Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
Cause-Related Marketing and effectiveness on the Purchase Behavior: A study of University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand Post-Covid 19
Abstract :
The Consumer behavior has shifted drastically during pandemic. Consumers now a day are more mindful and concerned about environmental degradation. They are keen to embrace brands that stand for its eco-friendly business practices or contributions made towards different charities. Marketers infuse in various strategies for aligning with consumer behavior. There has been sudden upward acceleration towards eco-friendly products in the market. Marketing efforts are also integrating cause-related marketing campaigns in their brand awareness efforts. The recent trends post Covid-19 is also reflecting upward inclination towards cause-related marketing. Recent reports also align with the importance of cause-driven campaigns in modern marketing. The present study makes an effort to identify how cause related marketing programs influences the purchase behavior of students pursuing management courses (private and government as well) at both UG & PG level in Jharkhand. To achieve this objective, 220 students were surveyed online using Google form on their purchasing behaviour. The findings show that the cause-related marketing influences significantly the attitudes of the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand; thus, affecting their purchase behavior for a brand. The study also highlights the major factors affecting the purchase behavior of the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand post Covid-19.
Keywords :
cause-related marketing, Students, Consumer Behavior, Covid-191. Introduction
The coronavirus (COVID-19) global pandemic has forced the organization to adapt to more innovative ways to attract consumers. It has resulted in significant change in advertising, marketing, promotional and media spends, forcing businesses and brands to re-examine their thinking about current and future advertising and marketing campaigns to maintain a steady stream of income. Cause-Related Marketing (CRM) is a flexible and rising activity in the domain of marketing providing a golden opportunity to the organization and consumers as well to participate in a social cause (Varadarajan & Menon, 1988). The first CRM campaign officially named in this way was carried out in 1983 in the United States by American Express (AMEX). The purpose of this program in addition to increase the usage of the AMEX credit card was to collect money to be donated for the renovation of the Statue of Liberty. Cause-related marketing (CRM) majorly centers round promoting social cause messages for a brand. A large number of business houses have shown support to social/cause-related marketing programs.
The students are considered as one of the major market segments spending a significant amount of money. They are very much engaged with the society at large. They are desperate and keen to create the difference and want to see valid transformation in their lives and communities. Many students prefer to purchase from brands that support a cause. This makes them a huge target market for companies and brands. The students many a times willingly reward and support the companies affiliated to social causes and reject and punish the companies that doesn’t. The importance of ascertaining the distinct factors that affect the students’ purchase attitudes and pattern has increased immensely and has become a major focus of the consumer research. Although CRM is said to have a huge acceptance and seen as a strategy to deliver the crucial benefits, various recent researches have focused primarily on the extent to which it affects the students as consumers and also does it has any impact on their perceptions about brand and their buying behaviour.
Review of Literature
Marketing in today’s economy plays a key role and is crucial to organizational success (Kotler, 1994). The competition between enterprises has become more and more fierce with the continuous development of the market economy, and the understanding of customer citizenship has continued to increase, thus demanding higher requirements for enterprises to fulfill their social responsibilities (Lu et al., 2020). The more specific benefits to companies of being engaged in CRM is generating publicity, breaking advertising clutter and affecting the preference of the consumer for the particular brand (Gupta & Pirsch, 2004; Barone et. al., 2000; Brown & Dacin, 1997). CRM is considered to be one of the key strategies in order to achieve long-term engagement with target segments (Lafferty et al., 2016). Previous research has reflected positive effects of CRM on consumer behavior, such as purchase intent and brand loyalty (Patel et al., 2017; Randle et al., 2019). Consumers, with a cause or social related involvement believe that the association with such brands is relevant (Zaichkowsky, 1994) and in turn have positive linkage (Sherif et. al., 1965).
Research Objectives
1. To understand University students attitude pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand towards cause-related marketing programs.
2. To explore whether the shopping/purchase habits of the University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand are influenced by cause-related marketing.
3. To determine whether the involvement of University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand with cause-related marketing affects their brand perception, preference and attitude.
4. To indicate the issues and social causes that influences the purchase behaviour.
5. To find the reasons that discourages the University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand to respond positively against cause-related marketing.
