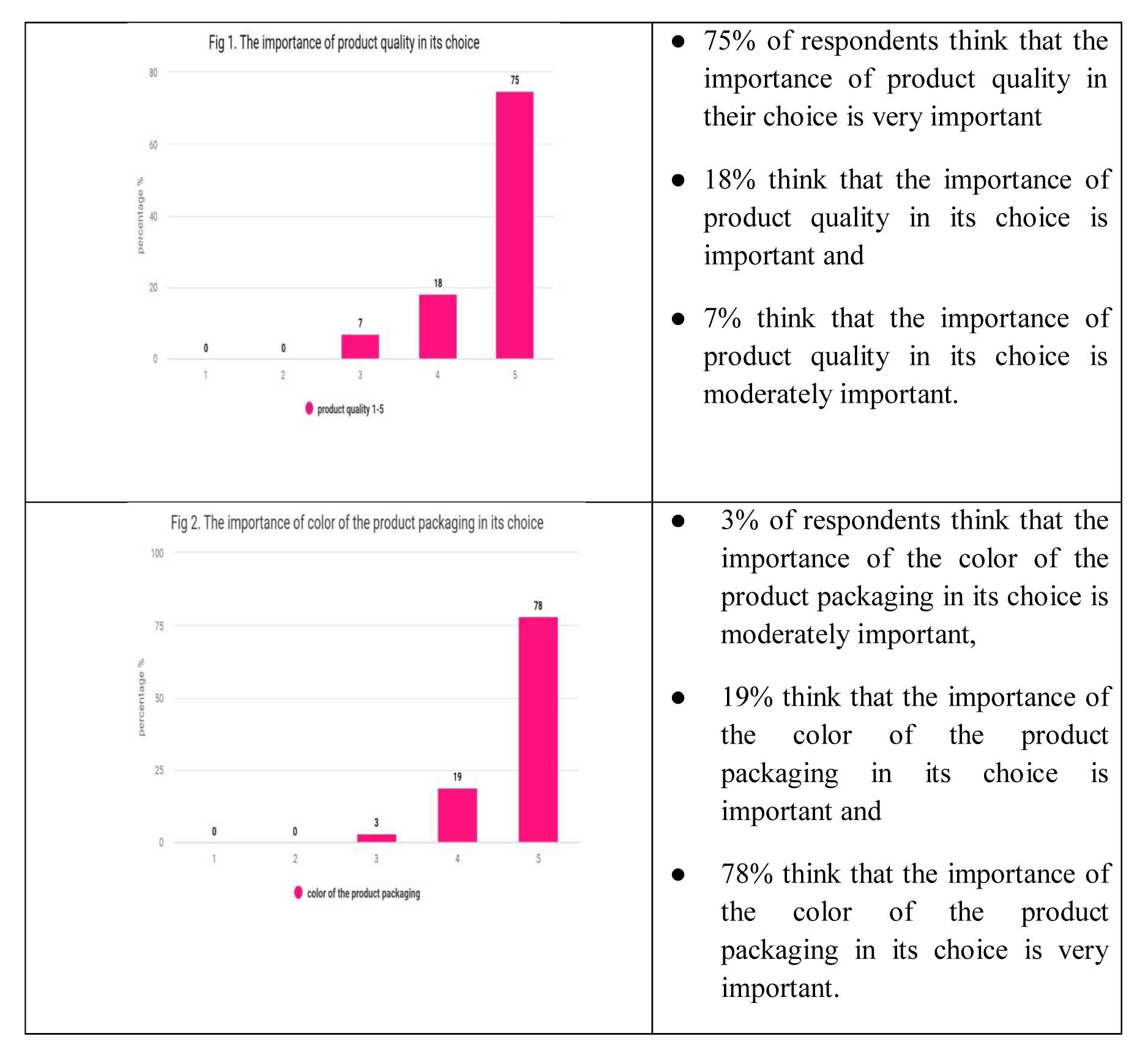
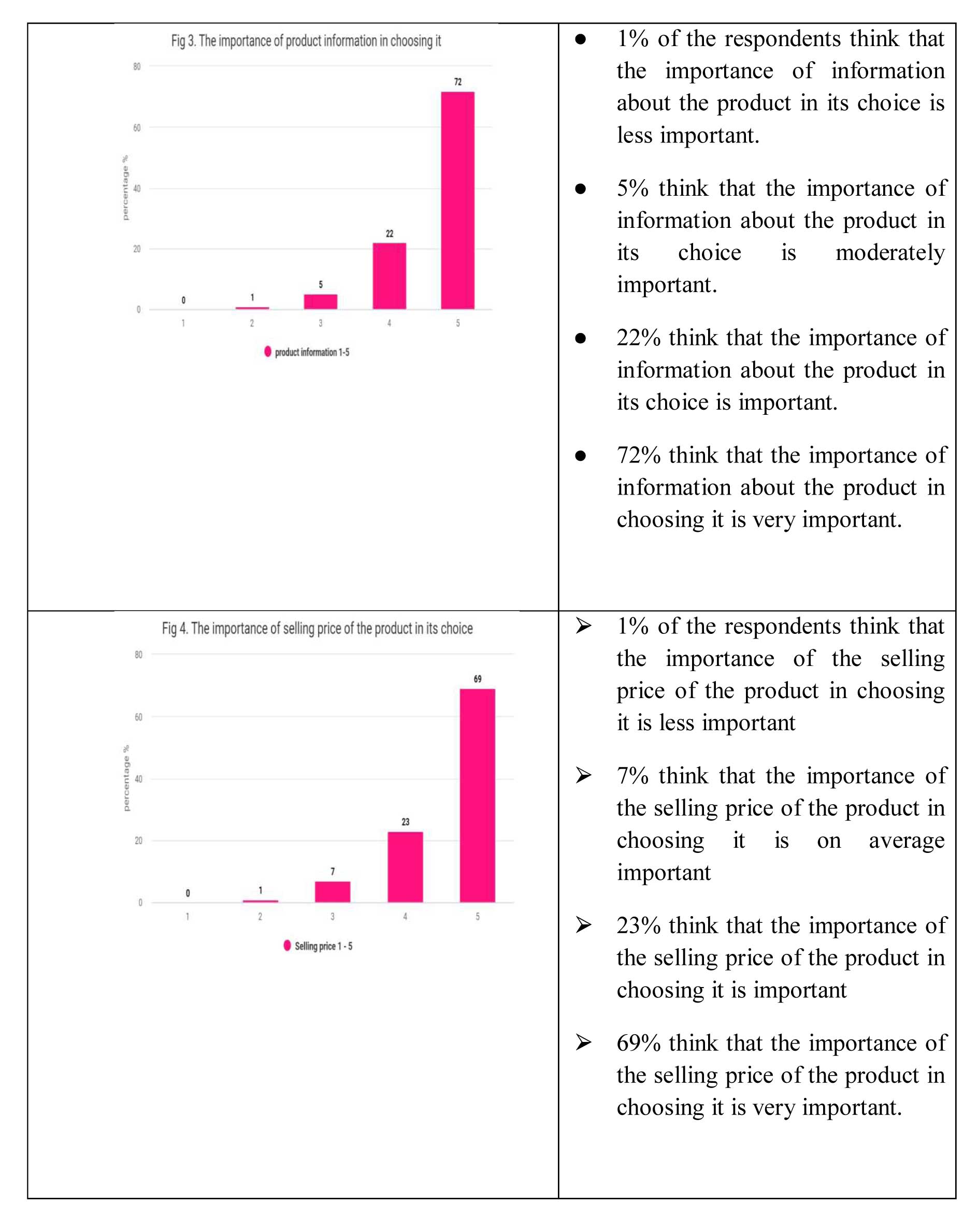
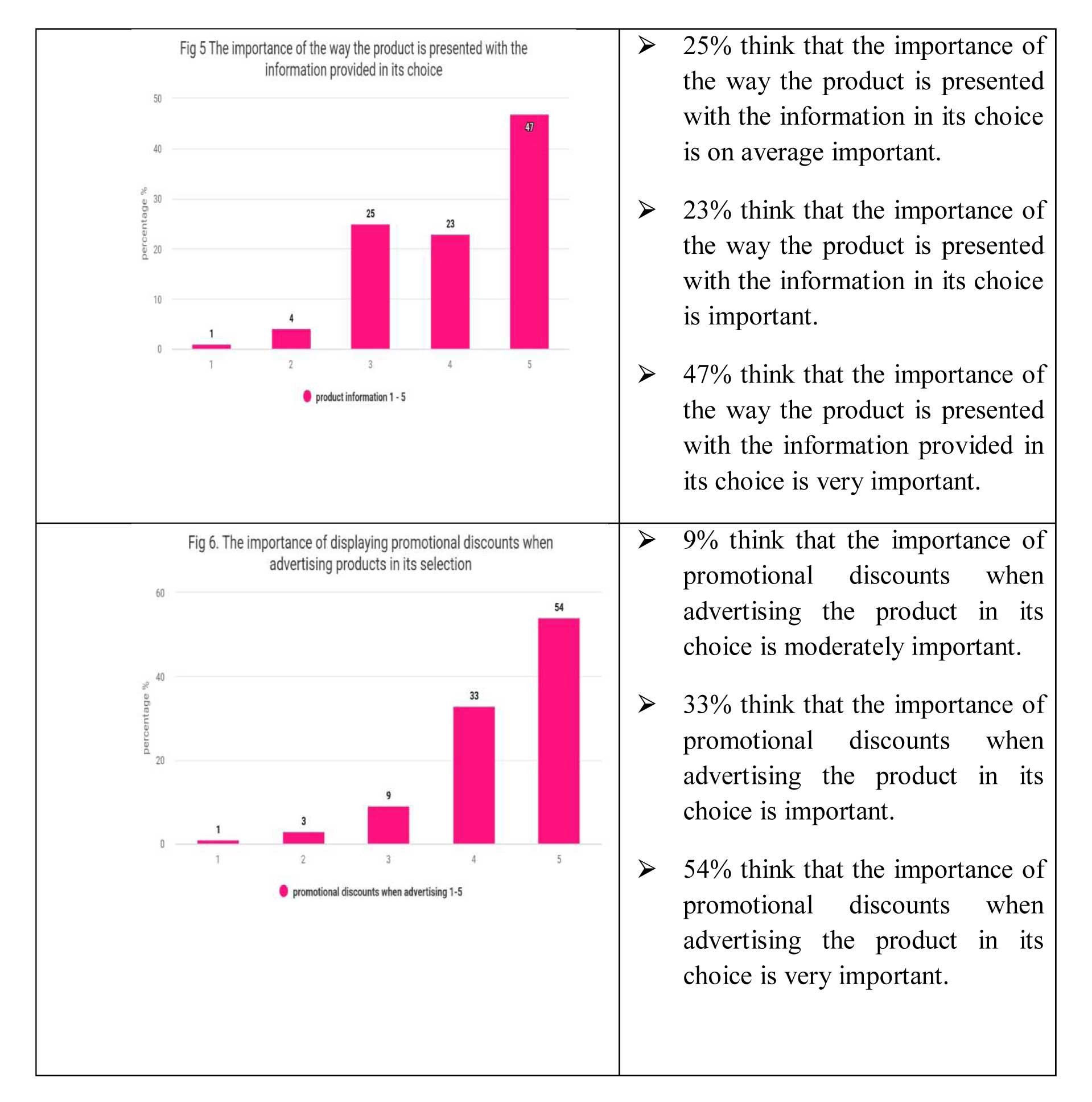
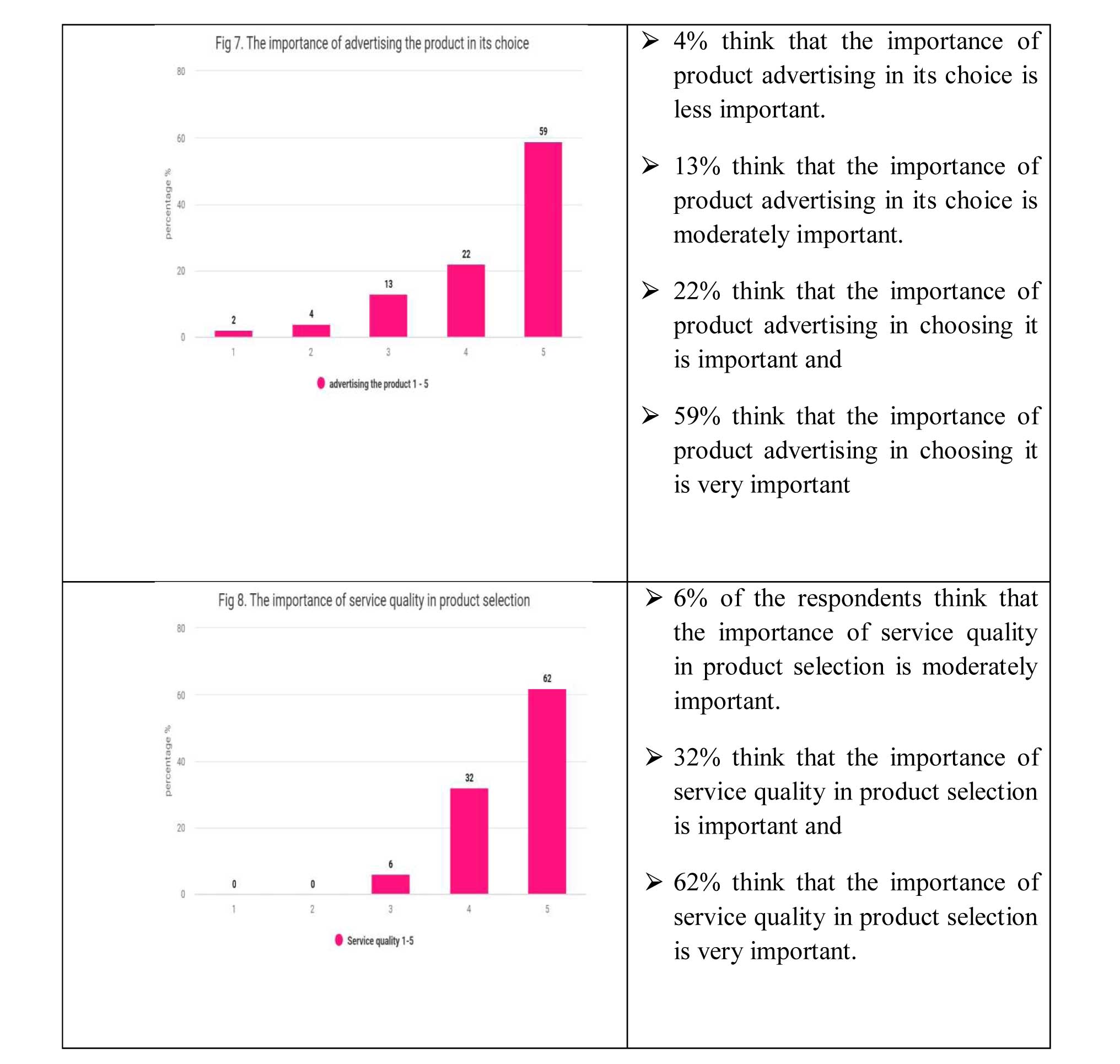 The research indicates that 75% of the individuals surveyed prioritize product quality the most when making a purchase decision, which supports the first hypothesis (H1). Additionally, 18% of the respondents believe that the color of product packaging is significant in their purchasing decision, while 72% of them consider product information to be very important, which supports the second hypothesis (H2).
Furthermore, the study also found that 69% of the participants consider the price to be of great importance in their purchasing decision, and 54% of them regard promotional discounts as crucial in their decision-making process. Overall, the findings suggest that neuromarketing can aid companies in modifying and selecting relevant advertisements that can impact a consumer's product choice, as indicated by the third hypothesis (H3) of the research.
