Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Social and Relationship Capital Scenario and Corporate Sustainability – A Study of Selected Companies from Indian Manufacturing Sector
Abstract :
Social and Relationship capital has gained strong foothold in the arena of business. Days are gone when corporates considered social obligations as discretionary. However, there were some companies which always cared for the society and did noteworthy work for the upliftment and betterment of the society. But the Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 acted as a game changer.
The mentioned section states that every company having net worth of rupees five hundred crore or more, or turnover of rupees one thousand crore or more or a net profit of rupees five crore or more during any financial year must spend every financial year, at least two percent of the average net profits of the company made during the three immediately preceding financial years, in pursuance of its Corporate Social Responsibility Policy.
Now companies from various sectors incur expenditure on various activities covered under social and relationship capital, i.e., corporate social responsibility (CSR) such as eradicating hunger, poverty and malnutrition, promoting health care including preventive health care and sanitation; promoting education, including special education and employment enhancing vocation skills especially among children, women, elderly and the differently abled and livelihood enhancement projects; Ensuring environmental sustainability, ecological balance, protection of flora and fauna, animal welfare, agroforestry, conservation of natural resources etc.
In this research paper, the scenario of social and relationship capital (CSR) will be focused for selected companies of Indian manufacturing sector, as it has been observed that emission of carbon / GHG (Green House Gases) emission tends to be higher in case of manufacturing sector-based organisations. The sample of companies that will be considered for the research study will be eclectic, i.e., companies from diverse industries covered under the manufacturing sector of India, i.e., cement, steel, crude oil and fertiliser . From each mentioned industry two companies will be selected randomly for undertaking analysis of social and relationship capital. Relevant statistical tools will be used to draw inferences pertaining to the social and relationship capital scenario of the companies selected from the above mentioned industries. Further, this research paper will also make an endeavour to reconnoitre the sustainability of the selected companies by gauging their performance on vital financial parameters.
Keywords :
Genesis of CSR; Social and Relationship Capital Scenario; Gauging Sustainability.Introduction
Social and relationship capital refers to co-operative ties between a company and different communities and stakeholders’ group that engage with each other for social welfare. For business organisations or companies, social relationship capital captures the institutions and relationships within and between communities, groups of stakeholders and other networks, and the ability to share information to increase individual and collective well-being.
The World Business Council on Sustainable Development (WBSCD) defines Social Capital as "the resources and relationships provided by people and society." This definition includes human capital (people’s skills, knowledge and wellbeing), social capital (societies’ shared values, norms and institutions) and relationship capital (connections and networks).
Social capital plays a crucial role in ensuring success of the business organisations. The following points explicate the significance of social capital-
i) Robust relationships: One of the most essential facets of any organisation is its relationships with stakeholders. Social capital emphasize on building an edifice of robust relationships with stakeholders of the organisation, especially the external stakeholders. A strong bonding with stakeholders assist immensely in achieving competitive advantage.
ii) Sharing of more information: Today we are living in knowledge economy wherein an organisation’s value is determined largely on the magnitude of awareness of its people. Since more the people associated with the organisation are conversant with latest updates and facts, more is the possibility of having innovative ideas, superior practices, risk mitigation, and optimum decisions.
iii) Sharing of more resources: Similar to shared information, social capital can contribute prodigiously in resource sharing too. This can prove to be advantageous for the business organisations in two ways-
a) Stakeholders may provide access to resources that may contribute to value addition which in turn assist in accomplishing organisational goals.
b) Organisation may be in better position to provide resources that will add value back to the society and other stakeholders.
iv) Trust: It has a very close linkage to the social capital. To build trust, a business organisation needs to meet the expectations of its stakeholders on continuous basis. In view of this, strong focus on social capital may go a long way in building trust among the stakeholders, thereby enhancing the goodwill of the organisation.
v) Efficiency: As social capital entails sharing of information and resources, thereby gaining trust, in view of this, if it is adhered to in true letter and spirit then it may assist the business organisation to get the work done faster and efficiently.
vi) Maintaining pace with social change: One of the noteworthy changes in the recent years pertains to increase in social network platforms. Social networks can put social capital on steroids, thereby assisting people to-
a) Connect directly with their existing network.
b) Create new relationships and groups on the basis of shared connections, interests, and experiences.
c) Seek for succour, information, recommendations, and resources.
d) Share information, introductions, reviews, and resources that might assist people in their networks or groups.
vii) Foster Reciprocity: Social capital fosters reciprocity. Brands that build robust relationships with their stakeholders might derive benefits from more positive mentions, shares, recommendations, and support on social media platforms. Those brands which fails to build a good relationship with its stakeholders may witness a debilitating impact on organisational growth.
viii) Strengthen Participation: Participation in groups is considered to be an essential element of social capital. But it’s interesting to note that societies with more social capital are likely to have higher magnitudes of participation and civic engagement. Further, stakeholder participation and engagement can prove to be beneficial in many aspects.
ix) Resilience: Social capital is considered as an element of social resilience. To put differently, it can assist communities, organisations, and individuals to surmount challenges and cataclysms. Better the scenario of social capital is, the stakeholders will be placed better to withstand various hiccups or disasters.
x) Success: Enhanced social capital can be a yardstick of success, as higher social capital implies higher stakeholder engagement.
Objectives of the study
- To comprehend the contribution of companies selected from the manufacturing sector of India towards corporate social responsibility (CSR), a vital component of social and relationship capital.
- To ascertain the sustainability of the companies selected for the research study as to whether they can sustain the CSR expenditures.
Research Methodology
- F-Test (One Factor Model): This statistical tool will assist in ascertaining whether there is a significant difference or not in the CSR expenditure of the manufacturing companies selected for the research study.