Research Hypotheses
Previous researches and secondary literatures have helped in the formulation of the following alternate hypotheses:
Ha1: There is a significant influence of Cause-related marketing on the attitudes of University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand for a brand.
Ha2: Awareness about cause-related marketing programs will influence University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand purchase intentions.
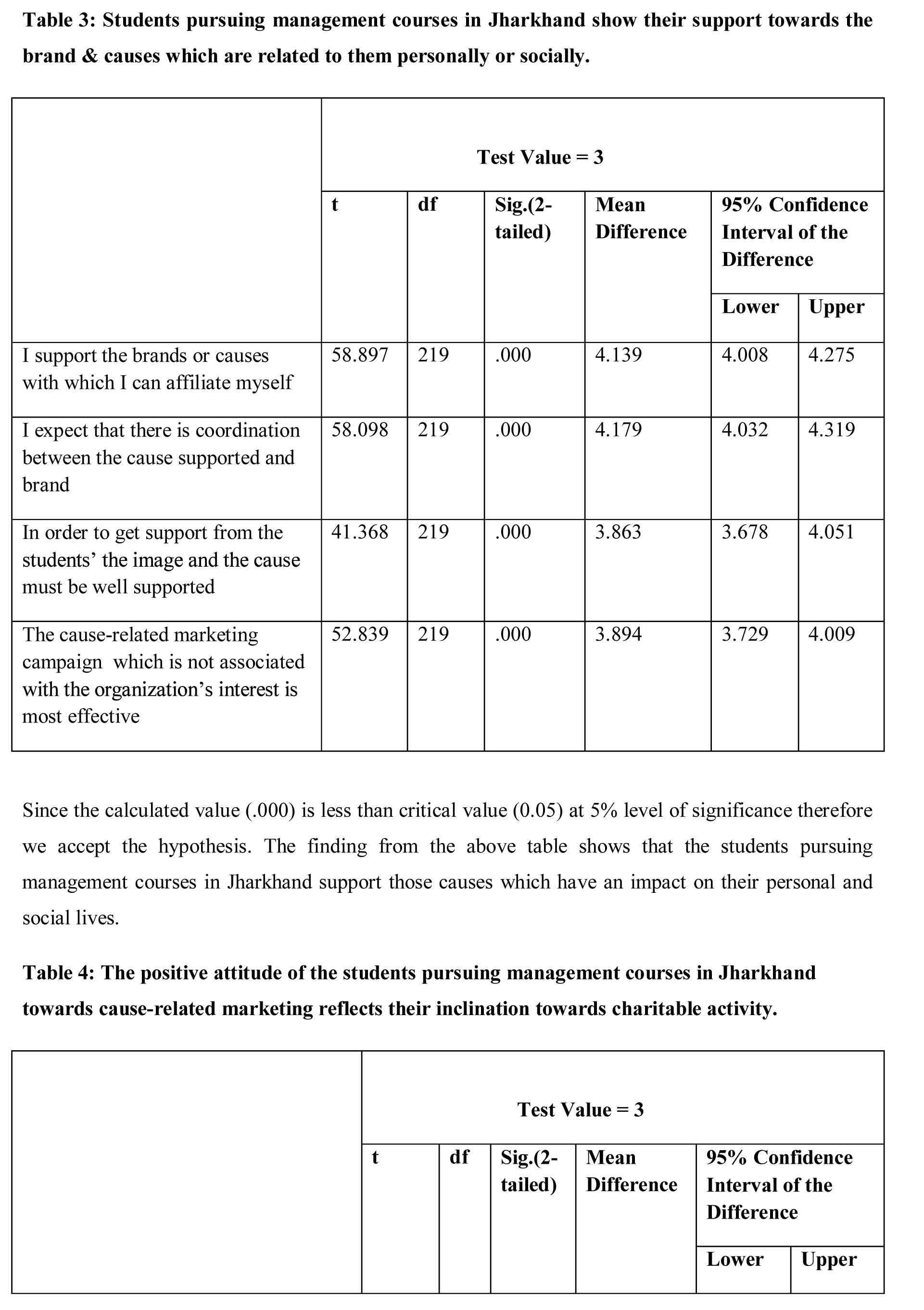
Ha3: University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand show their support towards the brand & causes which are related to them personally or socially.
