Subscribe now to get notified about IU Jharkhand journal updates!
The Impact of Green Human Resource Management
Abstract :
HRM is a crucial part of management which oversees the most valued assets of the Green HRM concerns the awareness of an organization towards environmental issues but it also manages the social and economic well-being of both the company and its employees. It has the goal of developing a green workforce that comprehends values and practices green initiatives actively. Hence, a key dimension is the actual engagement and commitment of employees. The focus on spreading the knowledge of how to cope with the issues of sustainability, what actions are required in order to carry out the green programs and how the environment can benefit from them. Various practices related to recruitment, performance and appraisal management, personnel development and reward systems are deemed powerful contributors when aligning employees with the environmental strategies of companies.
Keywords :
HRM, appraisal management, personnel development, reward systems, employees , environmental strategies1. Introduction
The following chapter includes a description of the project context in which the study was conducted. The fundamental objective sanded limitations of the thesis area is presented in the chapter together with the research methodology employed.
1.1 Project Context
Much recent interest has been paid to the environmental issue of climate change which is also activities such as burning of fossil fuels, industrial production activities, etc. This necessitates
the need for immediate action from the producers of green house gasses in order to reduce their carbon footprints.
The report emphasized the key role Human Resource Management (HRM) has in aiding companies in their pursuit of sustainable competitive advantage. According to the report
Compromising the ability of future generations to of change in which the exploitation of resources, the direction of investments, the orientation of technological development; and institutional change area ill harmony and enhance both current and future potential to meet human needs and aspirations"
It is to be expected that not only governments but also organizations are taking steps in terms of improving their environmental performance and reducing their ecological footprints. In addition, businesses are encouraged to find the balance between the concern for sustainable development and social responsibility on the one hand, and their profitability initiatives on the other. Companies can also report their environmental performance data with the help of generally accepted standard methods such as the ISO 14000 series of certifications, the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Index, etc. The successful implementation of such sustainable corporate strategies heavily depends on all departments of the company, with the Human Resources (HR) department being the most influential when it comes to introducing "green" polices and changes.
HRM is a crucial part of management which oversees the most valued assets of the Green HRM concerns the awareness of an organization towards environmental issues but it also manages the social and economic well-being of both the company and its employees. It has the goal of developing a green workforce that comprehends values and practices green initiatives actively. Hence, a key dimension is the actual engagement and commitment of employees. The focus on spreading the knowledge of how to cope with the issues of sustainability, what actions are required in order to carry out the green programs and how the environment can benefit from them. Various practices related to recruitment, performance and appraisal management, personnel development and reward systems are deemed powerful contributors when aligning employees with the environmental strategies of companies.
Recruitment, performance and appraisal management, personnel development and reward systems are deemed powerful contributors when aligning employees with the environmental strategies of the companies.
Organizations are likely to meet certain risks when engaging in sustainability, some of which include lack of support from or capacity or knowledge. Another difficulty can be the uncertainty of whether the expected results can, in fact, be realized in which case, companies are advised to deliberately evaluate the risks of investing in such a strategy. Organizations are also encouraged to clearly communicate the purpose of undertaking green policies to their staff so that the voluntary participation becomes apparent and counter productive effects eliminated.
1.2 Objectives and Scope
This section introduces the aim to soften the thesis that the authors attempt to accomplish as well as any delimitations that are regarded as necessary.
The primary motive for writing the master thesis is to investigate how Green HRM can bring sustainable competitive advantage to organizations. However, such an endeavor would require really broad research that cannot be completed over the period of a few months and really in-depth knowledge that the authors are currently not in possession of as a result, certain delimitations are applied and the thesis focus is narrowed down solely to Danish companies in the Building field. Even so, introduction of relevant international and EU data is also included, so that a better picture of the research can be achieved.
To perform this study, the use of a questionnaire is deemed the most appropriate information collection method which can provide data essential for concluding on the current state of GHRM in Denmark.
Factors impacting on the successful implementation of Green HRM strategies are to be analysed together with their importance to organizations. On the one hand, the role of employees as the potential driving force of executing green practices or completely disregarding them is discussed. On the other hand, the key function of HR Managers are highlighted as the leaders whocan either promote and secure environmental understanding and opportunities or strongly object to bringing in sustainable policies. Afterwards, the obtained knowledge about the Danish approach towards GHRM is to be applied to the determination of whether Green HR Policies can promote sustainable competitive advantage in organizations in the building sector or not.