In summary, we can infer that consumers start gathering information about a product once they recognize the need for it. The importance of the product information and its presentation plays a significant role in influencing the consumer's decision-making process. Once the consumer has decided on a product, the most crucial moment arises, which is the actual purchase of the product. However, this is not the end of the process, as the consumer continues to evaluate the product after its purchase
Criticisms of neuromarketing
Neuromarketing has been criticized for ethical issues related to privacy, transparency, and informed consent. Here are some of the criticisms:
Invasion of Privacy: Neuromarketing techniques involve monitoring and recording an individual's brain activity, which raises concerns about privacy. Participants may not be fully aware of what is being monitored, and the data collected may be used for purposes other than the study, leading to potential violations of privacy.
Lack of Transparency: The use of neuromarketing techniques is not always transparent, and consumers may not be aware that their behavior is being monitored or that their personal data is being collected. This lack of transparency can lead to a loss of trust between companies and consumers.
Informed Consent: Informed consent is an essential ethical principle in research, but it can be challenging to obtain in neuromarketing studies. Participants may not fully understand the risks and benefits of the study, and they may feel pressured to participate due to the potential benefits of the study.
Misuse of Data: Neuromarketing data can be misused, leading to potential harm to individuals. For example, data on an individual's preferences and behavior could be used to target them with marketing messages, leading to manipulation and exploitation.
Social Implications: Neuromarketing could lead to social implications such as the reinforcement of stereotypes and prejudices, which could have a negative impact on society.
To address these ethical issues, guidelines and best practices should be developed to ensure that neuromarketing is used responsibly and transparently.
Current State of Research:
Despite the potential benefits of neuromarketing, the field is still in its infancy, and much remains to be learned. One of the challenges facing neuromarketing is the lack of standardization in methodology. Different researchers use different techniques and equipment, making it difficult to compare results across studies. This lack of standardization also makes it difficult to replicate studies and validate findings.
Another challenge facing neuromarketing is the ethical implications of using neuroscience techniques to influence consumer behavior. Critics argue that neuromarketing raises concerns about privacy, autonomy, and the potential for manipulation. Proponents of neuromarketing, on the other hand, argue that the field can be used to create more ethical and effective marketing strategies.