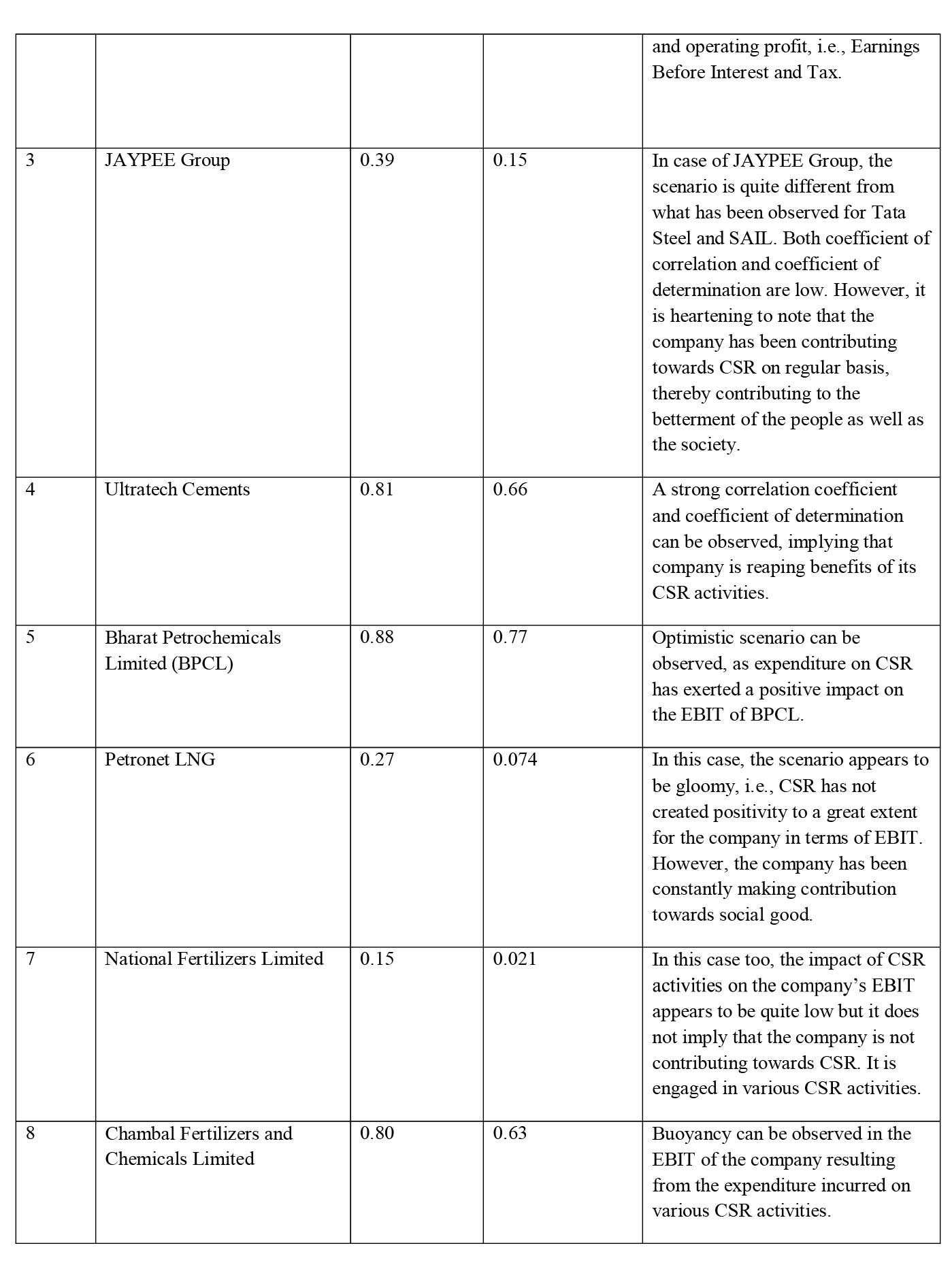
- Regression Analysis: This statistical tool will assist in determining the impact of CSR expenditure by the manufacturing companies selected for the research study on two crucial financial variables, i.e., Earnings Before Interest and Tax (EBIT) and Profit after Tax (PAT).
- Parabolic Trend Equation: This statistical tool will help in undertaking the prognosis of EBIT and PAT of the manufacturing companies considered for the research study. An increasing trend of EBIT and PAT will indicate financial sustainability of the selected manufacturing companies.
Limitations of the study
Ascertaining CSR Expenditure Pattern of Companies
In this section, the analysis of CSR expenditure of the companies considered for the research study from steel, cement, crude oil and fertilizers have been undertaken. To comprehend as to whether there exists no or significant difference in the CSR expenditure of the selected companies, F-Test (One Factor Model) have been applied. The details of the companies chosen for the analysis are as under:
i) Steel Sector- Tata Steel Limited (Private Sector) and Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) (Public Sector).
ii) Cement Sector- JAYPEE Cements Limited (Private Sector) and Ultra Tech Cement Limited (Private Sector).
iii) Fertilizers Sector- National Fertilizers Limited (Public Sector) and Chambal Fertilizers and Chemicals Limited (Private Sector)
iv) Crude Oil Sector- Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (Public Sector) and Petronet LNG Limited (Private Sector).
To conduct the analysis, the postulate formed and CSR expenditure of the companies (please refer Table 1) have been provided below-
Null Hypothesis (H0): There is no significant difference in the CSR expenditures of the steel, cement, crude oil and fertilizers companies considered for the research during the period 2018-2022.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is no significant difference in the CSR expenditures of the steel, cement, crude oil and fertilizers companies considered for the research during the period 2018-2022.