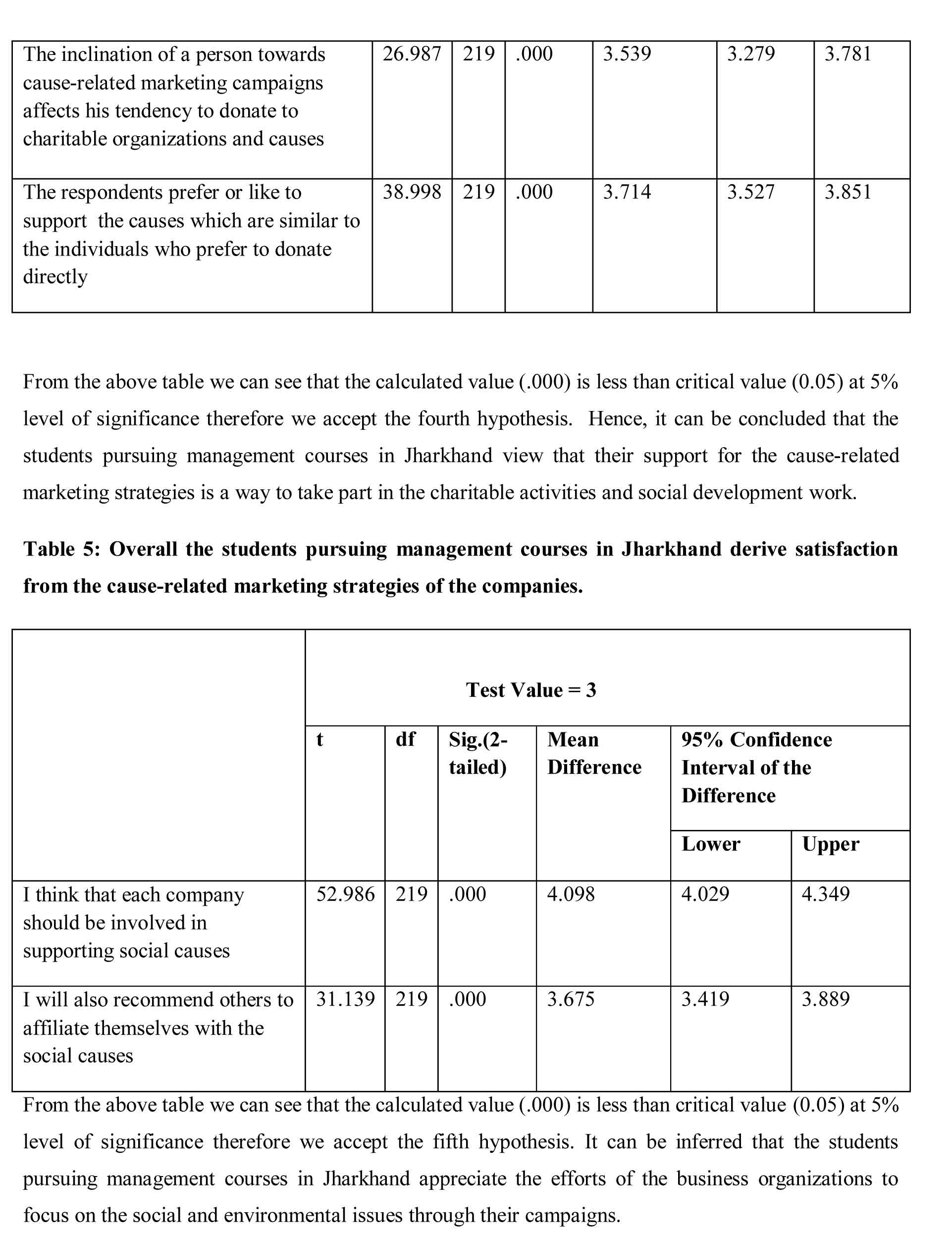
Ha4: The positive attitude of the University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand towards cause-related marketing reflects their inclination towards charitable activity.
Ha5: Overall the University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand derive satisfaction from the cause-related marketing strategies of the companies.