1.3 Methodology
The Descriptive and Elaborative Research Methodology has been adopted to find out the good ways and means of "Green HRM".
In order to ensure the correct execution of the master thesis, the need for a suitable methodology emerged. Therefore, the aim of this sub-chapter is to provide the basis for the over all methodology used in the thesis. The following sub-sections present the research design, research strategies and the data collection techniques that are implemented. The selection of a research framework which aids the design and structure of the research strategy.
1.3.1 Research Design
A research design is necessary for the formulation of the research focus. Research design is defined as "something people undertake in order to find things in a systematic way, thereby increasing their knowledge. (...) 'Systematic' suggests that research is based on logical relationship and not just beliefs.(...) 'To find out things' suggests there is a multiplicity of possible purposes for your research.
These may include describing, explaining, understanding, criticising and analysing. Therefore, by establishing the research design the authors of the dissertation are able to state, analyse and approach the research focus.
Research Philosophy
For the execution of the master thesis, the specific knowledge regarding sustainable competitive advantage achieved through Green Human Resource Management in Danish building organizations is required. Therefore, the need for a research philosophy emerged. The research philosophy used in the master thesis is the positive approach. The positive philosophy is based on quantitative observations which lead to statistical analysis that are used for testing the hypothesis (Saunders, et al., 2009).
The focus of the authors of the thesis is to test the hypothesis "Gaining sustainable competetive advantage through Green HRM" through a Quetionnaire aimed at Danish Construction Companies.
Research Approach
The authors of the dissertation need to illustrate the purpose of the research so that the research focus can be established. The thesis begins with theory regarding "Green HRM" and sustainable competitive advantage. Then, it proceeds to a hypothesis which states that Green HRM can bring sustainable competitive advantage to organisations. Afterwards, by conducting a Questionnaire provided to Danish Companies in the building sector as well as conducting multiple analyses, the authors aim to test the theory and either support or refute the hypothesis. The above mentioned reasons guided the decision of selecting the deduction research approach as it is considered the most suitable one. The deduction approach or theory of testin stems from research in the natural sciences "where laws present the basis of explanation, allow the anticipation of phenomena , predict their occurrence and therefore, permit them to be controlled." It involves the development of a theory that is subjected to a rigorous test"
Methodological Choice
For the selection of a suitable data collection method, it is important to define what data collection methods are to be utilized. In order to refute or support the chosen hypothesis for the master thesis, the theory needs to be tested. For that reason, the use of a questionnaire is very appropriate as it provides results that can be analyzed using statistical tools. As a result, the selected methodological choice is quantitative method as it asks questions such as "How many", "How long", "The degree to which". The quantitative methodological choice focuses on quantities and creates results from a sample of the population of interest (Saunders, et al., 2009). In the case of this master thesis, the interest is placed on organizations in the Danish building industry.
Research Strategies
The purpose of the dissertation is to examine to what extent Green HRM is implemented in Danish building companies and to measure how competitive they are on the market. Therefore, the master thesis is carried out using a survey design. According to Creswell
2014," A survey design provides a quantitative or numeric description of trends, attitudes, or opinions of a population by studying a sample of that population. From sample results, the researcher generalise or draws inferences to the population". The survey strategy is associated with the deductive approach and serves to answer questions such as "What", "Who" and "How many".
The authors select this particular strategy because it allows the collection of a large amount of data from companies in the Danish building industry. The survey for this study is conducted through a Questionnaire and the gathered data are later quantitatively analysed using statistical tools.
Time Horizons
The research of this master thesis is conducted in a cross-sectional research study. The collected data provide information from a single point in time (Saunders,et al., 2009). Therefore, through the cross-sectional survey the authors are able to measure the data provided by Danish companies in the building industry as well as their incidents over a specific time.
1.1.1 Data collection Method Techniques and Procedures
The research for this thesis is conducted using primary and secondary data collection. "The primary data are those which are collected afresh and for the first time and thus happen to be original in character. The secondary data, on the other hand, are those which have been collected by someone else and which have been already been passed through the statistical process" Kothari, 2004).