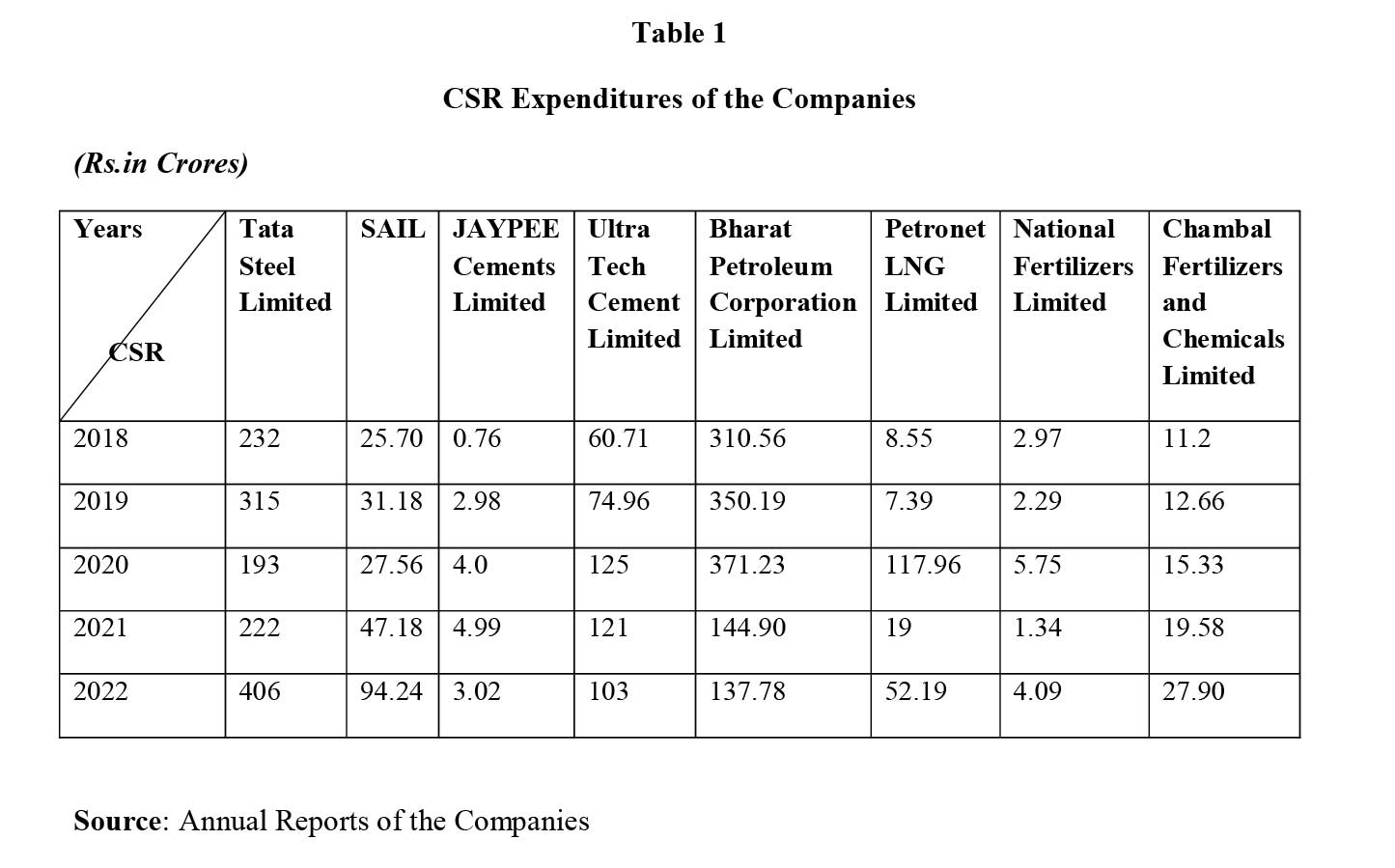
The companies have been selected on random basis and CSR dimension has been considered for the analysis since CSR covers vital activities like eradicating hunger, poverty and malnutrition, encouraging health care and sanitation, promoting education including special education and employment enhancing vocational skills especially among children, women, elderly and the differently abled and livelihood enhancement projects, promoting gender equality and empowering women etc. which focus on both social and environmental facets.
The analysis using F-Test (One Factor Model) is provided in table 2 below-