Ha6: University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand usually support the local and national causes rather than the international.
Ha7: There is a significant relationship between gender of University students pursuing Management courses in Jharkhand and their support for cause-related marketing activities.
Research Methodology
The data has been collected from 220 students pursuing management courses (private and government as well) at both UG & PG level in Jharkhand. The Cities considered for collecting the data for research work were Ranchi and Jamshedpur The data was collected online using Google form. The questionnaire contains items for gathering information regarding their preference for brand, their purchasing attitude and their perception. Likert scale has been used to gather the data in which numeral 1 is for ‘strongly disagree’ and numeral 5 is for ‘strongly agree’.
Since the value of Cronbach's alpha was 0.732 hence the scale was considered to be reliable. The sample has been determined through Non-Probabilistic Sampling technique. For the analysis of data both the descriptive and inferential statistics have been used.
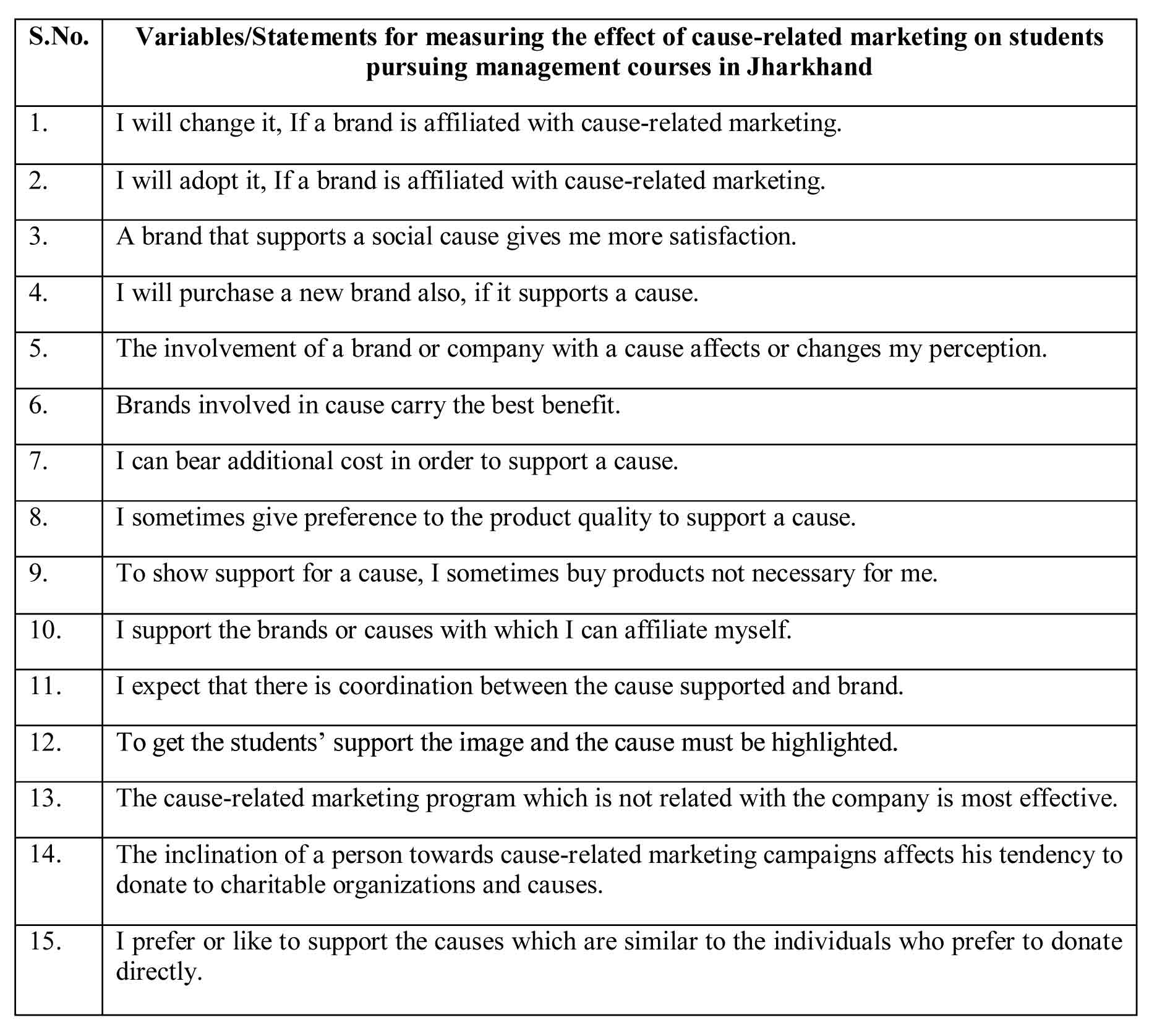

Data Analysis and Findings
One sample t test has been used for testing hypotheses 1to 6, while correlation is used to test hypotheses 7.