1.1.1.1 Collection of Primary Data- Survey
The primary data for this study are collected from employees working in the Danish building sector. The method used for the collection of primary data is a self-administered online survey, which guarantees the anonymity of the respondents. The authors of the master thesis distribute the link to the online survey to the target population across the country. The aim of the survey is to examine to what degree employees in the Danish building sector are familiar with the concepts of "Green HRM" and its practices as well as to revies whether sustainable competitive advantage can be achieved through an improved environmental performance.
The respondents are given a series of options and are asked how much they agree or disagree with the statements by using a sliding scale : "Strongly Disagree", "Disagree", "Nither Disagree nor Agree", "Strongly Agree". Fusrthermore, the respondents are asked to complete the survey within 1 to 2 weeks and after that time are reminder e-mail is sent to the minor minder to minimize the non-response rate (MacDonald & Headlam, 2009).
The authors of the dissertation choose to conduct an online Questionnaire because of its easy design and administration. Among other benefits, electronic surveys are inexpensive and are delivered fast to the target population. On the other hand, a challenge for the electronic survey is that respondents must have access to a computer connected to the internet and willingness to participate in the Questionnaire Survey.
Target Population
According to Cooper & Schindler (2003), target population includes all the elements from which the sample originates. The target population for this study is comprised of employees having different job positions in the Danish building sector. The Questionnaire was sent to 187 employees of which 13 (22%) completed the survey and 18 (30%) partially completed it. Therefore, the target population for the study was 187 employees in the Danish building sector. They represented a variety of positions such as HR Managers, Health and Safety Managers (EHS), Executive Managers, Administrative Managers, Sales Managers, Architects, Engineers and others.
Response Rate
Response rate is an important parameter for the evaluation of the data collection in any research study. The response rate is calculated by dividing the number of respondents by the total number of people to whom the Questionnaire was distributed. The denominator includes every person in the target population (Fowler,2012). The response rate of this study is :
Therefore, the response rate equals 16.57 %. As already mentioned, 13 people completed the survey and 18 partially completed it leading to a total number of 31 people who participated in the questionnaire. According to Manfreda, et al. (2008), the web-based surveys can result in low response rate compared to the survey models. The response rate for a web-based survey depends on the target population. According to Erwin & Wheelright (2002), achieving a high response rate from the target population is significant for the validity of the data and to be able to develop outcomes of the study. For this study, the survey was distributed to 187 employees of the Danish building sector, 16.57% of which responded to the survey. This relatively low rate can be explained as unwillingness of the employees to participate in the questionnaire, language barriers since the survey is written in English, lack of availability.
Probability Sample
According to Sekaran (2013), "When elements in the population have a known chance of being chosen as subjects in the sample, were sortd to a probability sampling design". The probability sampling used in this master thesis is restricted or complex probability samplingbecause it has less potential for bias. Additionally, more information can be obtained for a given sample size (Sekaran, 2013).
Sampling Technique
For the purpose of the dissertation, the stratified random sampling is used for the identification of a representative sample. Through this basic generalizations are deduced. In the stratified random sampling method each member of the target group has an equal and independent possibility to be included in the sample. It is a technique where sub-groups within the population can be identified and selected to form a sample. According to Shiu, et al. (2009), the stratified random sampling is "a probability sampling technique in which the defined target population is divided into groups". Stratification ensures homogeneity in each stratum to ensure fair representation of the population in the sample. Stratification is an effective research sampling method which obtains more information from a given sample size. (Sekaran, 2013)
Data Collection Instruments
The data collection for this study is carried out using a Survey Questionnaire. The survey is prepared by the authors of the dissertation using the online survey platform called Survey Xacto offered by AAU. It is constructed with relevant questions for the topics of Green HRM and sustainable competitive advantage.
The responses are measured by a ranking based on the sliding scale to determine to what degree the respondents agree or disagree with the statements of the Questionnaire.
Pilot Testing
The research tool used for the survey is pre-tested before the final distribution. Respondents for the pre-test have a basic knowledge and understanding of HR. For the pre-test process they are asked to evaluate the Questions in terms of their clarity, comprehension, relevance and meaning as well as the completion time. According to Mugenda & Mugenda (2003), the pre-testing permits the researchers to detect errors in the survey or in the research instrument before the actual collection of data begins. Additionally, 1% of the population is considered acceptable for pilotstudy(Mugenda & Mugenda, 2003).