Despite these challenges, there has been a growing body of research on neuromarketing in recent years. Studies have examined topics such as the role of emotions in decision-making, the effectiveness of different marketing messages, and the influence of social context on consumer behavior. This research has the potential to inform and improve marketing strategies across a range of industries.
Potential limitations and challenges
Despite significant advancements in neuroscience and neuromarketing research, there are still limitations that hinder its ability to generalize results as effectively as traditional methods of consumer research. One major limitation is the heterogeneity of the methods used, making it difficult to compare and replicate findings. Ethical concerns also pose a challenge to the development of research in neuroscience applied to the consumer. These concerns include invasion of privacy and the threat to free choice, as personal data obtained through neuromarketing techniques could be used to influence consumer choice without their knowledge or control. Additionally, there are nuances regarding the purpose, type of organization, and industrial sector in which neuromarketing studies are conducted, which may impact their ethical implications. The lack of publication of results by companies using neuromarketing methodology is also an obstacle, as they may want to preserve their competitive advantage. However, publishing these results in academic literature would be valuable. Furthermore, the use of proprietary software to interpret neuroimaging data can also lead to problems in replication studies due to the lack of review and comparison of already-made studies.
Future directions for research
Here are some potential future directions of research in neuromarketing:
Application of Artificial Intelligence: The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms can help in better understanding customer behavior and preferences. This can be done by analyzing big data from various sources such as social media, online browsing behavior, purchase history, etc. AI can also be used to personalize marketing messages and offers, leading to better engagement and conversion rates.
Integration of Multi-Modal Neuroimaging Techniques: Currently, neuromarketing research is mostly conducted using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG). However, the integration of other techniques such as magnetoencephalography (MEG), near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) can provide a more comprehensive view of the brain's response to marketing stimuli.
Cross-Cultural Studies: The cultural differences in consumer behavior are well documented, and it is important for marketers to understand these differences to create effective marketing campaigns. Cross-cultural studies using neuromarketing techniques can provide insights into the universal and culturally specific aspects of consumer behavior.
Development of Neuromarketing Ethics: The use of neuromarketing raises ethical concerns regarding the privacy and autonomy of individuals. Future research can focus on developing ethical guidelines for the use of neuromarketing techniques and ensuring that these techniques are used in a responsible and transparent manner.
Focus on Behavioral Economics: Behavioral economics is an interdisciplinary field that combines insights from psychology, economics, and neuroscience to explain how people make decisions. The integration of neuromarketing with behavioral economics can provide a more complete understanding of consumer behavior and help in developing effective marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Neuromarketing is a relatively new and exciting field that has the potential to transform the way we understand and interact with consumers. By using neuroscience techniques to measure the brain’s responses to marketing stimuli, researchers can gain insights into the unconscious processes that drive consumer behavior. Although there are challenges facing the field, such as standardization and ethical concerns, the growing body of research on neuromarketing suggests that this technology has the potential to improve marketing strategies and create more effective and ethical business practices.
Neuromarketing is a valuable tool for identifying customer preferences and selecting advertisements that resonate with them. Attention to detail is crucial when advertising a product and the presentation of promotional discounts significantly impacts product selection. By focusing on individual needs and preferences, businesses can apply neuromarketing to identify customer preferences and develop products that meet those needs.To aid in consumer decision-making, businesses should provide comprehensive information about the product and be mindful of the pricing strategy. Observing consumer behavior and understanding their needs and wants in the market is crucial to developing successful marketing strategies. Neuromarketing methods and techniques can facilitate the identification of customer preferences and needs, thereby solving the problem of marketing. In summary, the consumer decision-making process and the application of neuromarketing can help businesses meet the needs of customers and increase their competitive advantage in the marketplace.
References
The research indicates that 75% of the individuals surveyed prioritize product quality the most when making a purchase decision, which supports the first hypothesis (H1). Additionally, 18% of the respondents believe that the color of product packaging is significant in their purchasing decision, while 72% of them consider product information to be very important, which supports the second hypothesis (H2).
Furthermore, the study also found that 69% of the participants consider the price to be of great importance in their purchasing decision, and 54% of them regard promotional discounts as crucial in their decision-making process. Overall, the findings suggest that neuromarketing can aid companies in modifying and selecting relevant advertisements that can impact a consumer's product choice, as indicated by the third hypothesis (H3) of the research.