Table 1: Effect of Cause-related marketing on students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand regarding attitude towards the promoted brand.
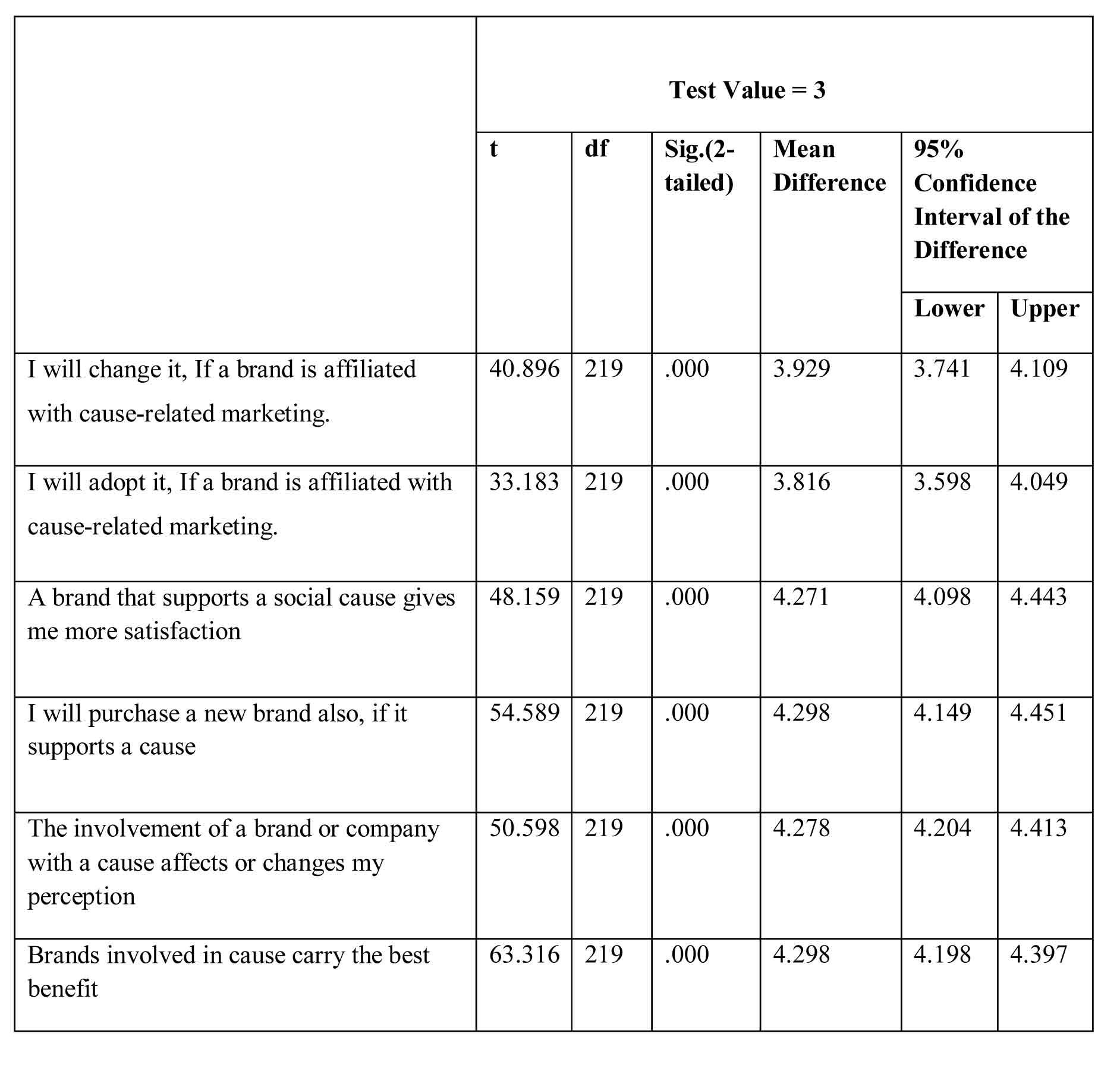
From the above table it can be analyzed that the cause-related marketing strategies of the business organizations affect and can also change the attitude of the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand towards a particular brand. Since the calculated value (.000) is less than critical value (0.05) therefore we accept the hypothesis and come to a conclusion that cause-related marketing can bring a positive change in the attitude of the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand.