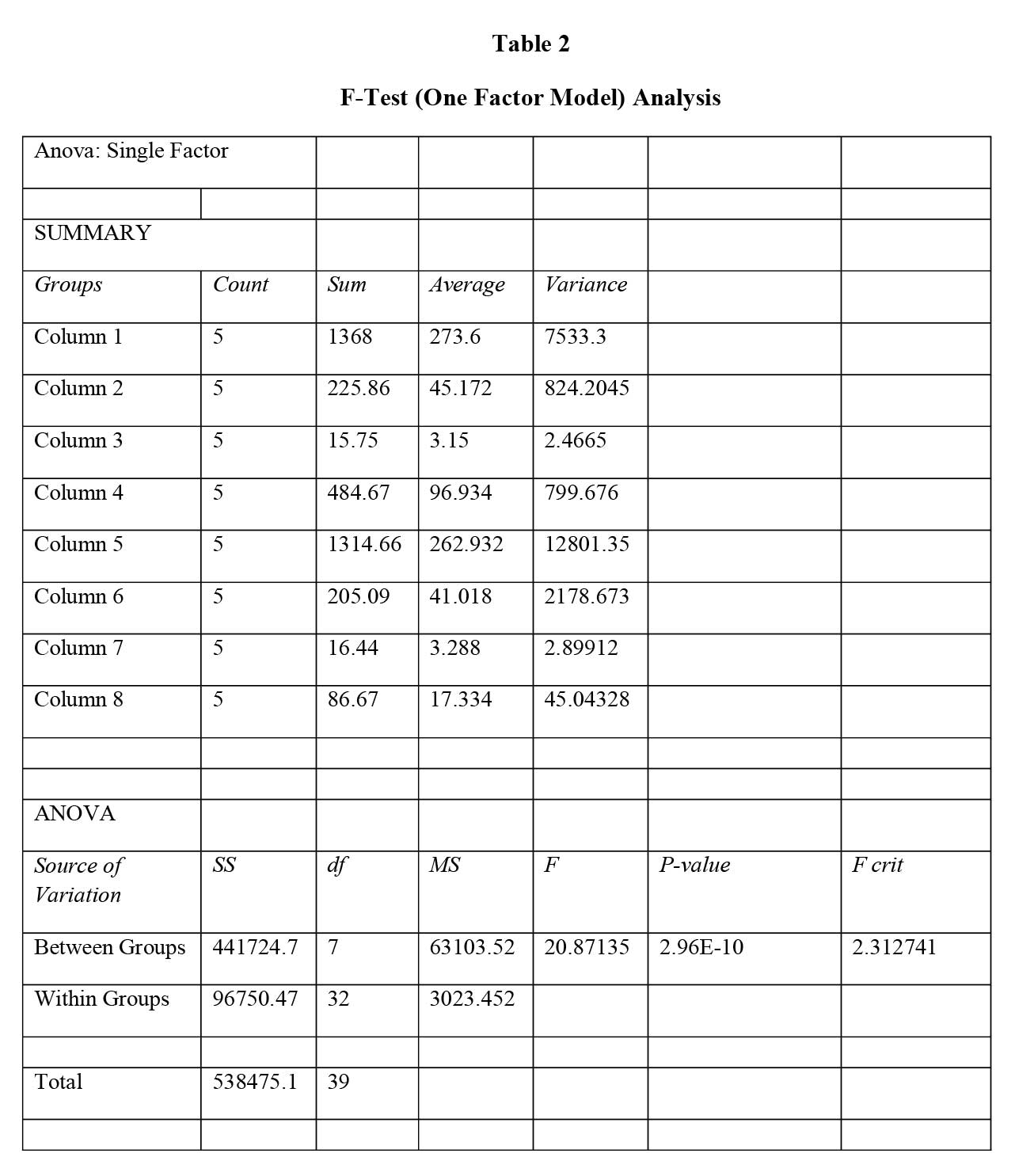
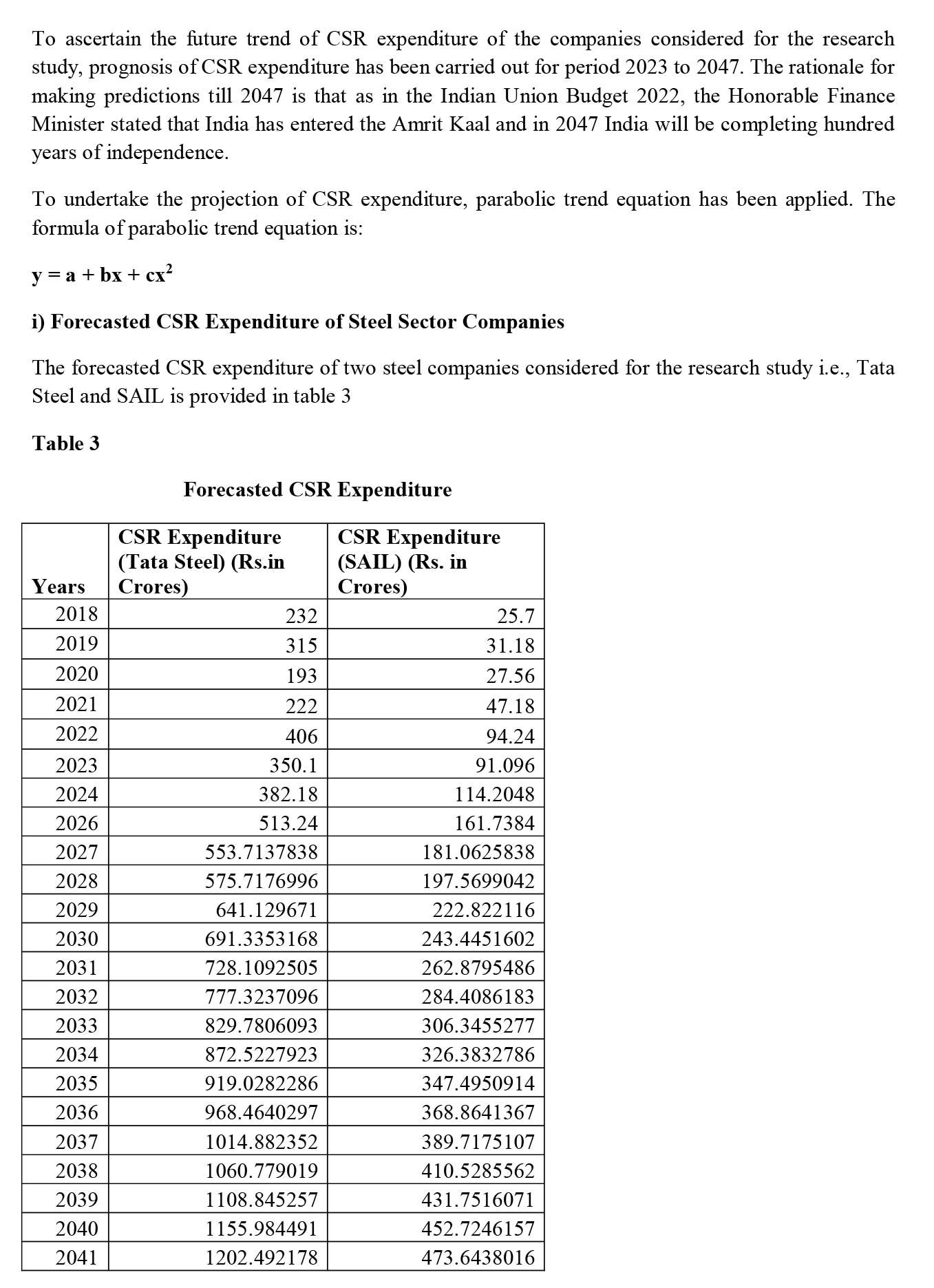
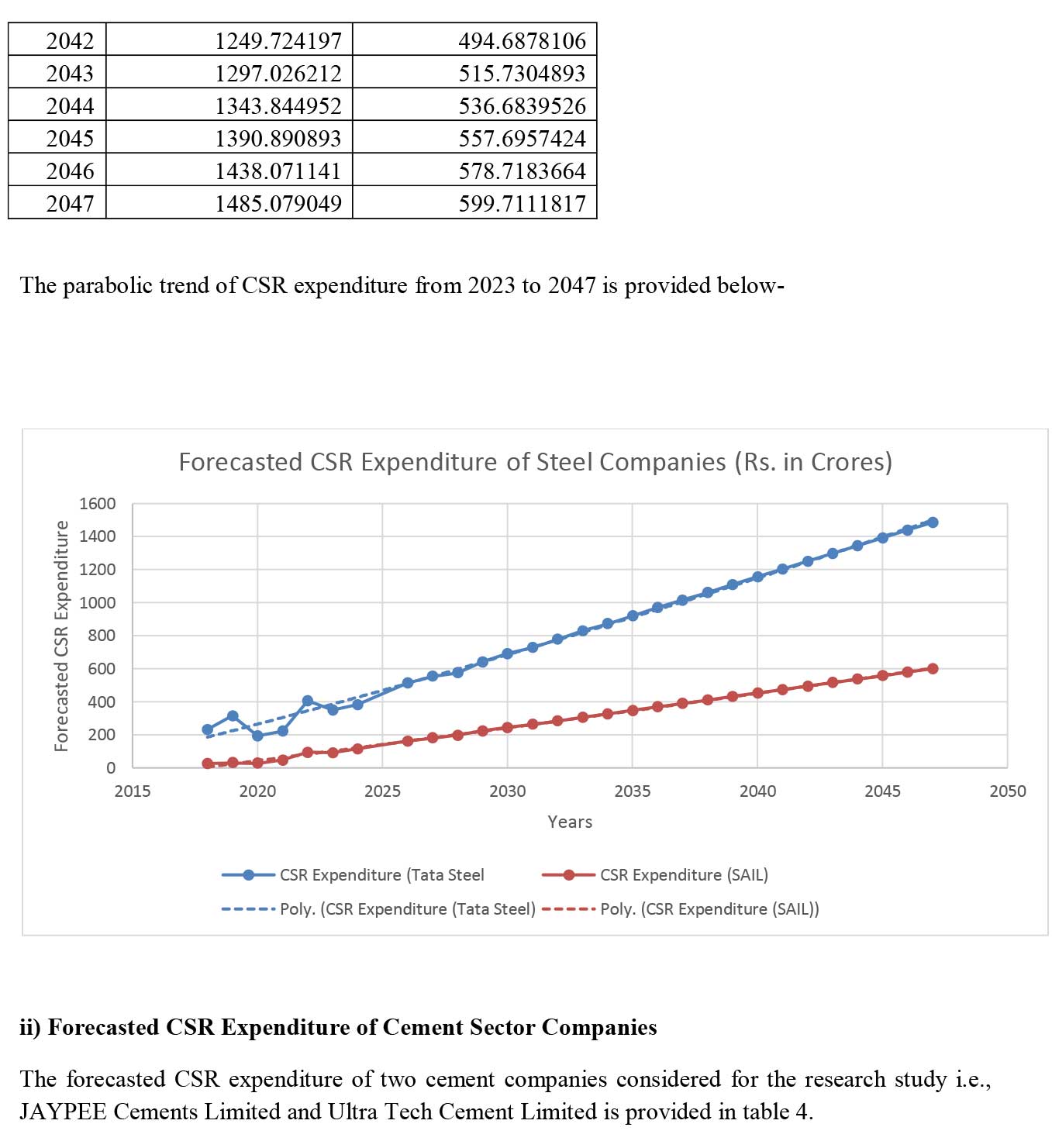
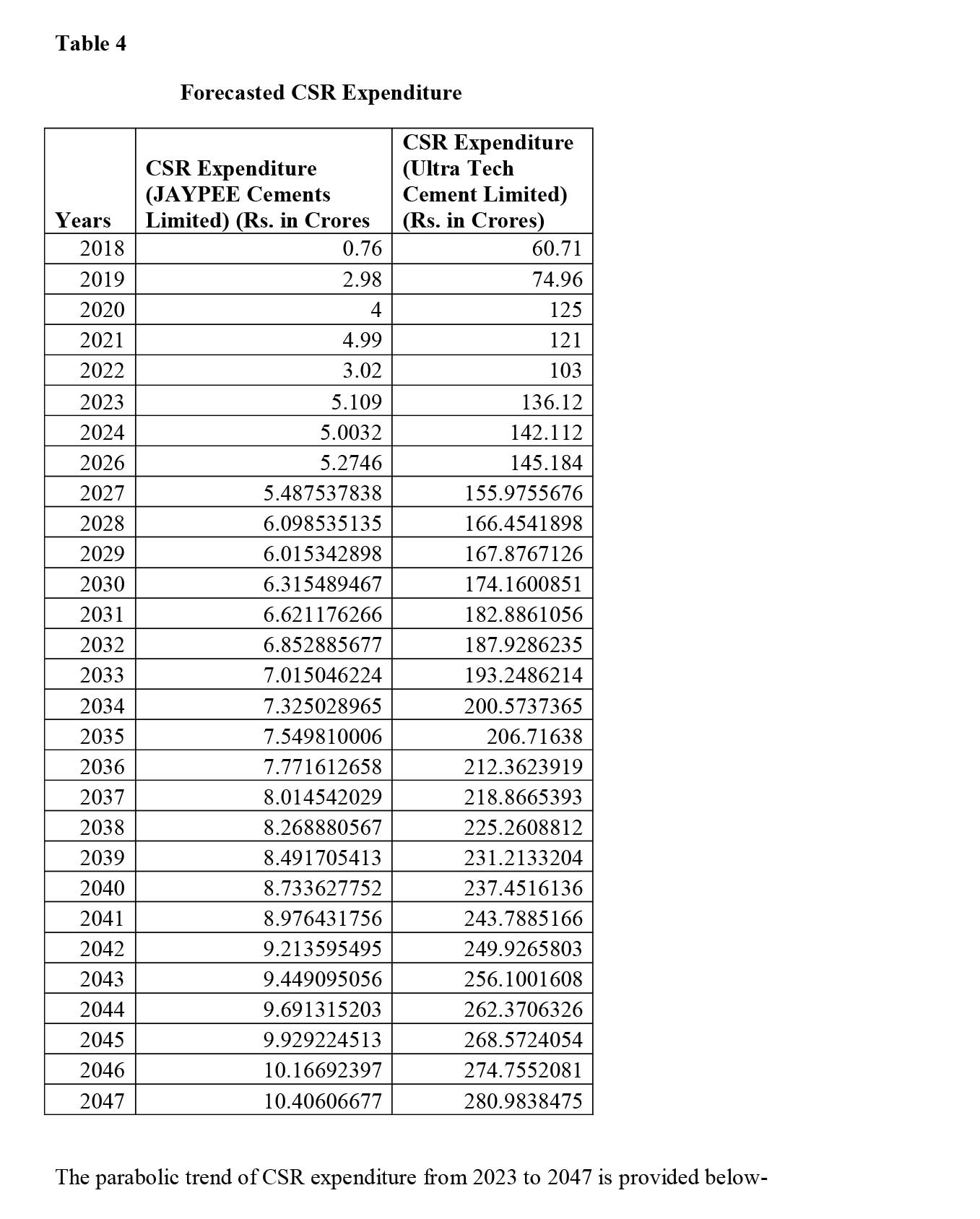
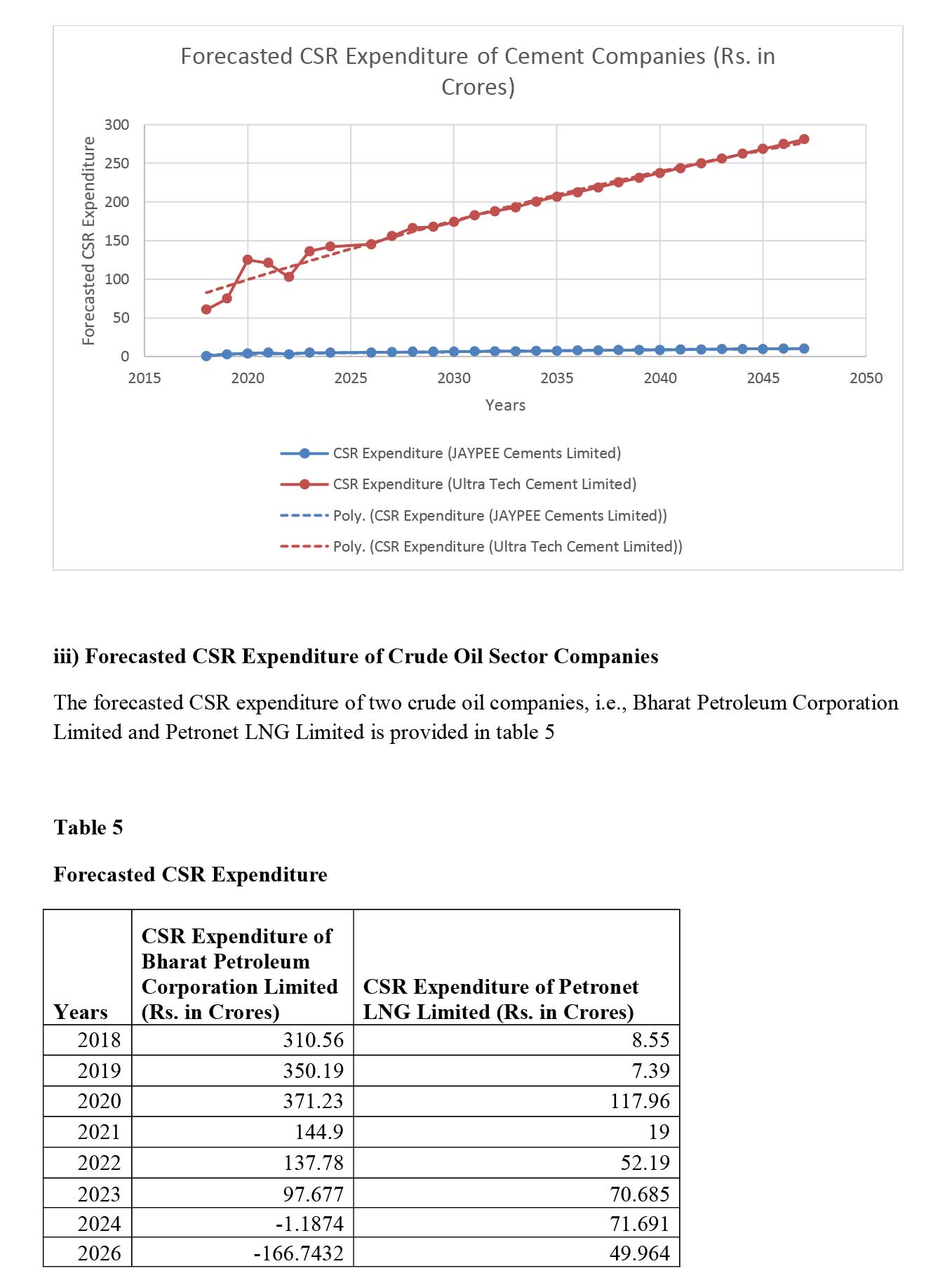
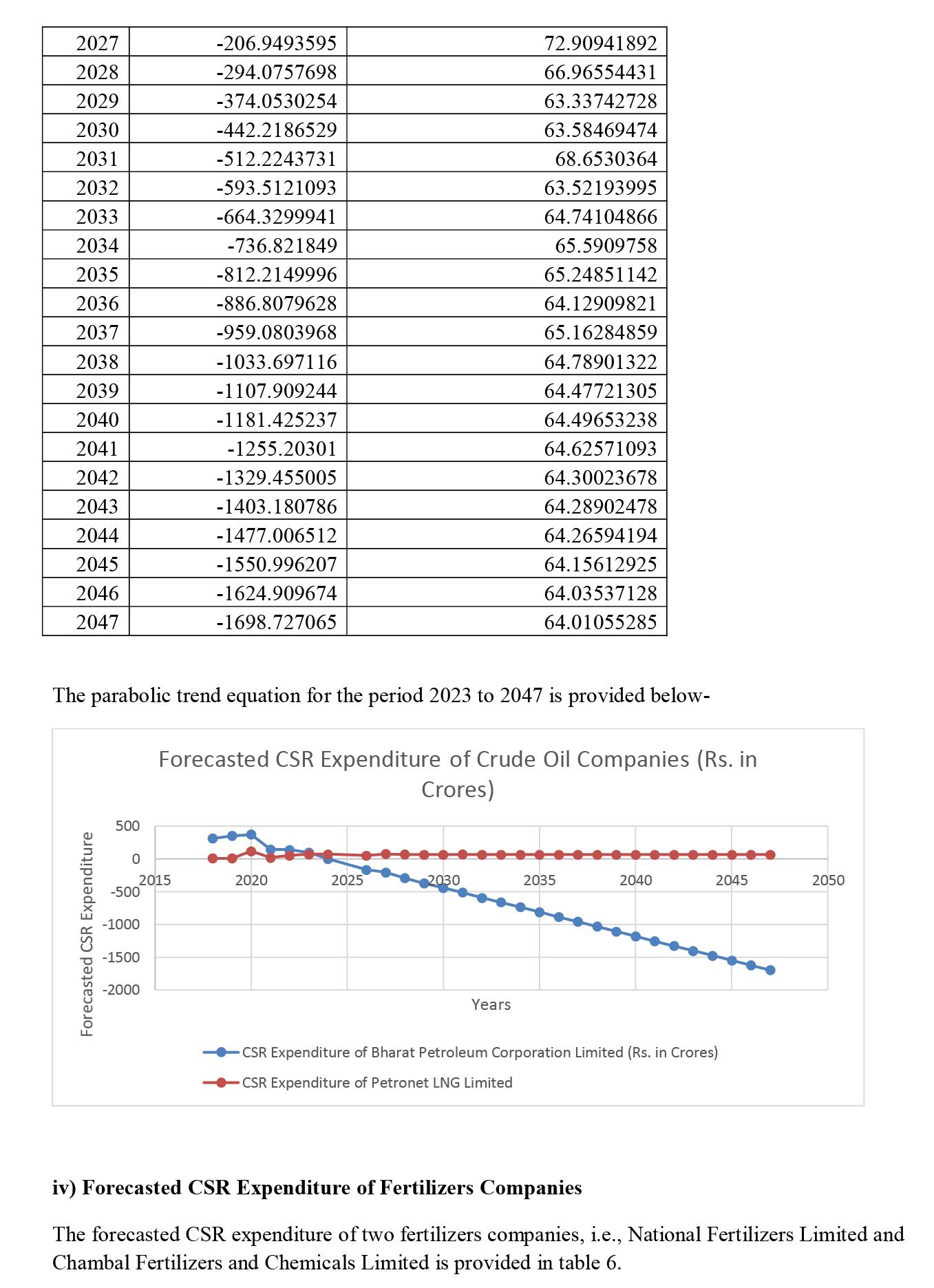
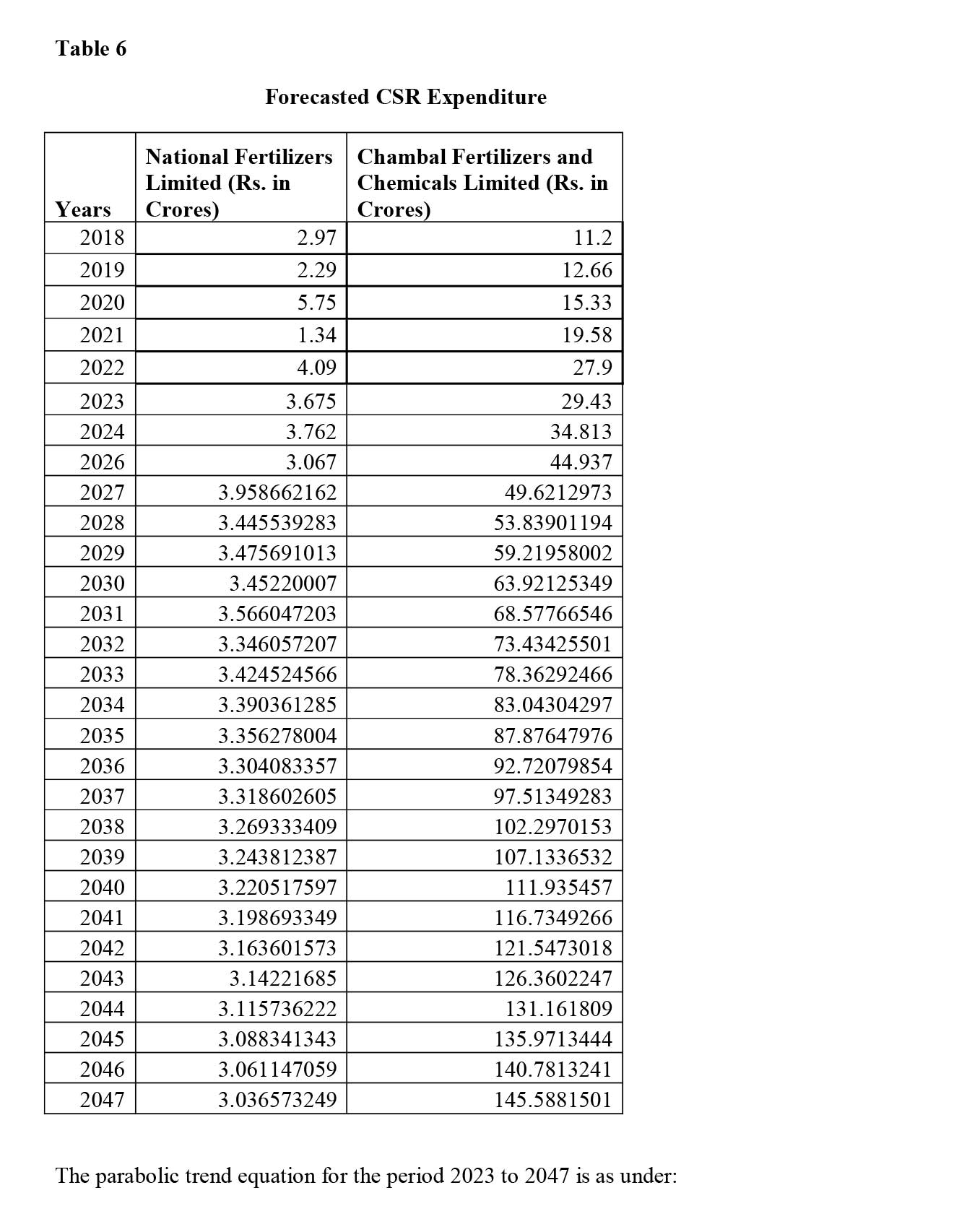
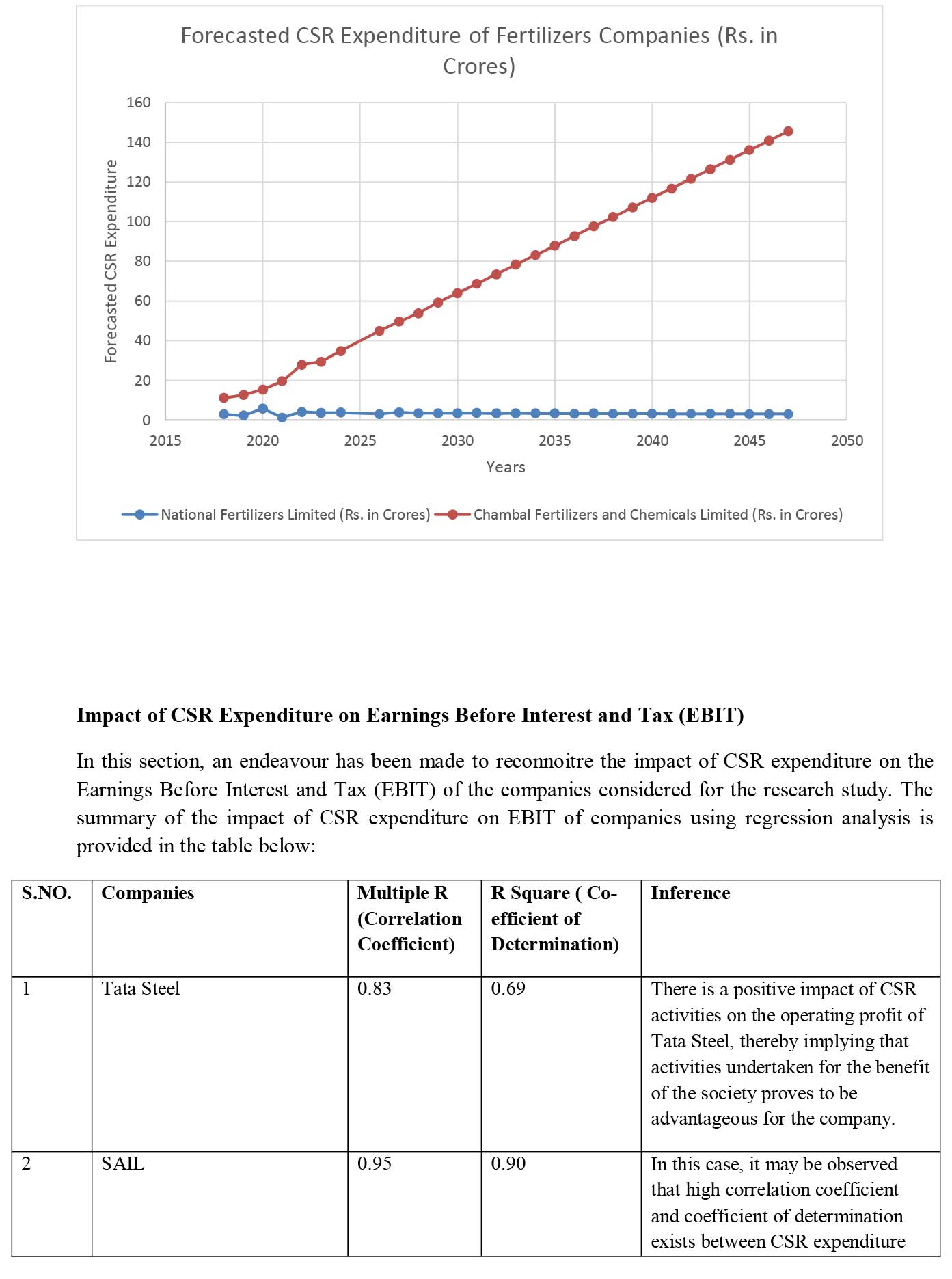
Conclusion
Social and Relationship capital has gained strong foothold across the globe. Today corporate houses has recognized the fact that they do not exist only for increasing revenues and earning profits. Rather along with earning profits, they also need to care for people and planet. As business organisations draw resources from the society