In summary, we can infer that consumers start gathering information about a product once they recognize the need for it. The importance of the product information and its presentation plays a significant role in influencing the consumer's decision-making process. Once the consumer has decided on a product, the most crucial moment arises, which is the actual purchase of the product. However, this is not the end of the process, as the consumer continues to evaluate the product after its purchase
Criticisms of neuromarketing
Neuromarketing has been criticized for ethical issues related to privacy, transparency, and informed consent. Here are some of the criticisms:
Invasion of Privacy: Neuromarketing techniques involve monitoring and recording an individual's brain activity, which raises concerns about privacy. Participants may not be fully aware of what is being monitored, and the data collected may be used for purposes other than the study, leading to potential violations of privacy.
Lack of Transparency: The use of neuromarketing techniques is not always transparent, and consumers may not be aware that their behavior is being monitored or that their personal data is being collected. This lack of transparency can lead to a loss of trust between companies and consumers.
Informed Consent: Informed consent is an essential ethical principle in research, but it can be challenging to obtain in neuromarketing studies. Participants may not fully understand the risks and benefits of the study, and they may feel pressured to participate due to the potential benefits of the study.
Misuse of Data: Neuromarketing data can be misused, leading to potential harm to individuals. For example, data on an individual's preferences and behavior could be used to target them with marketing messages, leading to manipulation and exploitation.
Social Implications: Neuromarketing could lead to social implications such as the reinforcement of stereotypes and prejudices, which could have a negative impact on society.
To address these ethical issues, guidelines and best practices should be developed to ensure that neuromarketing is used responsibly and transparently.
Current State of Research:
Despite the potential benefits of neuromarketing, the field is still in its infancy, and much remains to be learned. One of the challenges facing neuromarketing is the lack of standardization in methodology. Different researchers use different techniques and equipment, making it difficult to compare results across studies. This lack of standardization also makes it difficult to replicate studies and validate findings.
Another challenge facing neuromarketing is the ethical implications of using neuroscience techniques to influence consumer behavior. Critics argue that neuromarketing raises concerns about privacy, autonomy, and the potential for manipulation. Proponents of neuromarketing, on the other hand, argue that the field can be used to create more ethical and effective marketing strategies.
Despite these challenges, there has been a growing body of research on neuromarketing in recent years. Studies have examined topics such as the role of emotions in decision-making, the effectiveness of different marketing messages, and the influence of social context on consumer behavior. This research has the potential to inform and improve marketing strategies across a range of industries.
Potential limitations and challenges
Despite significant advancements in neuroscience and neuromarketing research, there are still limitations that hinder its ability to generalize results as effectively as traditional methods of consumer research. One major limitation is the heterogeneity of the methods used, making it difficult to compare and replicate findings. Ethical concerns also pose a challenge to the development of research in neuroscience applied to the consumer. These concerns include invasion of privacy and the threat to free choice, as personal data obtained through neuromarketing techniques could be used to influence consumer choice without their knowledge or control. Additionally, there are nuances regarding the purpose, type of organization, and industrial sector in which neuromarketing studies are conducted, which may impact their ethical implications. The lack of publication of results by companies using neuromarketing methodology is also an obstacle, as they may want to preserve their competitive advantage. However, publishing these results in academic literature would be valuable. Furthermore, the use of proprietary software to interpret neuroimaging data can also lead to problems in replication studies due to the lack of review and comparison of already-made studies.
Future directions for research
Here are some potential future directions of research in neuromarketing:
Application of Artificial Intelligence: The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms can help in better understanding customer behavior and preferences. This can be done by analyzing big data from various sources such as social media, online browsing behavior, purchase history, etc. AI can also be used to personalize marketing messages and offers, leading to better engagement and conversion rates.
Integration of Multi-Modal Neuroimaging Techniques: Currently, neuromarketing research is mostly conducted using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG). However, the integration of other techniques such as magnetoencephalography (MEG), near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) can provide a more comprehensive view of the brain's response to marketing stimuli.
Cross-Cultural Studies: The cultural differences in consumer behavior are well documented, and it is important for marketers to understand these differences to create effective marketing campaigns. Cross-cultural studies using neuromarketing techniques can provide insights into the universal and culturally specific aspects of consumer behavior.
Development of Neuromarketing Ethics: The use of neuromarketing raises ethical concerns regarding the privacy and autonomy of individuals. Future research can focus on developing ethical guidelines for the use of neuromarketing techniques and ensuring that these techniques are used in a responsible and transparent manner.