Table 2: Awareness about cause-related marketing programs and its influence on students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand towards their purchase intentions.
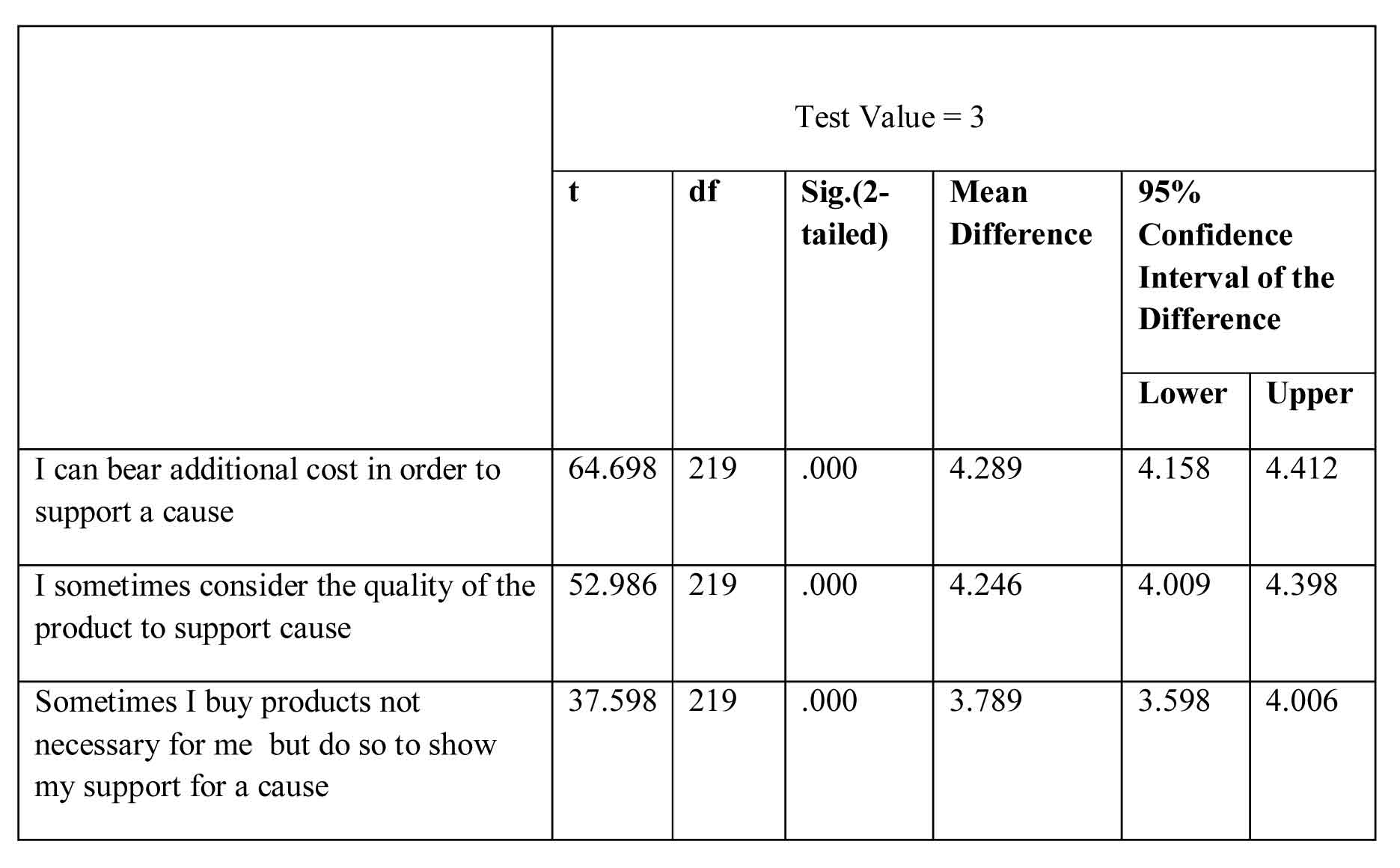
Since the calculated value (.000) is less than critical value (0.05) therefore we accept the second hypothesis. It can be concluded from the above table that if a company designs and communicate its cause-related marketing strategies effectively then it can also affect the purchase intentions of students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand.