to carry out its production process or operations, so there is an obligation on the owners or management of business enterprises to contribute to the society in various ways, especially by undertaking activities mentioned under Permitted CSR activities (Schedule-VII of Companies Act, 2013) like eradication of hunger, promotion of health care including preventive health care and sanitation, making available safe drinking water, promoting education, including special education and employment enhancing vocation skills particularly among children, women, elderly and the differently abled and livelihood enhancement projects, empowering women etc.
CSR is no more a choice for a company fulfilling certain regulatory requirements as per the Companies Act, 2013. It is to be noted that companies mandated by the Companies Act, 2013 to undertake CSR activities are required to constitute a CSR Committee whose roles and responsibilities mainly are- formulate and recommend to the Board, the Corporate Social Responsibility Policy and the activities to be undertaken by the company, recommend the amount of expenditure to be incurred on CSR activities and monitor the Corporate Social Responsibility Policy from time to time.
Thus, it may be opined that corporate social responsibility has become an integral element of corporate sector and it do exert an impact on the sustainability and growth of business to a great extent.
References
- "Human Capital, Social & Relationship Capital and Intellectual Capital", Accessed from https://steemit.com/business/@kiligirl/human-capital-social-and-relationship-capital-and-intellectual-capital-2-of-3-in-a-series-of-posts-on-the-six-capitals
- "Social Capital and Stakeholder Relationship Management", Accessed from https://simplystakeholders.com/social-capital/
- "Financial Statements of Tata Steel Limited", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
- "Financial Statements of SAIL", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
- "Financial Statements of JAYPEE Group", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
- "Financial Statements of Ultratech Cement Limited", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
- "Financial Statements of Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
- "Financial Statements of Petronet LNG Limited", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
- "Financial Statements of National Fertilizers Limited", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
- . "Financial Statements of Chambal Fertilisers and Chemicals Limited", Accessed from https://www.moneycontrol.com/stocks/company_info/print_main.php