Reliability Tests
According to Shiu, et al. (2009), it is important to identify whether the test instruments are consistent and whether the same results can be found if the test is repeated. Based on Hair, et al.(2007), a test is reliable if its scale or question consistently measures the concept. Bryman & Bell (2007) and Hair, et al. (2007) suggest the use of the Cronbach alpha test for the determination of the internal reliability. It is considered as a valuable test for multi-item scales at the internal level of measurements (Blumberg, et al., 2005). In this study the Cronbach alpha test is used to determine the internal consistency of the sample. Lastly, the results of Cronbach alpha range between 0 to1 and a value bigger or equal to 0.7 is considered as a reliability indicator (Blumberg,etal., 2005).(See 4 Chapter Findings and Interpretation)
Data Processing and Data Analysis
The gathered data for this study are initially checked for their completeness and comprehensibility. The data are then analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences Tool (SPSS) and both a descriptive and inferential analyses are performed. The descriptive analysis of the data is used to determine to what degree the "Green HRM" practices are implemented in the Danish building industry. Whereas, the inferential analysisis carriedout through Pearson Correlations where the authors of the dissertation test the correlations within each and among all the "Green HRM" practices. (See 5 Chapter Detailed Analysis).
Collection of Secondary Data
For the realisation of this study the collection of secondary data was essential because "secondary data can provide a useful source from which to answer, or partially to answer your research question" (Saunders, et al., 2009). Secondary data are defined as the data that have already been collected by someone else. This thesis includes mainly published data such as scientific papers, books, journal, articles, and internet sources.
1. Literature Review
According to Hart (1998), literature review is characterised as "the use of ideas in the literature to justify the particular approach to the topic, the selection of methods, and demonstration that this research contributes something new".
Webster and Watson (2002) provides a further explanation of what literature review is, stating that literature review "creates a firm foundation for advancing knowledge. It facilitates theory development, closes areas where a plethora of research exists, and uncovers areas where reasearch is needed".
The data for the execution of this research are collected through comprehensive literature reviews that the concept of "Green HRM" and the sustainable competitive advantage can be determined. By doing so, the authors obtain a better understanding and are able to define the impacts, practices and benefits of Green HRM and how that can bring sustainable competitive advantage to organizations. Additionally, the authors of the thesis are able to identify potential limitations and barriers in the implementation of "Green HRM" and its practices.
The research as already mentioned includes several secondary data such as scientific papers and journal, articles as well as environmental legislations. Last, the authors of the dissertation make use of the data with objectivity and trustworthiness from verified and recent sources.
The literature review used in this study is compiled by the authors employing resources from the University Library. The search of resources was narrowed down by typing several different headings in the library's base. For the validity of the sources, the authors decided to exclude some sources from the library's base such as audio-visual, newspapers articles, scores and "others". Additionally, by typing "AND" or "OR" the authors of the report marked the explicit search criteria (See Table 1 : Search Resources 1 & Table 2: Search Resources 2). Once the search criteria was set in the database, the wide range of available sources needed to be narrowed down again. Firstly, the authors were focusing strictly on English publications and on publication years from 1990 to 2018.
Moreover, the most preferable sources were the latest sources so that a better overview of the current situation could be obtained. According to Oliver (2012), a source year of publication and its valued opened on many factors. In some cases, it is more profitable to use older literature since some subjects can be old. Inf this dissertation, "Green HRM" is a relatively new concept, therefore, the majorities of the sources are published within the last 5 to 10 years with a few exceptions.
Afterwards, the authors selected the most appropriate bibliography based on the title, headline, description of the content as well as reading briefly the abstract of the sources.
However, due to the wide range of the library's available source (See Table 2: Table 2: Search Resources 2), it was impossible for the authors to review them all. Hence, the selected bibliography is based on the most relevant results from the first and second page of the libray's database.