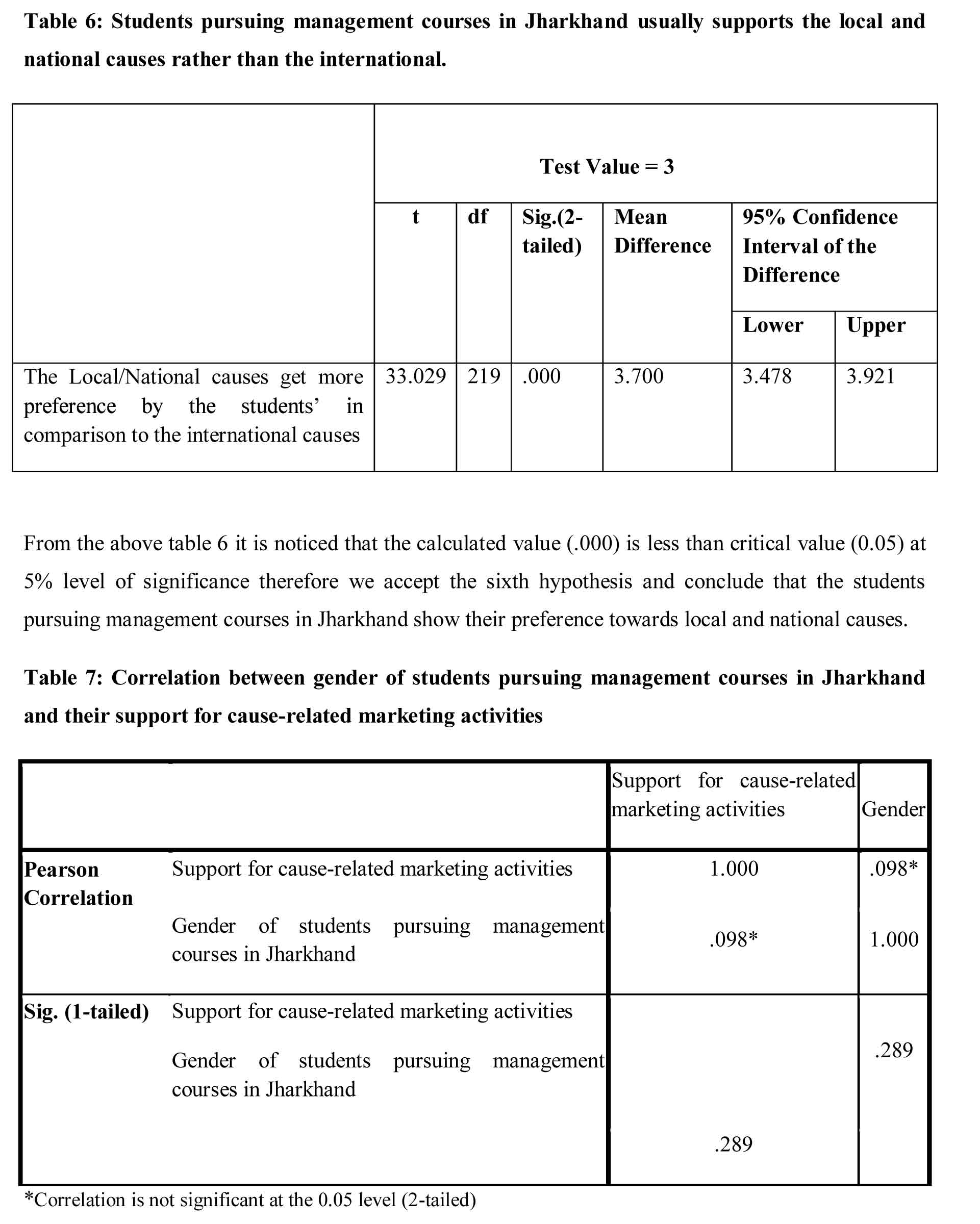
The above table 7 shows that 0.298 (calculated value) is higher than 0.05 (critical value) though it shows a positive correlation (r=0.098). Therefore we reject the hypothesis and conclude that the support towards a cause does not differ whether the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand is a male or female.