Focus on Behavioral Economics: Behavioral economics is an interdisciplinary field that combines insights from psychology, economics, and neuroscience to explain how people make decisions. The integration of neuromarketing with behavioral economics can provide a more complete understanding of consumer behavior and help in developing effective marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Neuromarketing is a relatively new and exciting field that has the potential to transform the way we understand and interact with consumers. By using neuroscience techniques to measure the brain’s responses to marketing stimuli, researchers can gain insights into the unconscious processes that drive consumer behavior. Although there are challenges facing the field, such as standardization and ethical concerns, the growing body of research on neuromarketing suggests that this technology has the potential to improve marketing strategies and create more effective and ethical business practices.
Neuromarketing is a valuable tool for identifying customer preferences and selecting advertisements that resonate with them. Attention to detail is crucial when advertising a product and the presentation of promotional discounts significantly impacts product selection. By focusing on individual needs and preferences, businesses can apply neuromarketing to identify customer preferences and develop products that meet those needs.To aid in consumer decision-making, businesses should provide comprehensive information about the product and be mindful of the pricing strategy. Observing consumer behavior and understanding their needs and wants in the market is crucial to developing successful marketing strategies. Neuromarketing methods and techniques can facilitate the identification of customer preferences and needs, thereby solving the problem of marketing. In summary, the consumer decision-making process and the application of neuromarketing can help businesses meet the needs of customers and increase their competitive advantage in the marketplace.
References
- Alwitt, L.F. (1985). EEG activity reflects the content of commercials. In Alwitt, L.F., Psychological Processes and Advertising Effects: Theory, Research and Applications (209-219). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Ariely, D. &Berns, G. (2010). Neuromarketing: the hope and hype of neuroimaging in business. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11(4), 284-292.
- Bolls, P.D., Lang, A., Potter, R.F. (2001). The effect of message valence and listener arousal on attention,memory and facial muscular responses to radio advertisements. Communication Research, 28(5), 627-651.
- Van Boxtel, A. (2010). Facial EMG as a Tool for Inferring Affective States. Proceedings of Measuring Behavior 2010 (Eindhoven, The Netherlands, August 24-27, 2010) Eds. Spink, A.J., Grieco, F., Krips O.E., Loijens L.W.S., Noldus L.P.J.J., Zimmerman P.H.
- Butler, M.J.R. (2008). Neuromarketing and the perception of knowledge. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 7, 415-419.
- Cacioppo, J.T., Petty, R.E., Losch, M.E., Kim, H.S. (1986). Electromyographic activity over facial muscle regions can differentiate the valence and intensity of affective reactions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 50(2), 260-68 In Ohme, R., Matukin, M., Pacula-Lesniak, B. (2011). Biometric measures for interactive advertising research. Journal of Interactive Advertising, 11(2), 60-72.
- Calvert, G.A. &Thensen, T. (2004). Multisensory integration: methodological approaches and emerging principles in the human brain. Journal of Psychology, 98, 191-205.
- Falk, E.B., Rameson, L., Berkman, E.T., Liao, B., Kang, Y., Inagaki, T.K., Lieberman, M.D. (2009). The Neural Correlates of Persuasion: A Common Network across Cultures and Media. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22(11), 2447-2459.
- Fugate, D.L. (2007). Neuromarketing: A Layman's Look at Neuroscience and its Potential Application to Marketing Practice. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 24(7), 385-394.
- Garcia, J.R. &Saad, G. (2008). Evolutionary neuromarketing: Darwinizing the neuroimaging paradigm for consumer behavior. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 7, 397-414.
- Gray, M., Kemp, A.H., Silberstein, R.B., Nathan, P.J. (2003). Cortical neurophysiology of anticipatory anxiety: an investigation utilizing steady state probe topography (SSPT). Neuroimage, 20, 975-986.
- Houwer, J. &Bruycker, E. (2007). The implicit association test outperorms the extrinsic affective Simon task as an implicit measure of inter-individual differences in attitudes. British Journal of Social Psychology, 46, 401-421.
- Kenning, P. &Plassmann, H. (2005). NeuroEconomics: An Overview from an Economic Perspective. Brain Research Bulletin, 67, 343-354.
- LaBarbera, P.A. &Tucciarone J.D. (1995). GSR reconsidered: A behavior-based approach to evaluating and improving the sales potency of advertising. Journal of Advertising Research, 35, 33-53.
- Laubrock, J., Engbert, R., Rolfs, M., Kliegl, R. (2007). Microsaccades are an index of covert attention: Commentary on Horowitz, Fine, Fencsik, Yurgenson, Wolfe. Psychological Science, 18, 364-366 In Zurawicki, L. (2010). Neuromarketing, Exploring the Brain of the Consumer. Berlin Heidelberg. SpringerVerlag
- Lee, N., Broderick, A.J., Chamberlain, L. (2007). What is "neuromarketing"? A discussion and agenda for future research. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 63, 199-204.