Firstly, the authors of the thesis had to find information regarding the Green Human Resource Management. Table 1: Search Resources 1 presents the typing order and the results from the research that the authors carried out in connection to the concept of "Green HRM"
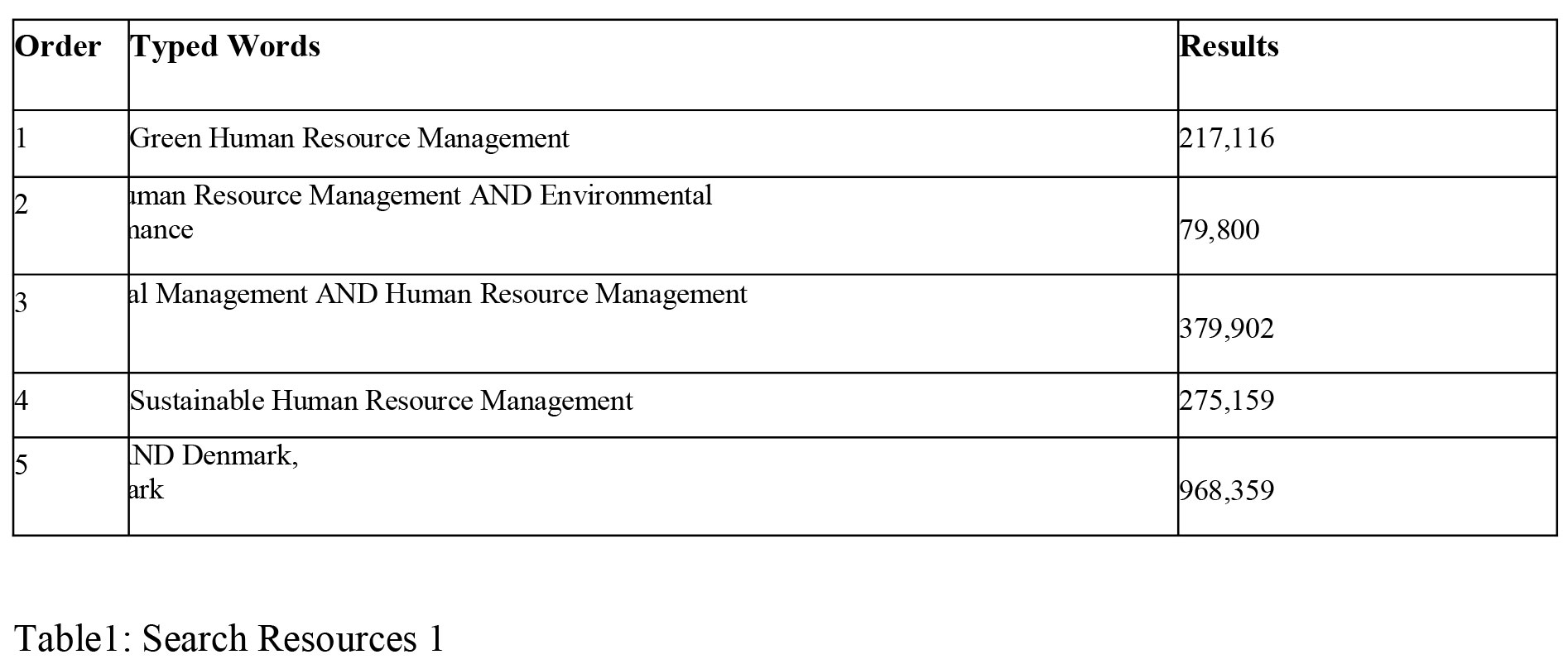
The second research was related to the sustainable competitive advantage. Therefore, similarly to the GHRM research, Table 2: Search Resources 2 presents the typing order and the results from the search, the authors carried out for the concept of sustainable competitive advantage. The sources available in the database did cover the research focus. The process of choosing the most relevant bibliography for both researches were conducted in the same way as described earlier in this section
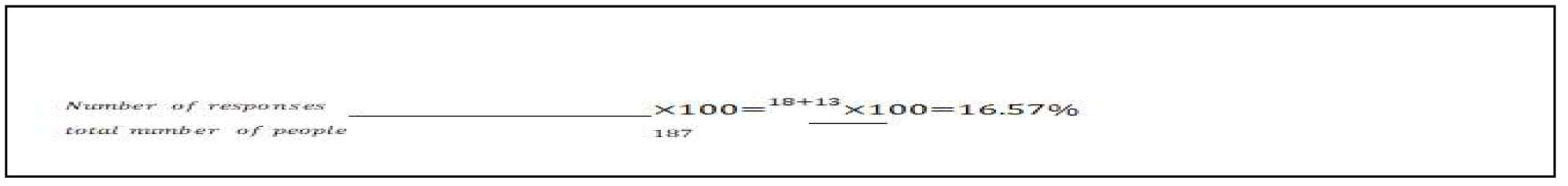
Therefore, the response rate equals 16.57 %. As already mentioned, 13 people completed the survey and 18 partially completed it leading to a total number of 31 people who participated in the Questionnaire Survey. According to Manfreda, et al. (2008), the web-based surveys can result in low response rate compared to their survey models. The response rate for a web-based survey depends on the target population. According to Erwin & Wheelright (2002), achieving a high response rate from the target population is significant for the validity of the data and to be able to develop outcomes of the study. For this study, the survey was distributed to 187 employees of the Danish building sector, 16.57% of which responded to the survey. This relatively low rate can be explained as unwillingness of the employees to participate in the questionnaire, language barriers since the survey is written in English, lack of availability.