Conclusion of the study
The study shows the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand are aware and support the companies’ cause related marketing activities. It acts as a stimulator in increasing the awareness of the CRM activities. It was found that most of the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand were aware of the term corporate social responsibility. Some of the respondents feel that the organizations are not serious about the social causes and these CRM activities are merely few attempts to increase their popularity. However, it is expected that as the awareness of student’s increases, their support for the social and environmental issues will also grow. The cause related marketing campaigns will also simultaneously affect the preference of the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand towards a brand or towards the company that supports social causes.
The present study reflects that if the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand are having knowledge of the cause related marketing campaigns by a company, it affects their mindset and they eagerly support and purchase from such companies and brands. A majority of students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand agree that the companies should associate themselves with social issues but they should not use these social causes/issues to make more profit. These campaigns affect the awareness, perception and views of the students pursuing management courses in Jharkhand and also inspires them. So the companies should initiate more such activities which can increase the awareness level of the customers. The companies should try to give priority to the important and current issues while choosing social causes.
References
Barone et al., 2000 M.J. Barone, A.T. Norman, A.D. Miyazaki The influence of cause-related marketing on customer choice: Does one good turn deserve another? Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 28 (2) (2000), pp. 248-262
Brown and Dacin, 1997 T.J. Brown, P.A. Dacin The company and the product: Corporate associations and consumer product responses Journal of Marketing, 61 (1) (1997), pp. 68-84
Gupta S, Pirsch J (2006). The company-cause-customer fit decision in cause-related marketing. J. Consumers. Mark, 23(6): 314–326.
Kotler, P. (1994). Marketing management: Analysis, planning, implementation and control (8th ed). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Lafferty, B. A., Lueth, A. K., & McCafferty, R. (2016). An evolutionary process model of cause-related marketing and systematic review of the empirical literature. Psychology & Marketing, 33(11), 951– 970. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.20930
Lu, J., Ren, L., Zhang, Ch, Qiao, J., Kováèová, M., and Streimikis, J. (2020). Assessment of corporate social responsibility and its impacts on corporate reputation of companies in selected Balkan countries former Yugoslavia states. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. 26, 504–524. doi: 10.3846/tede.2020.12069
Patel, J. D., Gadhavi, D. D., & Shukla, Y. S. (2017). Consumers' responses to cause related marketing: Moderating influence of cause involvement and skepticism on attitude and purchase intention. International Review on Public and Nonprofit Marketing, 14(1), 1– 18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12208-016-0151-1
Randle, M., Kemperman, A., & Dolnicar, S. (2019). Making cause-related corporate social responsibility (CSR) count in holiday accommodation choice. Tourism Management, 75, 66– 77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2019.05.002
Sherif, C. W., Sherif, M., & Nebergall, R. E. (1965). Attitudes and attitude change: The social judgment-involvement approach. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders
Varadarajan, P.R., & Menon, A. (1988). Cause-related marketing: A co-alignment of marketing strategy and corporate philanthropy. Journal of Marketing, 52(3), 58–74.
Zaichkowsky J. L. (1994). The personal involvement inventory: Reduction, revision, and application to advertising. Journal of Advertising, 23(4), 59–70.