- Levy, I., Lazzaro, S., Rutledge, R.B., Glimcher, P.W. (2011). Choice from Non-Choice: Predicting Consumer Preferences from Blood Oxygenation Level-Dependent Signals Obtained during Passive Viewing. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(1), 118-125.
- Morin, C. (2011). Neuromarketing: The New Science of Consumer Behavior, Symposium: Consumer Culture in Global Perspective, 48, 131-135.
- Morris, J.D., Klahr, N.J., Shen, F., Villegas, J., Wright, P., He, G., Liu, Y. (2009). Mapping a Multidimensional Emotion in Response to Television Commercials. Human Brain Mapping. 30, 789-796.
- O'Connel, B., Walden, S., Pohlmann, A. (2011). Marketing and Neuroscience. What Drives Customer Decisions? American Marketing Association, White Paper.
- Ohme, R., Matukin, M., Pacula-Lesniak, B. (2011). Biometric measures for interactive advertising research. Journal of Interactive Advertising, 11(2), 60-72.
- Perrachione, T.K. &Perrachione J.R. (2008) Brains and Brands: Developing Mutually Informative Researchin Neuroscience and Marketing. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 7, 303-318.
- Poldrack, R.A., Fletcher, P.C., Henson, R.N., Worsley, K.J., Brett, M., Nichols, T.E. (2008) Guidelines for reporting an fMRI study. NeuroImage, 40, 409-414.
- Reimann, M., Schilke, O., Weber, B., Neuhaus, C., Zaichkowsky, J. (2011). Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Consumer Research: A Review and Application. Psychology & Marketing Wiley Periodicals, 28(6), 608-637.
- Savoy, R.L. (2005). Experimental design in brain activation MRI: Cautionary tales. Brain Research Bulletin, 67, 361-367.
- Silberstein, R.B. (1995) Steady state visually evoked potentials, brain resonances and cognitive processes. In P. L. Nunez. Neocortical dynamics and human EEG rhythms. New York. Oxford University Press. 272-303.
- SHARMA, J. K.; SINGH, D.; DEEPAK, K. K.; AGRAWAL, D. P. (2010) Neuromarketing:A Peep Into Customers Minds, PHI Learning, ISBN: 9788120338685
- Stoll, M., Baecke, S., Kenning, P. (2008) What they see is what they get? An fMRI-study on neural correlates of attractive packaging. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 7, 342-359.
- Vechiatto, G., Toppi, J., Astolfi, L., De VicoFallani, F., Cincotti, F., Mattia, D., Bez, F., Babiloni, F. (2011a). Spectral EEG frontal asymmetries correlate with the experienced pleasantness of TV commercial advertisements. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 49, 579-583.
- Vechiatto, G., Astolfi, L., De VicoFallani, F., Toppi, J., Aloise, F., Bez, F., Wei, D., Kong, W., Dai, J., Cincotti, F., Mattia, D., Babiloni, F. (2011b). On the Use of EEG or MEG Brain Imaging Tools in Neuromarketing Research. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, article ID 643489.
- Wang, Y.J. & Minor, M.S. (2008). Validity, Reliability and Applicability of Psychophysiolgical Techniques in Marketing Research. Psychology & Marketing, 25(2), 197-232.
- Zchwarvalose, R.F., Backer, C.I., Kanwisher, N. (2005). Separate face and body selectivity on the fusiform gyrus. Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 1105-11059,
- Zurawicki, L. (2010). Neuromarketing, Exploring the Brain of the Consumer. (42-53). Berlin Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag
- WWW1: Neuromarketing Technology Market Size, Demand, Trends and Growth by Business Opportunities, Latest Innovation, Technology Trends and Forecast, https://www.reuters.com/brandfeatures/venture-capital/article?id=34591
- WWW2: Neuroscience Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report By Technology (Whole Brain Imaging, Neuromicroscopy, Electrophysiology), By Component, And Segment Forecasts, 2012 - 2020, https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/neurosciencemarket
- WWW3: Neurostimulation Devices Market Overview. https://www.variantmarketresearch.com/report-categories/medical-devices/neurostimulationdevices-market
- WWW4:COMMERCIAL ALERT (2008) Commercial Alertasks University To Halt. Neuromarketingexperiments. Commercial Alert News Release. http://www.Commercialalert.Org/Pdfs/ Neuromarketingrel.pdf