The research as already mentioned includes several Secondary Data such as scientific papers and journal, articles as well as environmental legislations. Last, the authors of the dissertation make use of the data with objectivity and trustworthiness from verified and recent sources.
The literature review used in this study is compiled by the authors employing resources from the University Library. The search of resources was narrowed down by typing several different headings in the l
For the validity of the sources, the authors decided to exclude some sources from the library's base.
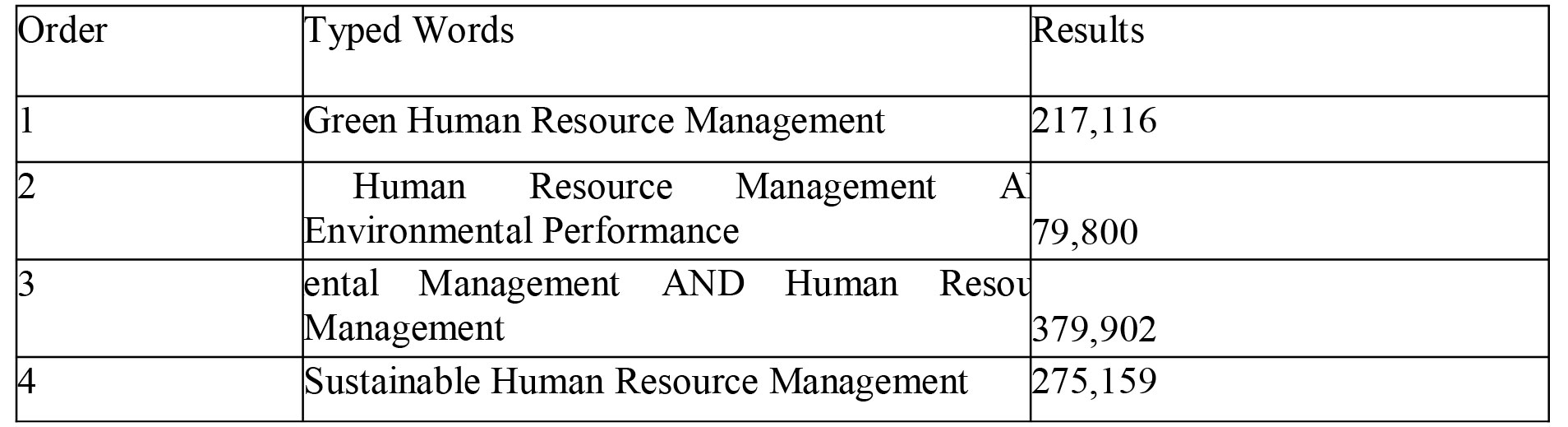
library's base such as audio-visual, newspapers articles, scores and "others". Additionally, by typing "AND" or "OR" the authors of the report marked the explicit search criteria (See Table 1:Search Resources 1&Table 2: Search Resources 2). Once the search criteria was set in the database, the wide range of available sources needed to be narrowed down again. Firstly, the authors were focusing strictly on English publications and on publication years from 1990 to 2018. Moreover, the most preferable sources were the latest sources so that a better overview of the current situation could be obtained. According to Oliver (2012), a source year of publication and its valued opened on many factors. In some cases, it is more profitable to use older literature since some subjects can be old. In this dissertation, Green HRM is a relatively new concept, therefore, the majorities of the sources are published within the last 5 to 10 years with a few exceptions. Afterwards, the authors selected the most appropriate bibliography based on the title, headline, description of the content as well as reading briefly the abstract of the sources. However, due to the wide range of the libray's available sources (See Table 1: Search Resources 1&Table 2: Search Resources 2), it was impossible for the authors to review them all. Hence, the selected bibliography is based on the most relevant results from the first and second page of the library's database.
Firstly, the authors of the thesis had to find information regarding the Green Human Resource Management. Table 1: Search Resources 1 presents the typing order and the results from the research that the authors carried out in connection to the concept of Green HRM.
Discussion & Conclusion :
Green HRM is a new concept in India. Maybe some Big Corporate Houses would have adopted this new concept. In this area, not much research has also been taken by researchers. However, the concept of Green HRM is quite popular in Denmark and neighbouring countries through which many reputed companies have worked on maintaining Environmental protection practices, made mandatory by its Government. Now, India is also more cautious about Global Warming and it is working towards environment protection by constituting National Green Tribunal (NGT) which is an autonomous Body and works independently, being a guiding entity to Central Pollution Control Board & State Control Boards, which frame the rules & regulations for entire Indian Industries to abide by these rules & regulations to be amended from time to time and also enforce to maintain requisite data for submission to concerned Pollution Control Board(s). PCBs also keep strict vigilance on all kinds of Industries and at any time if any Industry is found violating its rules & regulations towards environment protection, PCBs are also authorised to impose fines/penalties on errant Industries.
In my opinion, there is an emergent need for the Governments to lay more strict rules & regulations for environmental protection and enforce them on all kinds of Industries in India to abide and follow in an effective manner.
Limitations & Future Study :
There are also many limitations of this study which include : (1) the study is only limited to a lesser number of Private Sector Companies, which also requires to include Public Sector Enterprises, particularly in India.
The Green HRM practices as discussed in this study are very short in numbers. These Green HRM practices are taken from the research work already done by lesser researchers and according to the predominant Green HRM practices in a selected Private Sector Danish Building Sector, there is also an extreme need to cover Govt. Sector Companies in India also to ripe the fruits in an effective manner.
REFERENCES :
Mathews, Brian; Obereder, Lisa; Aust, Ina; Müller-Camen, Michael (2018). Renwick, Douglas
W.S. (ed.). Competing Paradigms : Status-quo and Alternative Approaches in HRM. Contemporary Developments in Green Human Resource Management Research. Abingdon, Oxon; New York : Routledge. Pp. 116-134. ISBN 9780367376871.
Wehrmeyer, Walter (1996). Wehrmeyer, Walter (ed.). Introduction. Greening People : Human Resources and Environmental Management. Sheffield : Greenleaf Publishing. Pp. 11-32. ISBN 9781874719151.
Renwick, Douglas W. S.; Redman, Tom; Maguire, Stuart (2013). "Green Human Resource Management: A Review and Research Agenda". International Journal of Management Reviews. 15 (1): 1 14. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2370.2011.00328.x. ISSN 1468-
2370. S2CID 145075051.
Ren, Shuang; Tang, Guiyao; E. Jackson, Susan (2018-09-01). "Green human Resource Management Jackson, Susan E.; Renwick, Douglas W. S.; Jabbour, Charbel J. C.; Muller- Camen, Michael (2011-05-01). "State-of-the-Art and Future Directions for Green Human Resource Management: Introduction to the Special Issue". German Journal of Human Resource Management: Zeitschrift für Personalforschung. 25 (2):99
116. doi:10.1177/239700221102500203. ISSN 2397-0022. S2CID 219931279.
Research in emergence: A review and future directions". Asia Pacific Journal of Management. 35 (3): 769 803. doi:10.1007/s10490-017-9532-1. ISSN 1572-9958. S2CID 158085553.
Renwick, Douglas W. S.; Jabbour, Charbel J. C.; Muller-Camen, Michael; Redman, Tom; Wilkinson, Adrian (2016-01-19). "Contemporary developments in Green (environmental) HRM scholarship". The International Journal of Human Resource Management. 27 (2) : 114- 128. doi:10.1080/09585192.2015.1105844. hdl:11449/168131. ISSN 0958-5192. S2CID 155611809.
Kim, Yong Joong; Kim, Woo Gon; Choi, Hyung-Min; Phetvaroon, Kullada (2019-01-01). "The effect of green human resource management on hotel employees' eco-friendly behavior and environmental performance". International Journal of HospitalityManagement. 76: 83 93. doi:10.1016/j.ijhm.2018.04.007. ISSN 0278-4319.
Pham, Nthat Tan; Tuckova, Zuzana, Chiappetta Jabbour, Charbel Jose (2019-06-01). "Greening the hospitality industry: How do green human resource management practices influence organizational citizenship behavior in hotels? A mixed-methods study". Tourism Management. 72: 386 399. doi : 10.1016/j.tourman. 2018.12.008. ISSN 0261-5177.
Daily, Bonnie F.; Bishop, John W.; Massoud, Jacob A. (2012-04-20). "The role of training and empowerment in environmental performance: A study of the Mexican maquiladora industry". International Journal of Operations & Production Management. 32 (5): 631 647. doi:10.1108/01443571211226524. ISSN 0144-3577.
Roscoe, Samuel; Subramanian, Nachiappan; Jabbour, Charbel J. C.; Chong, Tao (2019). "Green Human Resource Management and the enablers of green organisational culture: Enhancing a firm's environmental performance for sustainable development". Business Strategy and the Environment. 28 (5): 737 749. doi : 10.1002 /bse.2277. ISSN 1099-0836.
Aragón-Correa, J.A. and A. Rubio-López, E(2007). Proactive Corporate Environmental Strategies : Myths and Misunderstandings. Vol. (3) pp : 357 381.
Aragon-Correa, J.A., Martin-Tapia, I. and Hurtado-Torres, N.E (2013). Proactive Environmental Strategies and Employee Inclusion: The Positive Effects of Information Sharing and Promoting Collaboration and The Influence of Uncertainty. Organization & Environment,vol. (2) pp : 139 161.
Beard, C. and Rees, S. Green Teams and The Management of Environmental Change in a UK County Council. Environmental Management and Health ,vol. (1) pp : 27 38.
Bohdanowicz, P., Zientara, P. and Novotna, E.(2011)International Hotel Chains and Environmental Protection: An Analysis of Hilton's We Care! Programme (Europe, 2006-2008). Journal of Sustainable Tourism 19 vol. (7) pp : 797 816.
Boiral, O (2002). Tacit Knowledge and Environmental Management. Vol. (3) pp : 291 317.
Boiral, O(2002). Greening the Corporation through Organizational Citizenship Behaviors. Journal of Business Ethics 87 vol. (2) pp : 221 236.
Boselie, P., Paauwe, J. and Jansen, P(2001). Human Resource Management and Performance: Lessons From The Netherlands. The International Journal of Human Resource Management 12 vol. (7) pp : 1107 1125.
Brio, J.A. del, Fernandez, E. and Junquera, B (2007). Management and Employee Involvement in Achieving an Environmental Action-Based Competitive Advantage: an Empirical Study. The International Journal of Human Resource Management 18 vol. (4)
pp : 491 522.
Chen, Y.S. and Chang, C.H.(2012) The Determinants of Green Product Development Performance: Green Dynamic Capabilities, Green Transformational Leadership, and Green Creativity. Journal of Business Ethics 116 vol. (1) pp : 107 119.
Daily, B.F. and Huang, S.C.(2001) Achieving Sustainability Through Attention to Human Resource Factors in Environmental Management. International Journal of Operations & Production Management vol. (12) pp : 1539 1552.
Daily, B.F., Bishop, J.W. and Steiner, R.(2011) The Mediating Role of EMS Teamwork as it Pertains to HR Factors and Perceived Environmental Performance. Journal of Applied Business Research vol. (1).
Egri, C.P. and Herman, S.(2000) Leadership in the North American Environmental Sector: Values, Leadership Styles, and Contexts of Environmental Leaders and their Organizations. Academy of Management Journal vol. (4) pp : 571 604.
